UCI Bio 93 Midterm 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
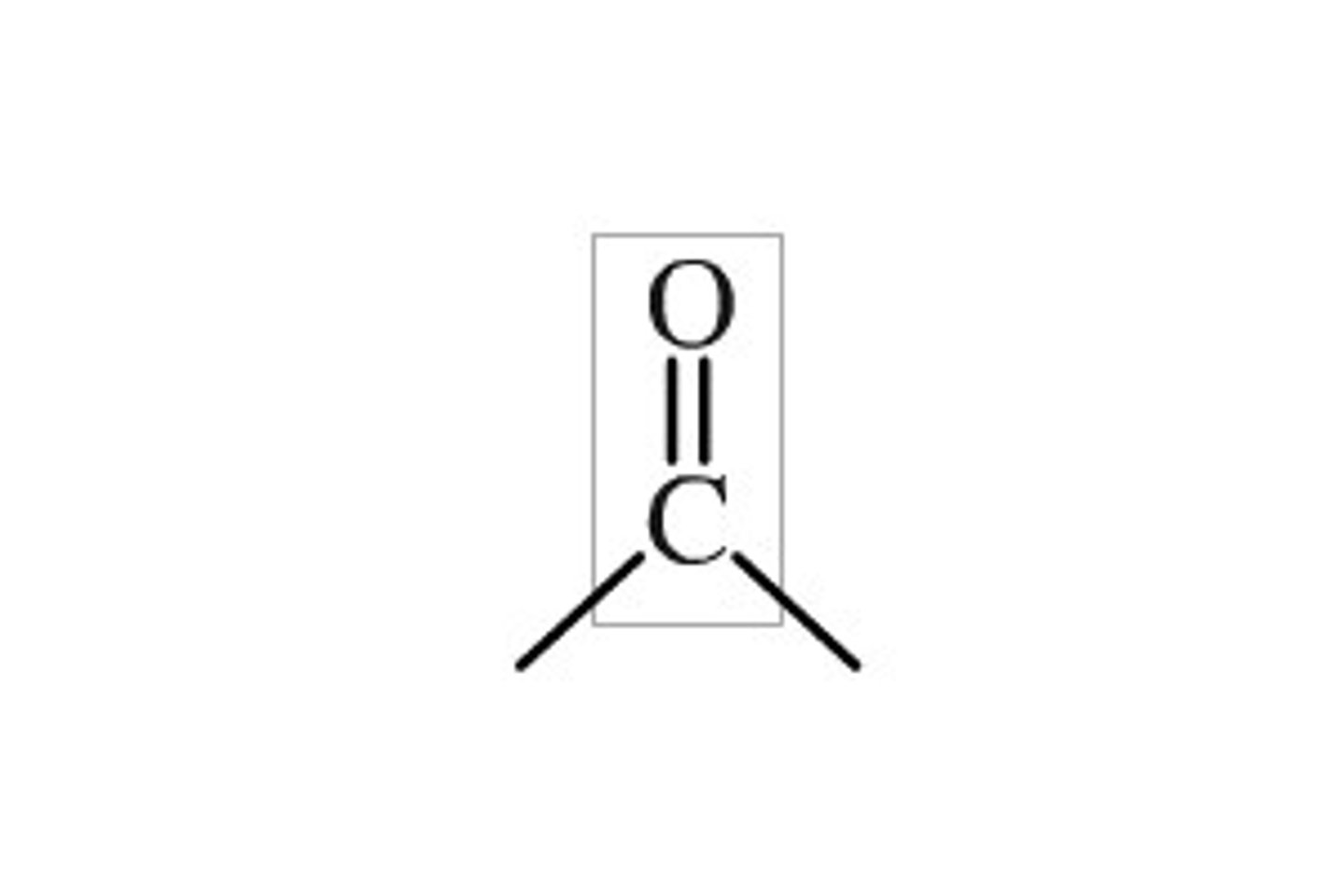
Carbonyl within a skeleton
Ketone
Carbonyl at the end of a skeleton
Aldehyde
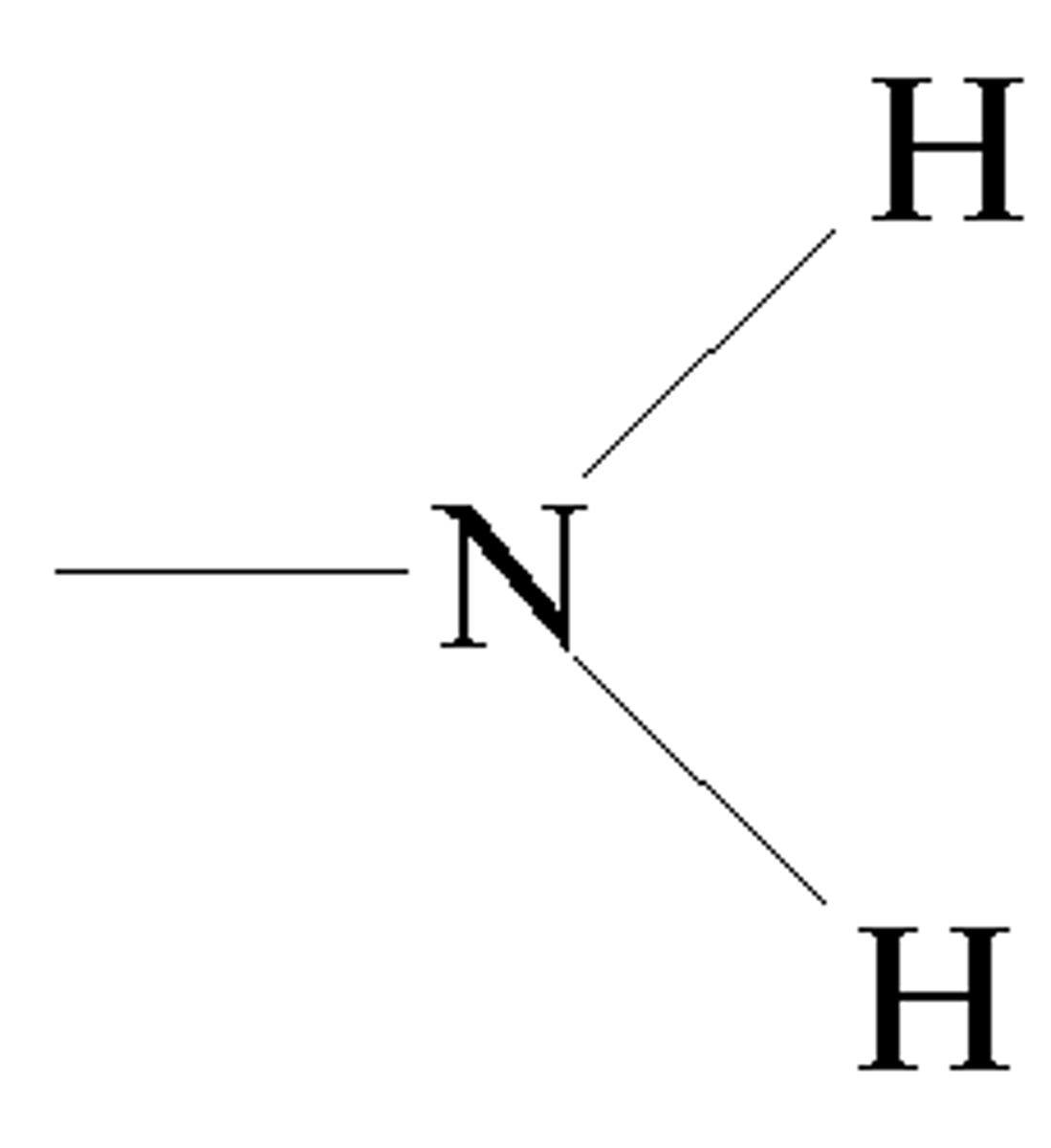
Amino
Is a weak base, (Monomer is amines)
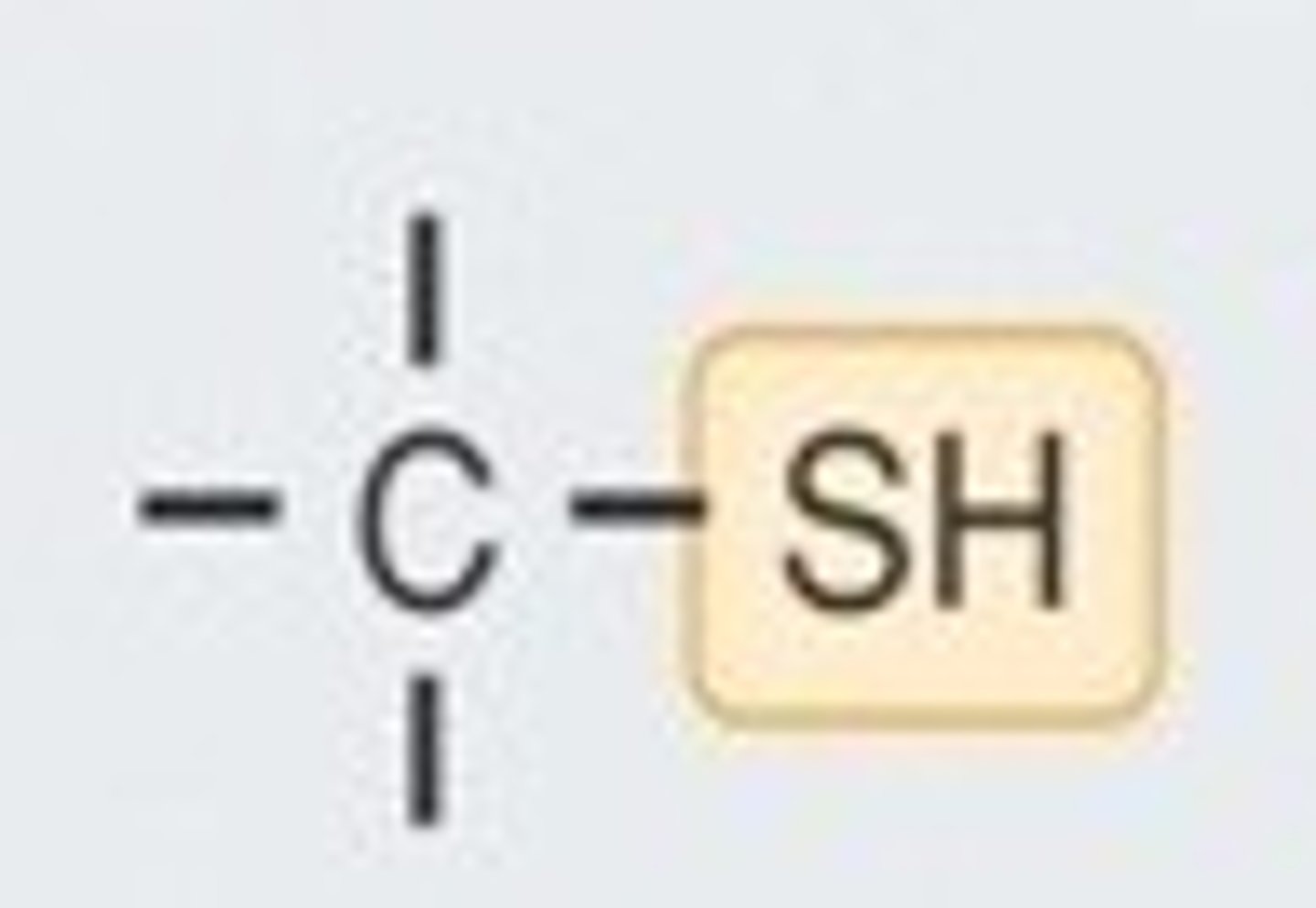
Sulfhydryl
