Unit 6 Energy Resources & Consumption (APES)
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Nonrenewable Energy
A source of energy that has a finite (fixed) supply capable of being exhausted.
(Long replenish rate)
- Fossil fuels (coal, oil, & natural gas)
- Nuclear Power
Renewable energy
A resource that has a theoretically unlimited supply and is not depleted when used by humans.
(Replenish rate is faster than consumption rate)
- Solar
- Wind
- Water
- Waves
- Geothermal
- Biomass
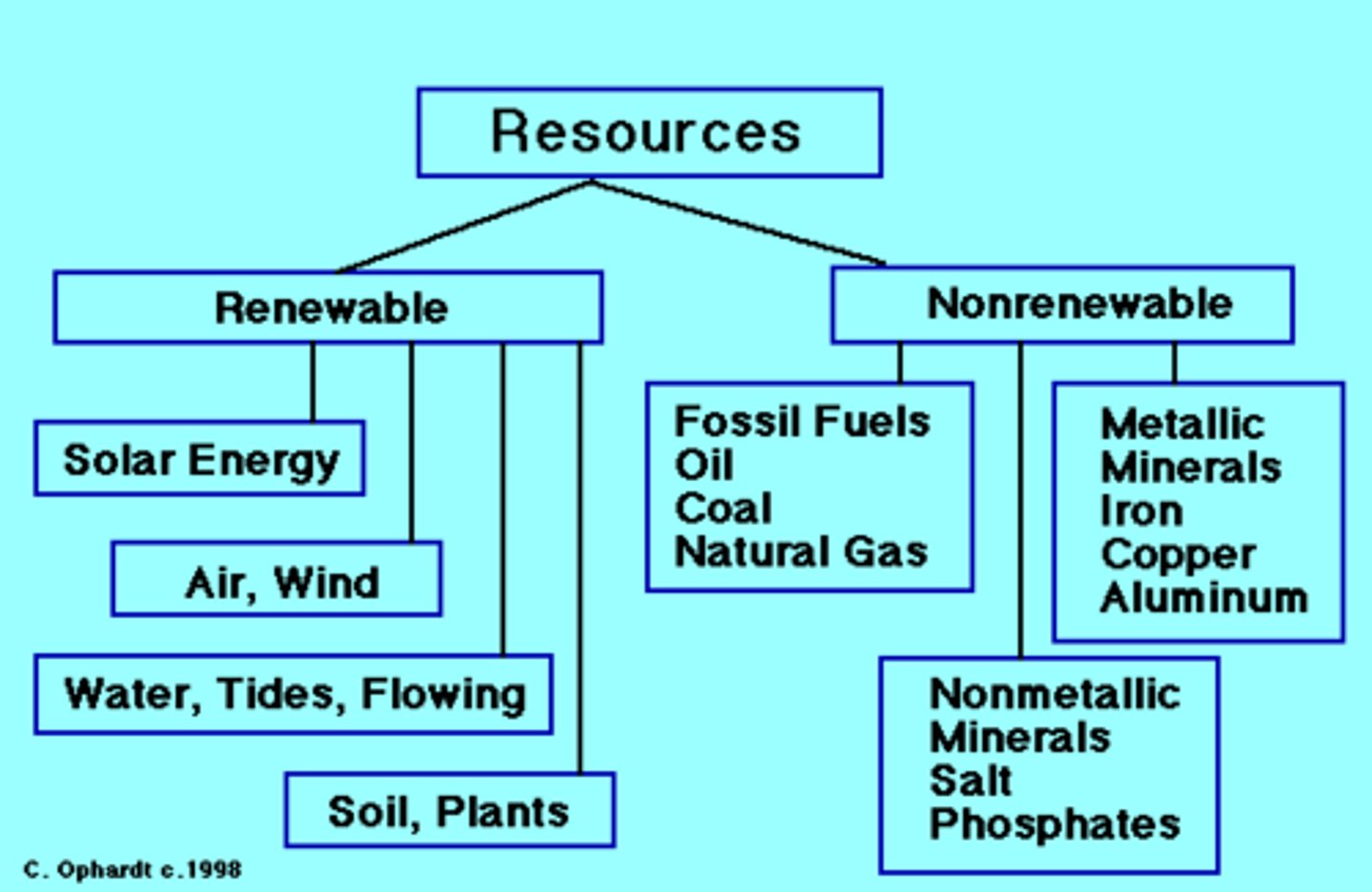
Examples of nonrenewable resources
Fossil fuels (oil, coal, natural gas), Uranium (nuclear), Oil Shale, Metals (iron, copper, aluminum, gold, silver, etc)
Examples of renewable resources
Tidal, Solar, Wind, Geothermal, Hdyroelectric, Biomass (wood, crop, manure, waste, topsoil, etc)
Trends in total world energy consumption
20% of the world's population consumes 80% of the world's total energy consumption
Uneven distrubtion pattern of energy use
Developed countries use more energy than developing countries.
Most widely use energy in the world
Fossil Fuels (coal, oil, & natural gas)
The drive for higher energy demand in developed countries
Industrialization
Factors that influce energy use
- Availabilty
- Price
- Government regulations Taxes increase (discourage use)
Subsidies, rebates, tax credits (encourages use)
Subsistence fuels
Supporting oneself - in developing countries biomass (wood, charcoal, manure, grass, etc) was commonly used to support the energy need for local households.

The country with the highest energy consumption
China (primarily coal)
The country with the 2nd highest energy consumption
United States
(fossil fuels such petroleum & natural gas account for about 70% total energy consumption)
Energy is measured in units called
Joules (J)
1 Watt (W) = 1 joules per second ( W = J/s)
All energy from fossil fuels comes from
Sunlight that has been captured by plants and stored in a form of carbon.
Electricity is generated by
using steam (from water boiled by fossil fuels or nuclear) or falling water to turn a generator
Turbine
A device with blades that can be turned by water, wind, steam, or exhaust gas from combustion that turns a generator in an electricity-producing plant
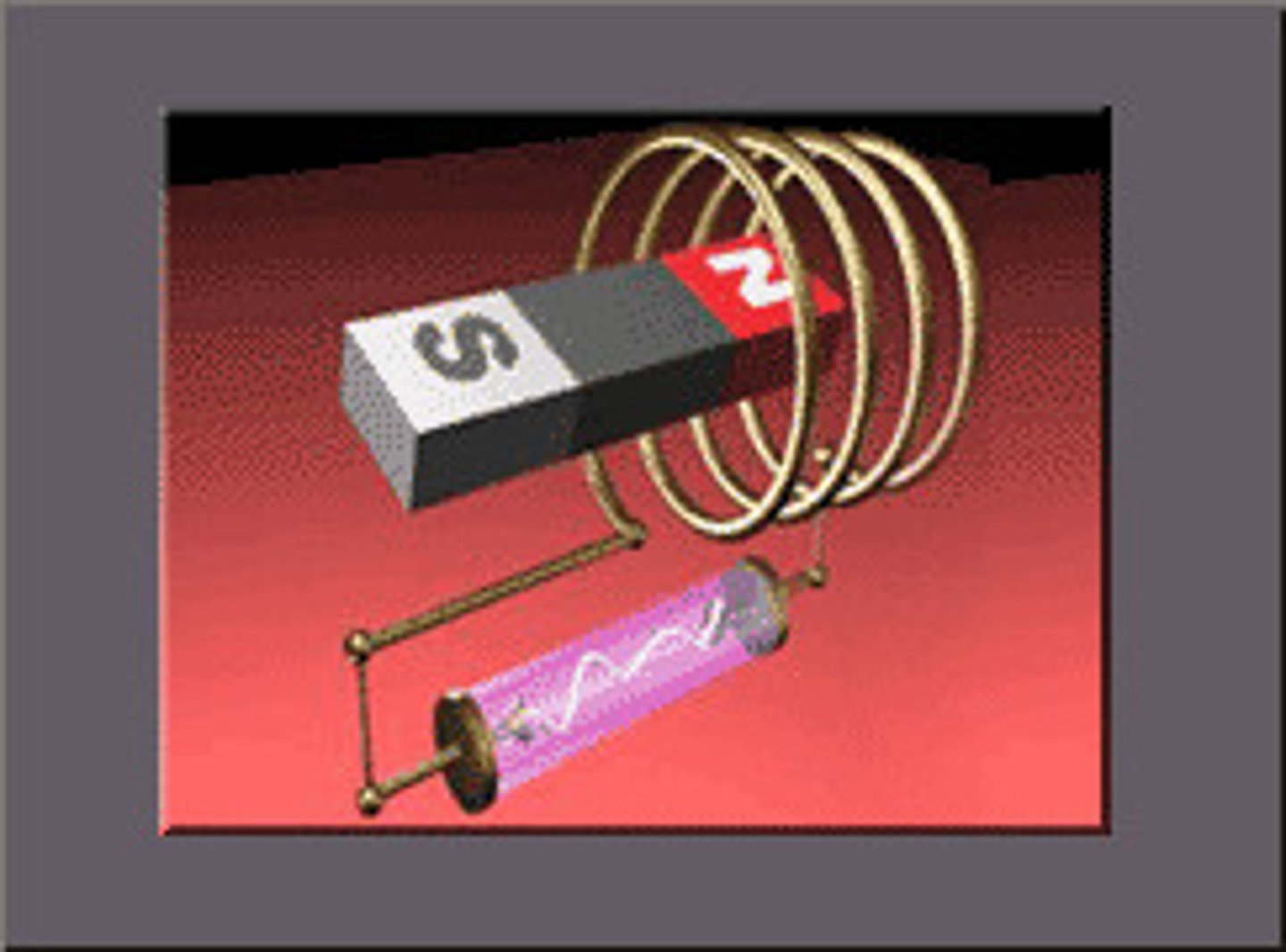
Generator
the induction of a potential difference in a wire, which is moving relative to a magnetic field, or experiencing a change in a magnetic field (make electricity using magnet and coil of wire "selenoid")
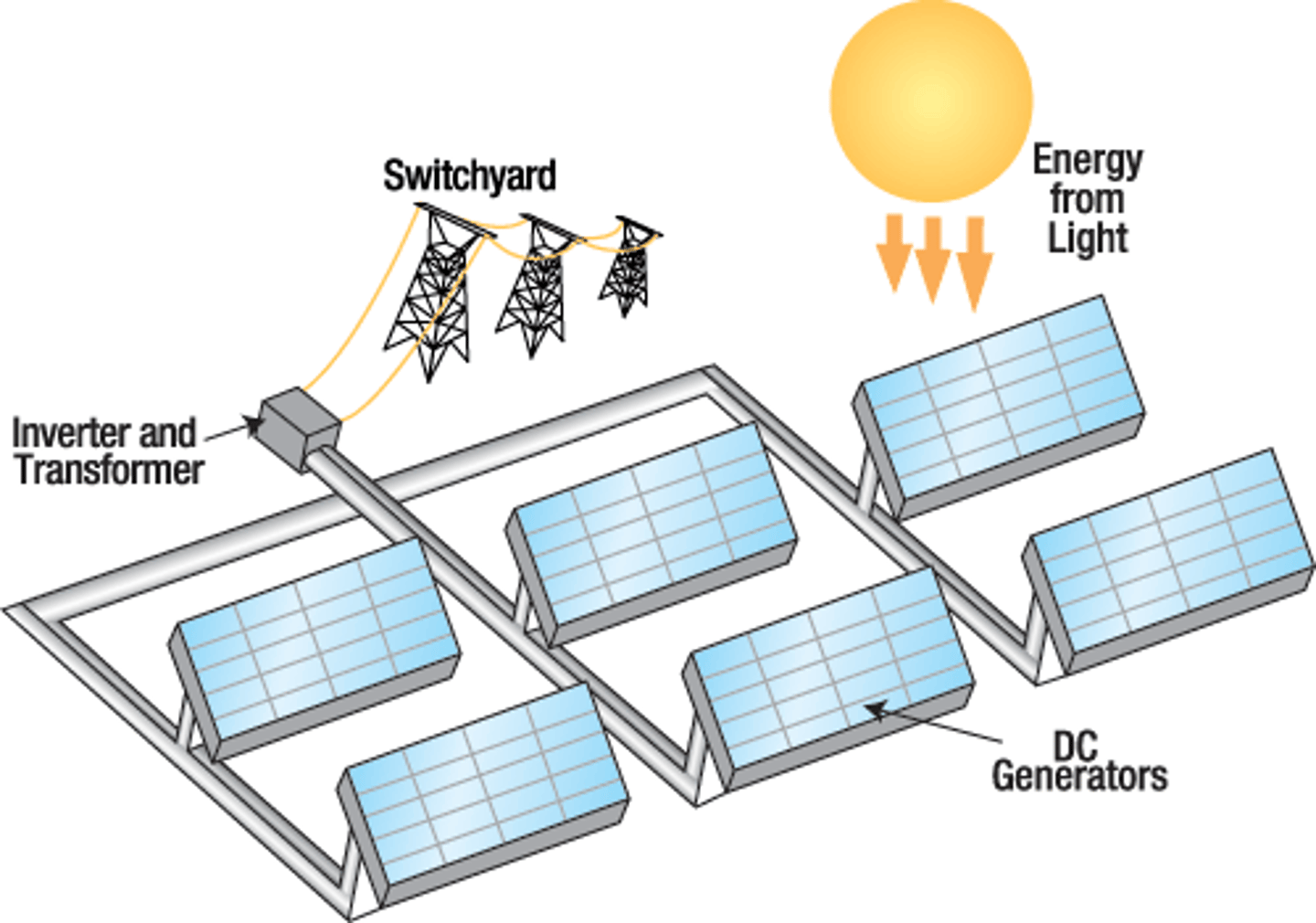
Solar cells
cells made of several layers of light-sensitive materials which convert sunlight directly into electrical energy
2 most common energy source for fuel in developing nation
Biomass:
- Wood
- Charcoal
Biomass fuel source disadvantages
Not as efficient at fossil fuels
"Dirty" energy (Release CO2 and partiulate polluting the air)
- Deforestation (habitat loss)
- Desertification
- Soil erosion
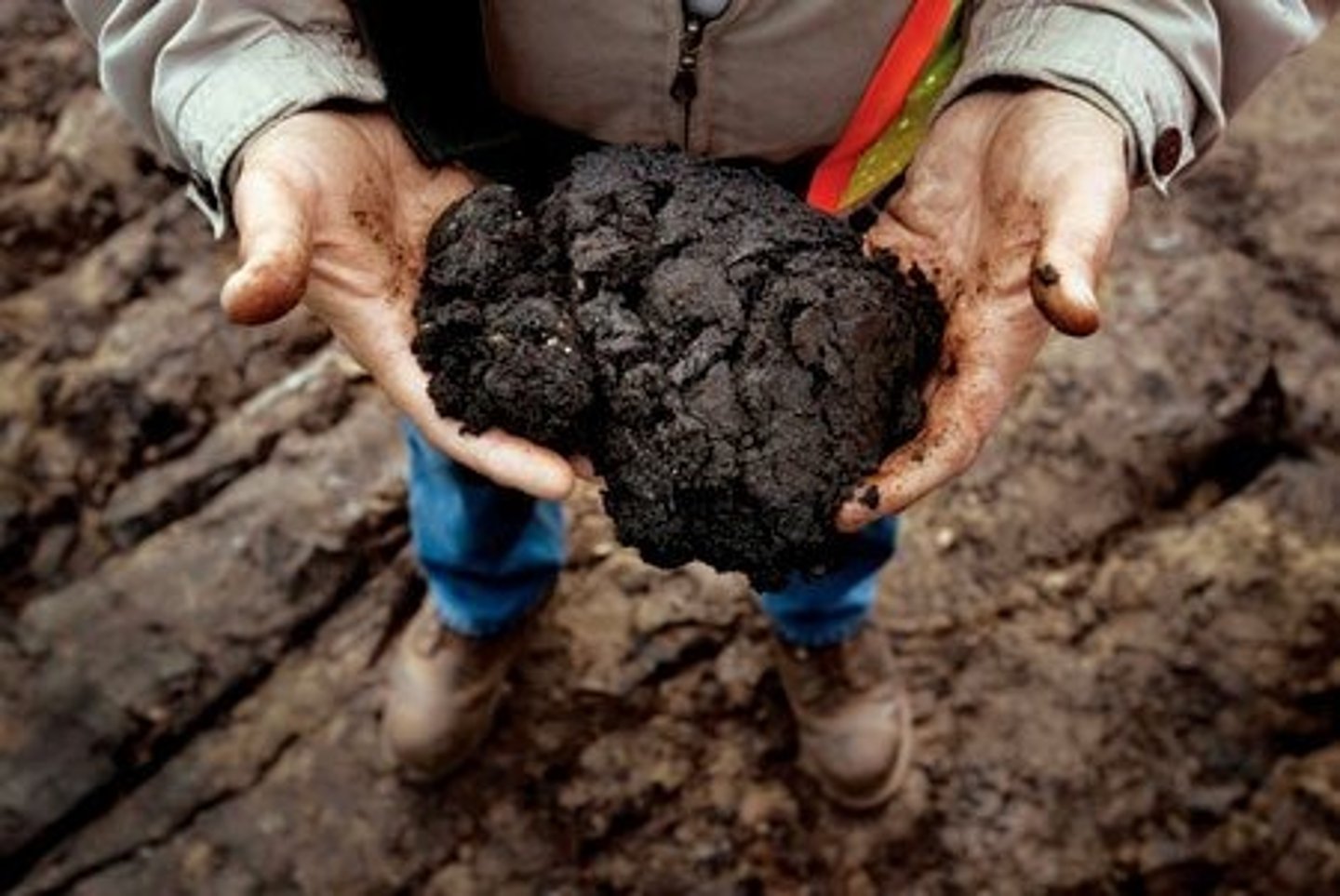
Coal formation order:
Peat, lignite, sub-bituminous coal, bituminous coal, anthracite coal.
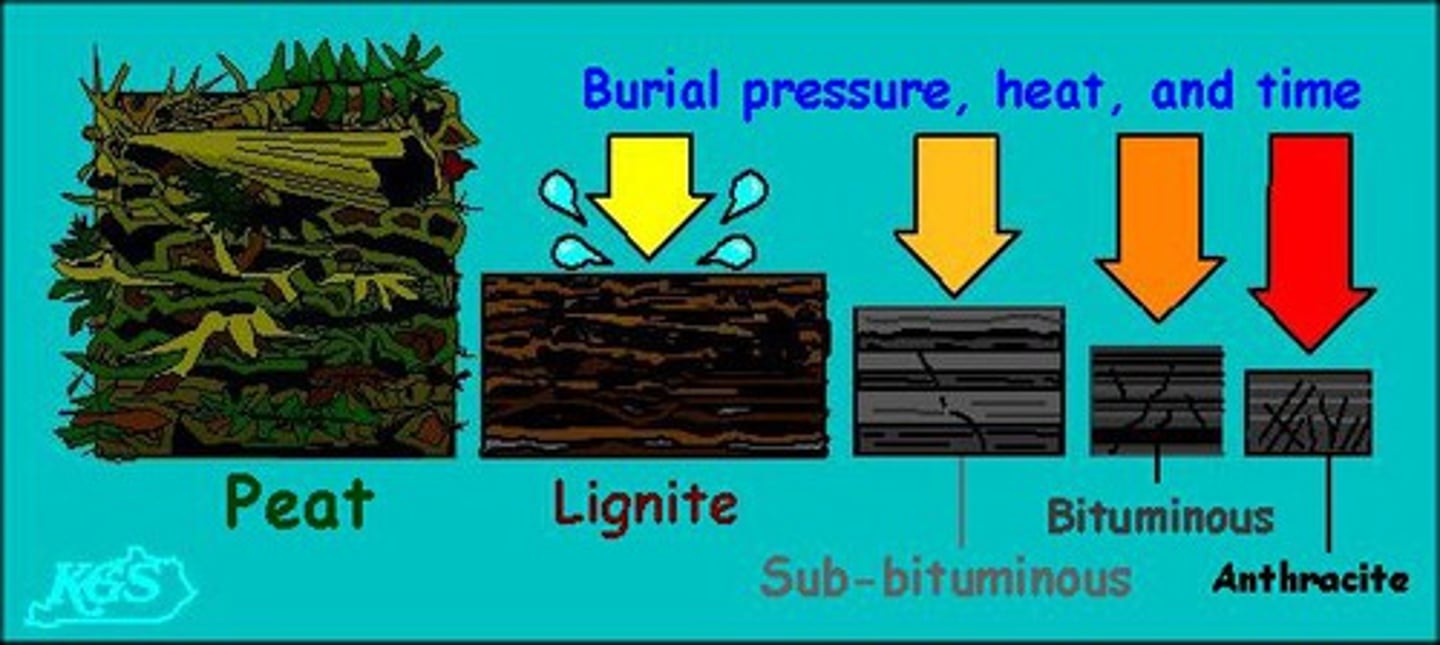
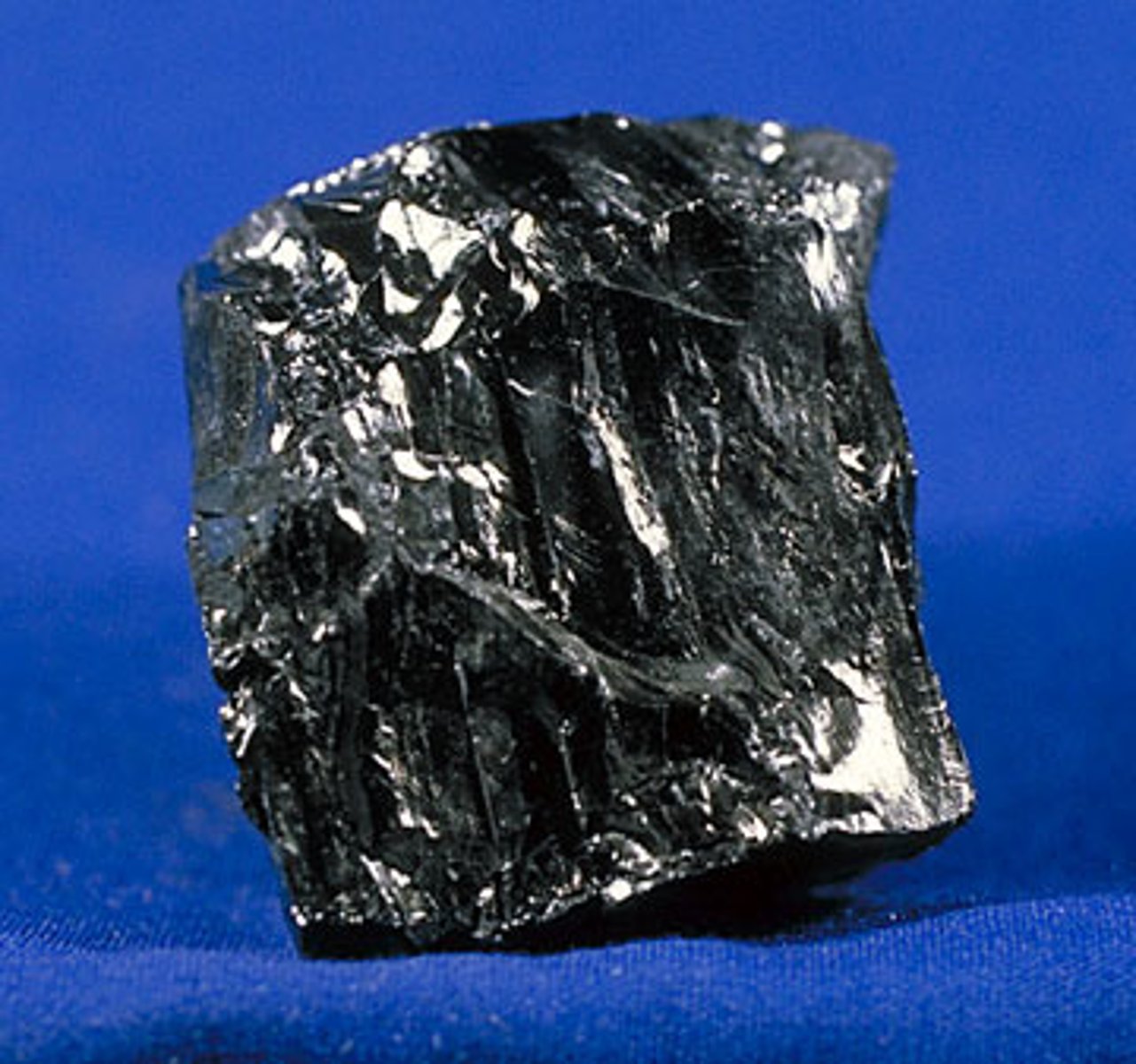
Anthracite coal
-Sedimentary
-Forms from bituminous coal
-Has the highest energy content of all coals
-High Luster (shiny)
- Cleaner burn compared to other coal form
- Burns hotter and longer

