Arteries, Capillaries, and Veins
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
How do arteries change from the heart to the tissue?
They change from elastic arteries to muscular arteries to arterioles
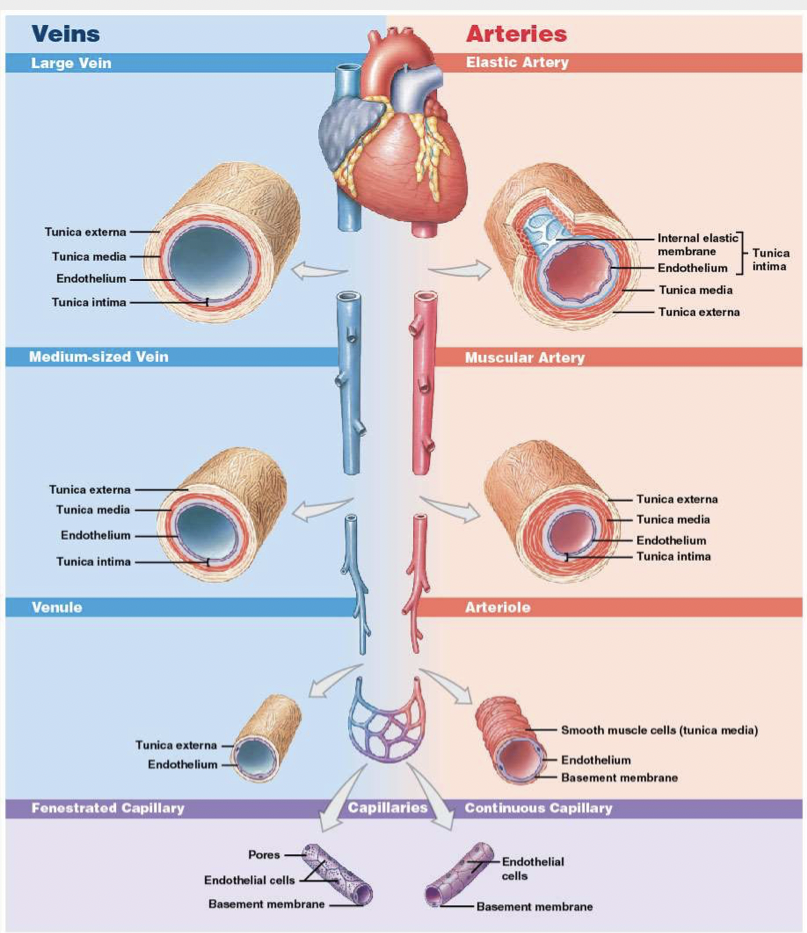
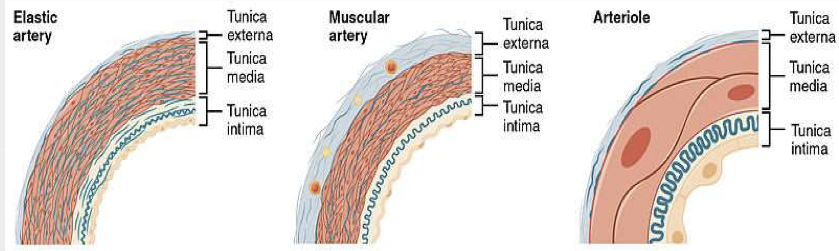
What do the different types of arteries look like?
What is the structure of a capillary like?
Endothelial tube inside thin basement membrane
No tunica media
No tunica externa
The diameter is similar to that of a red blood cell
Continuous, fenestrated and sinusoid
What are the three types of capillaries?
Continuous capillaries, fenestrated capillaries, and sinusoid
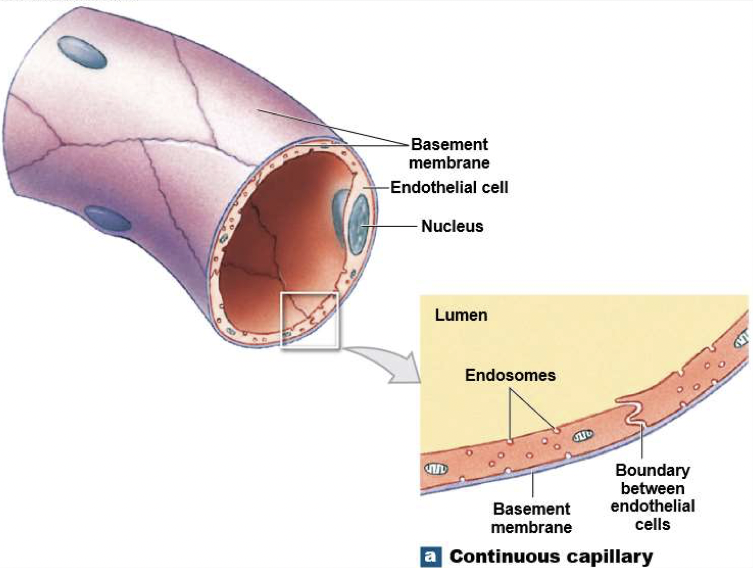
What are continuous capillaries?
