Unit 2: Foundations of American Democracy (Part 1) Key Terms
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
autocracy
When one person has all the power

monarchy
A government ruled by a king or queen

dictatorship
A form of government in which the leader total has control of their lives of the people who live in their territory

representative democracy
a form of democracy in which people elect officials to govern

direct democracy
a form of democracy in which the people vote on the issues

oligarchy
A government ruled by a few powerful people
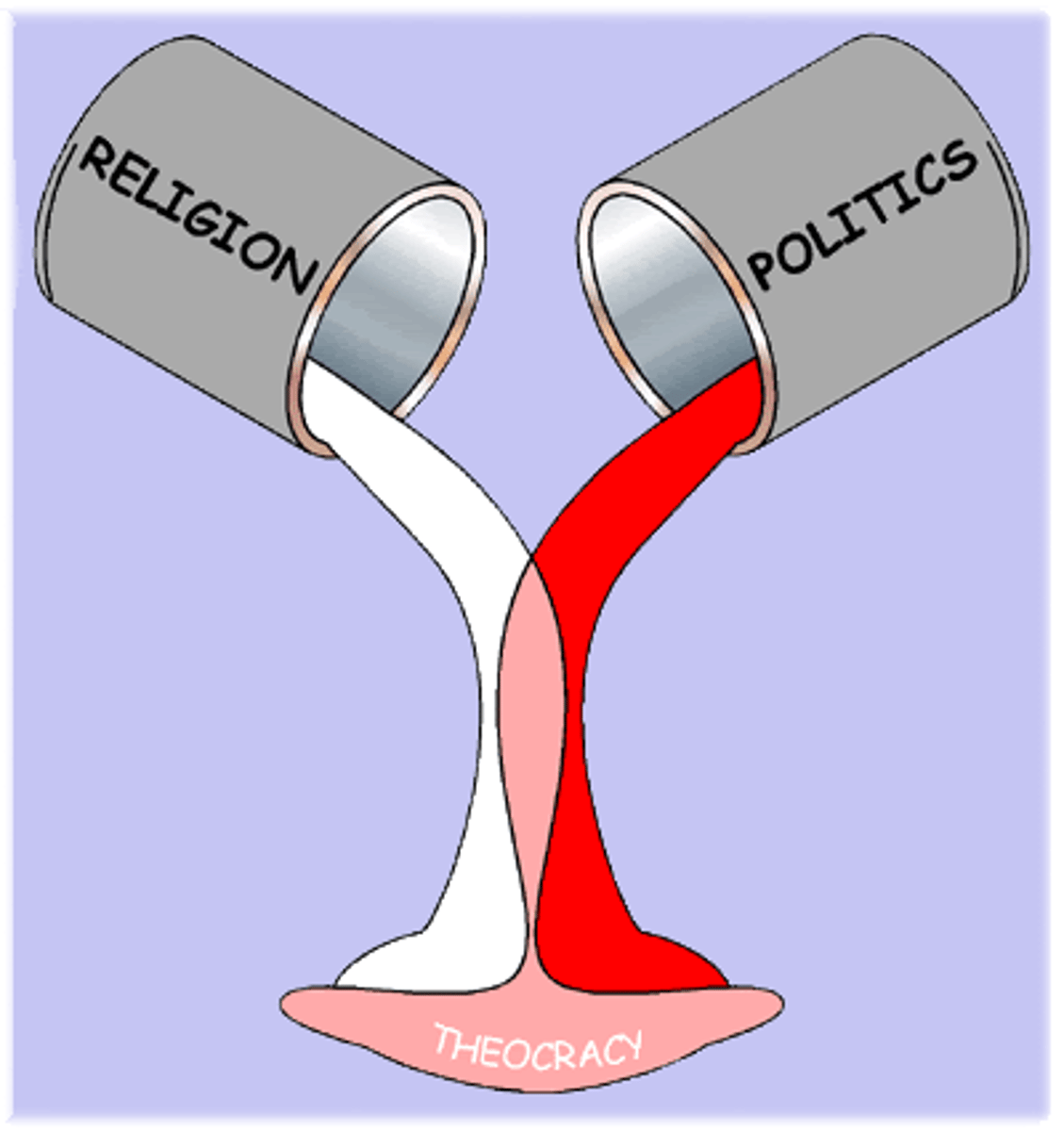
theocracy
A government controlled by religious leaders
anarchy
no government

Founders
the political leaders of the colonies

natural rights
the right to life, liberty, and property

social contract
an agreement to create a government and follow its laws

common good
citizens who put the community above their own interests

checks and balances
a system that prevents branches of government from abusing power.