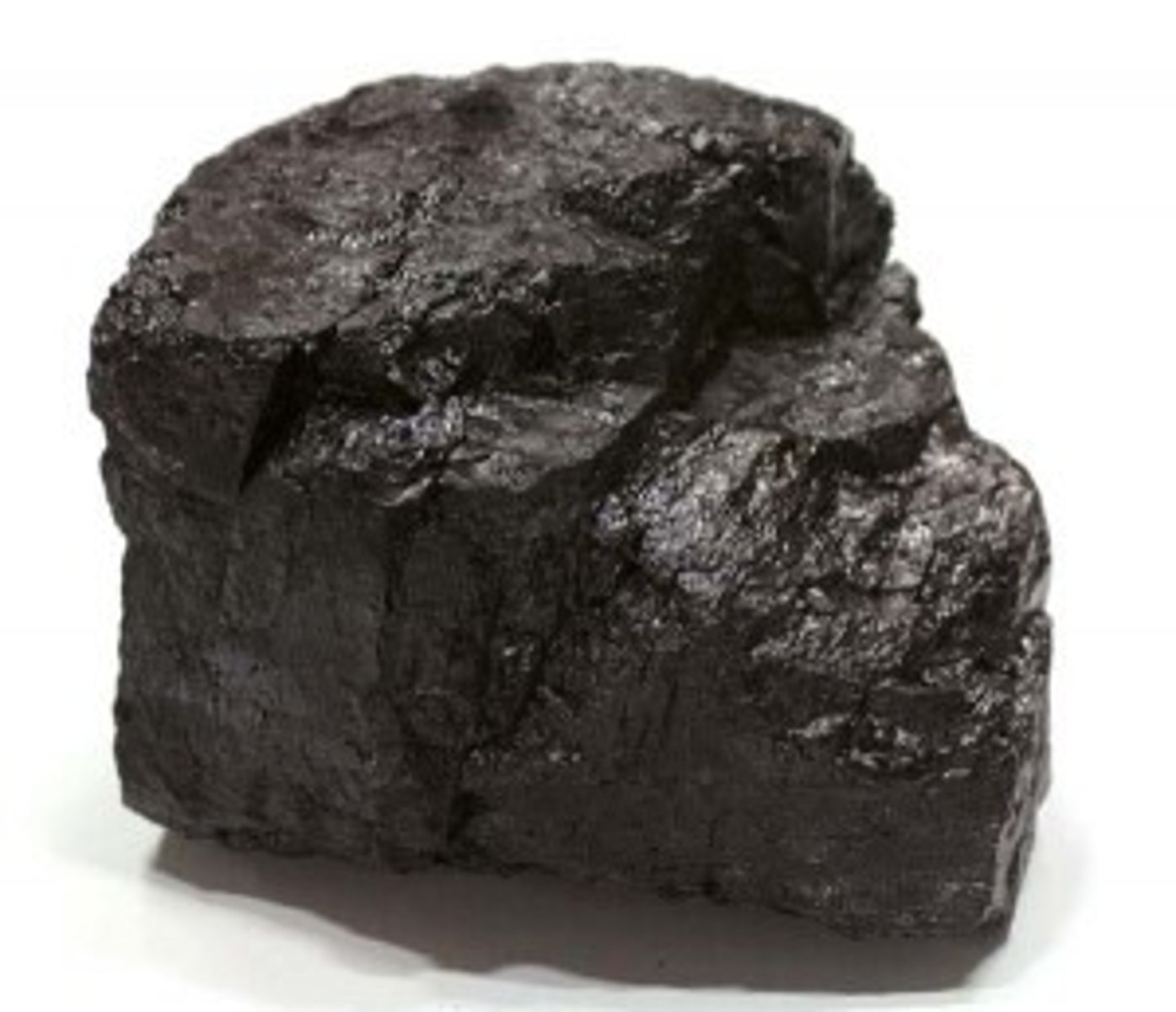
Bituminous (soft coal)
Sedimentary rock that is the result of more heat and pressure applied to lignite

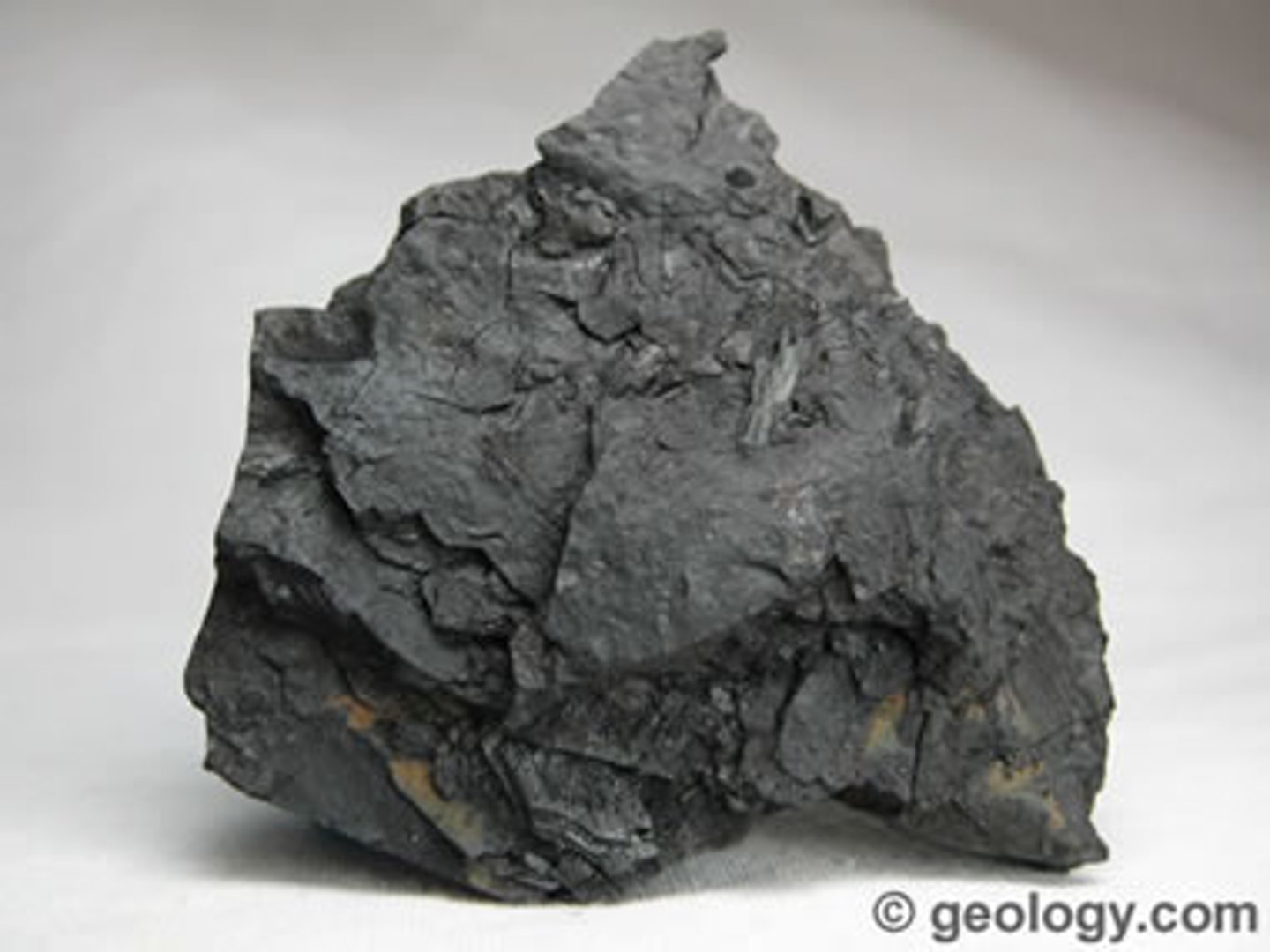
Lignite (brown coal)
-Lowest rank of coal, brownish black, visible plant material, crumbly, organic rock.

