AP Bio Cell Membrane
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:23 PM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
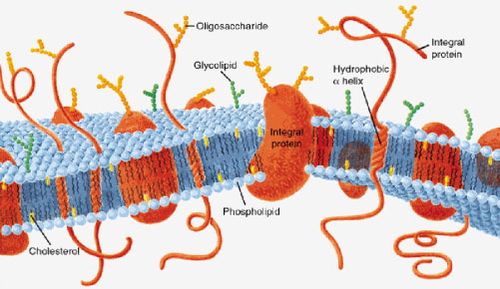
plasma membrane
seperates the living cell from its surroundings. Contros traffic in and out of the cell. Is selectively permeable.
2
New cards
selectively permeable
allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
3
New cards
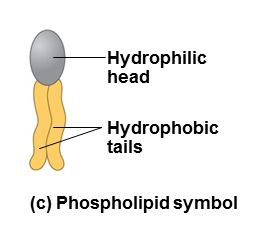
phospholipids
most abundant lipids
4
New cards
lipids and proteins
main macromolecules in membranes
5
New cards
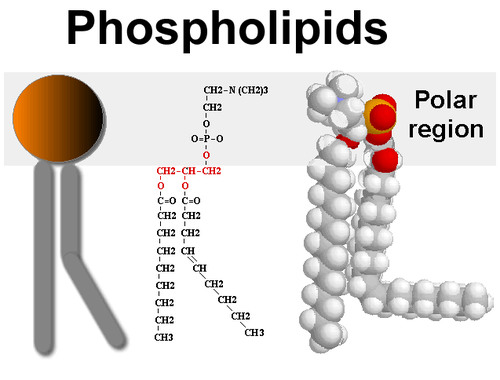
amphipatic molecules
have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
6
New cards
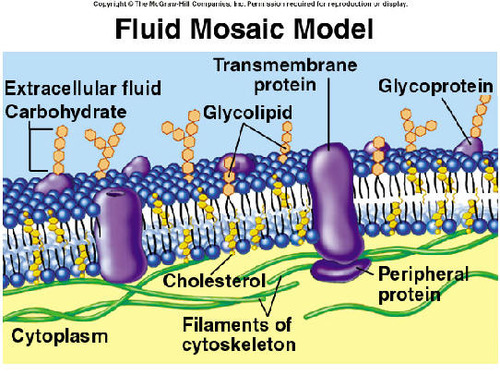
fluid mosaic model
The arrangement of phospholipids and proteins in biological membranes is described by the...
7
New cards
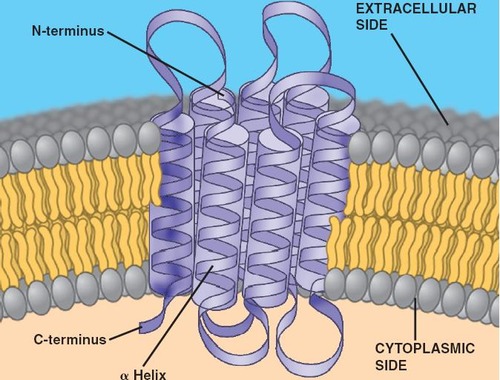
transmembrane proteins
the integral protein completely spans the membrane as...
8
New cards
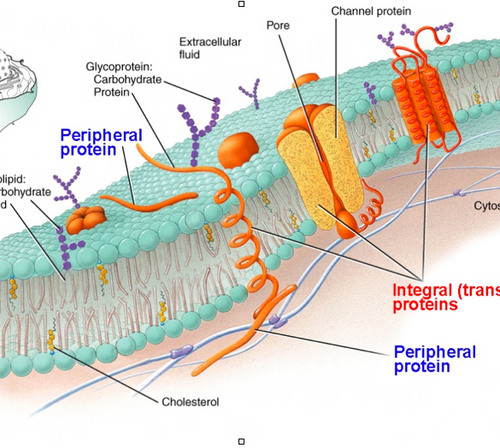
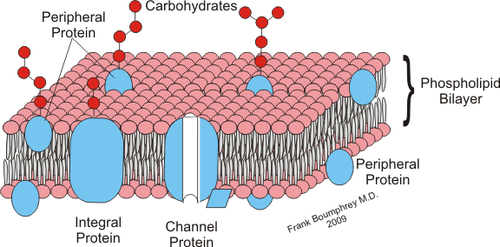
integral proteins
proteins that penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
9
New cards
peripheral proteins
proteins that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer
10
New cards
cell-cell recognition
the ability of a cell to disitnguish one type of neighboring cell from another.