(Thiols) Helps stabilize protein structure
Phosphate
Organic Phosphates (Monomer)
Phosphate
VERY important for ATP
Phosphate
Can add a neg. charge
React with Water, releasing energy
Carbonyl
Methyl
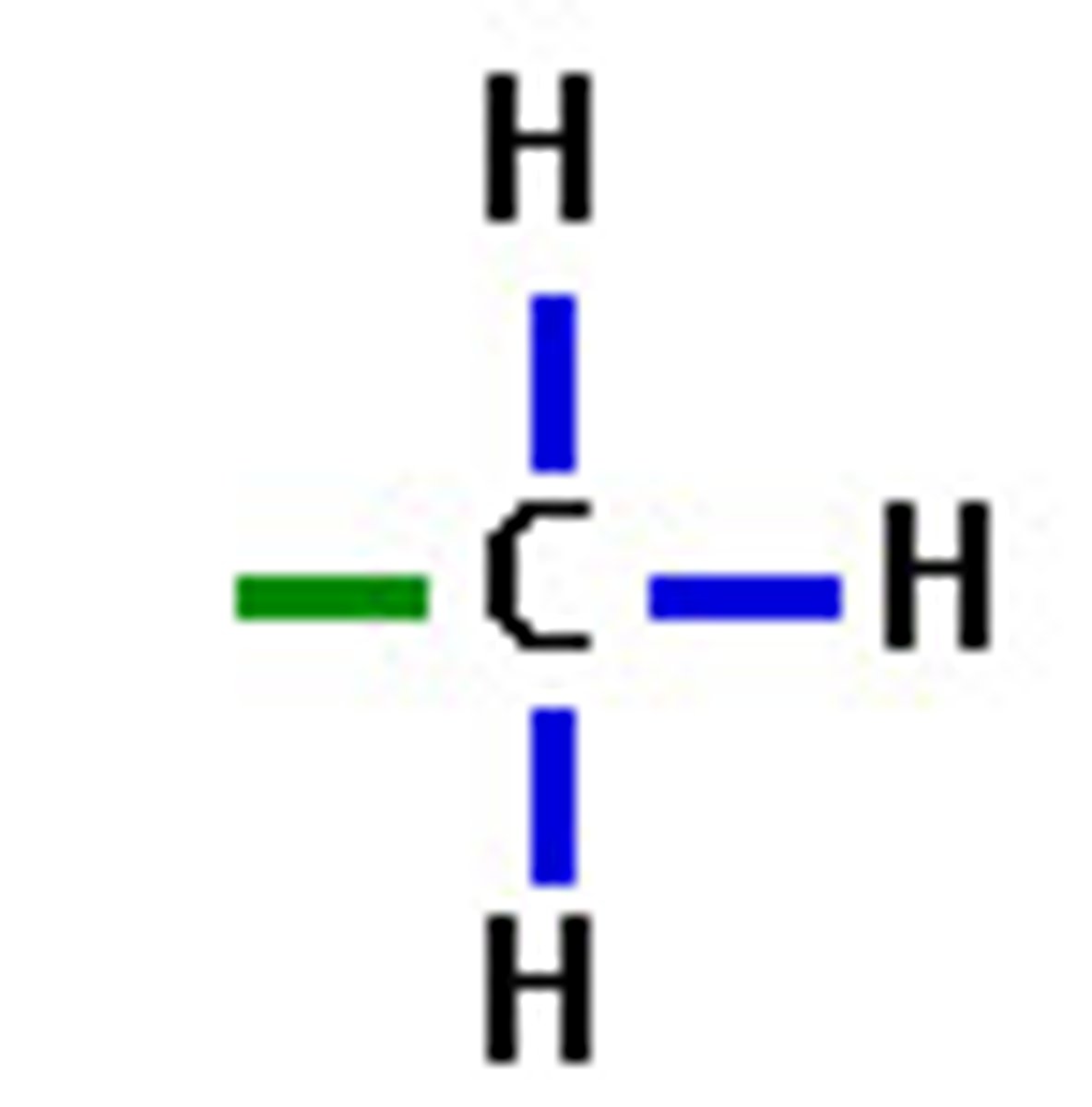
Methyl
Monomer is Methylated compounds
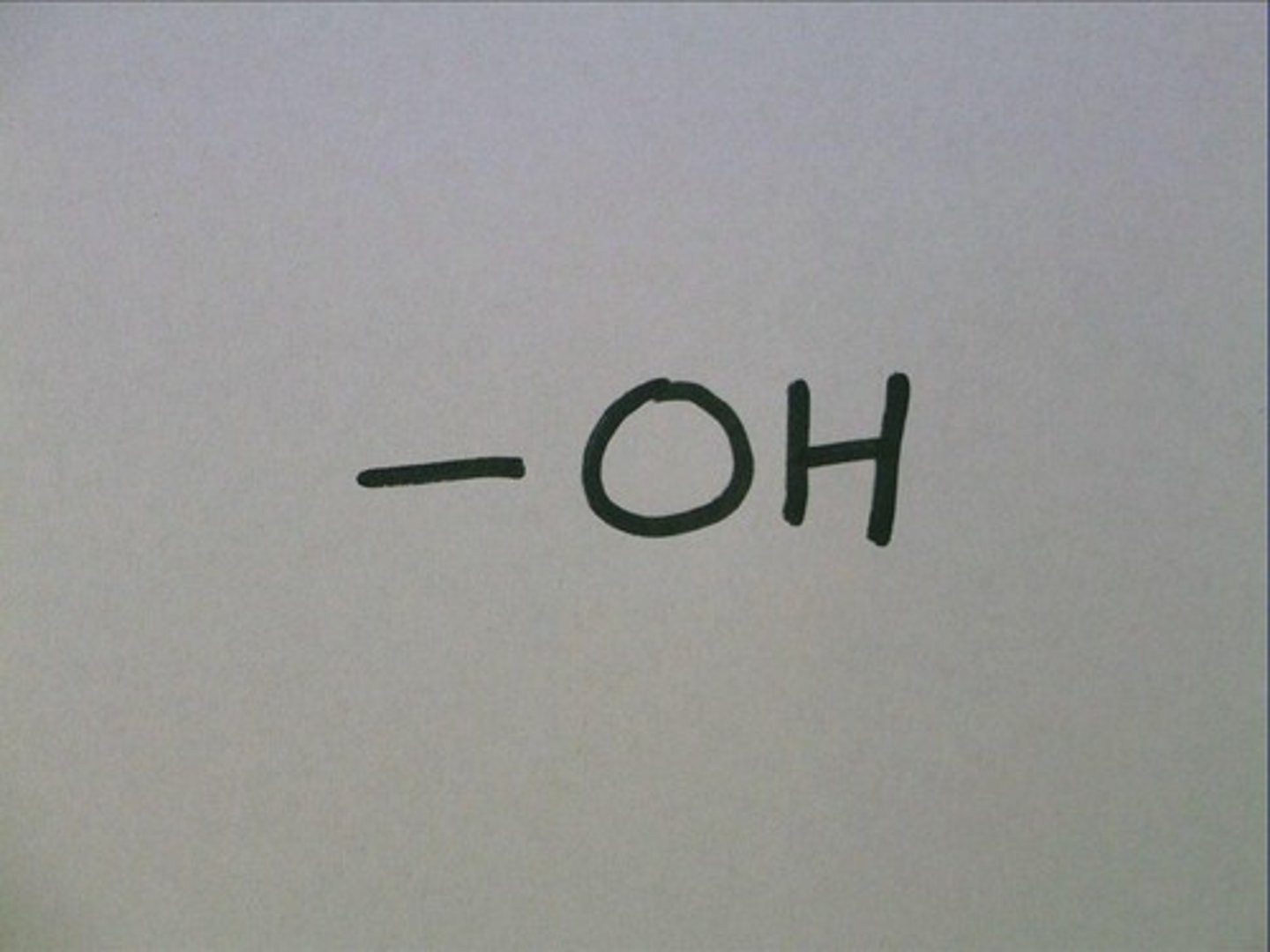
Hydroxyl
Methyl group + DNA
An effect in expression of genes