Peat
partially decayed plant matter found in bogs
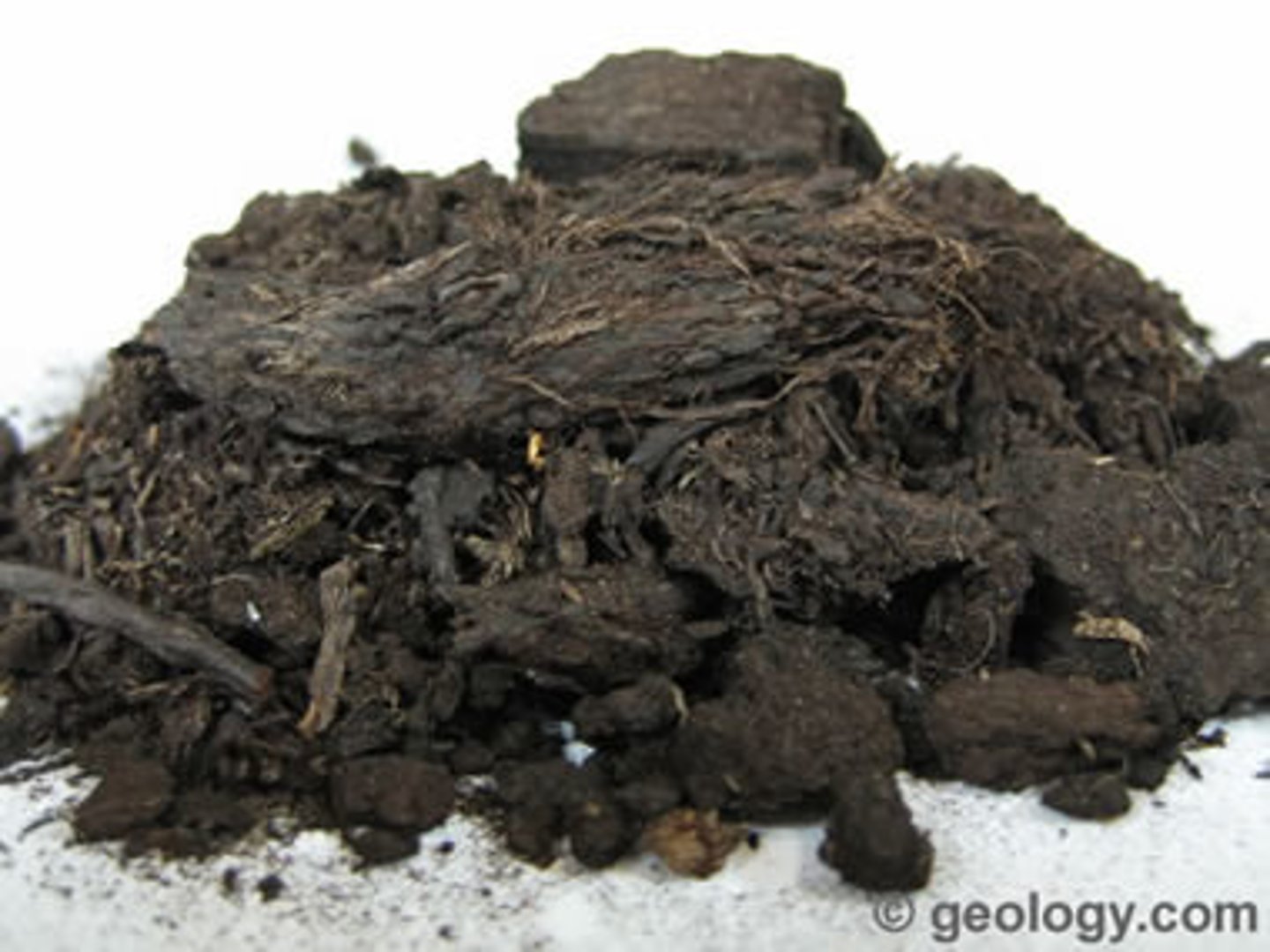

Coal uses
#1 Source used to produce electricity globally
- Natural gas = #2
Largest source of US electricity; also used in industrial processes (eg steel manufacturing)

Combustion reaction
A chemical reaction that occurs when hydrocarbons (fossil fuels) reacts with oxygen, releasing energy (heat + light), CO2, & Water
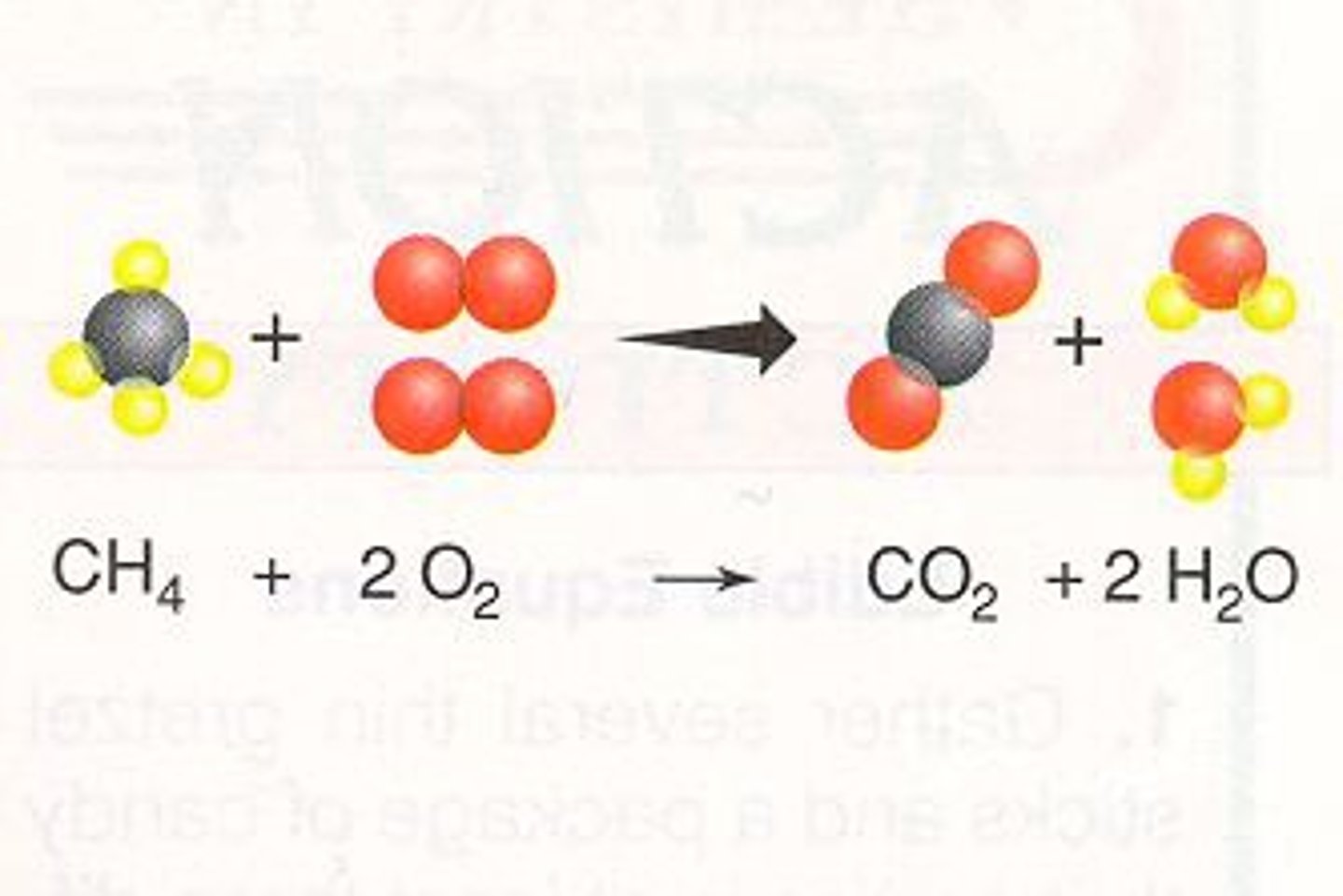
Steps to produce electricity
1) Heat used to boil water into steam
2) Steam turns a turbine
3) Turbine Powers Generator
4) Generator Produces Electricity
Sources that can be use to produce eletricity: Coal, oil, natural gas, biomass, & trash
coal disadvantages
- Habitat destruction from mining
Large amounts of CO2
-- CO2 (GHG) contributes to climate change
- Sulfur adds to acid deposition
- Air pollution in form of soot and ash (cause respiratory health issues in humans/animals)
- Pollute water (lead, mercury, and arsenic) - Disrupt nervous system and cause health issues
- Release SOx & NOx (sulfur/nitrogen) - irritates the respiratory system and contribute to smog and acid precipitation aka acid rain)

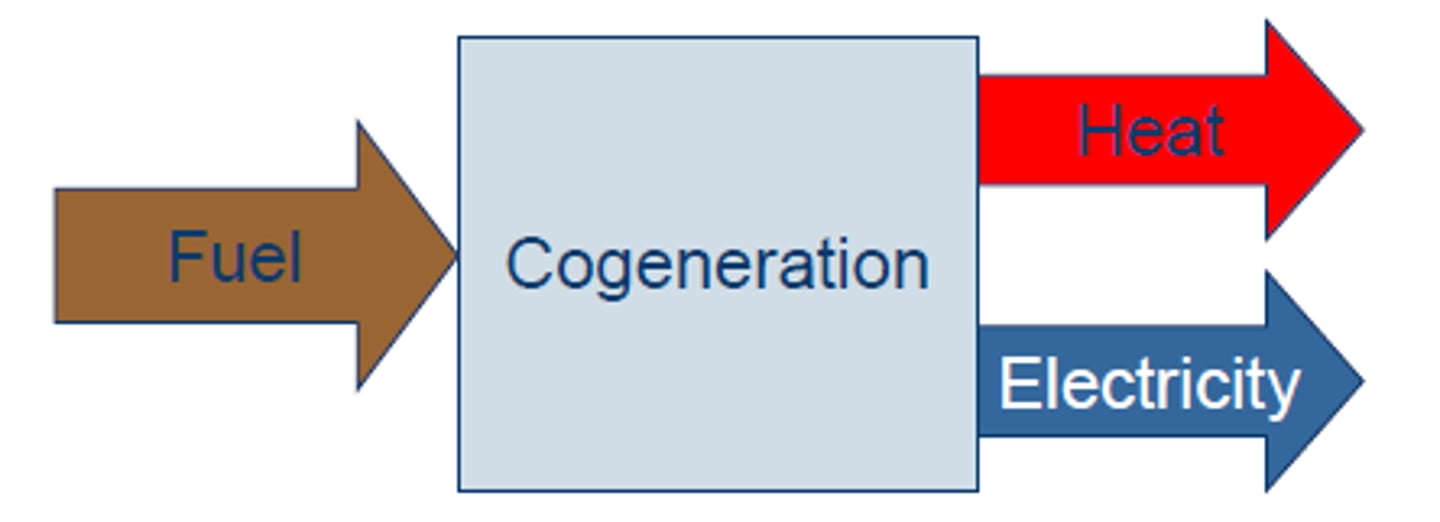
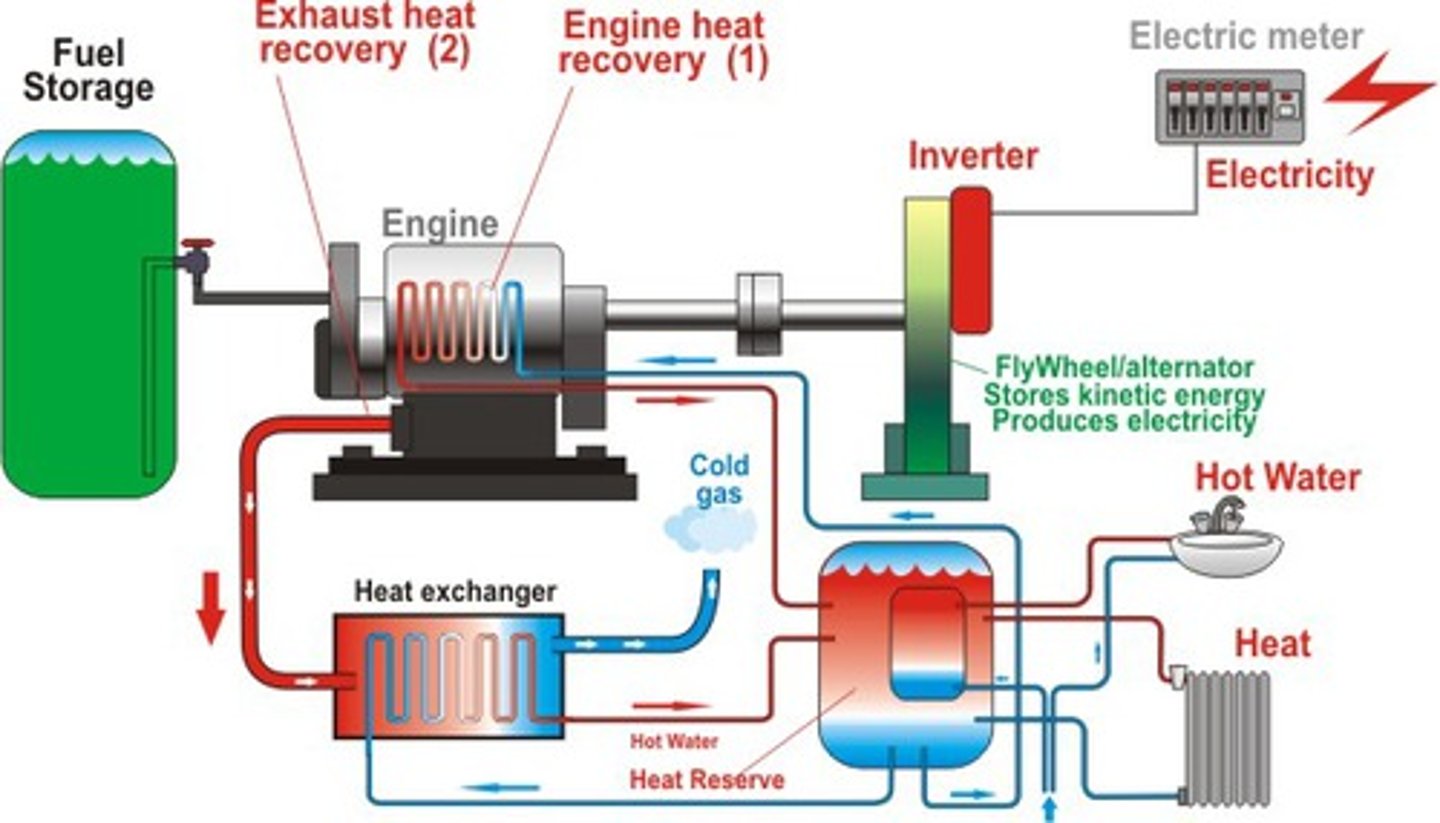
Cogeneration/combined heat and power (CHP)
The use of a fuel to generate electricity and produce heat which can be use for other things such as heating homes + water
-- Increase energy efficiency to about 90%
Coal only = 30%
Natural gas only = 60%
oil extraction
Crude oil is drilled or pumped out of the ground and then refined by heating and separating different components by their boiling points

tar sands/oil sands
sand or clay formations that contain a heavy-density crude oil (crude bitumen); extracted by surface mining

Oil disadvantages
(A) Water pollution from oil spills and leaks toxic = loss of Biodiversity
(B) Environmental costs not included in market price (habitat fragmentation)
(C) Releases CO2 and other air pollutants when burned
(D) Vulnerable to international supply interruptions