11
New cards
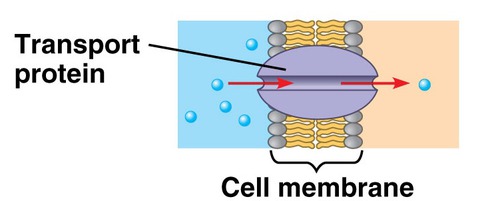
transport proteins
proteins that span the membrane.
12
New cards
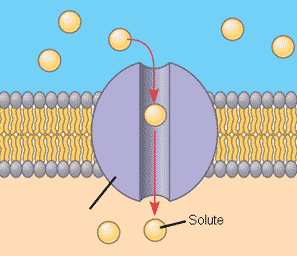
channel proteins
transport proteins that have a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or ions use as a tunnel though the membrane.
13
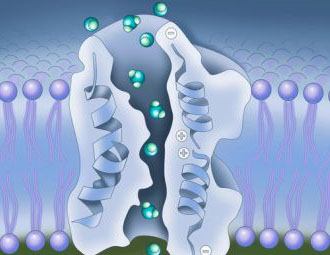
New cards
aquaporins
channel proteins that facilitate the passage of water
14
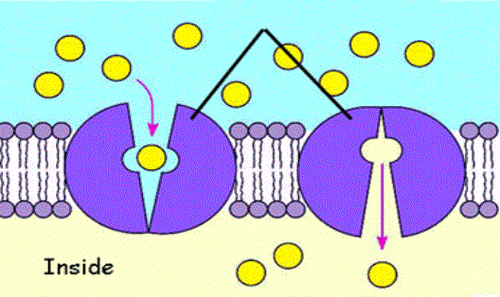
New cards
carrier proteins
transport proteins that bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across the membrane.
15
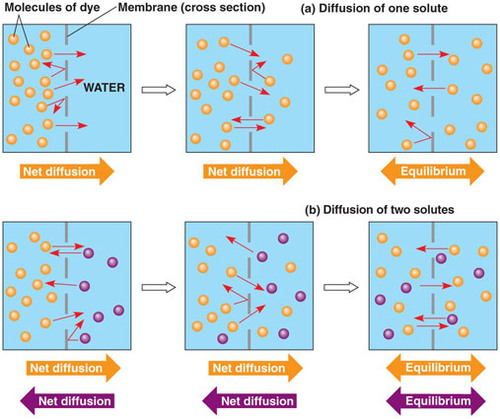
New cards
diffusion
movement of molecules of any substance to spread out in available space
16
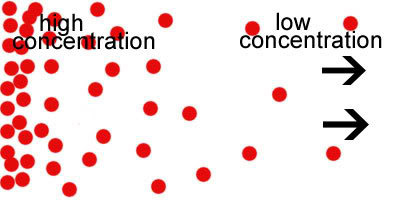
New cards
concentration gradient
the region along which the density of a chemical substance increases or decreases.
17
New cards
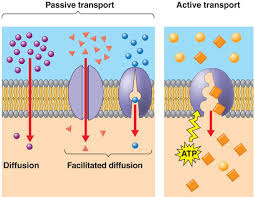
passive transport
transport that requires no energy from the cell to make it happen
18
New cards
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
19
New cards
tonicity
the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water.
20
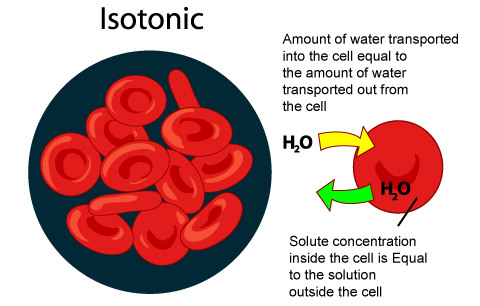
New cards
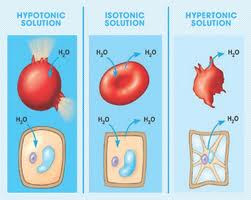
isotonic (animal cell)
if a cell with no cell wall is immersed in an enviroment where there is no net movement of water across the plasma membrane. Stays the same.