They are found in all tissues except epithelia and cartilage
Have complete endothelial lining
Permit diffusion of water, small solutes, and lipid-soluble materials (block blood cells and plasma proteins)
Specialised continuous capillaries in CNS and thymus that have very restricted permeability (eg. Blood brain barrier)
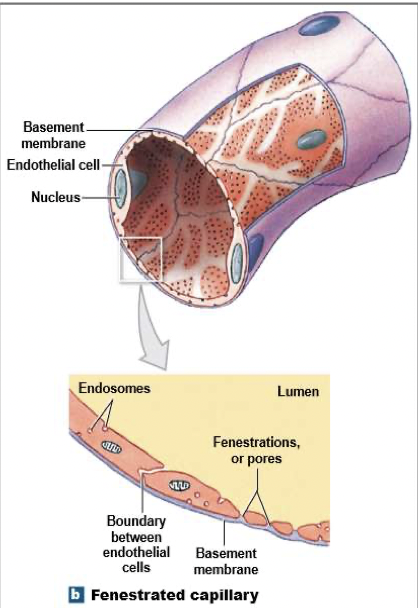
What are fenestrated capillaries?
Have pores in endothelial lining
Permit rapid exchange of water and larger solutes
Found in: choroid plexus (group of cells in brain that produce cerebrospinal fluid), endocrine organs, kidneys, intestinal tract
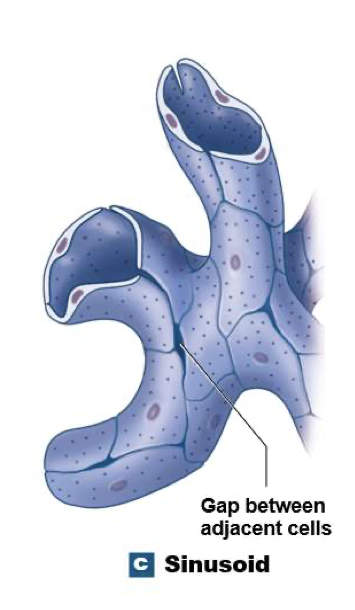
What is a sinusoid?
They ave gaps between adjacent endothelial cells
Permit free exchange of water and large plasma proteins
Found in: liver, spleen, bone marrow (produces red blood cells), endocrine organs
Phagocytic cells monitor blood at sinusoids
What does a continuous capillary look like?
What does a fenestrated capillary look like?
What does a sinusoid look like?
What does the capillary bed do?
The capillary bed (capillary plexus) connects one arteriole and one venule. The precapillary sphincter guards the entrance to each capillary and opens and closes, causing capillary blood to flow in pulses
What are thoroughfare channels?
Direct capillary connections between arterioles and venules
What do veins do?