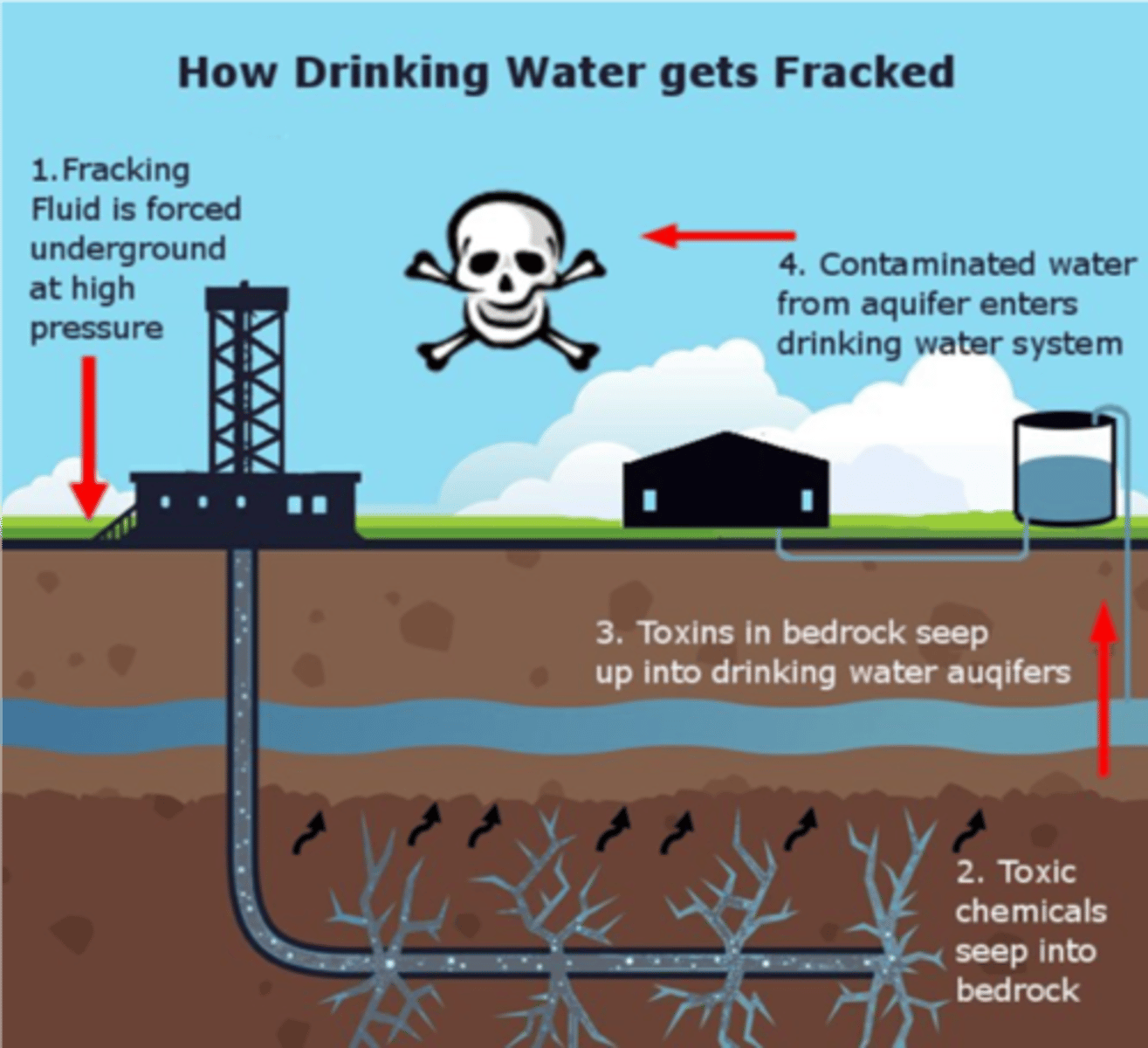
Fracking (hydraulic fracturing)
The pumping of water at high pressure to break apart rocks in order to release natural gas
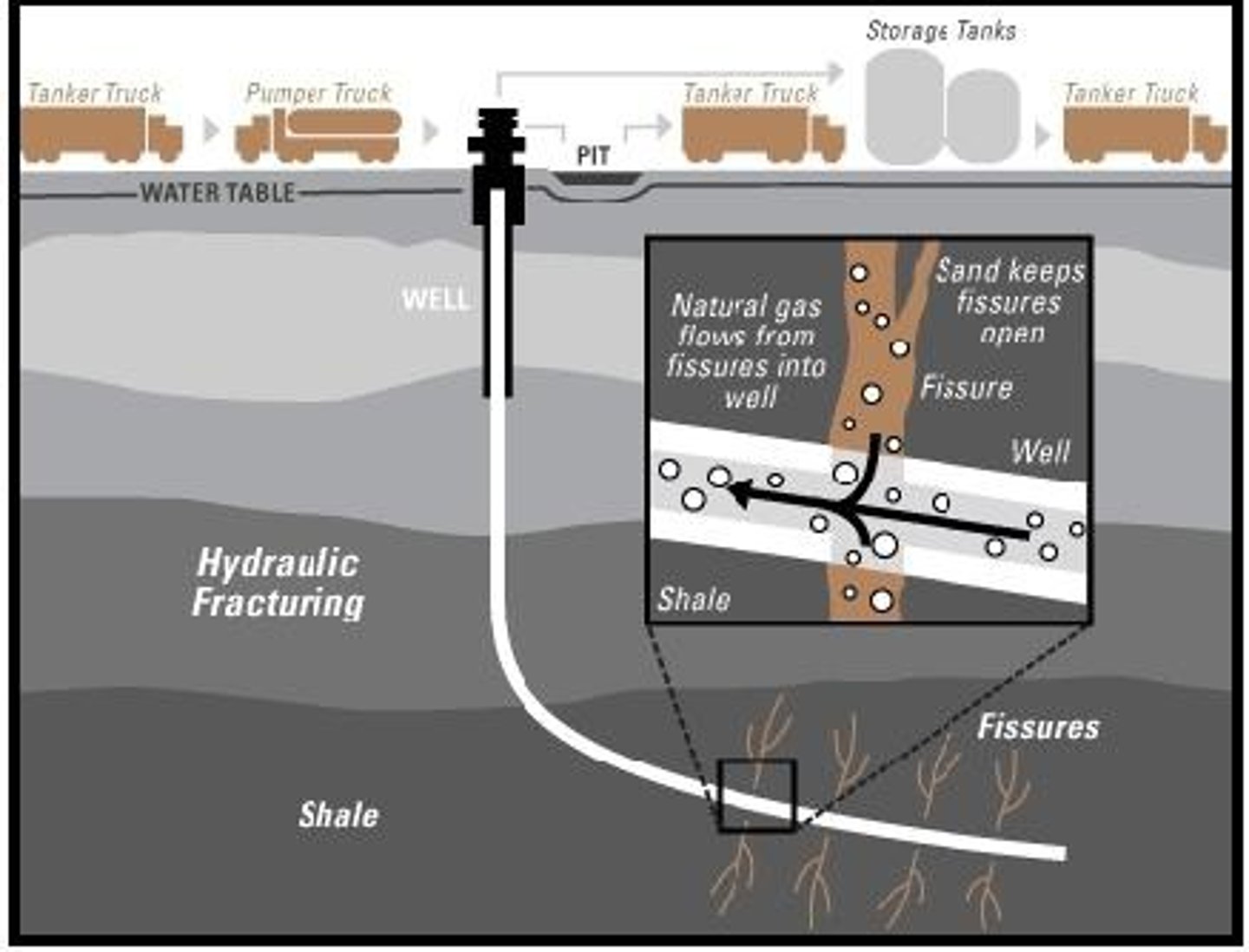
Fracking Disadvantages
1) Contamination of ground water (Can be toxic to plants and animals)
- Large amount of water used = depletion
2) Seismic activity
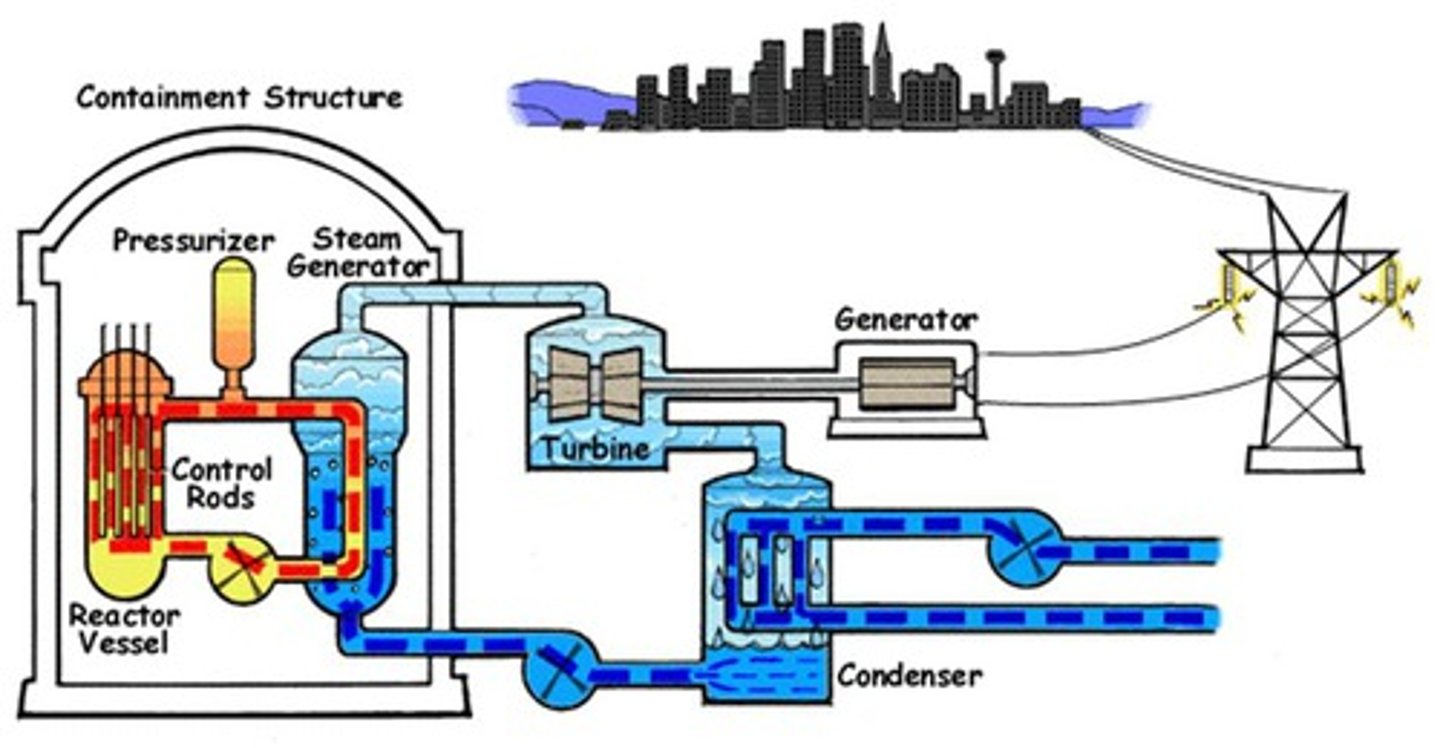
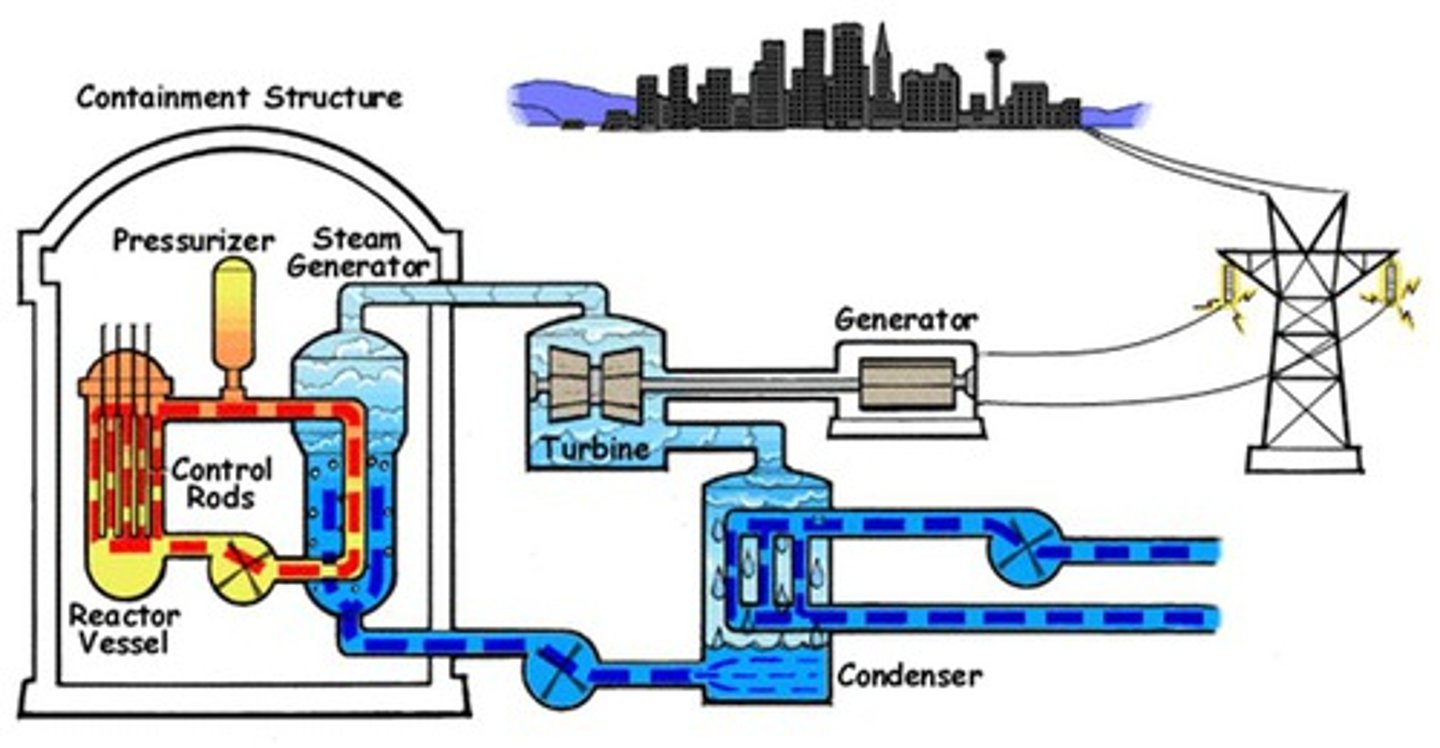
nuclear fission energy
Controlled nuclear chain reaction produces heat, driving steam turbines to produce energy.
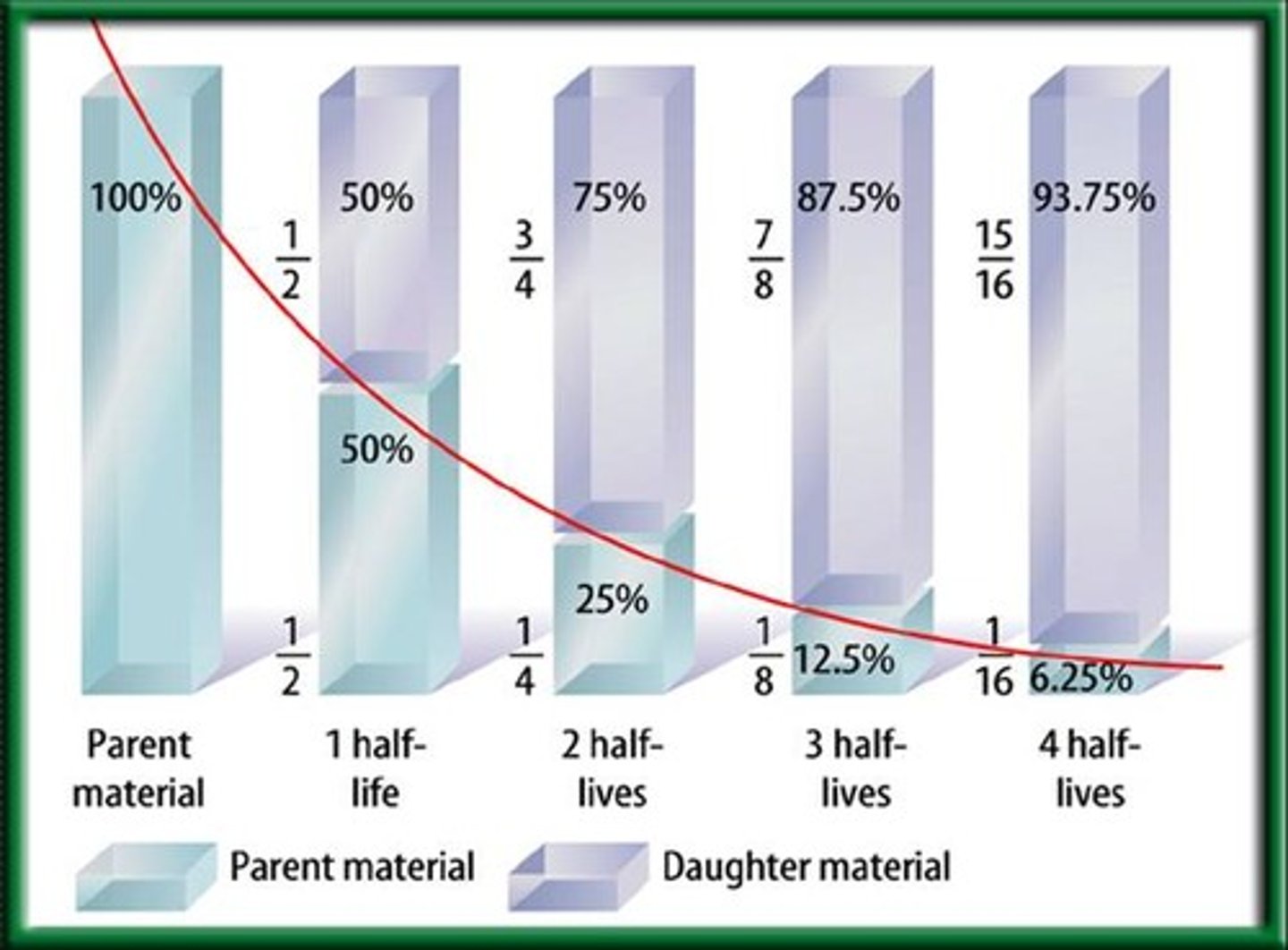
radioactive half-life
amount of time it takes for half a sample of radioisotopes to decay
Uranium-235
an isotope used to fuel most nuclear fission reactors
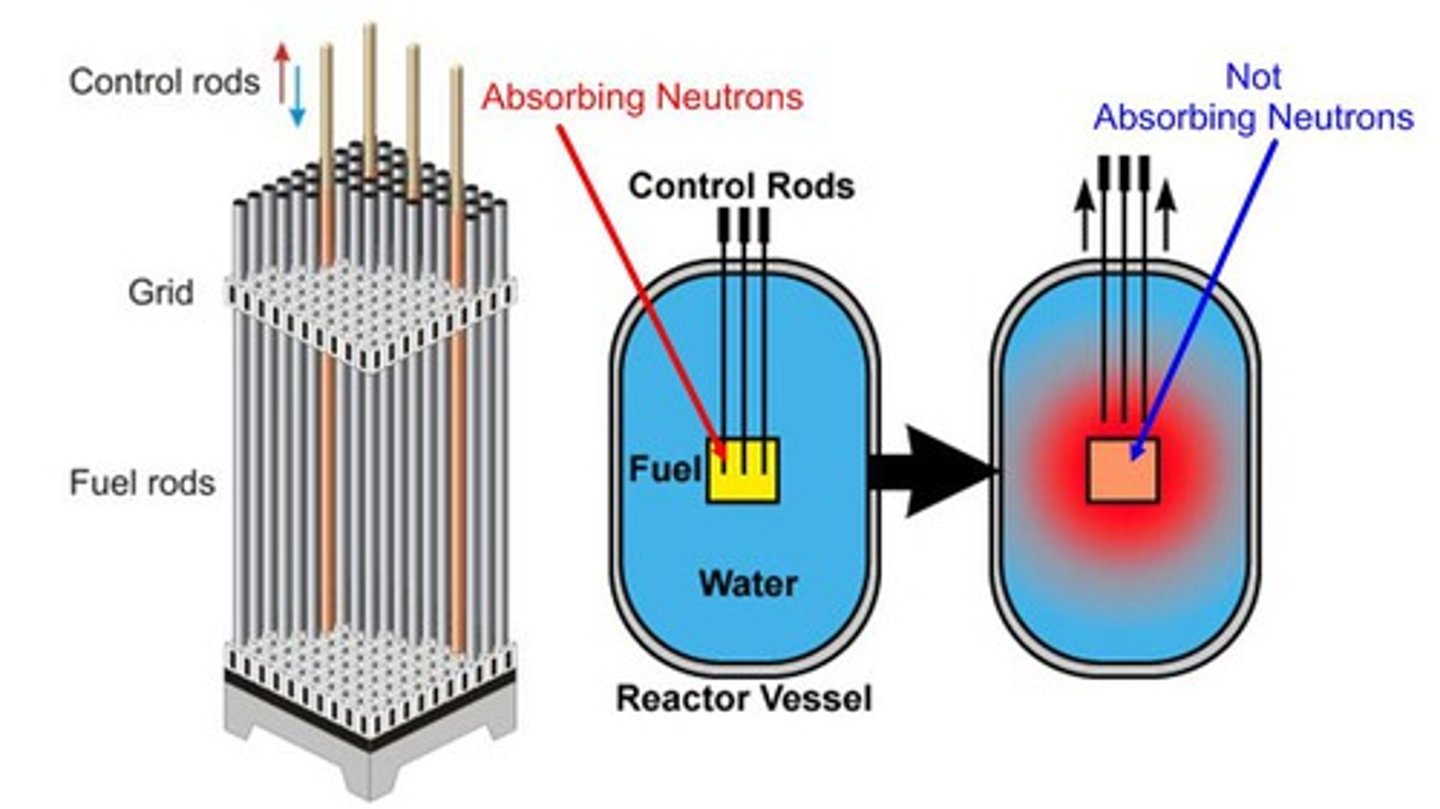
Control rods in a nuclear reactor are used to
Absorb neutrons to slow the reaction down and prevent meltdown (explosion)
cooling tower
Part of an electric power generating plant within which heated water is cooled.

