ch. 19- gastrointestinal and urologic emergencies
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
what does the abdominal cavity contain?
Gastrointestinal system
Genital system
Urinary system
mcburnery’s point
location of pain/ tenderness in cases of appendicitis
heel drop test, heel tap test
used to assess pain and tenderness of appendicitis and other abdominal conditions
heel drop: pt stands on toes and drops down onto their heels if pain then positive
heel tap: pt is supine, elevate their heel 10-20 degrees and firmly strikes it with the palm of their hand
what does injury to solid organ cause?
causes shock and bleeding
injury to hollow organ cause?
causes its contents to leak and contaminate the abdominal cavity
this pain radiates and is hard to locate- viceral
solid organs
liver, spleen, pancreas, kidney, ovaries
hollow organs
gallbladder, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, bladder
liver
secretes bile and assists in digestion of fats
filters toxic substances
creates glucose store
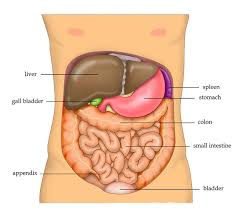
gallbladder
stores bile created by liver
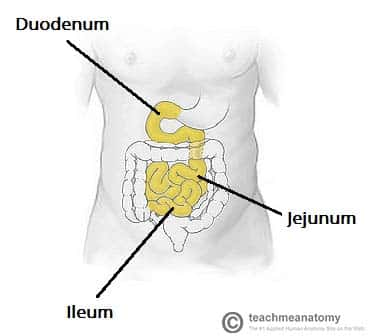
small intestine
duodenum- responsible for continuing the digestion process, neutralizing stomach acid, and facilitating absorption of essential nutrients
jejunum- absorbs digestive products, does most of work
illeum- absorbs nutrients that were not absorbed before and bile acids
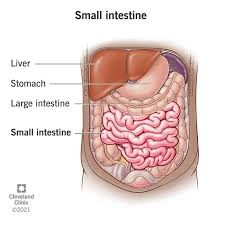
RUQ
bile duct, liver, gallbladder
LUQ
stomach, spleen, pancreas
RLQ
appendix
LLQ
intestine, rectum
why do bile acids need to be absorbed by ileum?
so they can be returned to the liver for future use and
vitamin B12 for making nerve cells and red blood cells
colon (large intestine)
food not broken down comes here, water is absorbed, stool is formed
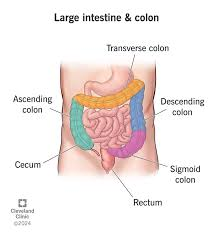
spleen
located in abdomen, no digestive function
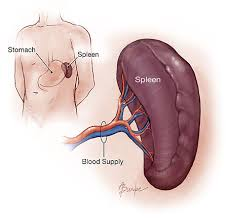
male reproductive system
Testicles