Hydroxyl
Alcohols (end in -ol)
Hydroxyl
Covalently bonded to Carbon
Soluble in Water
Phosphate
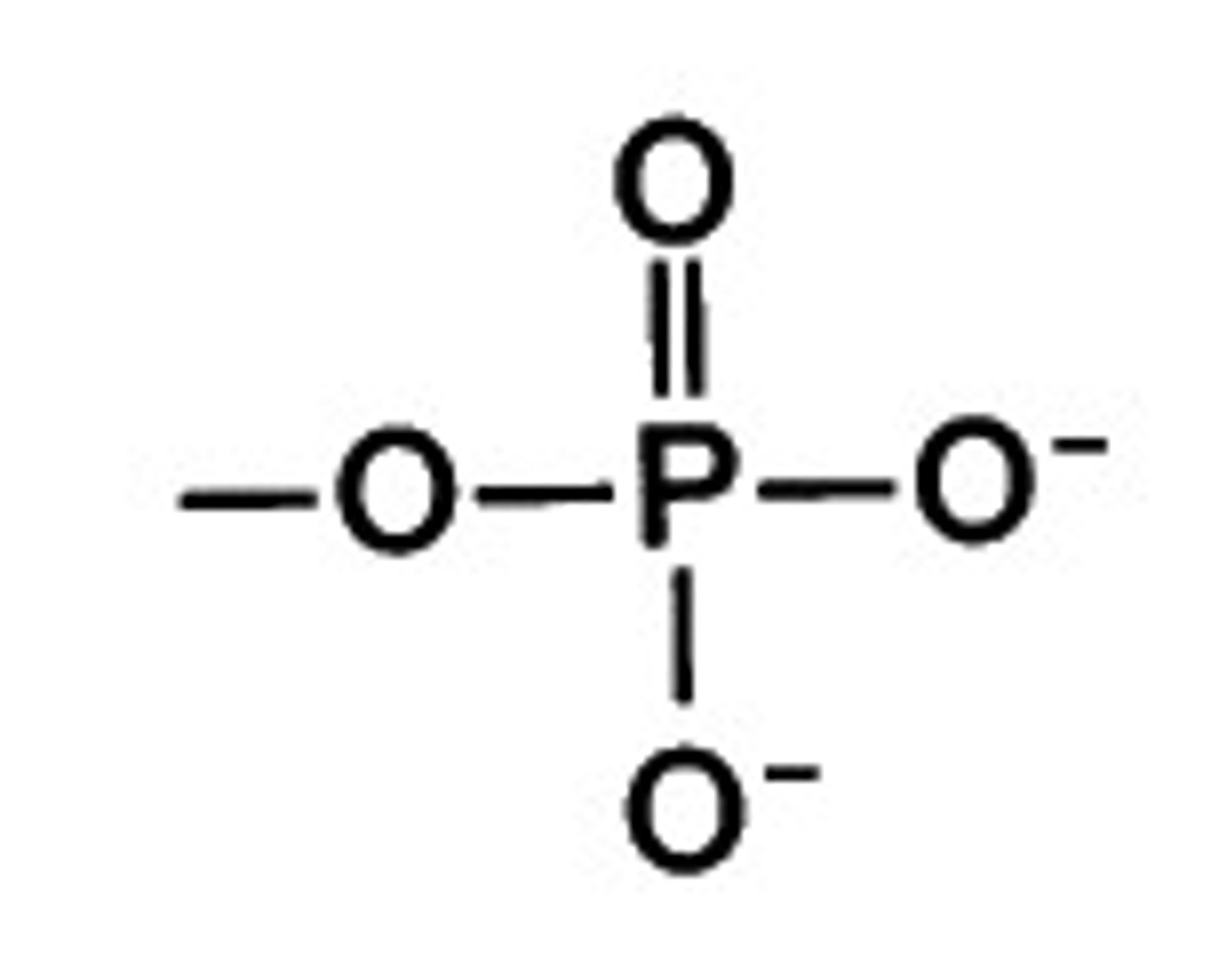
Amino
Carboxyl
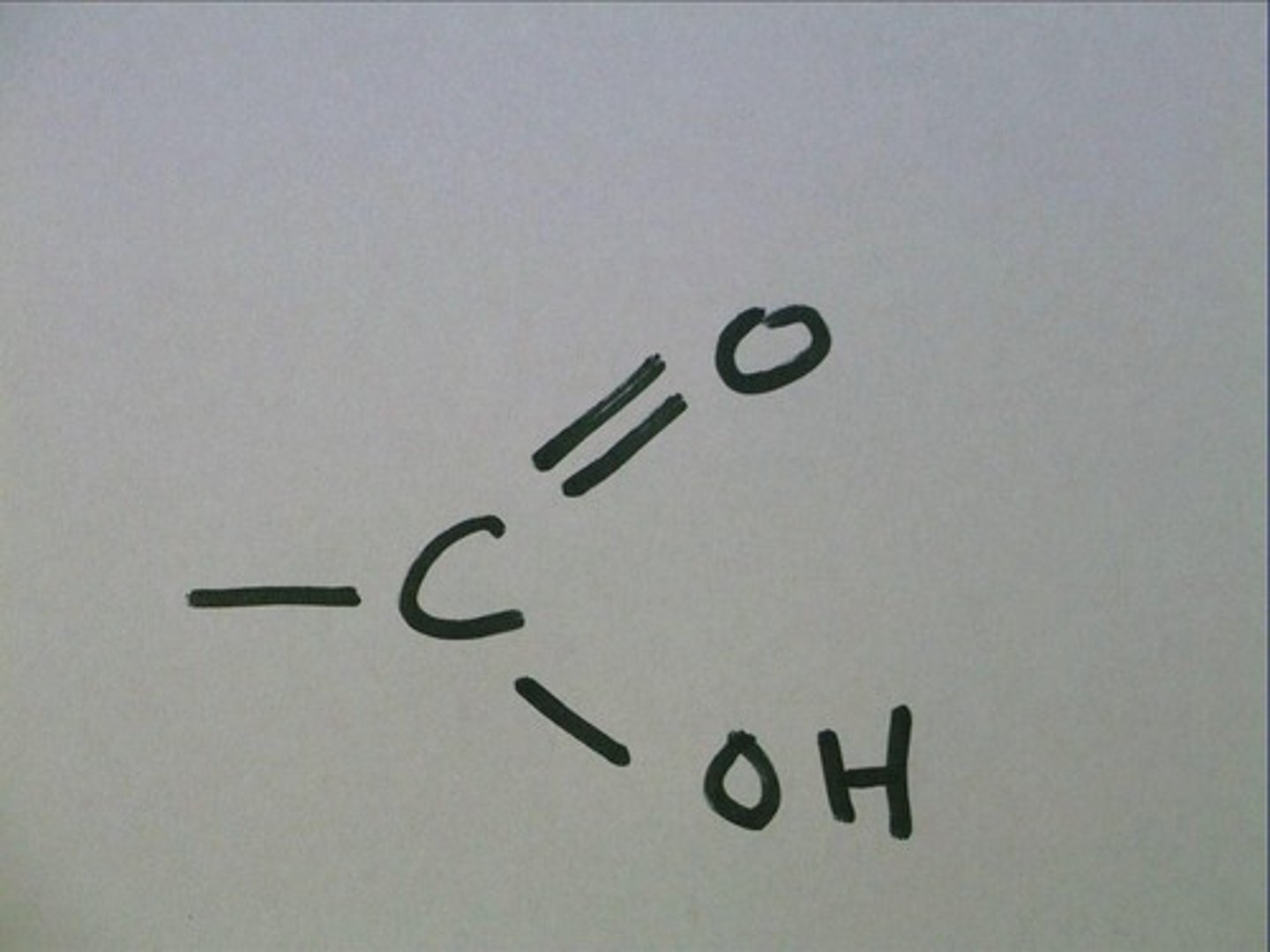
Carboxyl
Organic Acids
Carboxyl
Polar Covalent bond between O and H
Sulfhydryl
Intermolecular
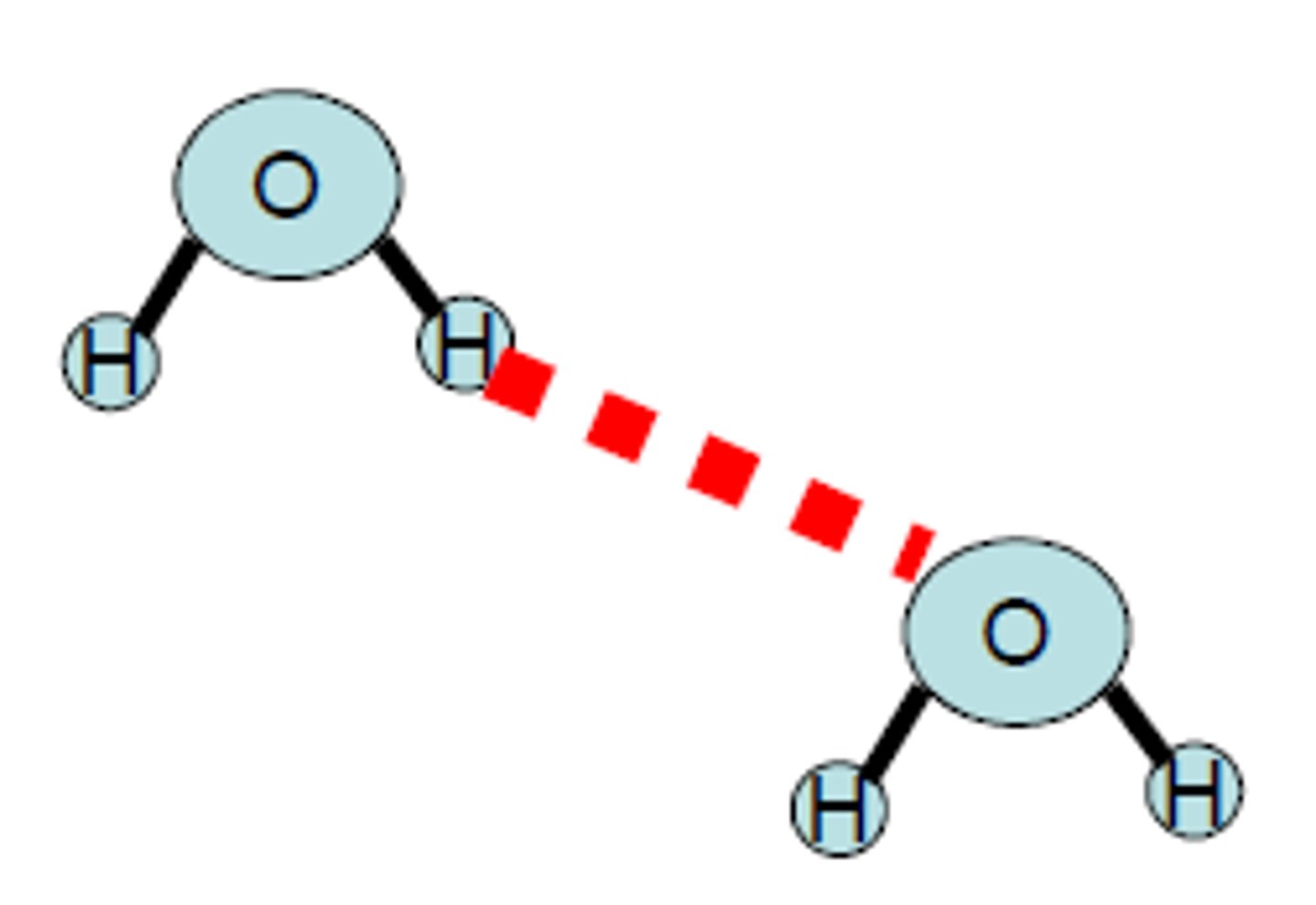