Nuclear Energy Pros
Produces a lot of energy; does not cause air pollution
- Cheap source of energy (after initial construction)
The only green house gas released is water vapor (but it stays in the atmosphere briefly)
Nuclear energy cons
- Accident can happen
- Expensive construction
- Nuclear waste last for millions of years
- High volume of water use
- Thermal pollution can decrease oxygen in the water and impact marine organisms.

Three Mile Island
1979 - A mechanical failure and a human error at this power plant in Pennsylvania combined to permit an escape of radiation over a 16 mile radius. Radiation level was not enough to cause any serious health issue.

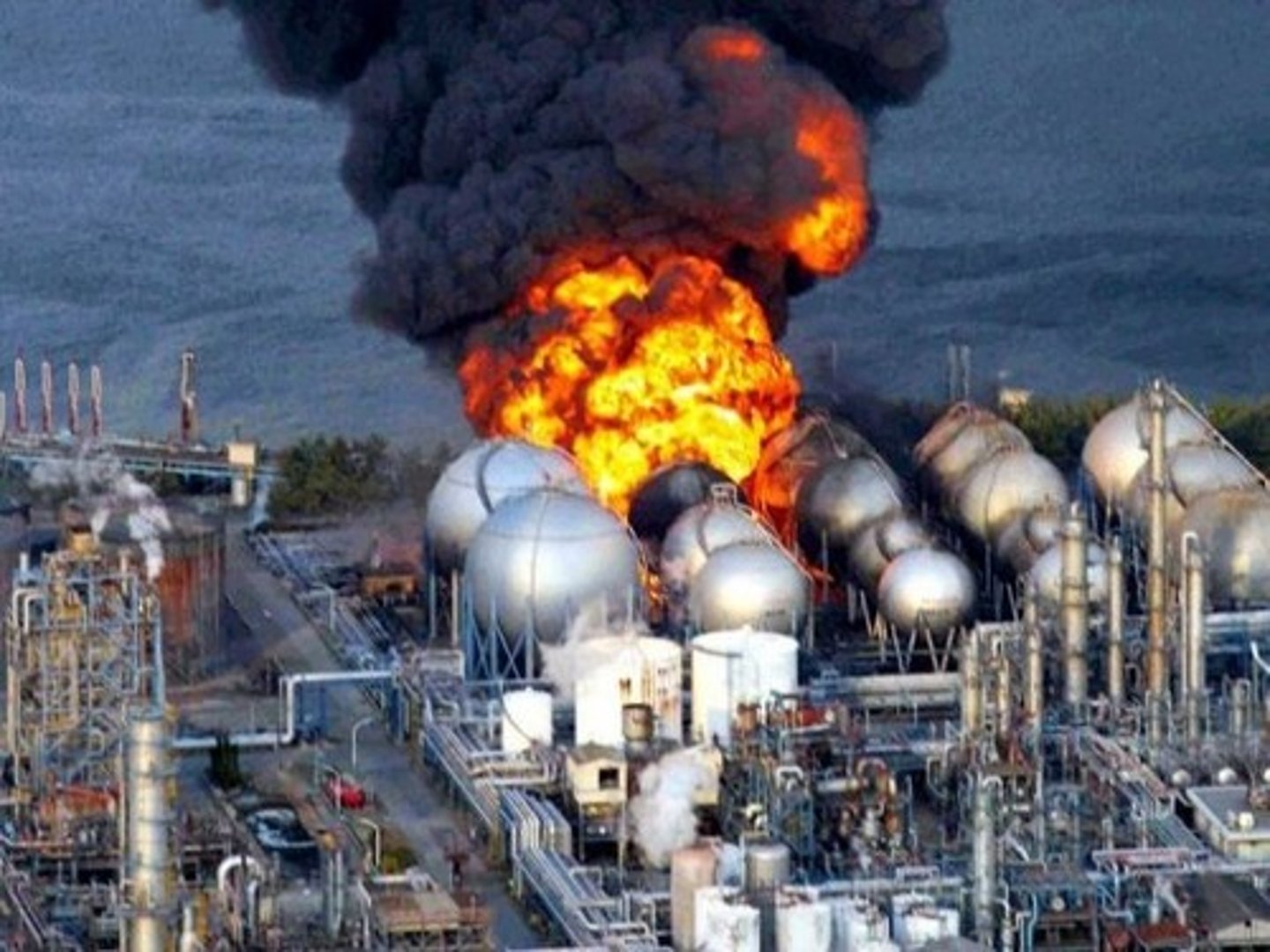
Fukushima Daiichi
Japanese nuclear power plant severely damaged by the tsunami associated with the March 2011 Tohoku earthquake that rocked Japan. Most radiation drifted over the ocean away from population centers, but the event was history's second most serious nuclear accident.

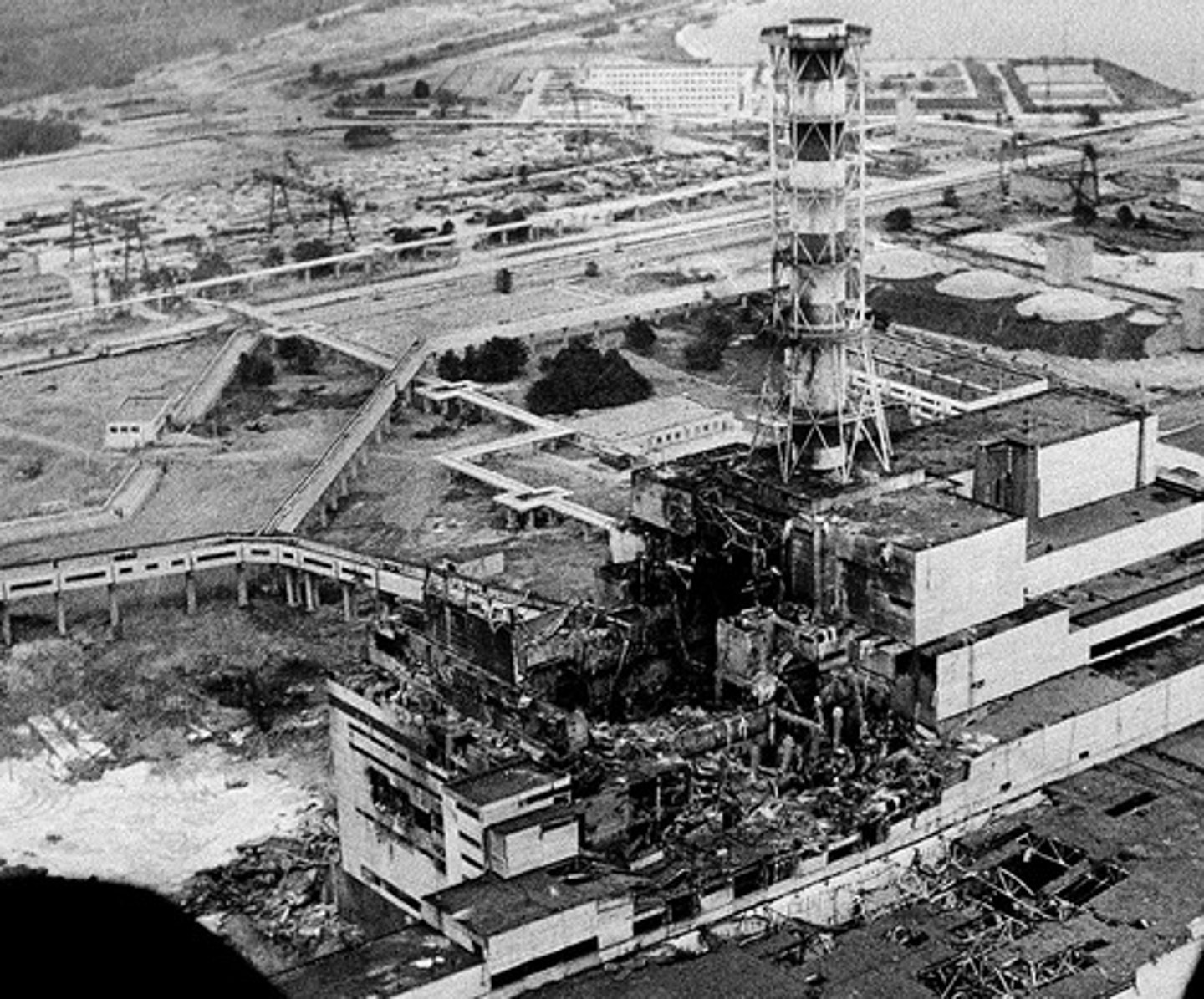
Chernobyl, Ukraine
On April 26, 1986, an unauthorized safety test led to a fire and explosion at a nuclear power plant-as a result, millions of people in Europe are exposed to unsafe levels of radiation.

Nuclear radiation impact on health
- Genetic mutation
- Kill cells
- Destroy bone marrow, destroy body immune cells
Biofuels
Fuels, such as ethanol or methanol, that are created from the fermentation of plants or plant products.

Biomass energy
energy produced by burning organic matter, such as wood, food scraps, and alcohol

Biomass pros and cons
PROS:
-no NET carbon release [doesnt add nor reduce carbon, where fossil fuels add]
-renewable (in theory)
-reduce methane emission
-reduce pollutant emissions
-waste → energy
CONS:
-monoculture agriculture: fossil fuel, fertilizer inputs [to grow]
-land conversion→deforestation, erosion, etc
-loss of FOOD crop production
Biomass impact health
- CO, NOx, PM, and VOCs can all cause respiratory issues
- Indoor buring of biomass can cause worsen asthma, bronchitis, COPD, emphysema, and eye irritation
Impact of biomass use on the environment
- Can cause deforestation
- Air pollutants
- Habitat loss
- Increase land erosion which can release CO2 into the atmosphere
- Decrease water filtration
- Release NOx, VOCs, and PM which form smog.
Corn Ethanol
Produced from corn by ethanol fermentation and distillation. Mainly used in fuel production.
- Added to gasoline to decrease oil use
- Allow gasoline to burn and not explode
- Less efficient than pure gasoline

