Transport in Humans
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Parts of the circulatory system
Heart - muscular pump that drives blood around the body
Blood - fluid tissue that carries various subs. around the body
Blood vessels - transports blood to other parts of the body
What is a double circulatory system
Blood is pumped through the heart twice in one circuit. Ensure blood is pumped to lungs at low pressure for blood to be properly oxygenated and blood is properly oxygenated and pumped out to rest of the body at a fast rate
Pulmonary circulation
Brings deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs and oxygenated blood from lungs to heart. Gaseous exchange in the lungs
Systemic circulation
Carry oxygenated blood from heart to rest of body and deoxygenated blood from body to heart. Hepatic blood vessels connected to liver and renal blood vessels connected to kidney
Composition of blood
55% plasma, 45% white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets
Function of blood
Transport food substances, heat, hormones, oxygen and waste products from one part of body to another. Protect body agaisnt foreign bodies and fighting infections
Plasma
Consists of 90% water 10% dissolved substances. Can involve mineral ions, digested food substances, metabolic waste products, plasma proteins, hormones and heat
Red blood cells (erythrocytes)
Produced in bone marrow (hemapoietic stem cells) and broken down in spleen. Lifespan of 4 months, transports oxygen to rest of body
Structural adaptation of red blood cells
Haemoglobin which binds reversibly to oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. Which helps to transport blood around the body. Each molecule of haemoglobin (Hb) can bind to 4 molecules of oxygen
No nuclleus to pack more haemoglobin into cell cytoplasm and transport more oxygen
Circular and biconcave in shape to increase surface area to volume ratio to allow quicker diffusion of gases in and out of the cell
Elastic and flexible cell surface membrane so cell can change shape while squeezing through capillaries
White blood cells
Larger and less numerous (700RBC:1WBC). Lifespan of only few days
Lymphocytes - round in shape with large round nucleus that produce antibodies. They rupture the cell surface membrane of the bacteria so destroying bacteria, cause bacteria to agglutinate easily ingested by phagocytes. Neutralise toxins produced by bacteria. Attach to virus and prevent them from binding to host cell
Phagocytes are more irregular in shape and multi-lobed/ bean shaped nuclei and squeeze out of capillaries carry out phagocytosis (engulf and ingest pathogens)
Platelets
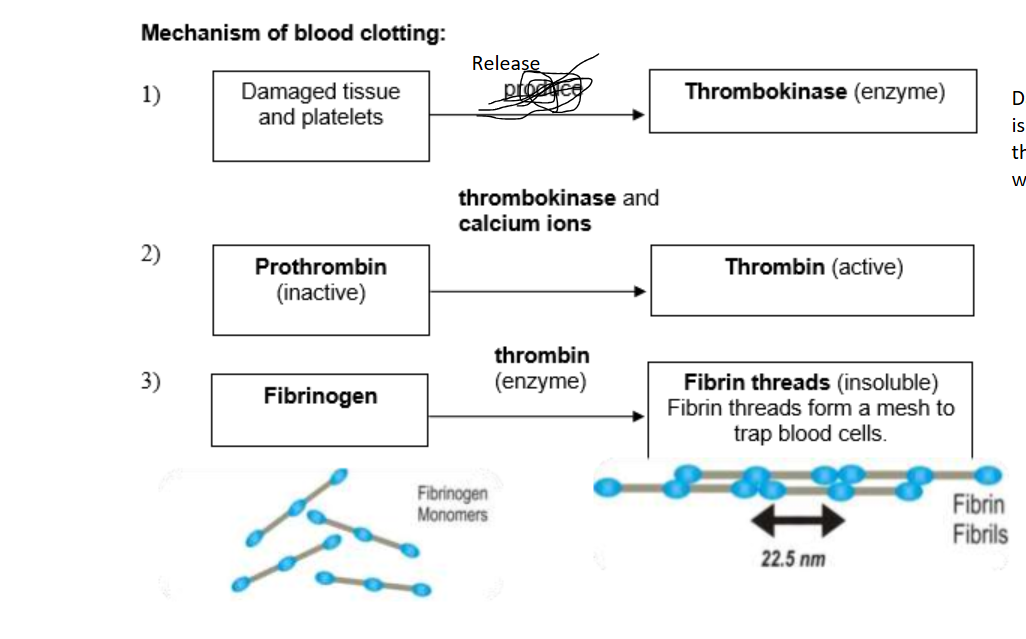
Membrane bound fragmens of larger bone marrow cells. Play important role in blood clotting to form sticky plugs at wound sites and prevent excessive blood loss and prevent entry of foreign bodies and pathogens
