dental caries and fluoride with ICDAS
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what is dental caries and dental plaque
pathological proceess resulting in localised destruction of tooth tissue
dental plaque ( a complex biofilm of mixed bacteria and the by products ) is a PRE-REQUISITE for dental caries development
sequelae of dental caries
dental plaque / microbial biofilm (prerequisitee)
frequent exposure of dietary sugar
increase in population of cariogenic bacteria
increase in organic acids
decreased ph of biofilm
enamel deminineralisation (loss of carbonated hydroxyapatite )
sequelae of pulp diseases (tg /short form)
pulpitis
pulp necrosis
infection of root canal
apical periodontitis
periapical abscess
spreading odontogenic infection
detail sequelae of pulp necrosis
reversible pulpitis
symptomatic irreversible pulpitis
asmptomatic irreversible pulpitis (pain and swelling absent )
hyperplastic pulpitis (pulp polyp )
internal resorption (till here pulp is vital )
necrobiosis (50%vital 50% non vital )
pulp necrosis ( non vital )
symptomatic necrosis (infected dead tissue )
asymptomatic pulp necrosis (non infected dead tissue )
apical periodontitis
symptomatic (acute )
asymptomatic (chronic )
apical infection
acute infection ( localised odontogenic infection )
spreading odontogenic infection (with/without severe systemic features )
spreading odontogenic infection (with severe systemic features )
risk factors of dental caries
diet
saliva quantity and quality
plaque characteristics
oral hygiene habits
use of fluoridated products
EARLY MODIFICATION OF THESE FACTORS IS THE PRIMARY PREVENTIVE STRATEGY
DENTAL CARIES MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
dietary modification :- avoid sucrose in sticky forms and limiting other sugars (eg acidic drinks ) and carbohydrates as snacks between meals
plaque reduction :- by cleaning teeth , brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste , interdentl cleaning
tooth surface modification :- using remineralizing agents , placing fissure sealants and other adhesive materials that protect tooth surface
saliva modification :- adressing causes of dry mouth , using low acid sugar -free chewing gum oe lozenges . non acidic coarse foods (carrots ) to increase salivary flow and buffering capacity of saliva
OTHER STRATEGIES :- acidulated / higher concentration fluoride products and non fluoride remineralising agents / CHX
high risk factors acc to ICCMS
head and neck radiation (pt related )
intraoral level caries risk factor
hyposalivation / gross indicators of dry mouth
PUFA ( exposed pulp , ulceration , fistula , absess )- Dental sepsis
other risk factors acc to ICCMS
pt level caries risk factor
dry mouth ( conditions , medications/recreational drugs / self report )
inadequate oral hygiene practices
deficient exposure to topical fluoride
high frequency/amount of sugary drinks /snacks
symptomatic driven dental attendance
socio economic stautus / health access barriers
for children high caries experience of mothers or care givers
intraoral level caries risk factors
caries experience and active lesions
thick plaque : evidence of sticky biofilm in plaque stagnation areas
appliances , restorations and other causes of increased biofilm retention
exposed root surfaces
how will you classify pt as low risk/moderate/high risk pt ?
low risk :- lack of any high caries risk factor and other risk factors are within safe ranges (sugary snacks, oral hygiene, fluoride )
moderate risk :- not deemed to be drfinitely at low risk or definitely at high risk of develping new caries lesions or of lesion progression
high risk :- any high risk factors or caregivers with very high caries experience or where several of lower risk factors suggest a combination likely to high risk status
ICDAS international caries detection and assessment system sound caries / code 0 ?
sound tooth structure (no changes in enamel )
ICDAS initial caries ?
initial caries = code 1 and code 2
code 1 :- first visual change in enamel
when wet - no color change
when dry - discoloration visible limited to pit and fissures
code 2 :- distinct visual change in enamel
color change is seen irrespective of wet/dry
wider than natural fissure/fossa
ICDAS moderate caries ?
code 3 or code 4
code 3
localised enamel breakdown with no dentin visible/no dentin shadow
code 4
underlying dentin shadow is seen (with/without enamel breakdown )
ICDAS advanced caries
code 5/6
code 5 :-
distinct cavity with visible dentin < half of occlusal surface
code 6 :-
extensive distinct cavity with visible dentin > half of occlusal surface
how will you differentiate active / passive lesions clinically ?