Intramolecular
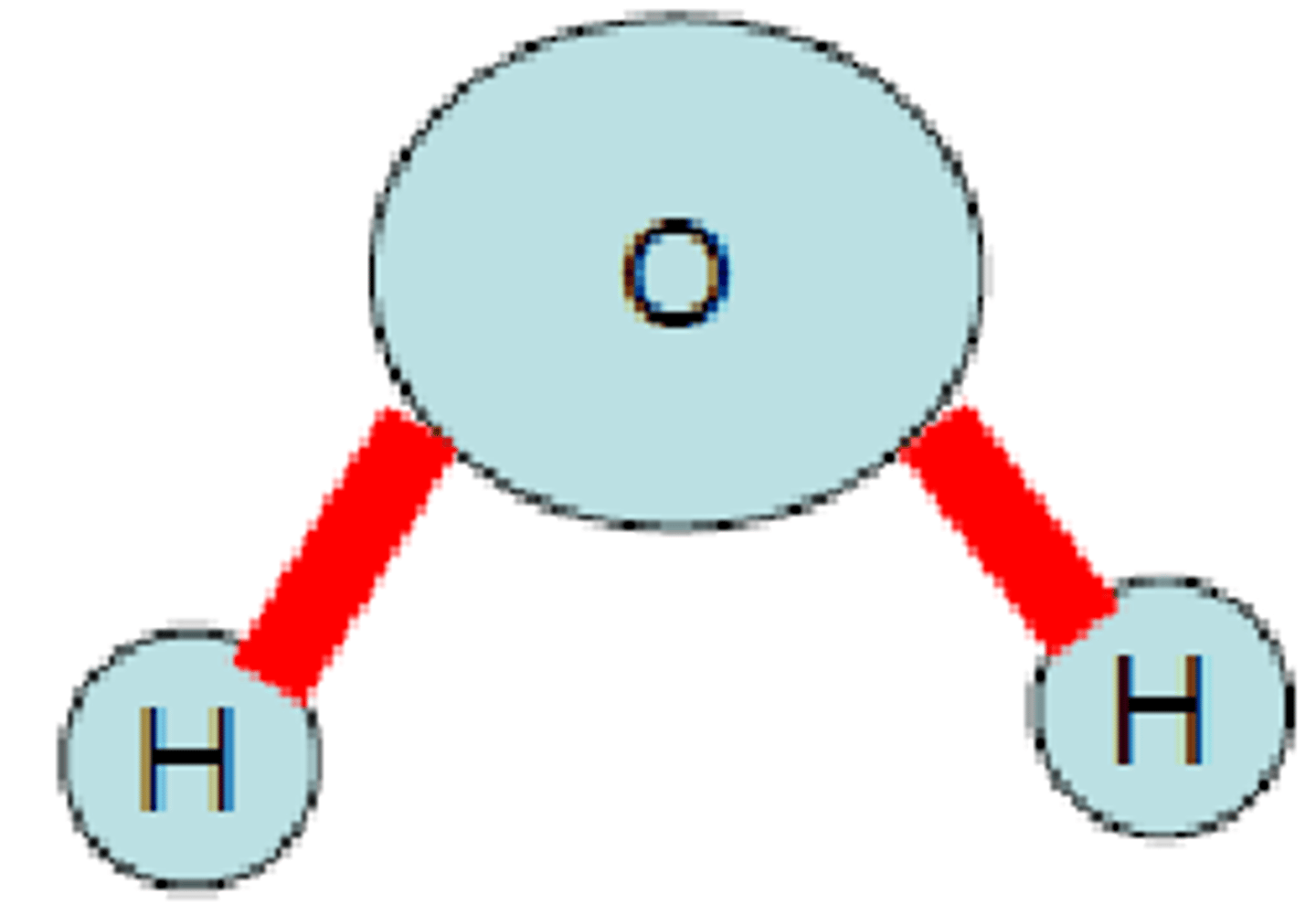
What bond links two monosaccharides together?
Glycosidic Linkage
Macromolecules
Carbohydrates, Nucleic Acids, Lipids, Proteins
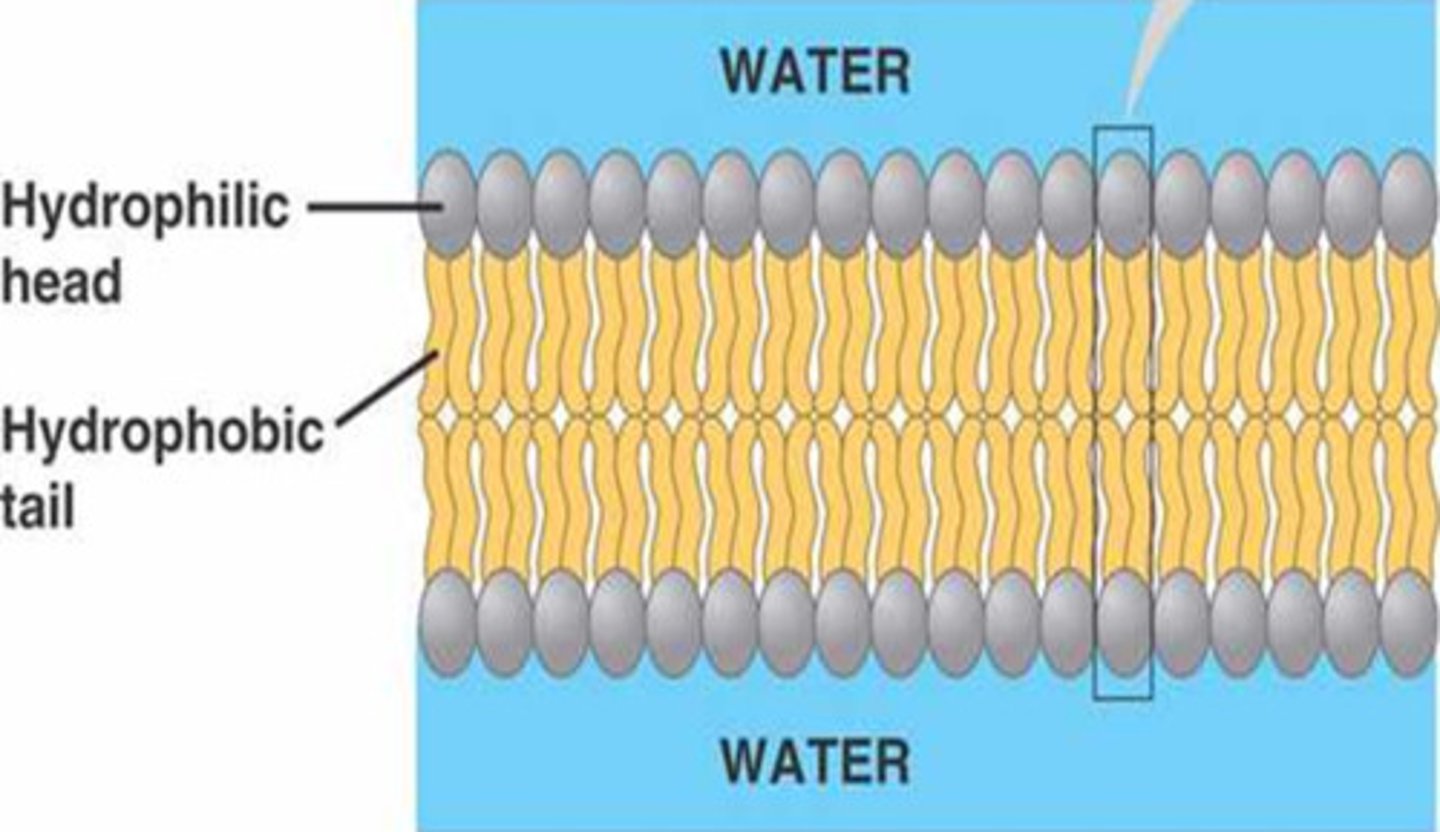
Phospholipid Bilayer
Diffusion
The movement of particles of any substance so that they spread out into the available space.