Damaged tissue and platelets release thrombokinase, which is an enzyme that activates prothrombin into thrombin with help of calcium ions, and fibrinogen is turned into fribrin threads to form mesh that traps blood cells
ABO blood groups
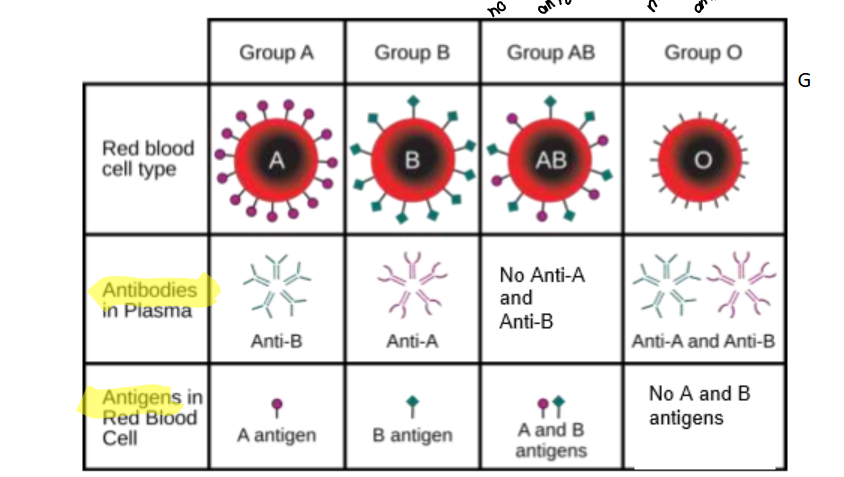
What is an antigen
Protein marker found on the cell surface membrane
What is a antibody
Y shaped protein that binds to antigen with a complementary shape to it
What is agglutination
Clumping of red blood cells which can be fatal. Happens when anti-A antibodies bind to antigen A or anti-B antibodies bind to antigen B
Wall of artery and vein contain 3 layers
Inner layer is endothelium, middle layer contains smooth muscle tissue and elastic fibres, outer layer contains connective tissue
Arteries
Carry blood away from heart. Always oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery. Blood flows rapid under high pressure. Thick muscular and elastic walls to withstand high pressure. Thick elastic walls enable artery walls to stretch and recoil to push the blood forward in splurts, maintain high pressure. Arteries branch into arterioles, arterioles branch to form tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Smaller lumen
Veins
Blood vessel carry blood to the heart, always deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein. Blood flows at low pressureure. Less thick and elastic walls due to low pressure. Contains semi-lunar valves to prevent backflow of blood. Veins located between between large muscles of the body. Contraction of the skeletal muscles squeeze vein and push blood up towards heart. Capillaries join together to form venules that join larger blood veins. Large lumen
Capillaries
Microscopic blood vessels that connect artery to vein and are found between cells of most tissues. Capillary walls are thin and only one cell thick and are partially permeable for substances to diffuse through. Branch repeatedly to cover wide surface area for more diffusion of substances in and out of cell
Blood plasma and tissue fluid
Cells in wall of capillaries do not fit together exactly, hence plasma can leak out from blood. Hence, there is tissue fluid which bathes the cell of tissues within the minute gapss between the tissue cells. Tissue fluid contains dissolved food substances (glucose and amino acids) as well as waste products and hydrogencarbonate ions. Proteins not fund in tisssue fluid (too large to squeeze within gaps of the capillary walls). Phagocytes can squeeze through but not RBC
What happens with the tissue fluid?
Oxygen and food substances diffuse quickly through walls of the blood capillaries from blood plasma to tissue fluid surrounding the cell, down concentration gradient.