21
New cards
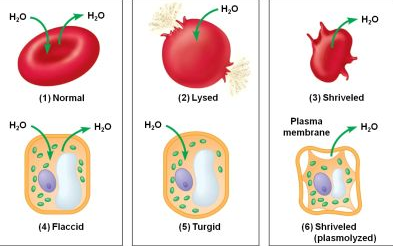
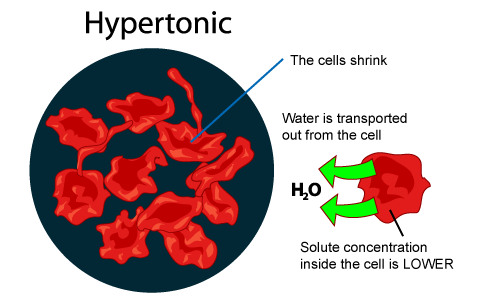
hypertonic (animal cell)
when the cell is immersed in a solution where it loses water to its environment, shrivels and probably dies.
22
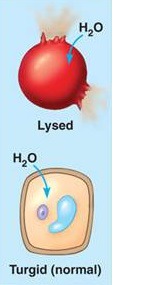
New cards
hypotonic (animal cell)
when a cell is immersed in a solution, water enters the cell faster than it leaves, it swells and lyses (explodes) like an overfilled water balloon.
23
New cards
osmoregulation
the control of water balance
24
New cards
Paramecium
is a protist that is hypertonic to the pond water in which it lives.

25
New cards
turgid
when the plant cell is very firm, which is a healthy state for most plant cells.
26
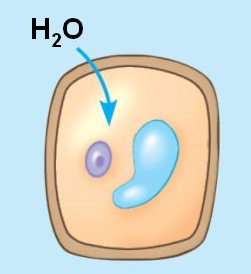
New cards
hypotonic (plant cell)
when a plant cell is immersed in a __________ solution the cell contents swell due to osmosis until the elastic cell wall exerts turgor pressure on the cell that opposes further water outake.
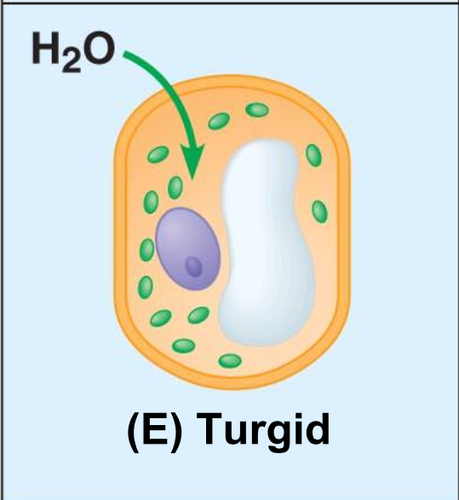
27
New cards
isotonic (plant cell)
when a plant cell is immersed in a _______ solution; there is no net movement. The cell becomes flaccid and the plant may wilt.
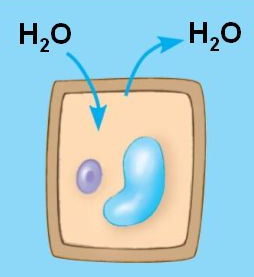
28
New cards
flaccid
limp, not firm or strong (If a plant is not watered enough, its leaves become droopy and flaccid.)
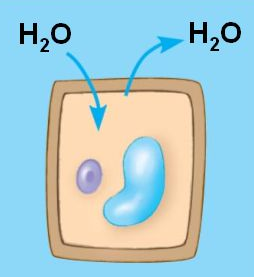
29
New cards
hypertonic (plant cells)
the plant cell loses water, its volume shrinks. The plasma membrane pulls away from the wall, this is plasmolysis. It is lethal to the cell.
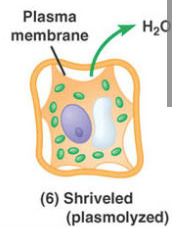
30
New cards
plasmolysis
This happens when a cell shrinks inside its cell wall while the cell wall remains intact. The plasma membrane pulls away from the wall.
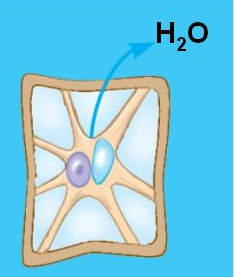
31
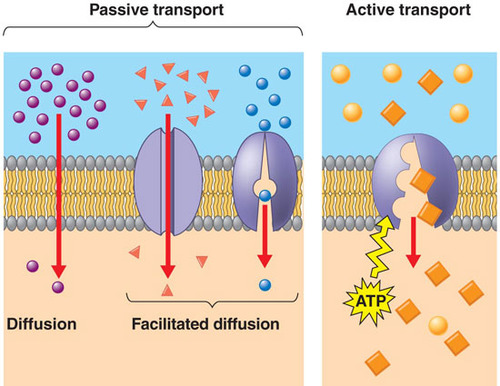
New cards
facilitated diffusion
the passive movement of molecules down their concentration gradient with the help of transport proteins.