Passive Transport
The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane
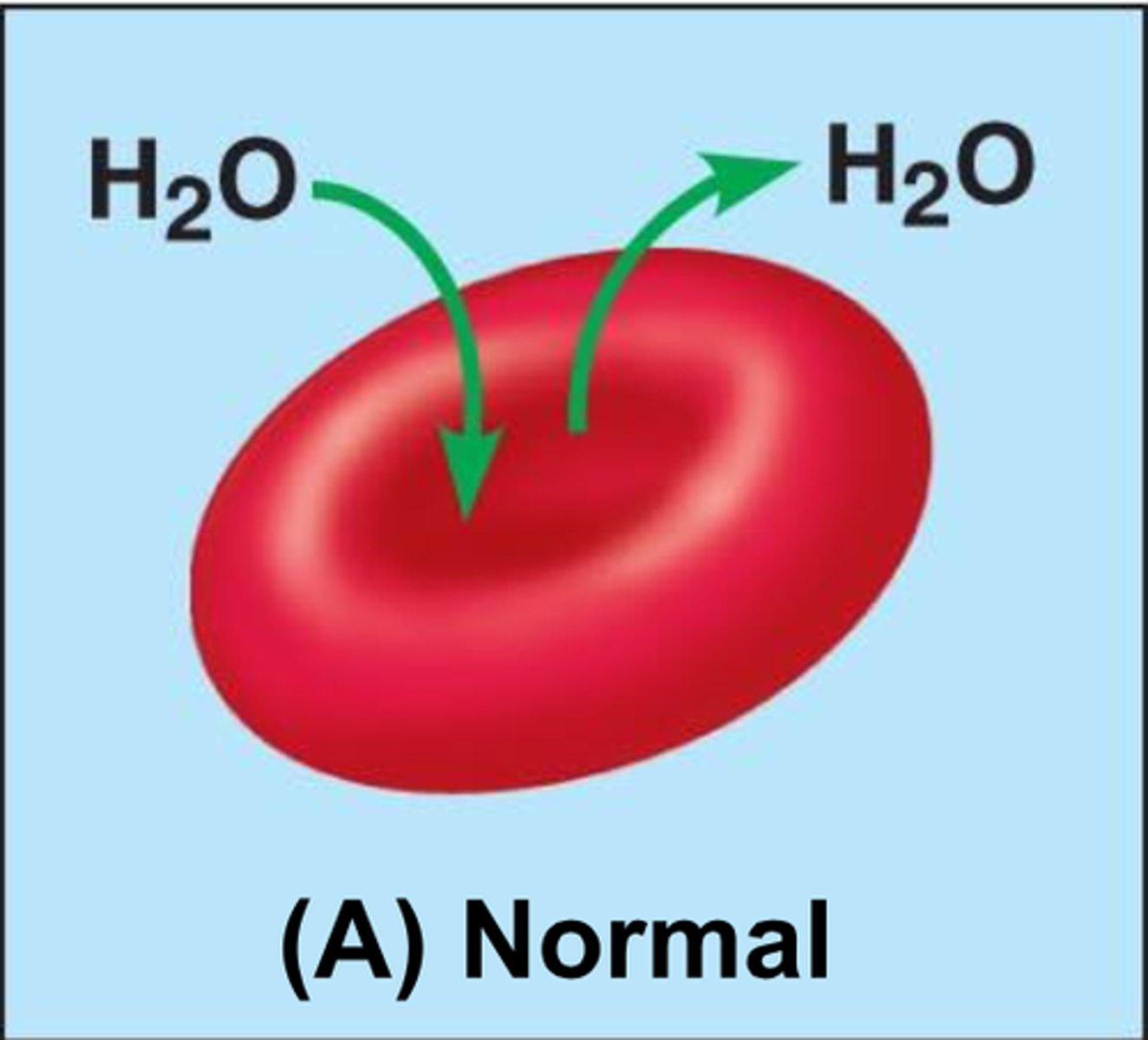
Osmosis
The diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane (Artificial or Cellular)
Tonicity
The ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Isotonic
No net movement of water across the plasma membrane.
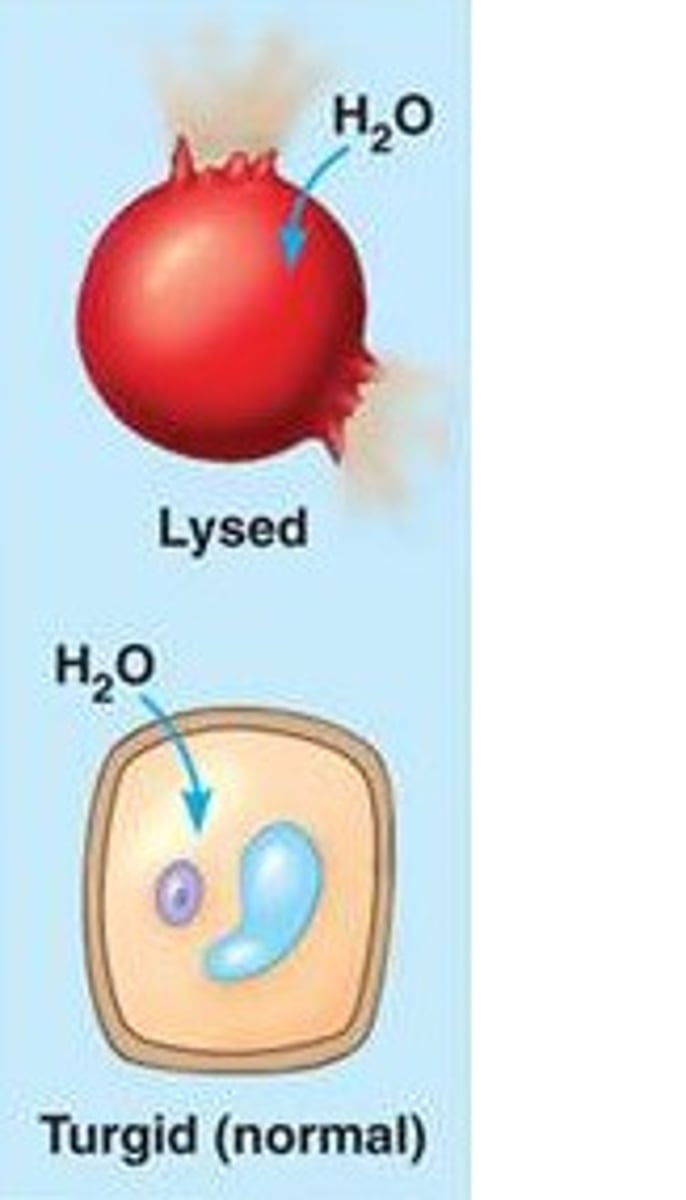
Hypertonic Solution
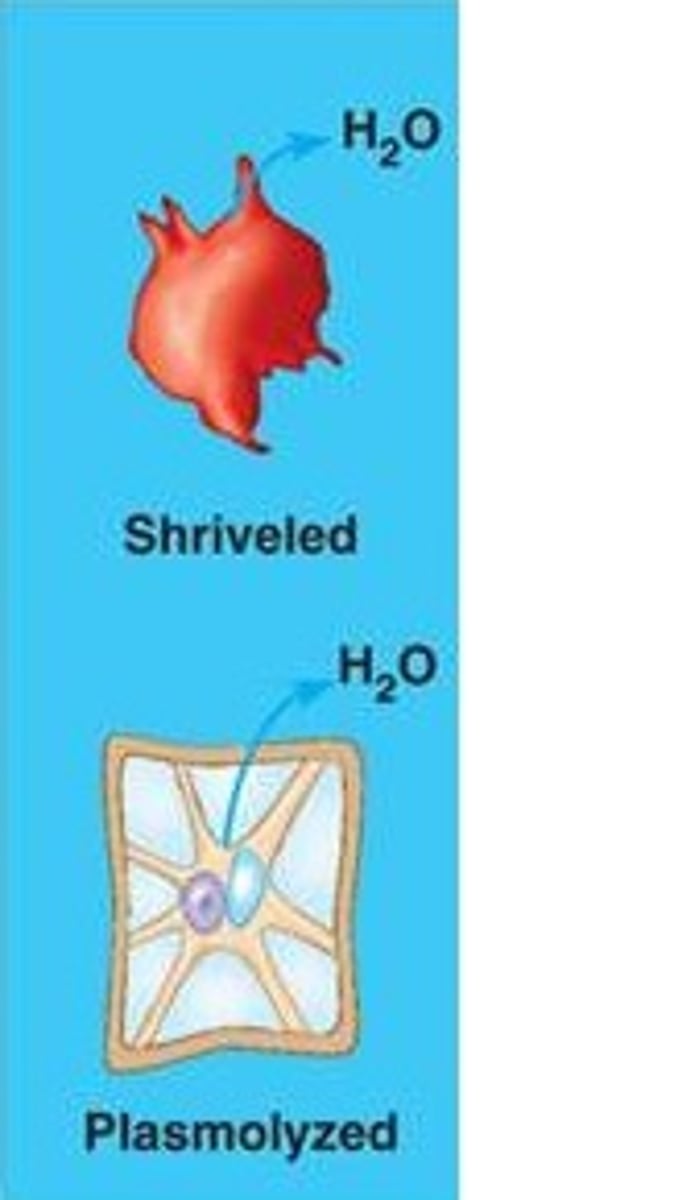
Hypotonic Solution
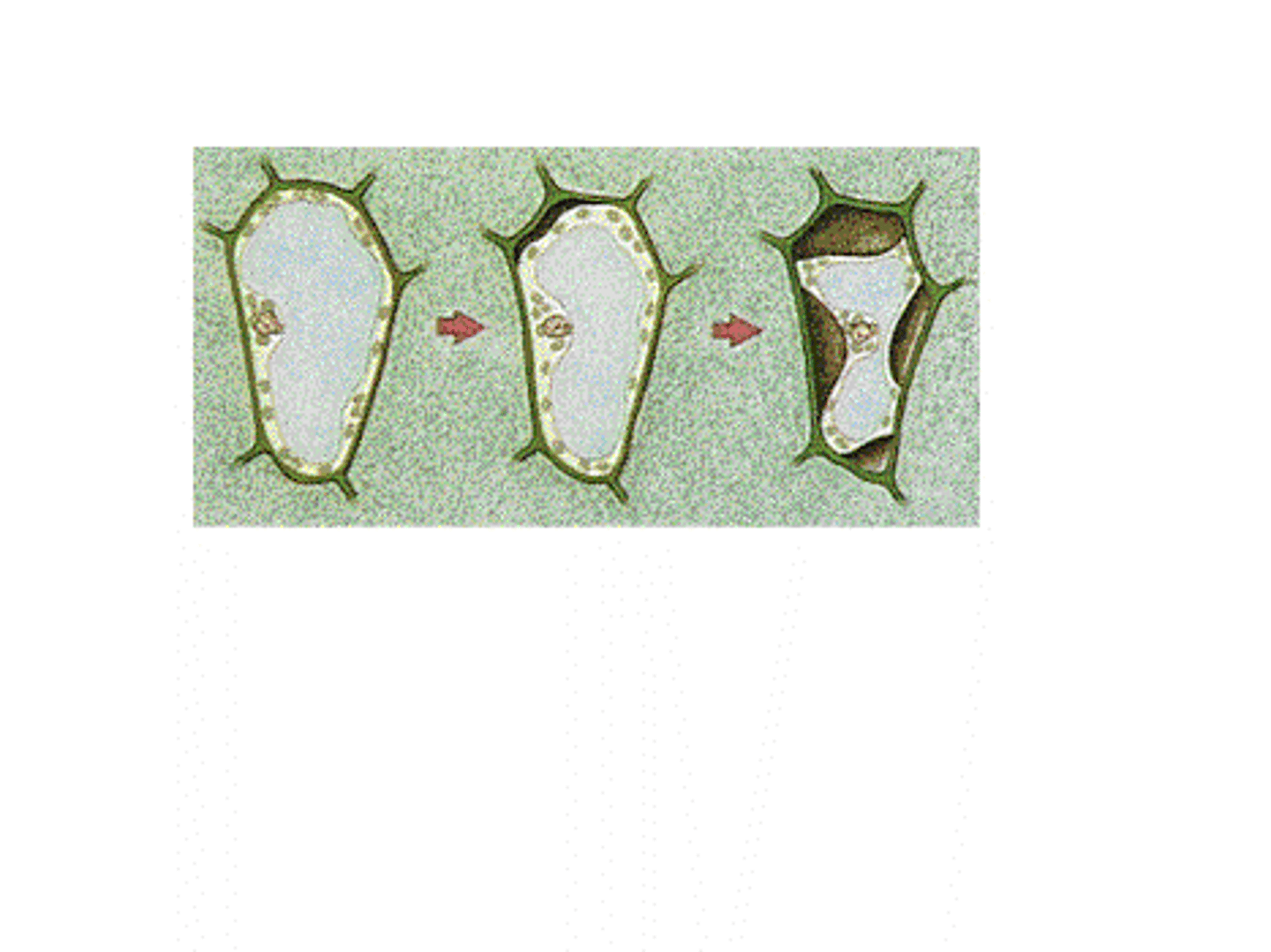
Plasmolysis
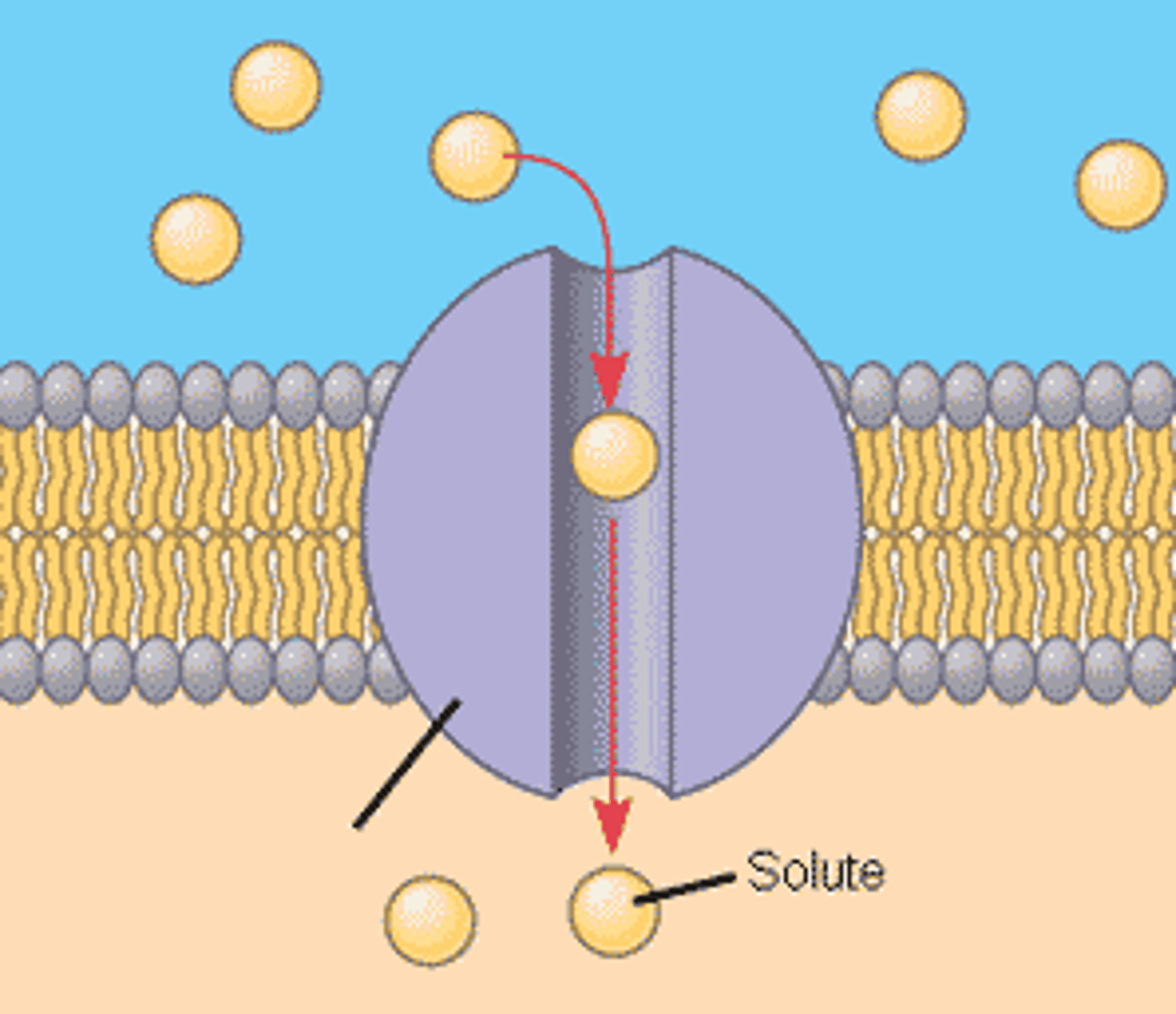