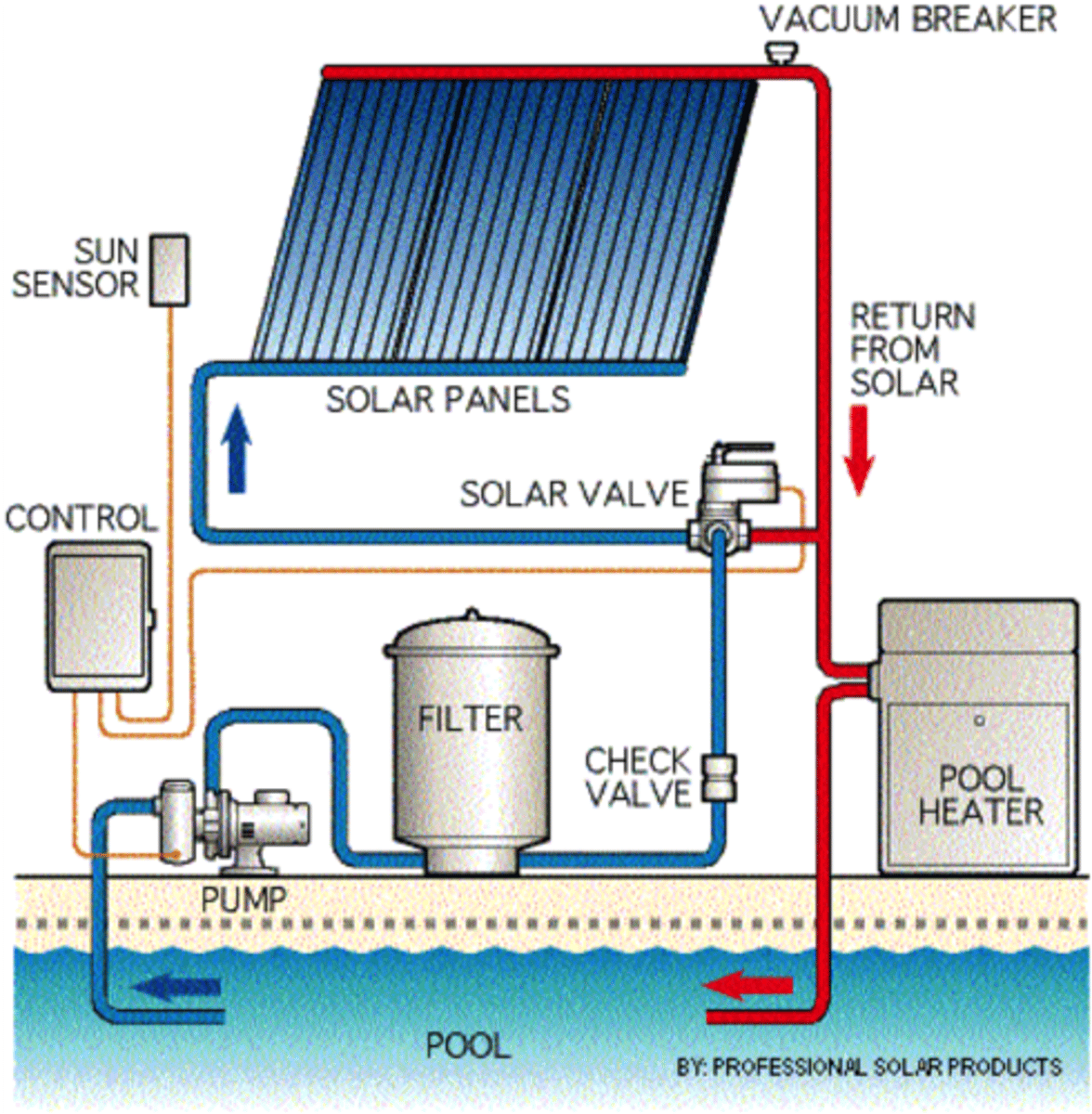
Active solar energy
Solar radiation is captured with photovoltaic cells that convert light energy to electrical energy or use direct sunlight to circulate heat water to warm homes.
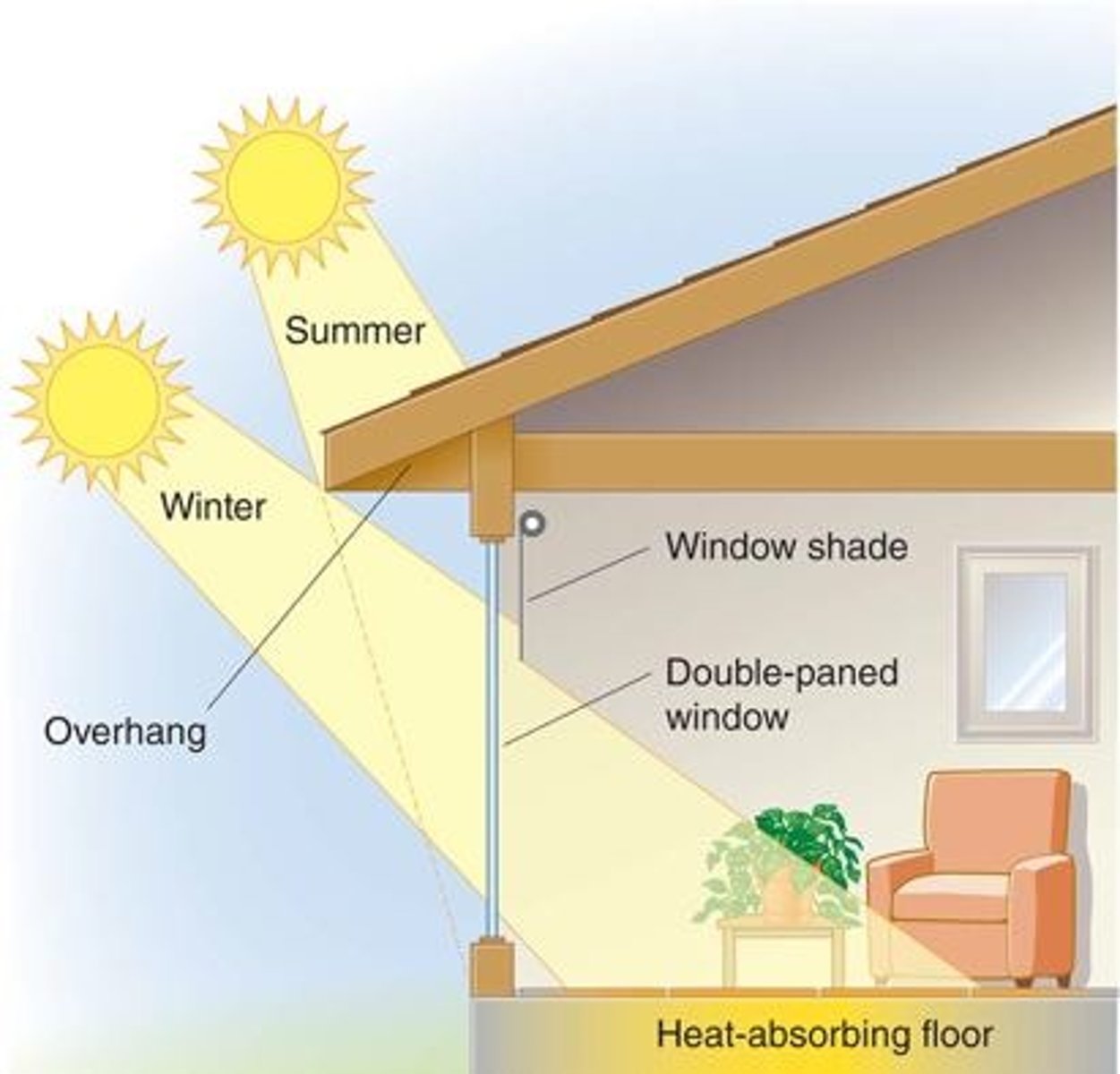
Passive solar energy
Solar energy systems collect energy without the use of mechanical devices.
- Solar oven to cook food
- Building design to block sunlight in warmer months and allow sunlight in during colder months
- Double-paned windows for insulation
- Southern facing windows with roof overhang
- Tree shades / Window shades
- Dark colors for absorbing more sunlight
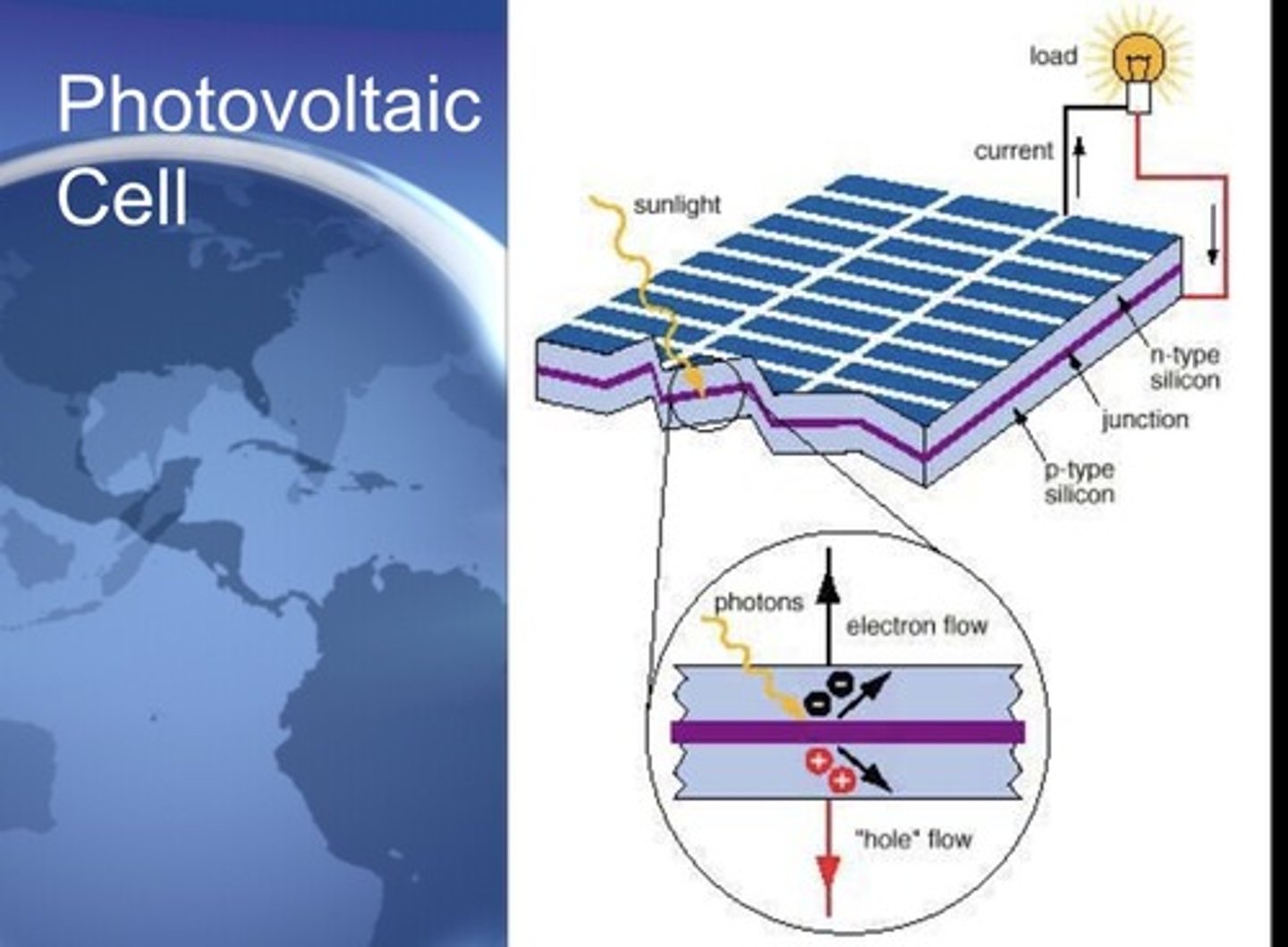
PV cells (photovoltaic)
convert sunlight directly into electrical energy (solar panels)
heliostats (Mirrors) - (concentrated solar thermal - CST)
Large stationary tracking mirrors concentrating sunlight to a central point

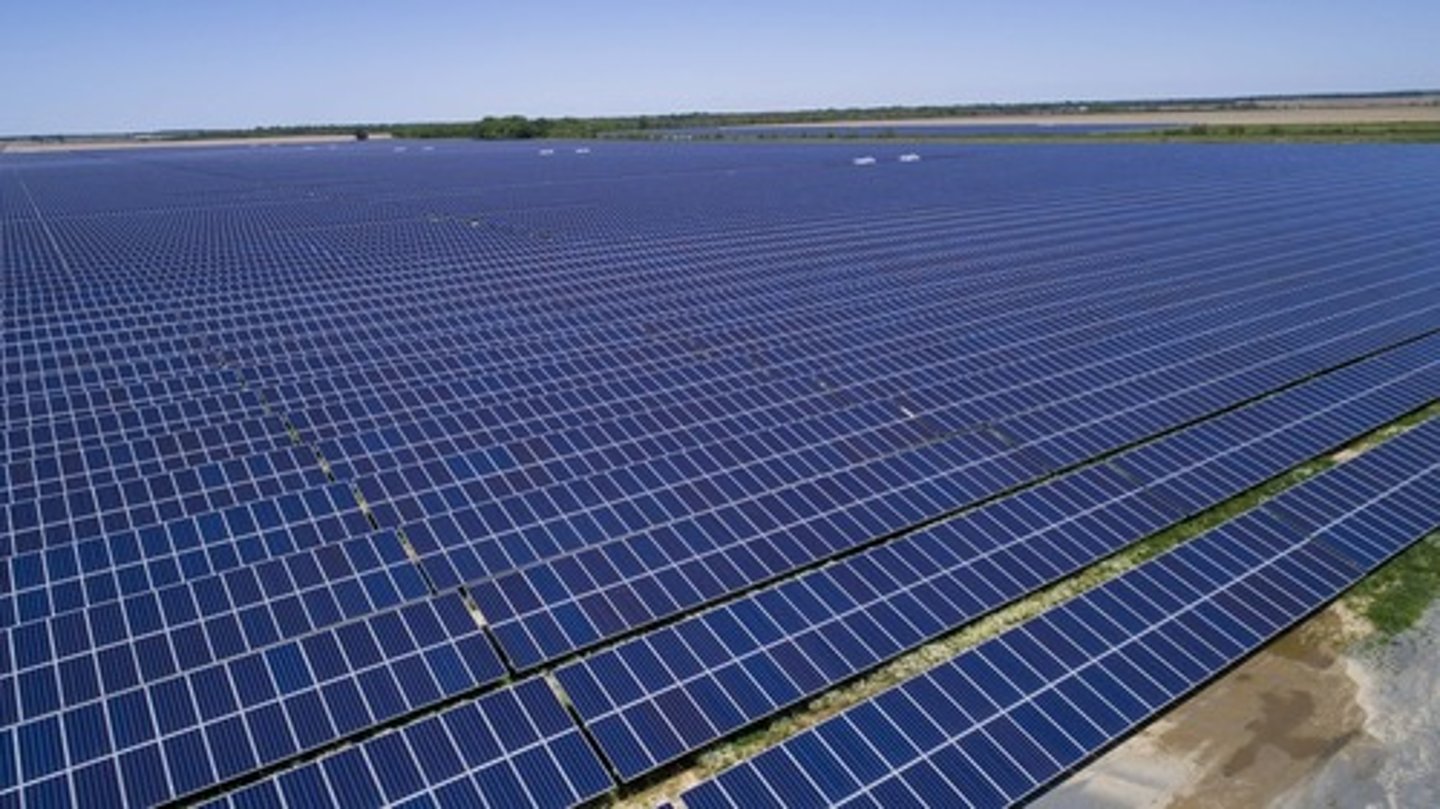
Solar Farms (Panels)
Large scale solar panels used to convert light to electricity.
- Take up a large amount of land
- Habitat loss / fragmentation

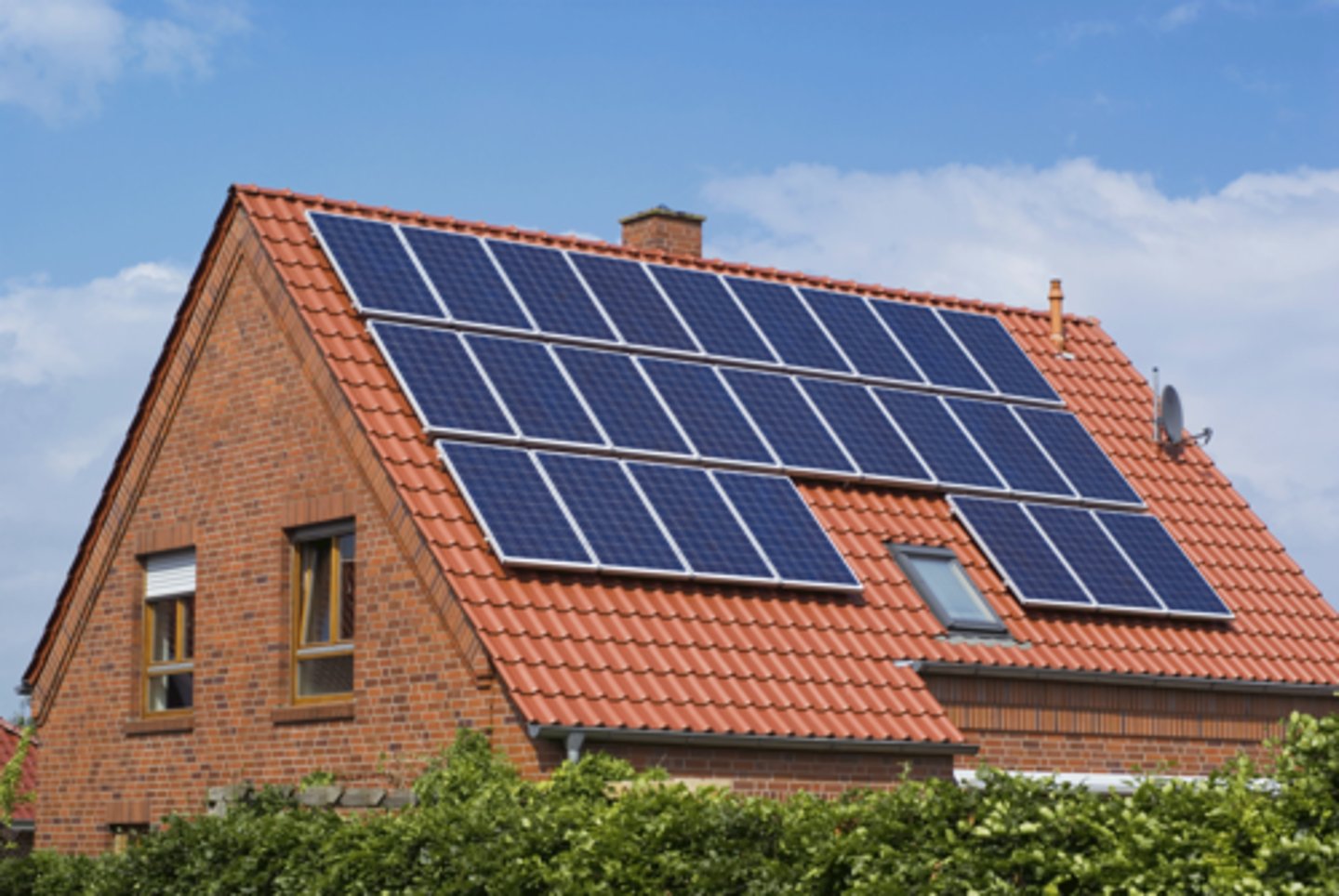
Rooftop Solar
Solar panels used by individual homes or businesses on top of building structures. Does not take up land but does not produce as much electricity as a solar farm.

Solar energy pros
Solar Energy:
Renewable clean energy
Abundant
Sustainable
Environmentally Friendly
Good Availability
Reduces Electricity Costs
Many Applications
Shared Solar
Silent
Financial Support from Government/State
Low Maintenance
Technology is Improving
- NO air pollutants

Solar energy cons
Solar energy:
-Expensive
-Intermittent (dependent on the time of the day)
-Energy Storage is Expensive
-Exotic materials like silicon still required via the mining process (habitat disruption/pollution of water)
- Metals used to make PV cells are toxic to the environment
-Requires a large amount of space (habitat destruction/fragmentation)