32
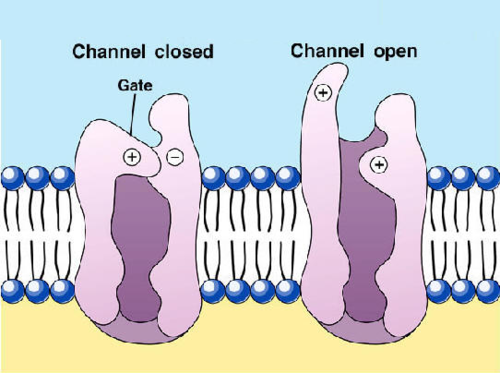
New cards
ion channels (gated channels)
Channels that open or close depending on the presence or abscence of an electrical, chemical, or physical stimulus.
33
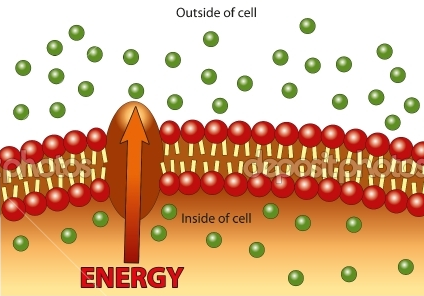
New cards
active transport
transport that requires the cell to expend metabolic energy and enables a cell to maintain internal concentrations of small molecules. Requires energy.
34
New cards
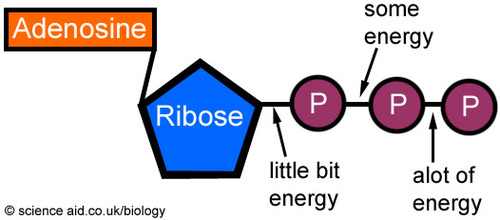
ATP
supplies energy for most active transport
35
New cards
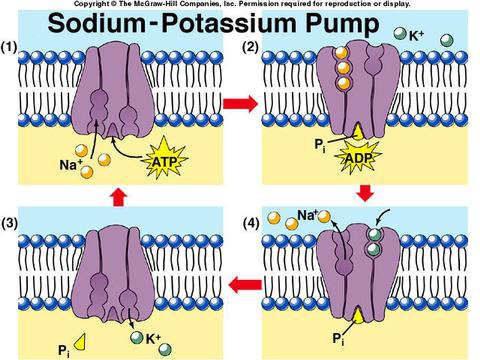
sodium-potassium pump
transport protein that, translocating the bound solute across the membrane. Exchanges sodium ions (Na) for potassium ions (K) across the plasma membrane of animal cells.
36
New cards
membrane potential
voltage across a membrane. Ranges form -50 to -200 millivolts. The inside of the cell is negative to the outside.
37
New cards
electrochemical gradient
2 combined forces drive the diffusion of ions across the membrane.
38
New cards
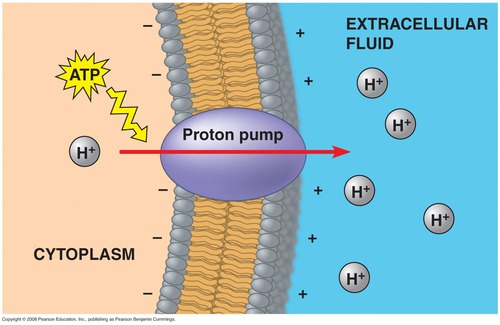
electrogenic pumps
special transport proteins that generate the voltage gradient across a membrane.
Ex. sodium potassium pump and proton pumps.
Ex. sodium potassium pump and proton pumps.
39
New cards
sodium-potassium pump
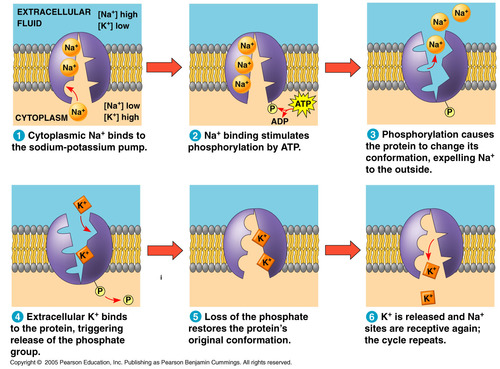
major electrogenic pump in animals. Restores the electrochemical gradient by setting up a concentration gradient. It pumps 2 K ions for every 3 Na ions that it moves out, it generates a voltage.