Facilitated Diffusion
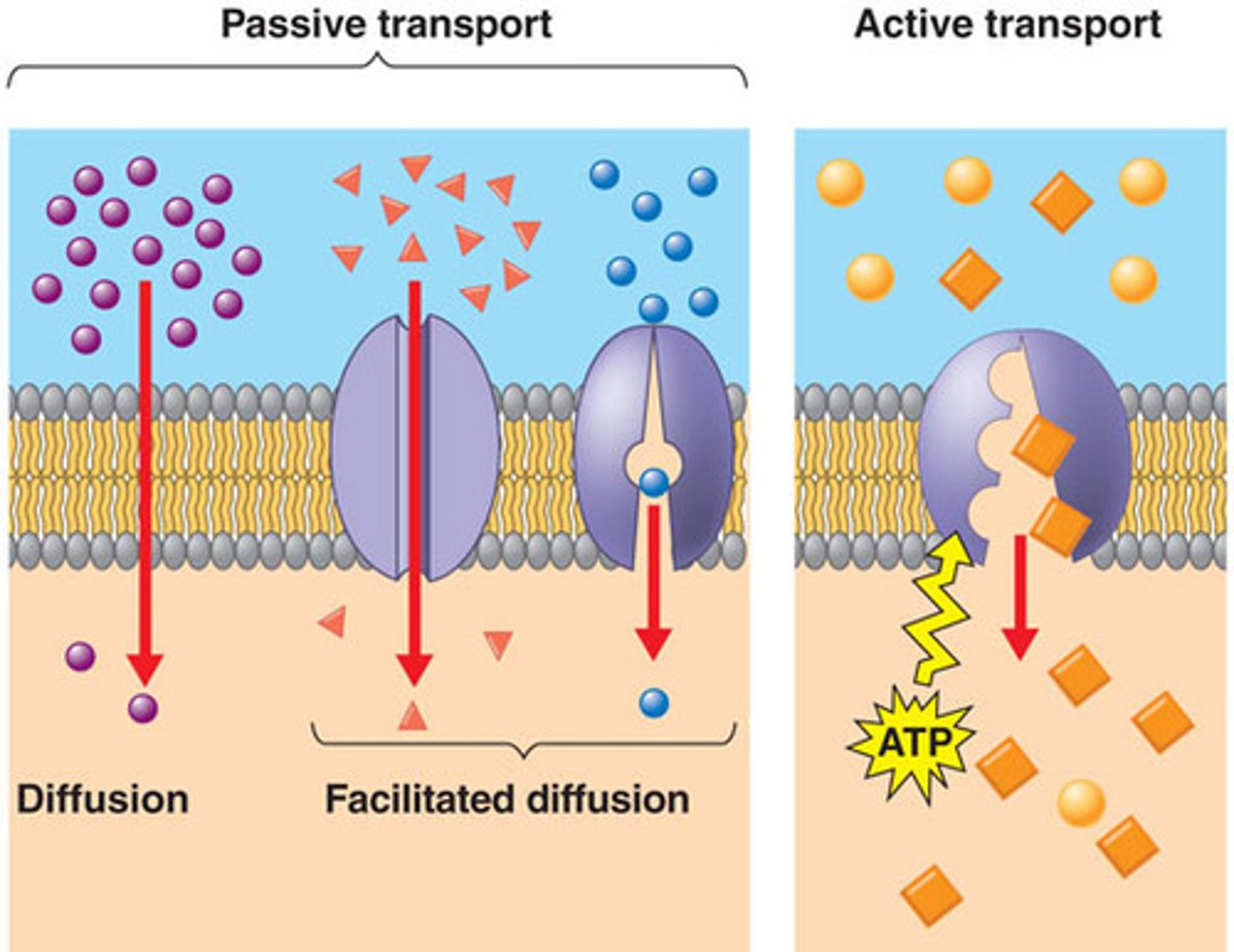
Active Transport
When a cell uses energy to pump a solute across a membrane.
Lyse
Burst
Phagocytosis
A cell engulfs a particle
Pinocytosis
a cell continually "gulfs" droplets of extracellular fluids into tiny vesicles.
Isotonic Solution
Have Direct passage through the lipid bilayer
Steroids, small hydrocarbons, nonpolar molecules, gases like CO2, O2
Needs transport proteins
Hydrophilic, charged ions, larger molecules
-Specific Transport protein for every substance.