Water impoundment systems (Dams)
The construction of a giant reservoir holds water back
behind a dam
•Floods upstream areas
•Pushes water through smaller channels via
gravity to turn turbines to generate electricity
•Largest in the US: Grand Coulee Dam in Washington
(6,800 MW at peak)
•Largest in the world: Three Gorges Dam on the
Yangtze in China (18,000 MW at peak = 11% of
China's energy demand)
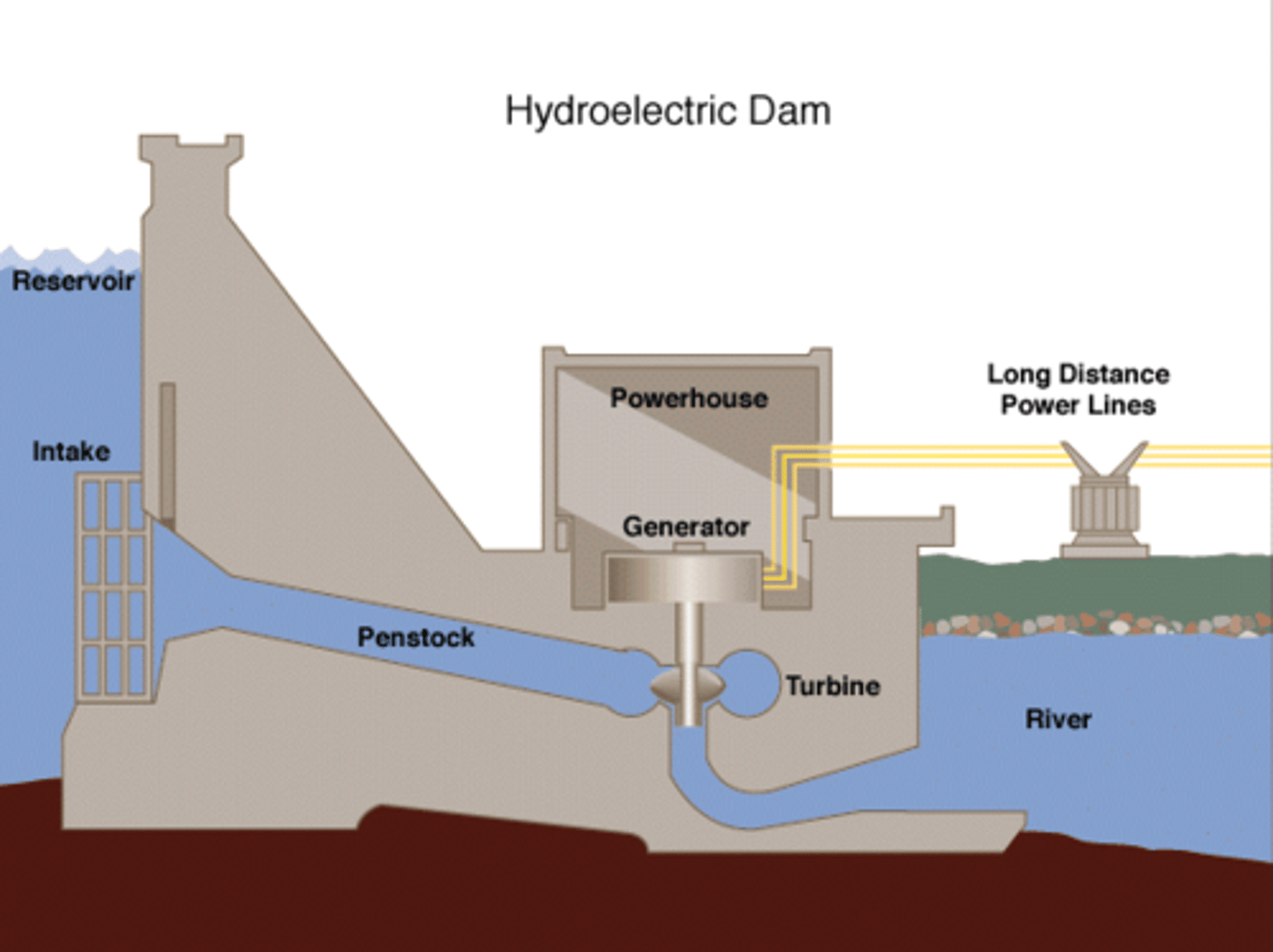
Advantages of dams
Creates jobs
hydroelectricity (cheap electricity)
freshwater supply
irrigation
better for accessing water
aesthetically pleasing
creates a bridge for transportation
recreational area (local income)
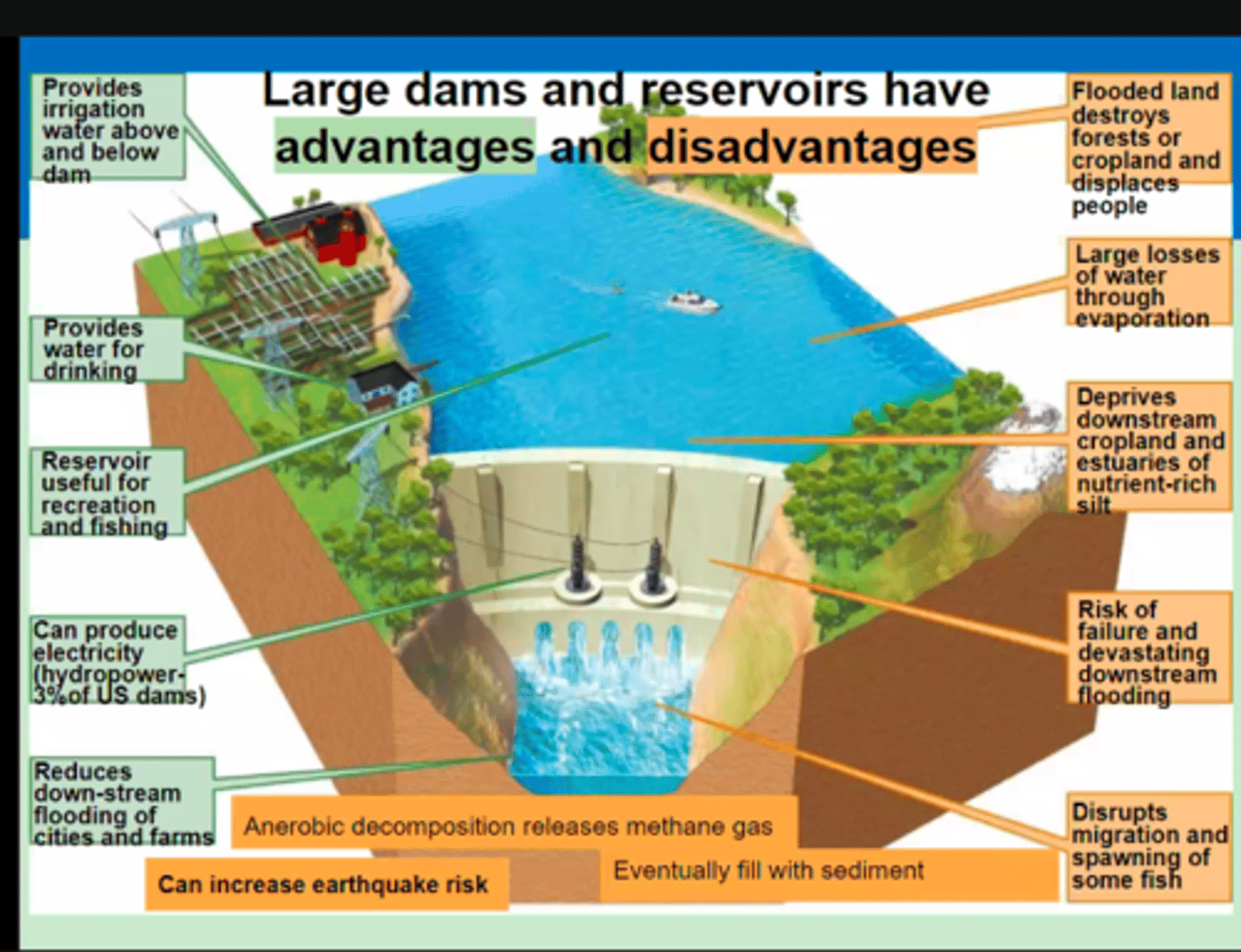
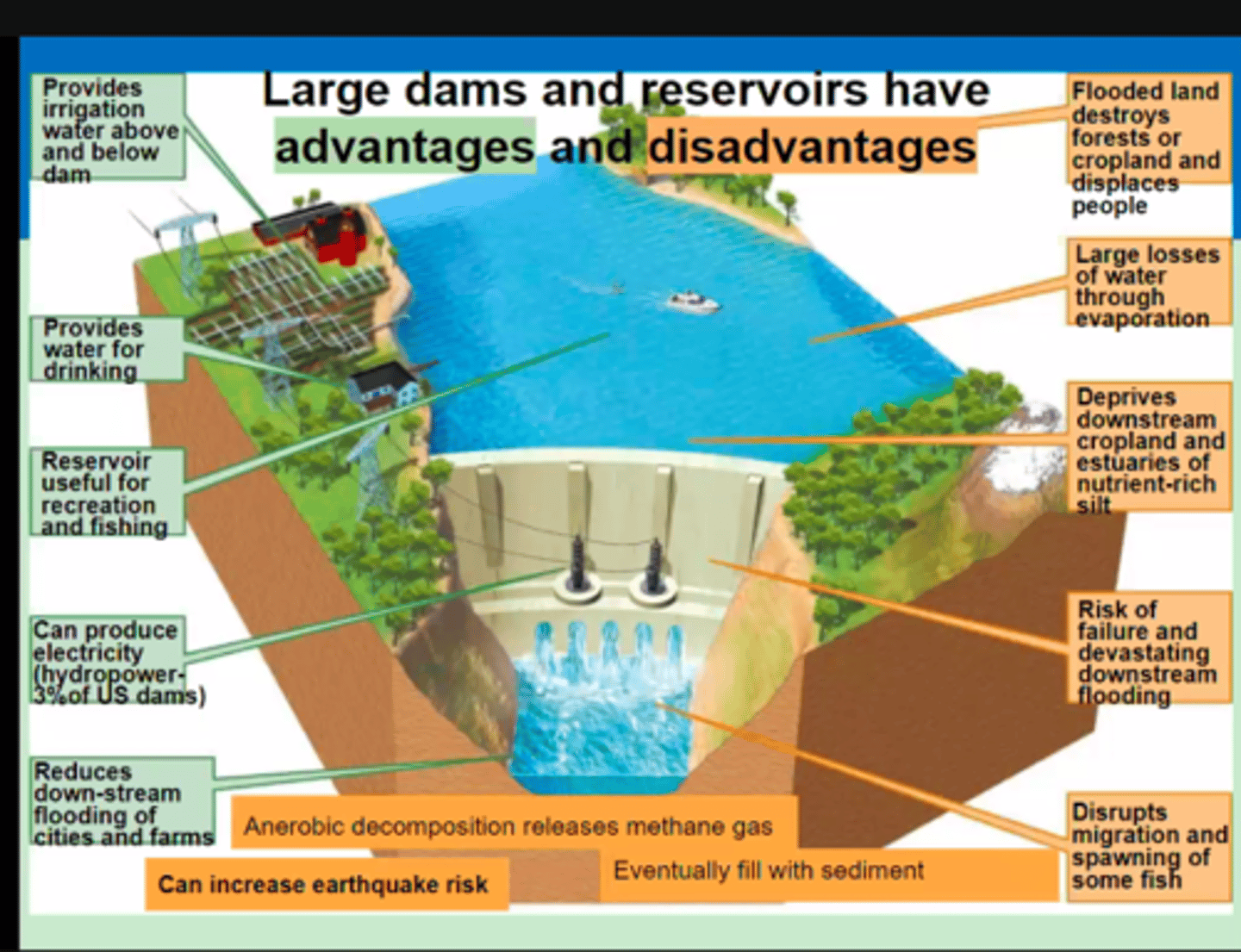
Disadvantages of dams
- Flooded land destroys forests/croplands
- Displaces people large losses of water from evaporation
- Deprives downstream croplands and estuaries of nutrient-rich silt
- Risk of failure and causing downstream flooding
- Disrupts migration and spawning of fish
- Sedimentation build-up (impact water quality)
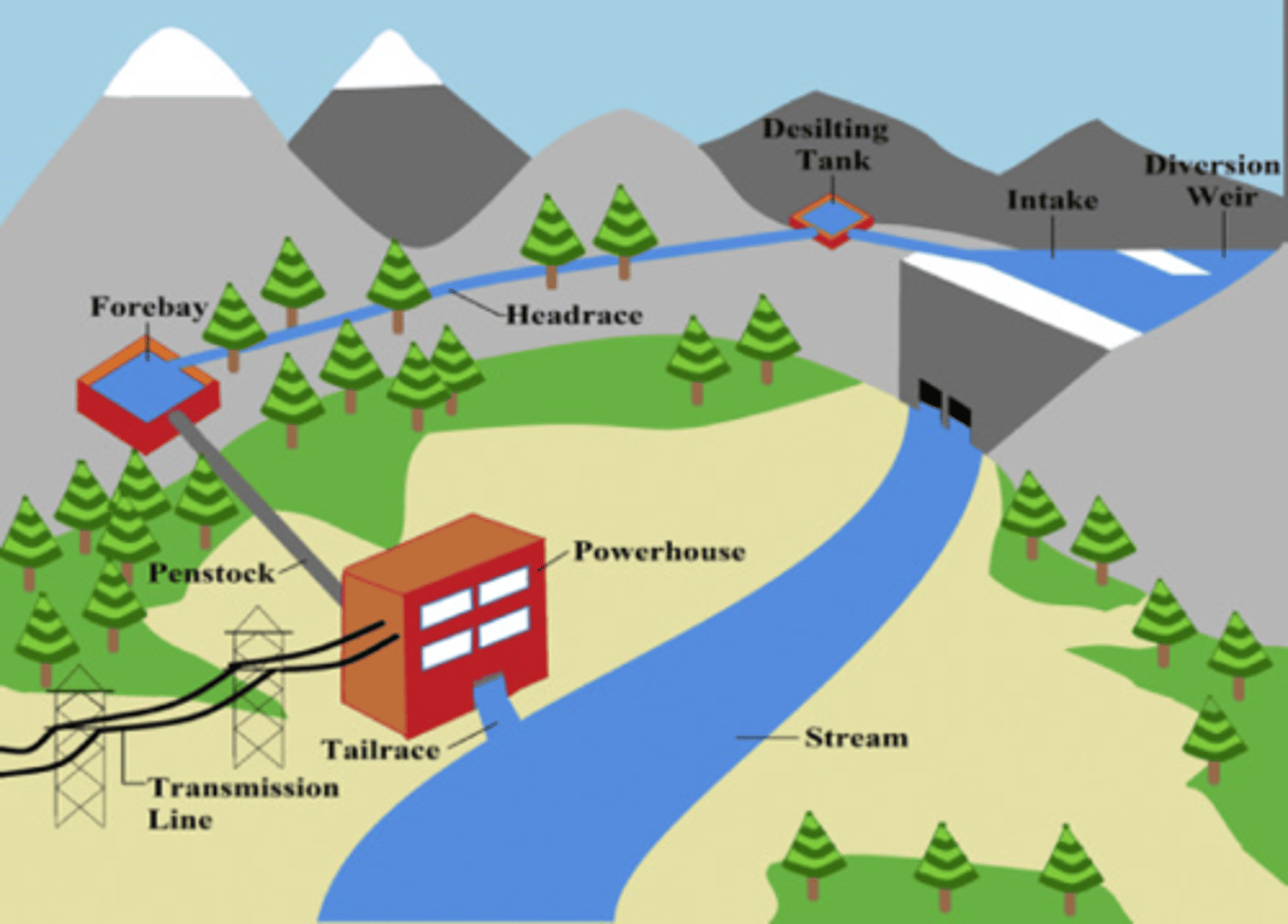
Run-of-the-river
Hydroelectricity generation, water behind a low dam and runs through a channel before returning to the river.
Tidal energy
The energy captured by transforming the wave motion of water into electrical energy using a turbine
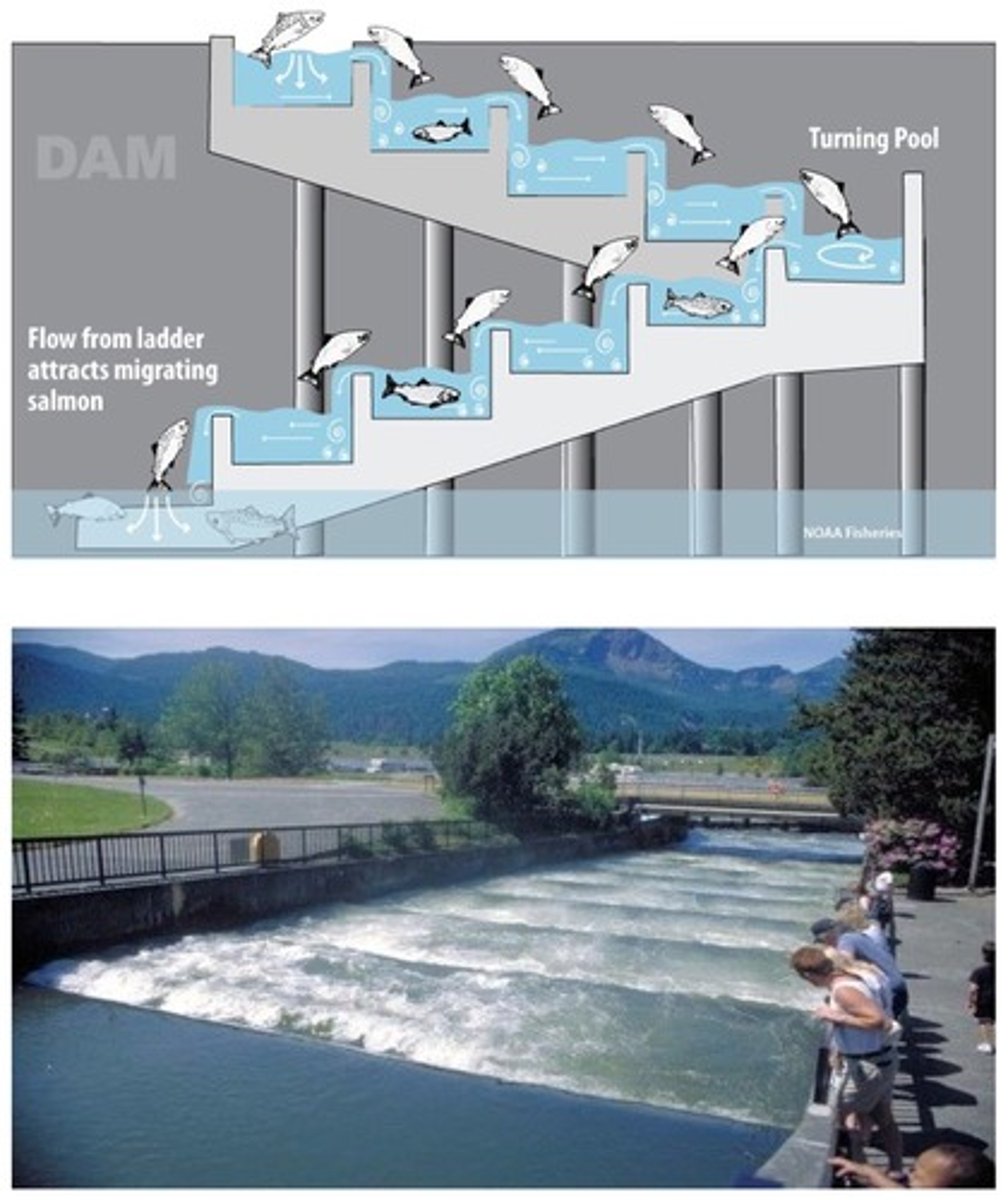
Fish ladder
a stair-like structure that allows migrating fish to get around a dam
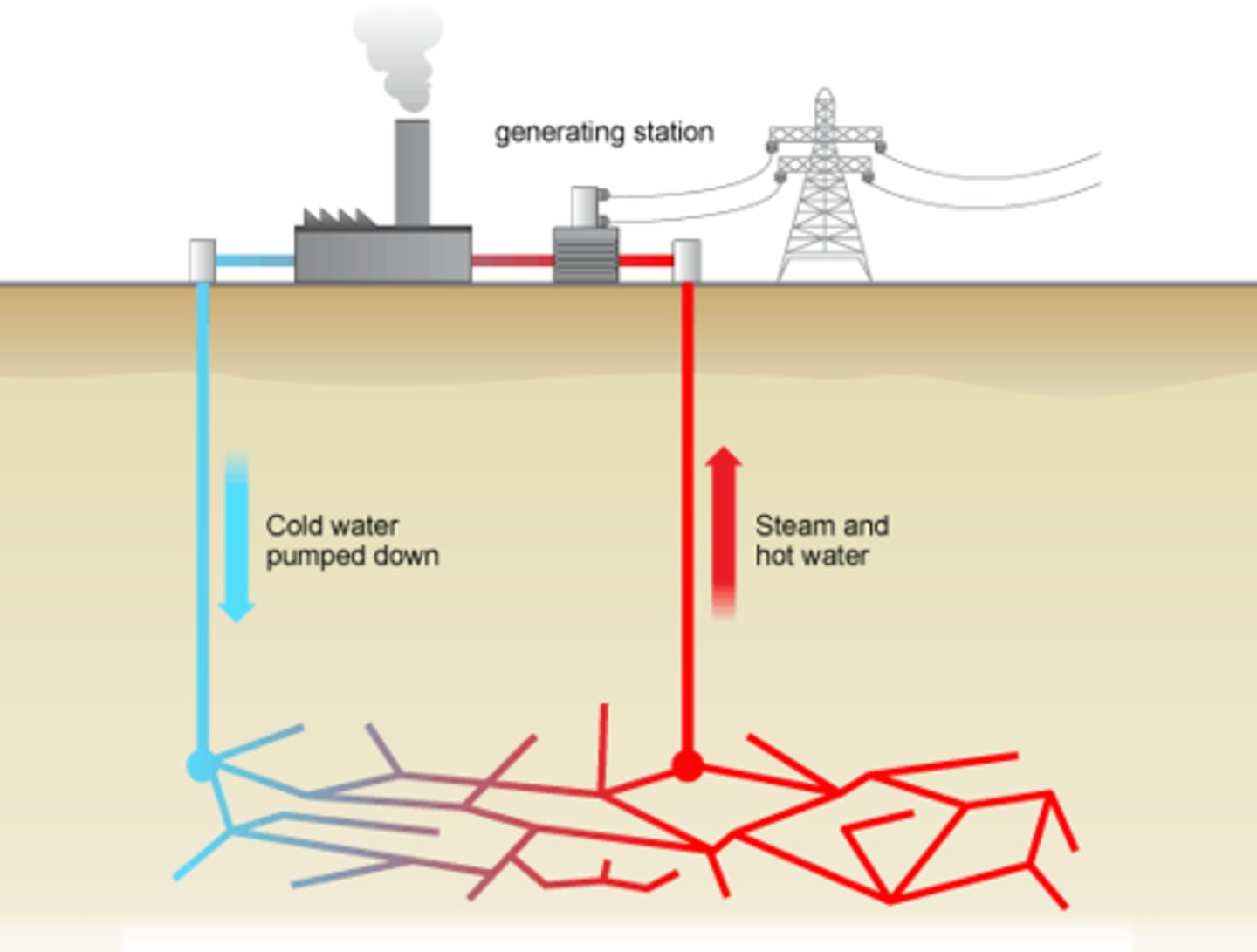
How geothermal energy works
Heat contained in underground rocks and fluids from molten rock, hot dry-zones, and warm-rock reservoirs produce pockets of underground steam, wet steam and hot water that drives turbines and generates electricity
advantages of geothermal energy
- Reliable (efficient) and relatively inexpensive (after initial construction cost)
- Cleaner energy
- Less CO2 emission to FF
- Less air pollutants
- Moderate environmental impact
- Does not require large land use