Jamestown
the first permanent English settlement in North America

John Smith
a leader in the Jamestown colony who helped to provide order

Mayflower Compact
This document established the first colonial claim for self-government in North America.

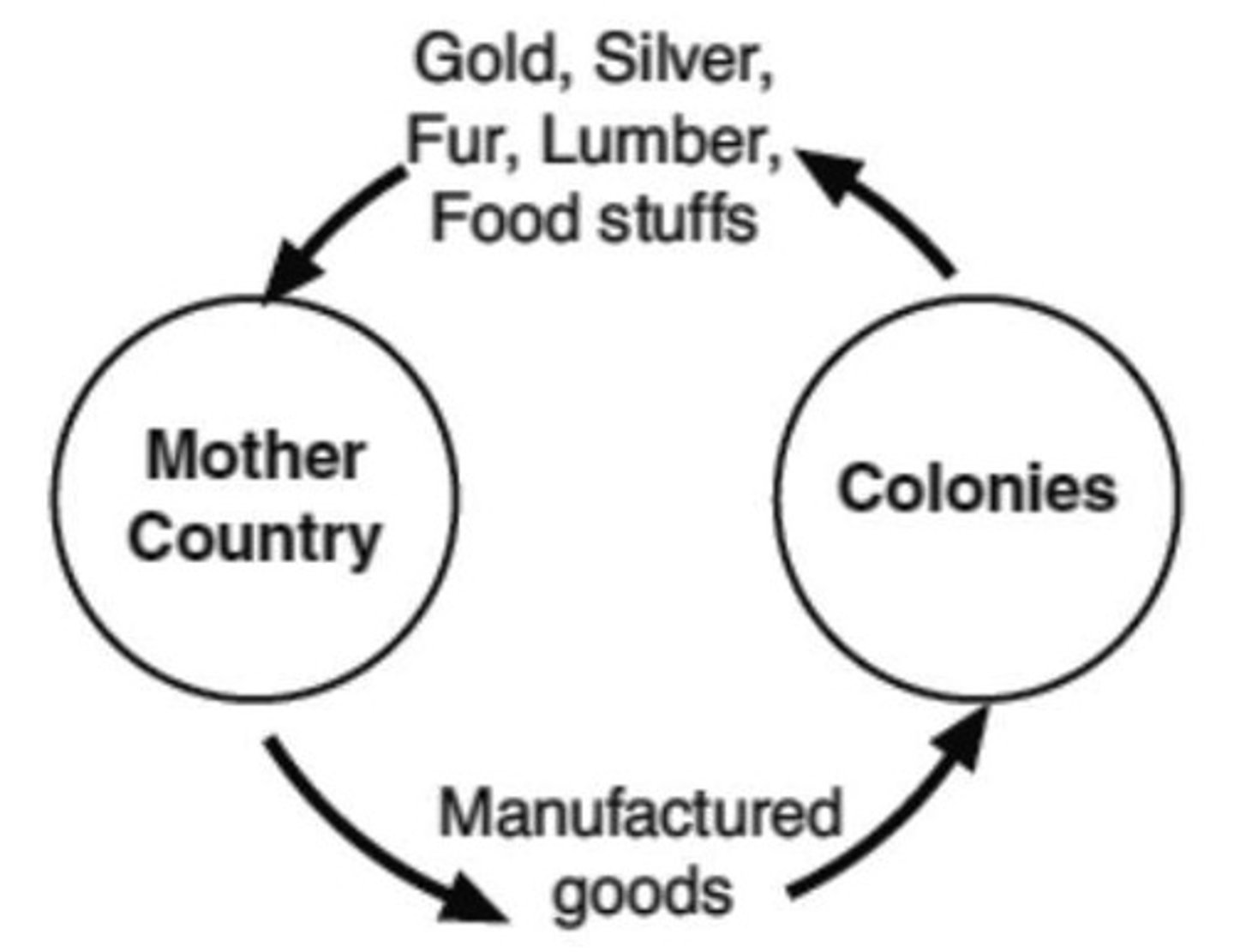
mercantilism
The idea that colonies would ship resources back to the mother country. In contrast, the mother country would turn these resources into manufactured goods for purchase in the colonies.
Thomas Hobbes
This philosopher believed that people were naturally greedy, selfish, and cruel.

John Locke
This philosopher believed that people are born naturally good and are born with natural rights.

Voltaire
This philosopher believed in the importance of freedom - freedom of thought, freedom of religion, and freedom of speech.

Charles de Montesquieu
This philosopher argued for the separation of powers so no one person or branch would have too much power.

separation of powers
the division of power among different branches of government