Epididymis
Vasa deferens
Seminal vesicles
Prostate gland
Penis
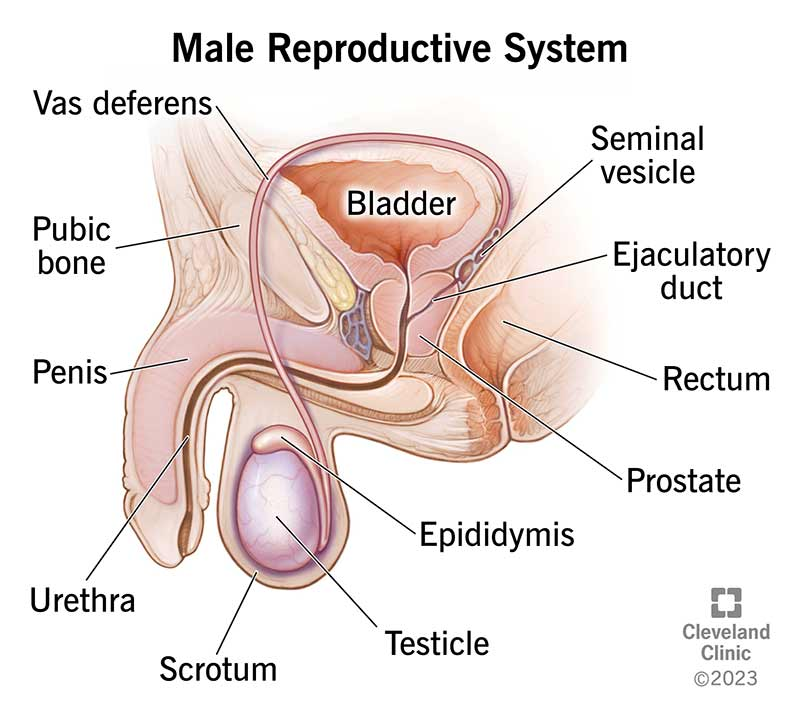
female reproductive system
Ovaries
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Cervix
Vagina
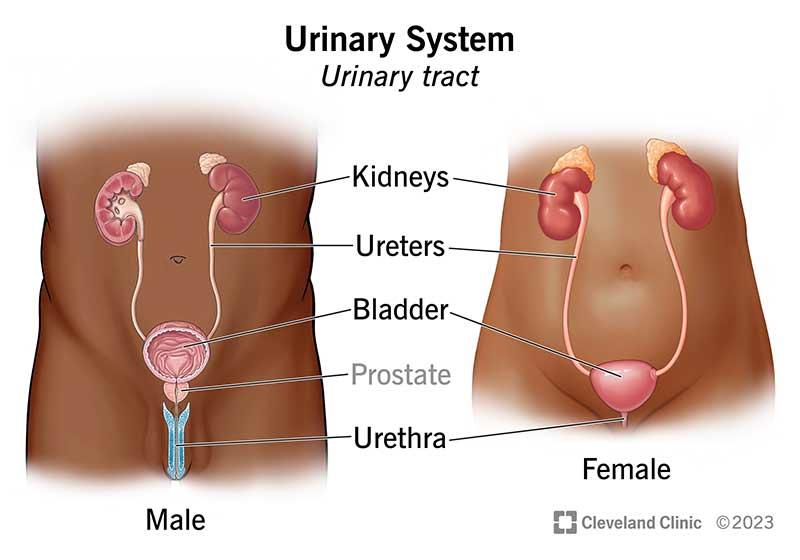
urinary system
controls discharge of waste materials filtered from blood by kidneys
bladder is behind pubic symphysis
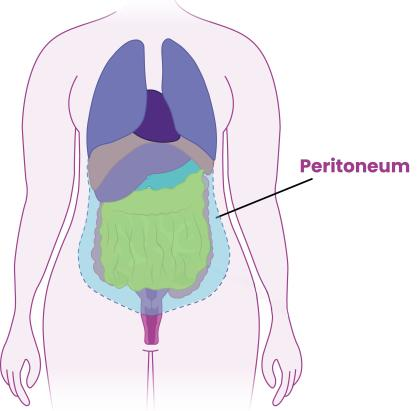
peritoneum: partial and visceral, what irritates it and what does it cause?
partial peritoneum lines wall of abdominal cavity
visceral peritoneum directly covers organs
peritoneum can be irritated by blood, pus, or bile causing peritonitis
acute abdomen
refers to sudden onset of abdominal pain, associated with sever progressive problems
peritonitis and what does it cause?
inflammation of peritoneum
typically causes ileus
illeus and what does it cause?
paralysis of muscular contractions
retained gas and feces causes abdominal distention and stomach empties by emesis (vomiting)
diverticulitis
inflammation of small pockets at weak areas in the walls of gastrointestinal tract muscles, mostly the colon
cholecystitis and what does it cause?
inflammation of gallbladder
heart burn after greasy meal, vomiting, right referred shoulder pain
acute appendicitis , pain associated, how to test for it
inflammation of appendix
RLQ pain, pain after releasing pressure (rebound tenderness)
heel tap test, heel drop test
nerves of parietal peritoneum vs visceral peritoneum
parietal: supplied by the same nerves as skin of abdomen
visceral: supplied by autonomic nervous system
acute abdomen and causes
sudden onset of severe abdominal pain
ulcers
gallstones
pancreatitis
appendicitis
gastrointestinal hemorrhage
esophagitis
esophageal varices
mallory- weiss sydrome
gastroenteritis
diverticulitis
hemorrhoids
ulcers
Protective mucus layer breaks down, allowing acid to eat into the organ
May lead to gastric bleeding and peritonitis
gallstones
may form and block its outlet.