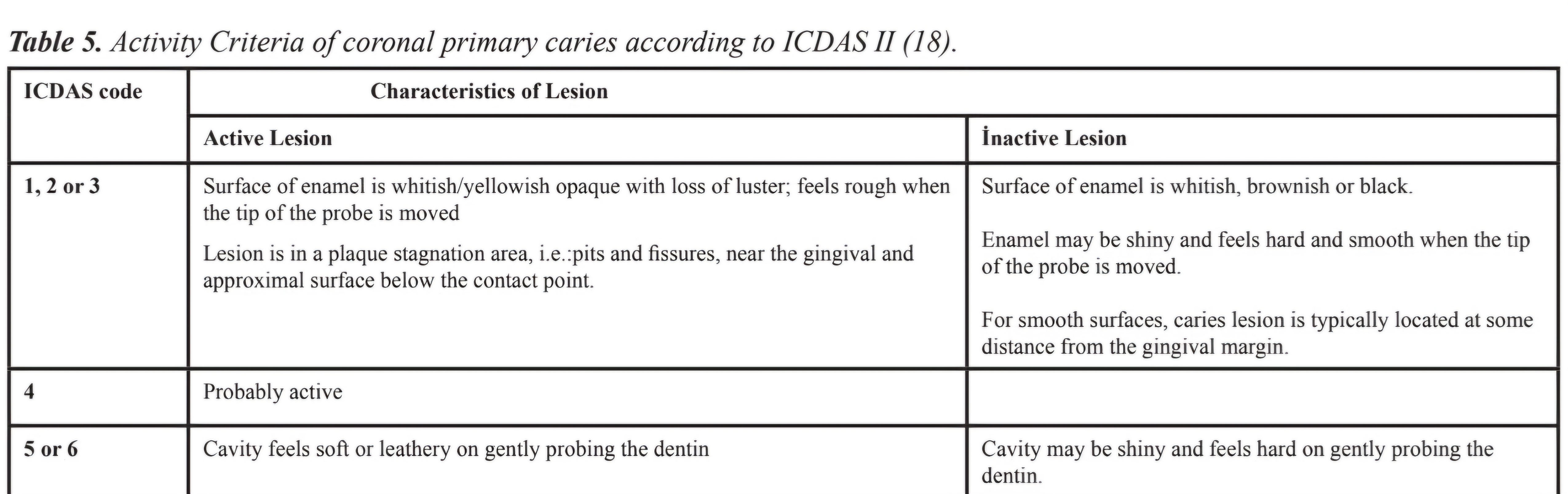
ICDAS 2 classification

how to determine likelihood of caries progression
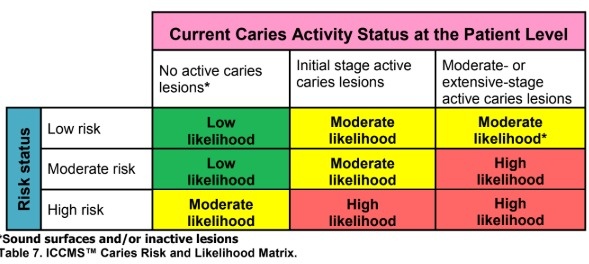
management protocol for diff carious lesioms (active/inactive and initial/moderate/extensive)
all inactive caries lesion (high/moderate/low) /sound :- preventive treatment (preventing new caries)
initial active caries- non operative care (NOC)
moderate active - tooth preserving operative care
extensive active - tooth preserving operative care (TPOC)
detailed management plan based on which area caries is in i.e. pits and fissures , mesial-distal (proximal) , free smooth
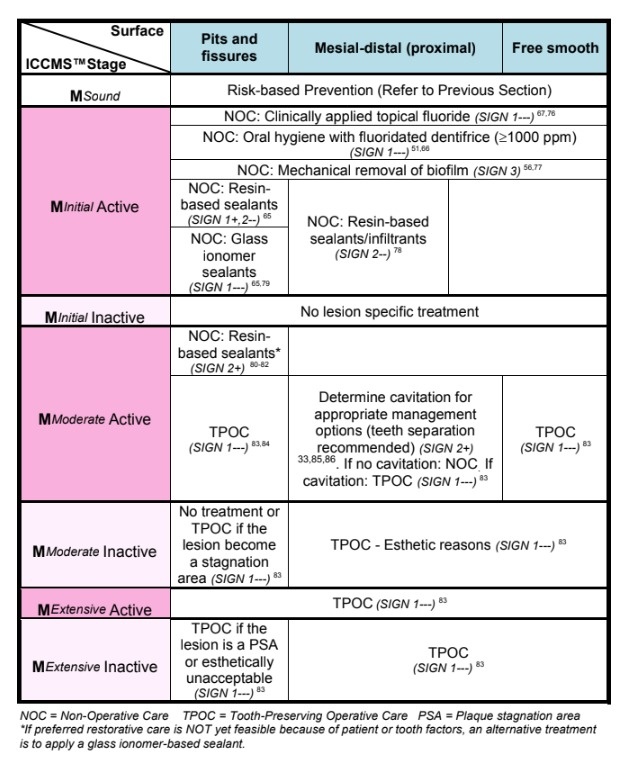
in cases of primary dentition what is the management protocol based on surface i.e. pits and fisures , mesial distal , proximal ?
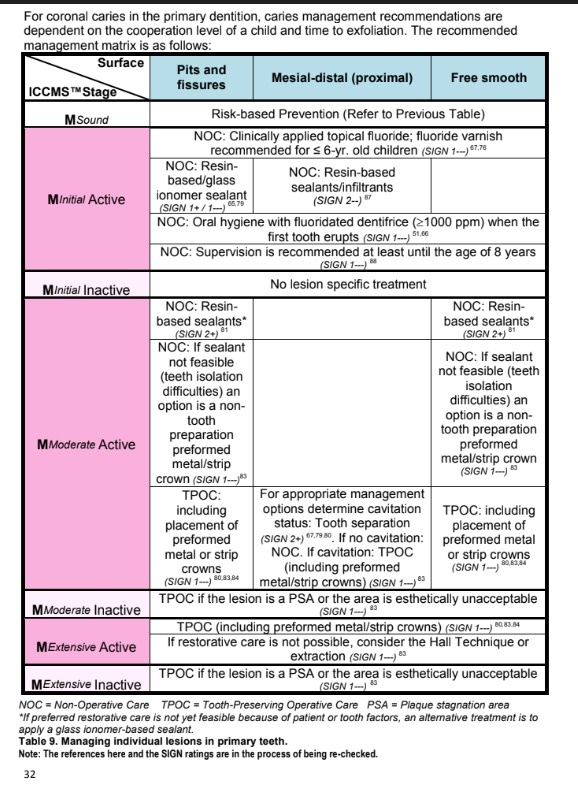
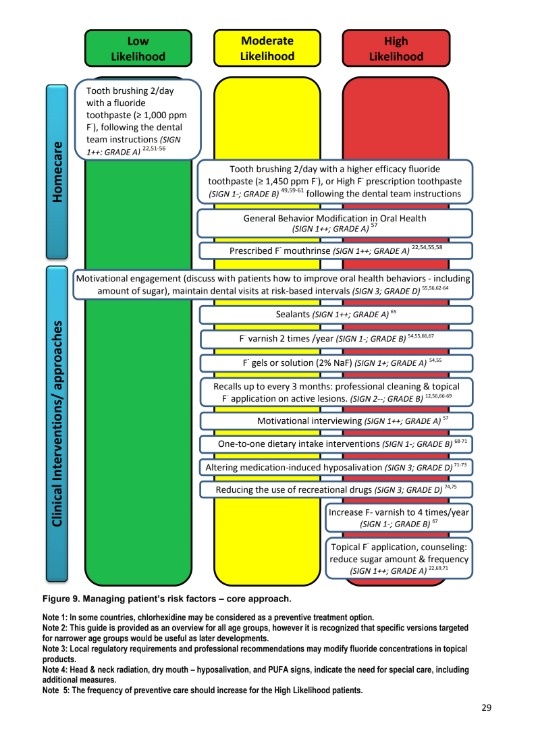
how will you manage a patients risk factors eg oral hygiene , salivation etc? based on risk low risk , moderate risk , high risk
toothpastes that do not contain fluoride provides little protection against dental caries (true/false)
true
children upto a age of 8 yrs are at an increased risk of dental flourosis (t/f)
false its 6 yrs instead of 8