Collect blood from capillaries and return it to the heart
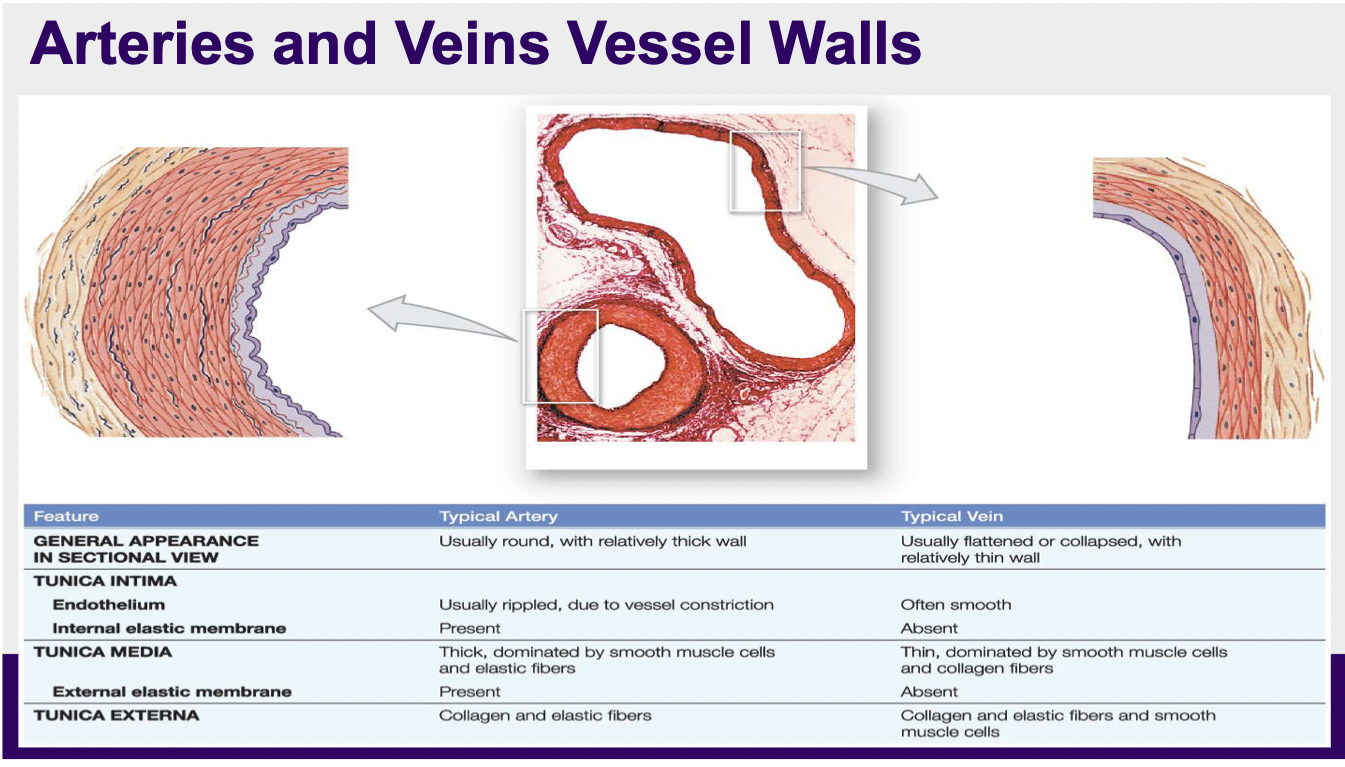
What is the structure of a vein like?
Compared to arteries, veins have: larger diameters, thin walls, lower blood pressure
Smooth muscle present in a vein wall is appropriate for allowing autonomic control over blood flow and pressure
The smooth muscle in veins can vasoconstrict to help with the propulsion of blood back to the heart
Also assisted by the skeletal muscle pump
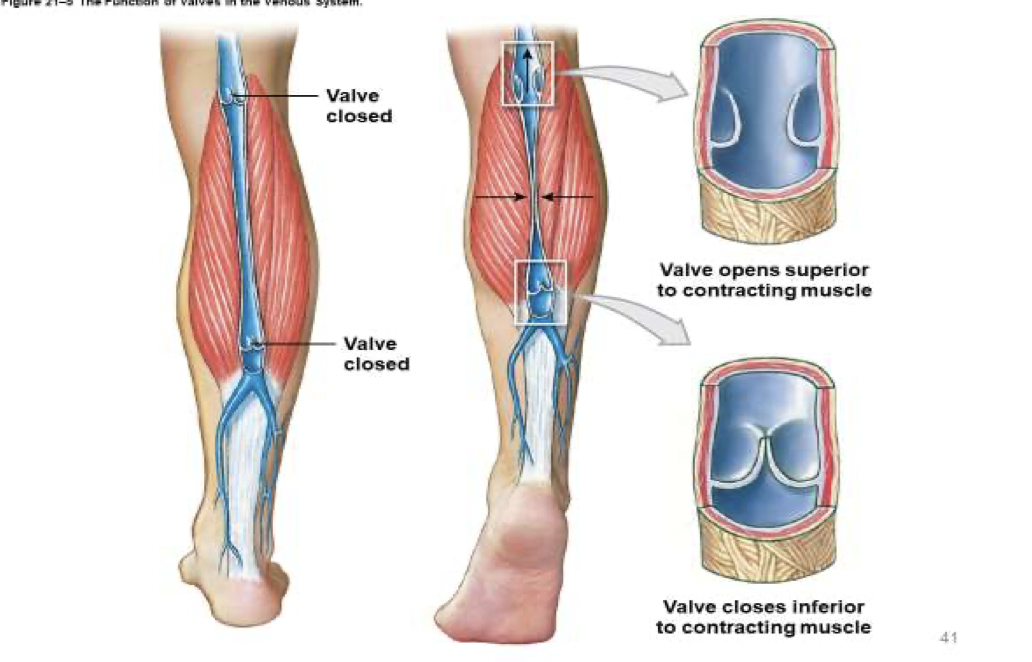
What are venous valves?
Folds of tunica intima
Prevent blood from flowing backward
Compression of veins pushes blood toward heart
When walls of veins near the valves weaken, varicose veins may result
What is the skeletal muscle pump?
The skeletal muscle pump plays a crucial role in blood circulation, especially during exercise.
When (skeletal) muscles contract, they squeeze the veins running through them. This increases pressure within the veins, forcing the one-way valves to open and pushing blood toward the heart. When the muscles relax, the valves close to prevent backflow. This mechanism helps venous return (the flow of blood back to the heart), which is important for maintaining circulation and preventing blood pooling in the lower limbs.
What are the difference between arteries and veins vessel walls?
What is a summary of veins, arteries, and capillaries?