disadvantages of geothermal energy
Can emit hazardous gases (hydrogen sulfide) - odor
- CO2 emission (GHG)
- Geographically limited
- Initial cost can be expansive
- Can run out if overused

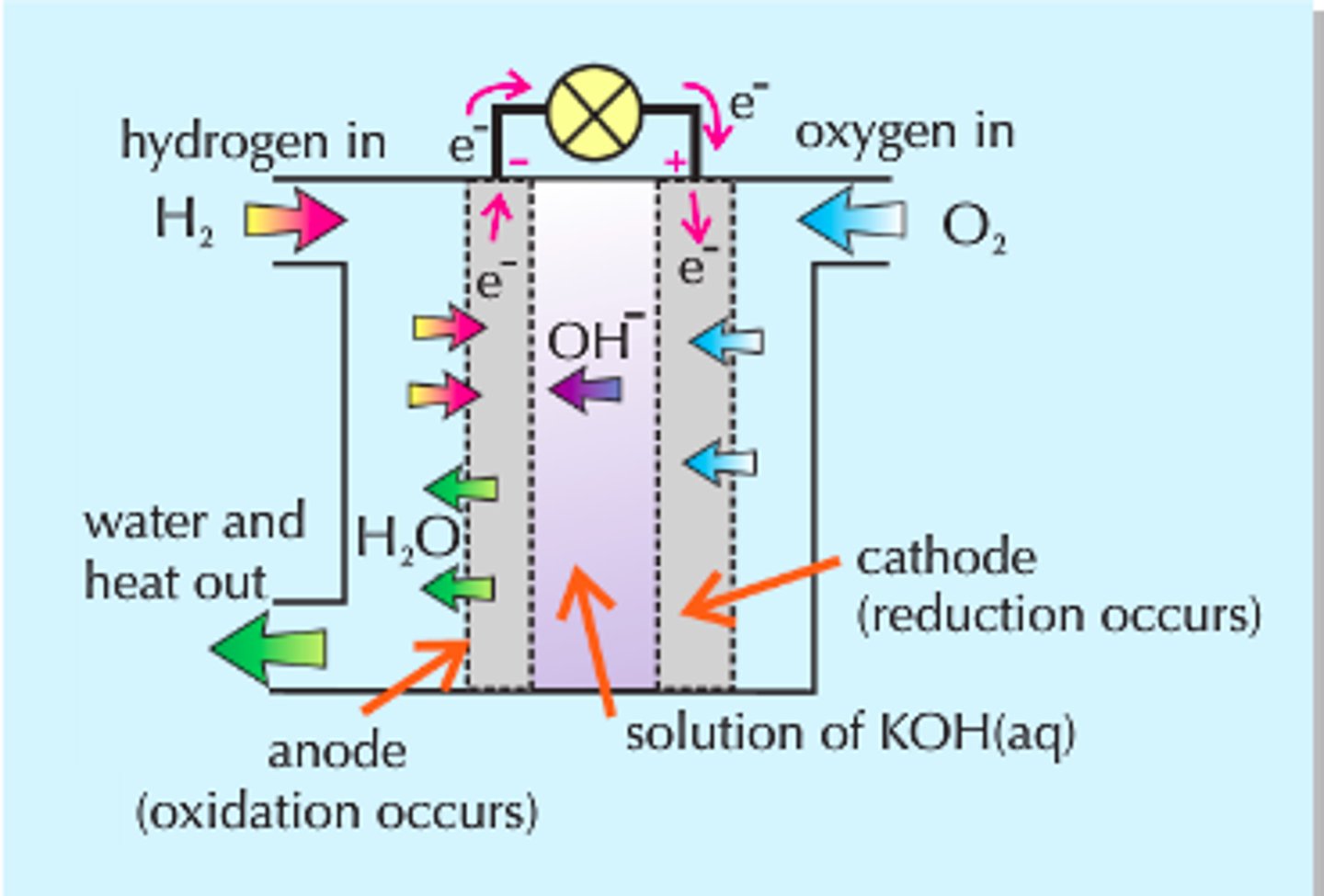
hydrogen fuel cell
Renewable fuel alternative that is used to generates electricity by reacting hydrogen with oxygen
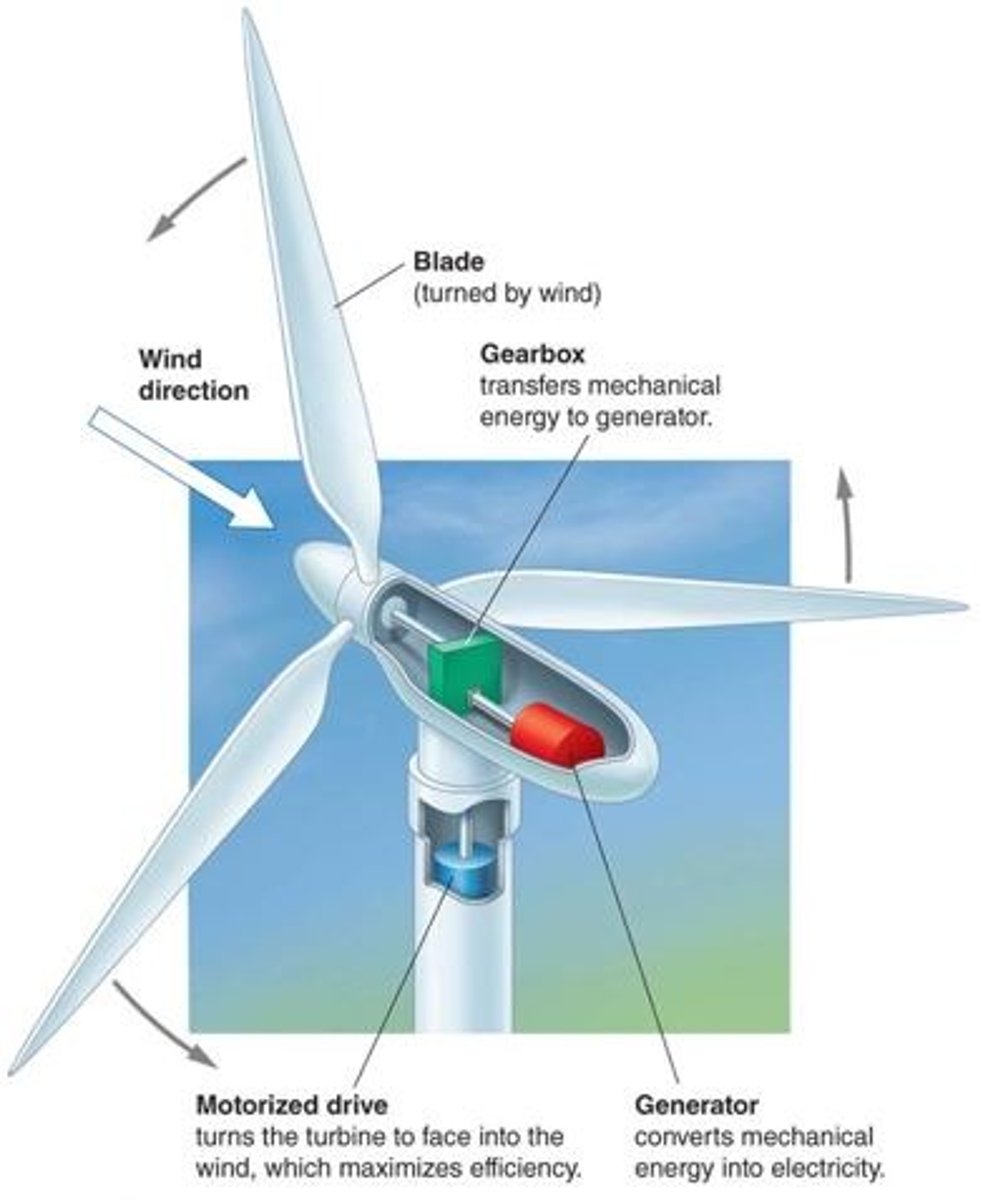
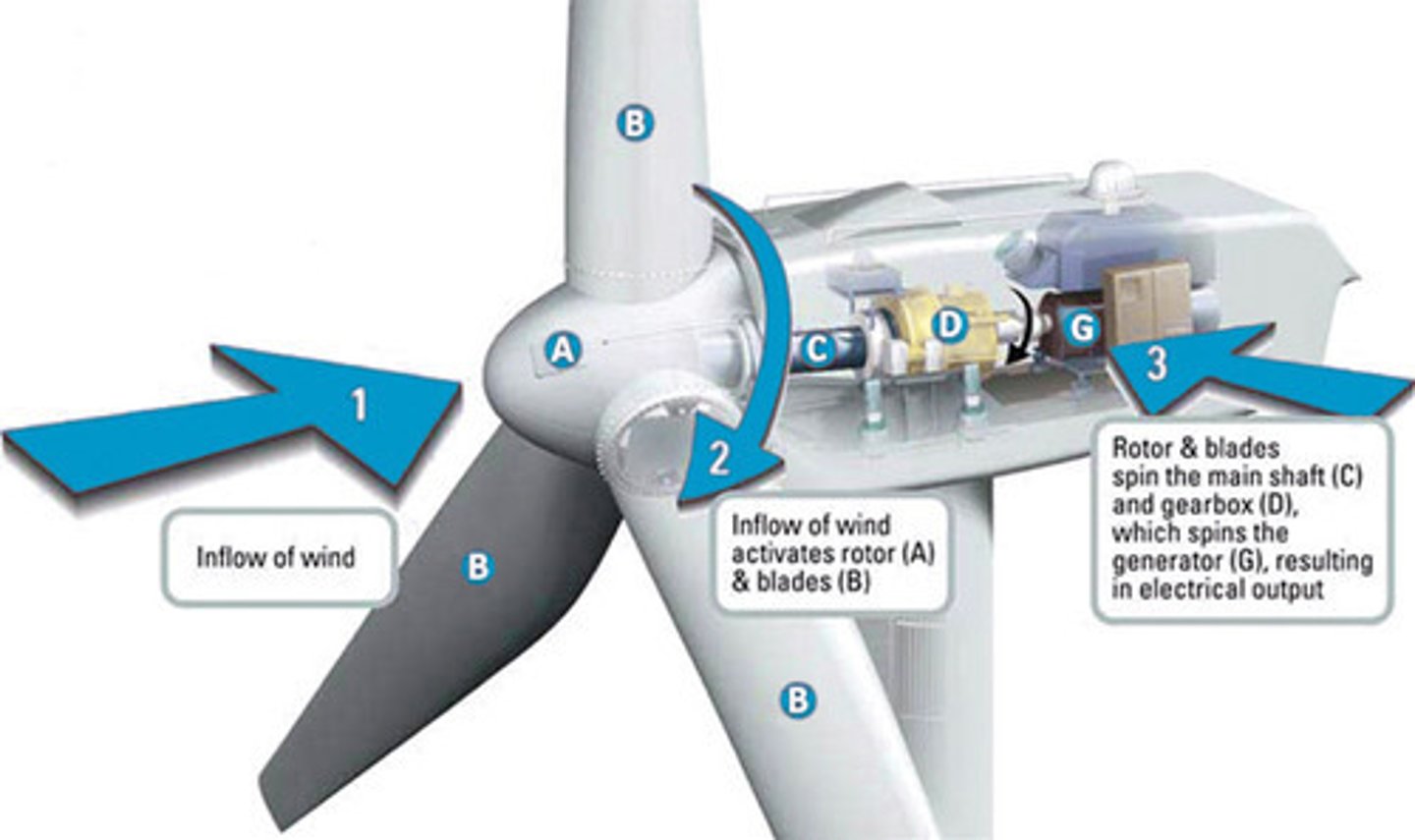
How wind turbines work
- Wind turns the blades of the wind turbines which spin a series of gearboxes. The gears create mechanical energy needed by a generator to produce eletricity.
(Mechanical --> electrical)
- The electricity is sent out into the electrical grid.
Wind turbine location
- Work best when in a cluster (wind project or wind farm)
- Can share the land with agricultural use
- Offshore wind (wind farm in ocean or lakes) allow for use of high wind speeds.

advantages of wind energy
- Renewable (clean energy)
- moderate to high net energy
- widely available / can share land (doesn't destroy habitat or cause soil/water issues)
- low electricity cost
- No direct CO2 emission contribute to GHG
- No air pollution such as NOx, SOx, or PM
-easy to build and expand

disadvantages of wind energy
- Turbine noise (noise pollution)
- Deaths of birds (especially migratory birds) and bats
- geographically limited to windy areas near transmission lines
- Aesthetically displeasing to some
- Storage batteries required for off-grid systems

energy conservation
the practice of finding ways to use less energy or to use energy more efficiently
Methods for energy conservation
- Lower thermostat (less heat or use of AC)
- Conserve water (use native plants, low flow showerhead, efficient toilets, dishwasher, dryers, etc.)
- Use of rain barrels
- Energy-efficient appliances (Energy Star Certified)
- Better home insulation
- Improve fuel efficiency (Regulation to set standard fuel economy for vehicles - CAFE)
- Subsidize/tax credit for electric/hybrid vehicles
- Increase public transportation use
- Green building design (green roof) / passive solar design
cogeneration/combined heat and power (CHP)
Production of two useful forms of energy, such as high-temperature heat or steam and electricity, from the same fuel source.