40
New cards
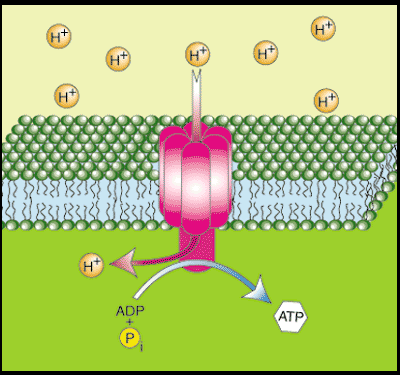
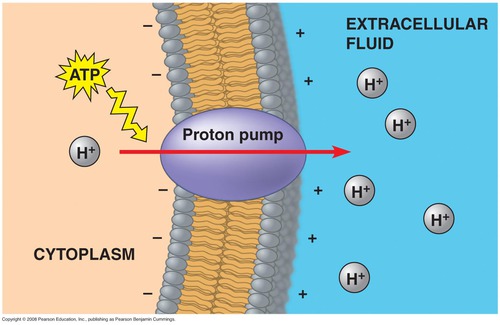
proton pumps
the major electrogenic pump. Transports protons out of the cell and transfers positive charge form the cytoplasm to the extracellular solution.
41
New cards
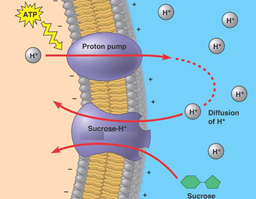
cotransport
single ATP-powered pump that transports a specific solute can indirectly drive the active transport of several other solutes in a mechanism.
42
New cards
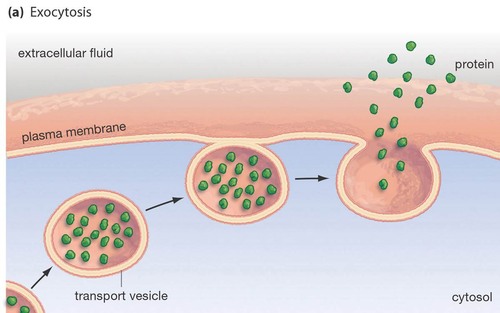
exocytosis
transport vesicle budded from the Golgi apparatus is moved by the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane. When the 2 membranes come in contact, the bilayers fuse spill the contents.
43
New cards
endocytosis
a cell brings in biological molecules and particulate matter by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane.
3 types: phagocytosis, pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis.
3 types: phagocytosis, pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis.
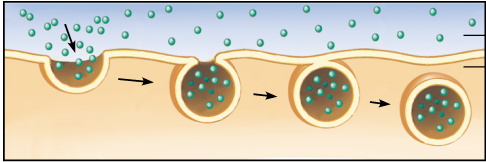
44
New cards
phagocytosis
a cell engulfs a particle in a vacuole. The vacuole fuses with a lysosome to digest the particle.
45
New cards
pinocytosis
molecules are taken up when extracellular fluid is "gulped" into tiny vesicles.
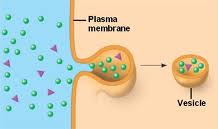
46
New cards
receptor-mediated endocytosis
endocytosis that enables a cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific materials that may be in low concentrations in the environment.
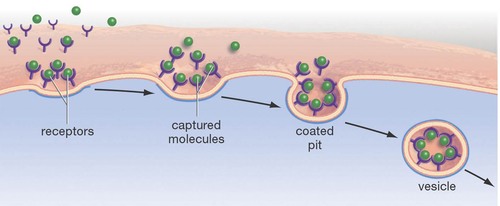
47
New cards
lipoproteins
complexes of proteins and lipids. Cholesterol travels in low density _______
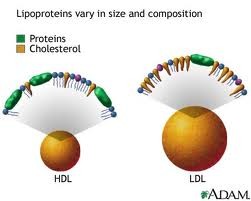
48
New cards
ligands
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
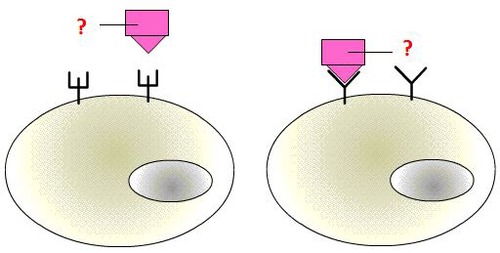
49
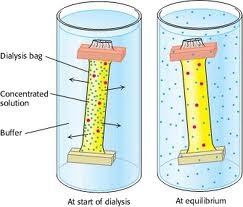
New cards
dialysis
movement of particles in a solution through permeable membranes. The diffusion of small solutes through a selectively permeable membrane.