PBS Principles of Biomedical Sciene PLTW Unit 3 Test WCHS Mrs.McCormick
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Prions
No cure
Submicroscopic proteins
Viruses
Influenza
Made of an outer protein shell and DNA or RNA
Bacteria
Treatment: Antibiotics
Unicellular prokaryotic organism
Fungi
Treatment: Antifungals
Mold
Protists
Treatment: Antiprotozoal medication
Single-celled eukaryotic, animal-like organism
Helminths
Eukaryotic Worms
Treatment: Deworming medication
True or False: You have more bacterial cells on your body then your own cells
True
True or False: All bacteria is bad
False
True or False: People with a disease or weakened immune system are more susceptible to infections
True
E.coli bacteria double in population using binary fission every thirty minutes. If the initial population is 10, what is the population of bacteria after 4 hours?
2,560
Ways in which pathogens are transmitted between hosts
Airborne, contact with infected people or surfaces, ingestion of particles, etc.
Direct contact
Touches infected object
Touches infected individual
Exposed to body fluids
Indirect contact
Inhale particles
Bitten by insect
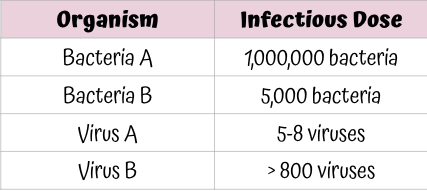
Which pathogen is most dangerous?
Virus A
Innate immunity
Enzymes
Tears
Stomach acid
Phagocytes
Cilia
Mucus
Breast Feeding
Non-specific defense
Acquired Immunity
Vaccine
T-cells
B-cells
Antibodies
Normal flora
Specific defense
There are 300 total cases and 50 new cases, calculate the R0
50/300 or 0.17
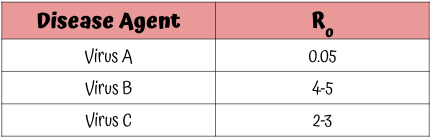
Which disease agent is the most contagious?
Virus B
Order of chain of infection
Agent of disease→Reservoir→Portal of exit→Mode of transmission→Portal of entry→ Susceptible host
Is there a way to break the chain of infection? Explain
Yes, through things like proper personal hygiene, quarantine, vaccination, etc.
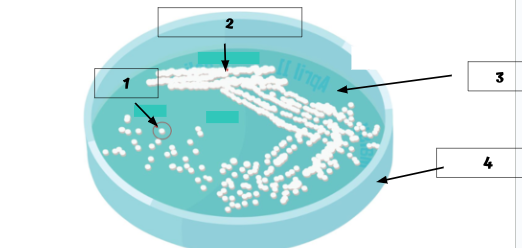
Label the image
Colony
Bacterial growth
Agar
Petri dish
What is the difference between macroscopic and microscopic?
Macroscopic is bigger while microscopic is smaller
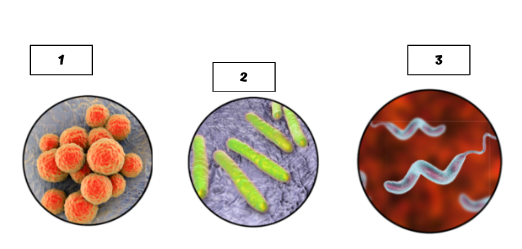
Label the bacteria to its morphology
Cocci
Bacilli
Spirilla
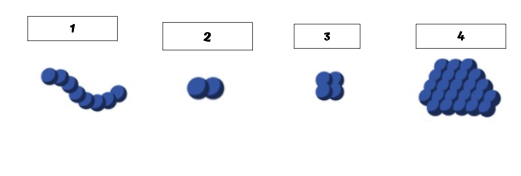
List the names of each cell arrangement
Chain of cocci
Diplococci
Stapphylococci
Tetrad
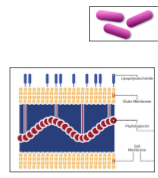
Gram-positive or Gram-negative?
Gram-negative
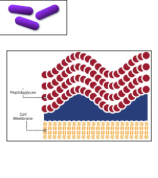
Gram-positive or Gram-negative?
Gram-positive
What is the MMWR?
The Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report
What is the average resting heart rate?
60-100 bpm
A patient’s heart rate is 105 BPM; is that high, low, or normal
It is slightly elevated
What does pale, cool, moist skin indicate?
This can indicate that the patient had a drop in blood pressure
What are the ABC’s of a primary assessment?
A: Airway- If the patient is breathing
B: Breathing- How well the patient is breathing
C: Circulation- Looks for a pulse and if there is any bleeding
You find a person unconscious, not breathing, with a broken finger and large abdominal cut. What injury do you tend to first?
Their breathing
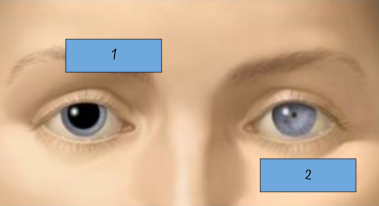
Label each eye
Dilating
Constricting
A patient’s blood pressure is 140/100; is the patient hypotensive, normal, prehypertensive, hypertensive, or in a hypertensive crisis?
The patient is hypertensive

Which patient is dehydrated?