Channel
Carrier Protein
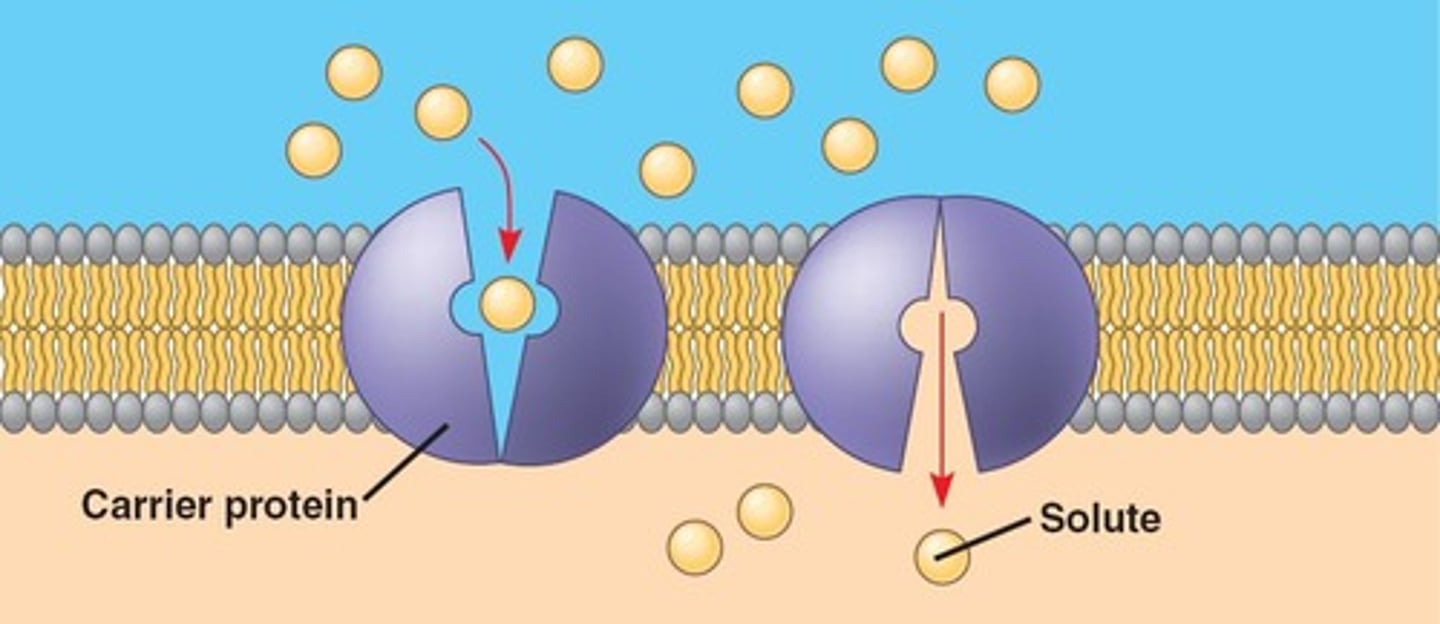
All transport proteins involved in active transport are ______________
Carrier proteins
Sodium Potassium Pump
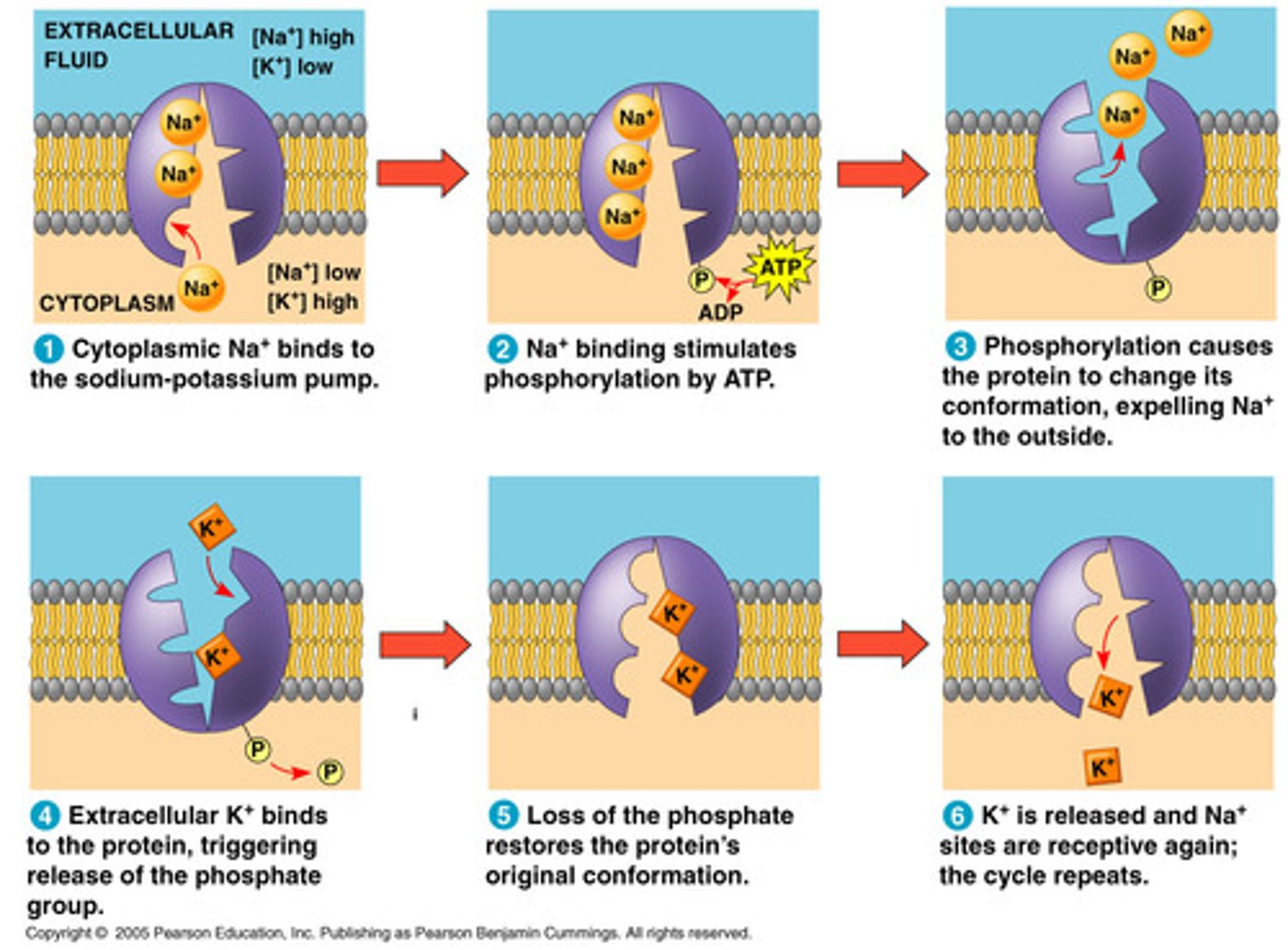
Takes in 3 Na, Then an ATP gives a phosphate, then Na is released and 2 K are taken into cell.
Sodium Potassium Pump
What is ATP after giving up a phosphate
ADP
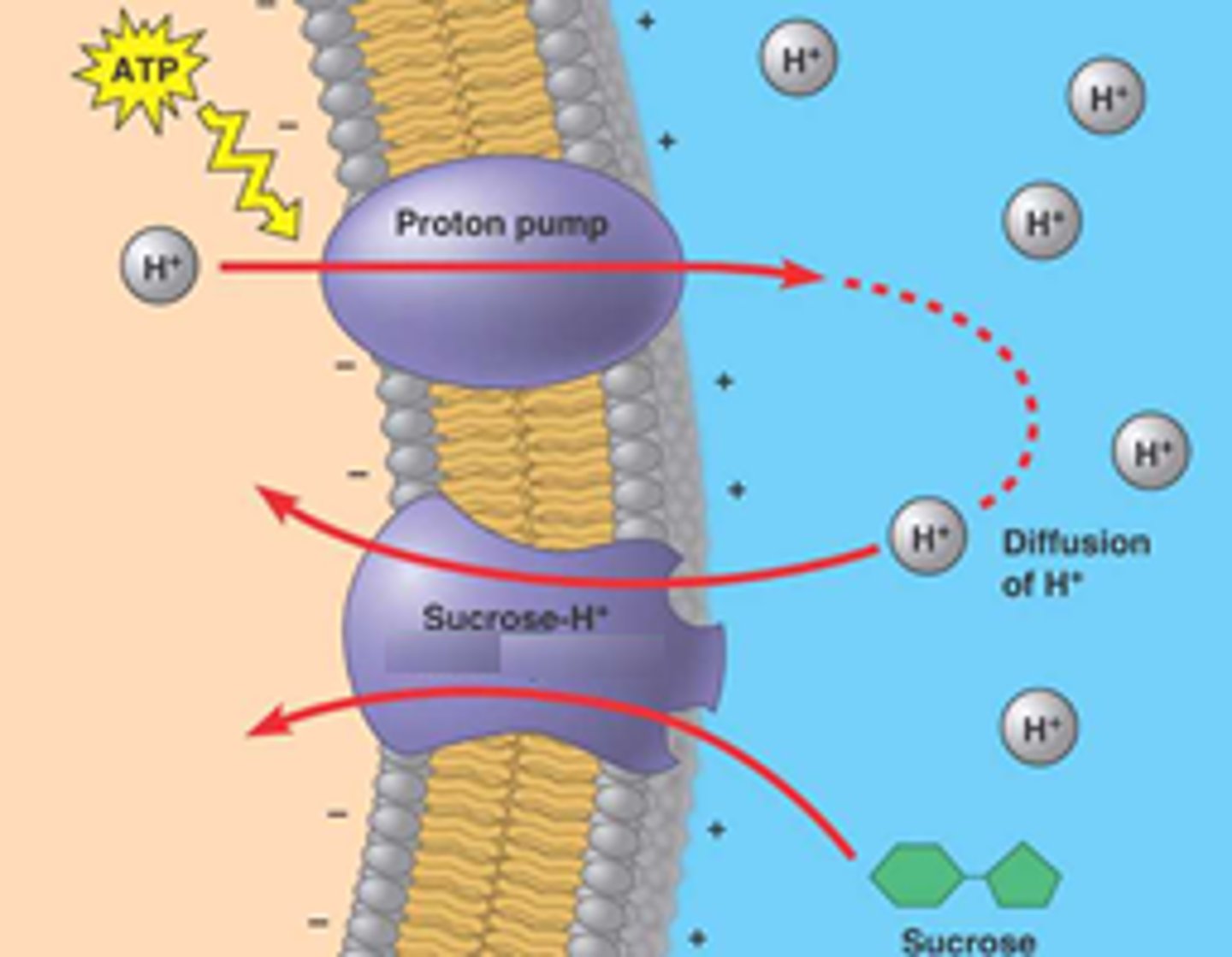
Co-Transporter
Endocytosis
Vesicle is former from plasma membrane, bringing external molecules inside cell
Exocytosis
Internal membrane vesicle fuses with plasma membrane, releasing molecules to outside
3 types of endocytosis
Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, and Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
LDL
Low Density Lipoproteins
HDL
High Density Lipoproteins
LDL Connects to ______, then _____ connects to the receptors, then ______ connects to the adaptin.