Cause pain
Lead to cholecystitis
pancreatitis, what causes it, sings and symptoms
Inflammation of the pancreas
Caused by obstructing gallstone, alcohol abuse, or other diseases
pain in LUQ and RUQ quadrants, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal distention.
Sepsis or hemorrhage may occur.
appendicitis
Inflammation or infection in the appendix
Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fever, chills, rebound tenderness
gastrointestinal hemorrhage
Bleeding within gastrointestinal tract
May be acute or chronic
esophagitis
Lining of the esophagus becomes inflamed by infection or acids from the stomach.
Pain in swallowing, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, sores in mouth
esophageal varices, signs and symptoms
bleeding in esophagus
Fatigue, weight loss, jaundice, anorexia, edema, abdominal pain
history of ETOH
mallory- weiss syndrome and its principle symptom
junction of esophagus and stomach tears
vomiting
gastroenteritis and principle symptom
Infection from bacterial or viral organisms or caused by noninfectious conditions
diarrhea
diverticulitis
Fecal matter becomes caught in colon walls, causing inflammation and infection.
Fever, malaise, body aches, chills
hemorrhoids
Created by swelling and inflammation of blood vessels surrounding rectum
Bright red blood during defecation
cystitis (bladder infection)
also called UTI
caused by bacterial infection
becomes serious if infection spreads to kidney
reports of urgency or frequency of urination
acute kidney failure
Sudden decrease in kidney function
Reversible with prompt diagnosis and treatment
what happens when kidneys fail?
uremia
chronic kidney failure
Irreversible
Progressive, develops over months/years
Eventually dialysis or transplant is required.
where does ovary, fallopian tubes, or uterus pain relate to usually?
lower quadrant
gynecologic problems are common cause of acute abdominal pain
AAA, what does pain feel like, what happens to bp
palpable pulsating mass caused by aorta that lies immediately behind peritoneum
ripping, tearing pain
bp less than 10 difference
hernias
Protrusion of an organ or tissue through an opening into a body cavity where it
does not belong
May not always produce noticeable mass or lump
Strangulation is a serious medical emergency.
serious hernia signs and symptoms
A formerly reducible mass that is no longer reducible
Pain at the hernia site
Tenderness when the hernia is palpated
Red or blue skin discoloration
primary assessment: ABC and transport decision
Airway and breathing
May cause shallow, inadequate respirations
Circulation
Ask about blood in vomit or black, tarry stools.
Check pulses in both feet.
Transport decision
Immediate transport is needed if there are signs of significant illness
History taking: SAMPLE
Nausea and vomiting
Change in bowel habits and urination
Weight loss
Belching or flatulence
Pain
Concurrent chest pain
Other signs or symptoms
secondary assessment: physical examination
check for tenderness or rigidity
Normal abdomen is soft and not tender.
Pain/tenderness: signs of acute abdomen
Expose and assess abdomen.
Palpate gently.
secondary assessment: vital signs
Check respiratory rate and pulse rate.
Avoid taking a blood pressure in the same arm where a dialysis shunt is.
reassessment
Frequent reassessment is important.
Assess interventions, including treatment for shock and emotional support.
Transport the patient in the most comfortable position.
emergency medical care
you can not treat causes of acute abdomen
Take steps to provide comfort and lessen effects of shock.
Treat for shock even when obvious signs are not apparent.
Low-flow oxygen may decrease nausea and anxiety.
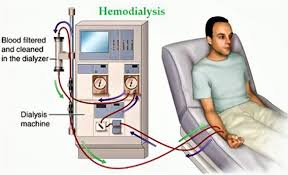
dialysis emergencies
Emergency care:
Manage XABCs. (external bleeding)
Provide high-flow oxygen if indicated.
Manage any bleeding from access site.
Position the patient:
Upright in cases of pulmonary edema
Supine if the patient is in shock
Transport promptly
dialysis and what can be caused if pt misses a treatment
only definitive treatment for chronic kidney failure
filters blood, cleans it of toxins, and returns it to body
pulmonary edema
dialysis machine function and adverse affects
functions like normal kidneys
adverse effects:
Hypotension
Dysrhythmias
Muscle cramps
Nausea and vomiting
Hemorrhage from access site
Infection at access site