The patient on the left
Enteral
Medications that enter the body through the digestive tract
Parenteral
Drugs are those that enter the body in a manner other than through the digestive tract
Is the following enteral or parenteral?: Pills, liquid, enema
Enteral
Is the following enteral or parenteral?: Shots, ointment, eye drops, inhaler
Parenteral
Fastest type of injection to go into effect, but harder to administer
Intramuscular
Injection that is quick to be absorbed and easier to administer
Intravenous
Injection that takes the longest to go into effect
Subcutaneous
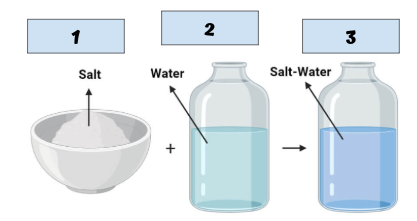
Label the picture
Solute
Solvent
Solution
Examples of life threatening bleeds
Blood will not stop coming out of the wound
Blood spurts out of the wound
Blood is pooling on the ground
Clothing is soaked with blood
Bandages continue to soak through with blood
Victim seems confused or is unconscious
Victim has lost all or part of an arm or leg
Are platelets an example of positive or negative feedback?
Positive
What are the ABC’s of bleeding control?
A: Alert- Call 911 or get someone to help
B: Bleeding- Find the source of bleeding and determine whether it is life threatening
C: Compress- Apply compression or firm pressure on the wound
Which type of bleed would typically be more urgent to treat, venous or arterial?
Arterial
Does packing the wound or compression create a stronger barrier to prevent blood from flowing from the vessel?
Packing the wound
How long does it take for a tourniquet to cause permanent tissue death to a limb
2 hours
Bloodborne pathogen
Infectious microorganisms, like viruses and bacteria, that can be transmitted through human blood or certain body fluids
Cervical fracture
A fracture of the cervical spine (neck)
Mechanism of injury (MOI)
The manner in which a physical injury occurred, including how, with what force, and to what part of the body the injury was inflicted
Stridor
An abnormal, high-pitched respiratory sound produced by irregular airflow in a narrowed airway
Bag valve mask resuscitator
A hand-held device used to provide positive pressure ventilation to a person who is not breathing or who is not breathing adequately
Consensual pupillary reflex
The change in pupil size in the eye opposite to the eye to which the light is directed
Intubate
To insert a tube into a body cavity or hollow organs, typically for a medical purpose like ventilation or feeding
Endotracheal tube
A flexible tube inserted into the trachea to help a person breathe, often in conjunction with a ventilator
Trachea
A vital part of the respiratory system, connecting the larynx to the bronchi
Skin turgor
The skin’s ability to return to its original position after being pinched or stretched
Anaphylaxis
A severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reactions that happens rapidly after exposure to an allergen
Antigen
Anything that stimulates an immune response
Antibody
A protein produced by B cells in the blood; works to impair pathogens. Also called an immunoglobulin
Epinephrine
Used to treat severe allergic reactions or sudden asthma attacks
Dehydration
Occurs when your body doesn’t have enough water to carry out its normal functions
Intravenous therapy
A medical technique where fluids, medications, nutrients, or blood are administered directly into a vein through a needle or catheter
Catheter
A flexible tube inserted through a narrow opening into a body cavity, particularly the bladder, for removing fluid
Semipermeable
A barrier that allows some molecules to pass through but not others
Diffuse
To spread out evenly in space, moving from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration
Osmosis
The movement of water across a membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a stable internal physiological conditions which enables the optimal functioning of an organism
Platelets
Small, colorless cell fragments in our blood that form clots and stop or prevent bleeding
Laceration
A tear or cut in the skin or underlying tissues caused by trauma or injury
Tourniquet
A device that is wrapped tightly around a leg or arm to prevent the flow of blood to the leg or the arm for a period of time
Ligate
The process of tying off blood vessels so that blood cannot flow to a part of the body or to a tumor
Hemostat
A medical tool used to control bleeding during surgery
Triage
The sorting and prioritization of patients based on the urgency of their need for care
Medical surge
A situation in which an influx of new patients challenges or exceeds a hospital’s ability to serve them
Surge capacity
The ability of a health facility to evaluate and care for a markedly increased volume of patients
Disaster response plan
A detailed, proactive strategy developed by healthcare facilities and systems to ensure a coordinated and effective response to emergencies and disasters that could significantly disrupt patient care or operations
Infrastructure
The essential facilities, systems, and resources needed to deliver healthcare and protect public health
Sporadic disease
A condition that occurs infrequently and irregularly, with cases scattered in different locations and time periods
Epidemic
A widespread occurrence of an infectious disease in a community at a particular time
Endemic
A disease that is constantly present in a certain geographic area or in a certain group of people
Microbes
A microscopic organisms, meaning it is too small to be seen with the naked eye and requires a microscope to be observed
Sequence of events for a disease defense team
Receives a call or email from a healthcare facility→ epidemiologists gather initial information → healthcare facility extends a formal invitation for DDT to help lead an on-site team → DDT arrive on-site and help gather information from interviews, chart reviews, observations, and conducts patient testing→ team analyzes the data to identify risk factors for infection and help develop control measures → DDT recommends new or revised measured and steps to prevent more patients from becoming infected → healthcare facility implements recommendations and checks to ensure the control measures are working → group communications continue to review what has worked and make adjustments as needed
Pandemic
An epidemic that has spread across several countries or continents and affects a large number of people
Outbreak
A sudden increase in the occurrence of a disease in a localized area
Most common examples of nosocomial infections
Pneumonia, urinary tract infections (UTI), gastrointestinal infections, bloodstream infections, and skin/soft tissue infections