patients with dental flurosis the porosity of subsurface enamel is decreased and discolouration can occur (white spots, mottling) (true/false)
false porosity increases
flouride supplements recommended are in the form of mouthwashes , gels , drops, lozenges (t/f)
false fluoride supplements in the form of drops/lozenges are no longer recommended because of limited efficacy and risk of dental fluorosis instead
varnish
mouthwash
gel
foam
toothpaste
is recommended
recommended concentration of fluoride and brushing habits according to age for low risk pts
child younger than 18 months- (twice daily brushing without toothpaste )
child 18 months to younger than 6 yrs - 500-550 ppm (0.5-0.55 mg/g ) fluoride twice daily pea sized
child 6 yrs to adolecet - 1000 - 1500 ppm (1-1.5 mg/g ) fluoride twice daily
adolescent/adult - 1000-1500ppm (1-1.5mg/g) fluoride twice daily
fluoride toothpaste concentration for people at high risk
child younger than 18 months - twice daily brushing with fluoride may be recommended
child 18 months to younger than 6 yrs - 1000 ppm twice daily or more frequent use of 500-550ppm fluoride
child 6yrs to adolescent- more frequent use of 1000-1500 ppm fluoride
adolscent /adult - 5000 ppm twice daily or more frequent use of 1000- 1500 ppm fluoride
different flouride aplications their concentrations and their use in people at elevated risk.
REFER TG FOR USES AND AGE RESTRICTIONS pg 68-69
neutral fluoride mouthwash (220ppm/0.22mg/ml )
neutral fluoride mouthwash 900ppm /0.9mg/ml
neutral fluoride 2 5000 pm / 5mg/g
fluoride varnish 22600 ppm 22.6 mg/ml
acidulated phosphate fluoride gel/foam 12300 ppm 12.3mg/g
neutral fluoride gel /foam 5000- 9000 ppm / 5-9 mg/g
silver fluoride formulations (sdf)
fluoride + CPP-ACP 900 ppm + 10% cream
fluoride +CPP-ACP 22600 ppm + 2% varnish
fluoride significantly reduces the incidence of dental caries (t/f)
true
fluoride ions have antimicrobial effect at very high concentration formulations withlow ph acidulated phosphate fluoride also have some antimicrobial activity (t/f)
true
full form of CPP-ACP and its formulation types and when should it be avoided
CPP-ACP casein phosphopeptide - amorphous calcium phosphate
bioavailable calcium and phosphate ions which combine with fluoride to promote enamel remineralisation
CPP-ACP formulations includ
sugar free chewing gum
paste
varnish some of which also contains fluoride
AVOID CPP-ACP in patients with allergies to milk protiens