Carbon dioxide and waste substances diffuse from body cells into tissue fluid and subsequently into blood plasma to be carried to other parts of the body, down a concentration gradient
Parts of the heart
Muscular organ that consists of cardiac muscles which contract and relax to pump blood around the body
consists of 2 atria (upper chambers) and 2 ventricles (lower chambers)
Bicuspid valve (between left atrium and left ventricle) and tricuspid valve (between right atrium and right ventricle) and semilunar valve (pulmonary vein and aorta) → blood flows one directionally preventing backflow of blood
Left side oxygenated blood, right side deoxygenated blood
Median septum divided oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood
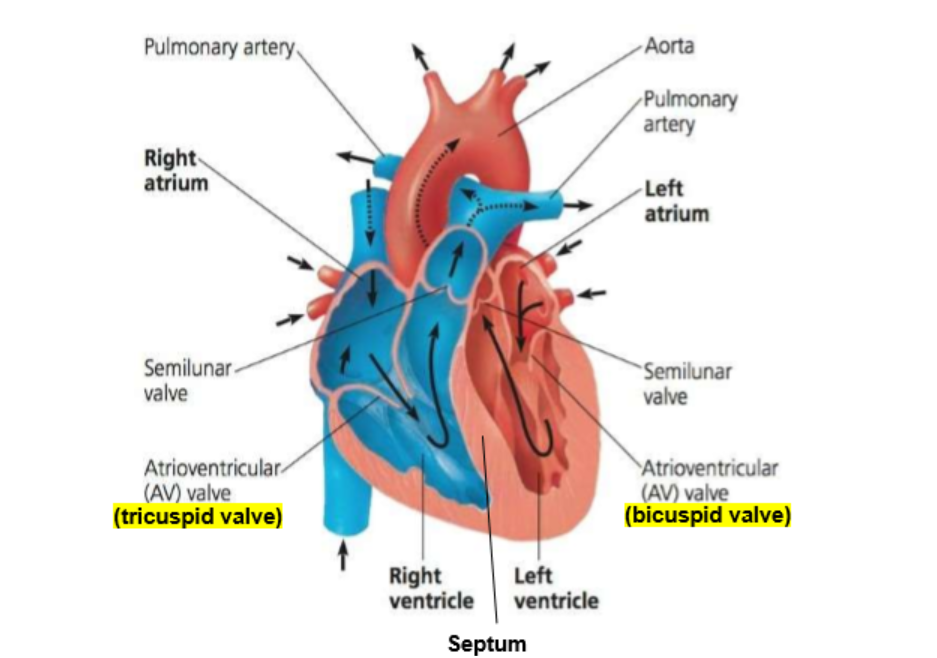
Why are venticular walls more thick and muscular than walls of atrium?
Ventricles responsible for pumping blood to rest of the body, thus thicker and more muscular walls to exert higher pressure ensuring blood reaches all parts of the body
Walls of the atrium only pump blood to ventricles, thus lower pressure because of less thick and elastic walls
Atrial systole
Muscles of the atrial wall contract, causing atrial pressure to increase. Bicuspid valve already open. Since atrial pressure exceeds ventricular pressure, blood flows from left atrium to left ventricle down pressure gradient. Since aortic pressure is beyond ventricular pressure, semi-lunar valve is closed
Ventricular systole
Ventricular walls contract, rising beyond atrial pressure, causing the bicuspid valve to close to prevent backflow of blood from left ventricle to left atriam. Ventricular pressure rises beyond aortic pressure, causing the semi-lunar valve to open and blood flows from left ventricle to aorta, down pressure gradient
Meanwhile, atrial diastole occurs. Muscles in the atrial wall relax, causing the pressure to decrease. Left atrium begins to be filled with blood from the pulmonary vein, increasing atrial pressure.
Ventricular diastole
Ventricular muscles relax, causing ventricular pressure to decrease below aortic pressure, causing semi-lunar valve to close. Ventricular pressure goes below atrial pressure, causing the bicuspid valve to open to allow blood to flow from left atrium to let ventricle, repeating the process.
Coronary heart Disease
Principle: Coronary arteries supply oxygen and nutrient to heart muscles. Build up of fatty deposits containing cholestoral within arterial walls as well in inner surface of coronary arteries (Atherosclerosis), increasing chances of blood clots (thrombosis) within coronary arteries, depriving heart of nutrients and oxygen, leading to heart attack
Causes: Diet high in cholestoral and saturated animal fats, lack of exercise, smoking and stress (increase blood pressure which narrows walls through build up of plaque)
Preventive measures: diet (reduce intake of saturated animal fats and cholestorol) avoid smoking and stress, regular exercise (strengthens heart and maintains elasticity of arterial walls)