LDL Receptors, Adaptin, Clathrin
What Organelle creates ATP
Mitochondria
The sites of photosynthesis in plant cells
Chloroplasts
Process that converts sunlight into sugars for the plant
Photosynthesis
Cristae
Inner membrane of mitochondria

Flattened interconnected sacs in Chloroplasts
Thylakoids
A Stack of thylakoids
Granum
Fluid outside thylakoids that contains Chloroplast DNA/Ribosomes
Stroma
A specilized metabolic compartment bounded by a single membrane.
Peroxisome
A network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Obvious function of the cytoskeleton
Support and maintain the shape of the cell
Cell motility
changes in cell location and movement
Interacts with the cytoskeleton to help it move
Motor Proteins
Fibers that make up cytoskeleton
Microtubules, Microfilaments, Intermediate Filaments
Which cytoskeleton fiber is the thickest?
Microtubules
What cytoskeleton fiber is the thinnest?
Microfilaments
Which cytoskeleton fiber has an average diameter?
Intermediate filaments
Hollow rod constructed from the protein tubulin
Microtubules
What is a Dimer?
A molecule made up of 2 subunits
Microtubules grow out from a ________
Centrosome
What are the 2 examples of passive transport?
Channels and Carrier Proteins
A Proton Pump is what type of transport?
Active
What maintains the protein gradient in a cell?
The Proton Pump
2 forms of vesicular transport
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Where is the cytoskeleton charged?
Ha a + end and a - end
What is an element of a cytoskeleton that allows for readiness?
Rapid assembly and disassembly
Where is the microfilaments located?
Cytoplasmic Mesh
What are some functions of the MF?
Contraction of muscle, structure and shape of cell, cell motility
What are some functions of the Intermediate Filaments?
Cell anchorage, cell shape
What are some functions of the microtubules?
Cell shape, Tracking of cellular components (Organelles, vesicles)
Denaturation
When a protein bonds/interactions are destroyed, so the protein unravels and loses its normal shape
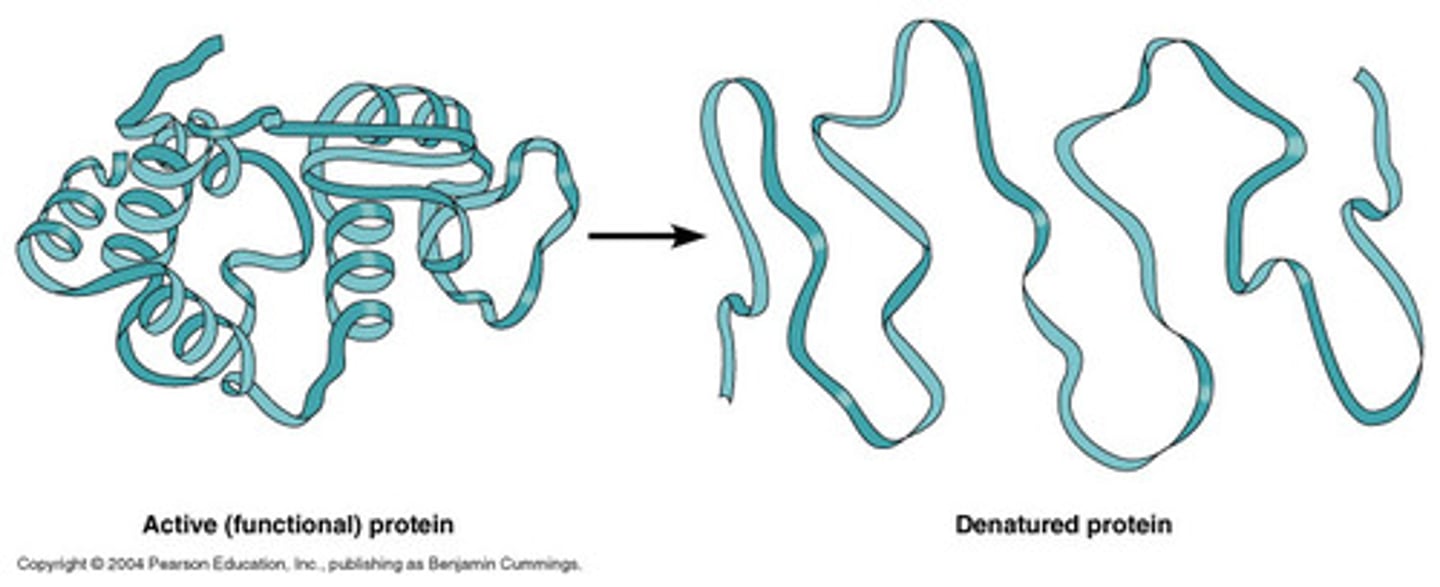
Renaturation
Opposite of Renaturation
Dehydration Reaction
2 monomers are bonded to each other, with a water being lost.
Hydroloysis
When water is added to a bond between monomers to break them apart.
What is a disaccharide?
2 monosaccharides
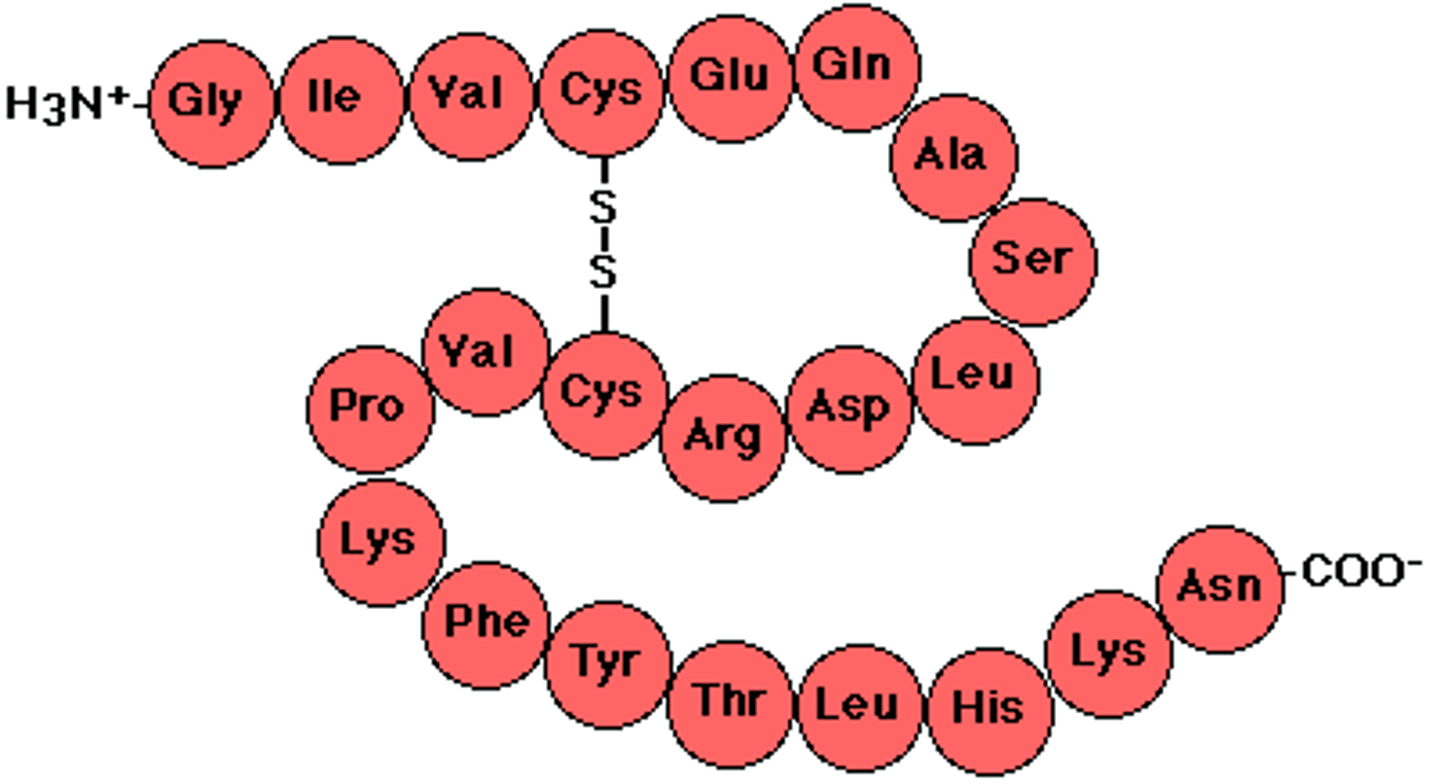
Polypeptide
A Polymer of amino acids
A protein is made up of _______
1 or more polypeptides
What does the alpha carbon have?
A carboxyl group, an amino group, a H, and a variable group R.
Catalysts
Chemical agents that speed up chemical reactions
Which of the functional groups is hydrophobic?
Methyl
How are fat molecules linked?
Ester linkages
What cell organelle's main role is digestion and waste disposal?
Lysosomes
Where does transcription happen?
The Nucleus
Where does translation happen?
The cytoplasm
What type of bond connects a sugar and phosphate group of adjacent
nucleotides to make a polynucleotide?
Phosphodiester linkages
What does cholesterol do with membrane fluidity?
It stabilizes it
Primary Protein Structure