bonding and hybridisation - building blocks of life
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
what are lone pairs
pairs of electrons occupying the same orbital in the valence shell
what is the octet rule
to reach maximum stability, main group elements seek to gain 8 electrons in their valence shell
what is hypervalency
a phenomenon where main elements (in the s and p block) accommodate more than 8 electrons in their valence shell
examples of hypervalent atoms
the phosphate anion and sulfur hexafluoride

how is hypervalency explained
ionic model - where some bonds are ionic - further explored by resonance (bonds switch around)
what is a covalent bond
forms when 2 atoms share a pair of electrons
the two electron clouds overlap and this attractive force decreases potential energy of system
what are the two main bonding theories
valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory
what is the valence bond theory
electrons in a chemical bond are localised between the two atoms, bonds are formed when valence orbitals overlap
pros/cons of valence bond theory
enables us to readily understand the shape and reactivity of biological molecules
cannot explain photochemical reactions
what is the molecular orbital theory
atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals, the atoms interact with eachother like waves, can be constructive or destructive interference
what does constructive interference lead to
bonding molecular orbitals
what does destructive interference lead to
anti-bonding molecular orbitals
pros/cons of molecular bond theory
conceptually challenging
allows to rationalise curly arrow notation
widely used in theoretical chemistry
what does the combination of 2 atomic orbitals form
a bonding molecular orbital (low energy) and an antibonding molecular orbital (high energy)
what are the two types of molecular orbitals
sigma and pi
what is a sigma orbital
formed by end-on overlap of atomic orbitals
what is a pi orbital
formed by side-on overlap of atomic orbitals
what is electronegativity
measure of attraction an atom has for electrons in a bond
influences the energy of valence electrons
what does an electronegativity difference of under 0.5 indicate
non-polar covalent bond
what does an electronegativity difference between 0.5 and 2 indicate
polar covalent bond
what is an ionic bond
a electrostatic bond often formed between nonmetals and metals which relies on the attraction between opposite charges
what is formed when a metal donates an electron to a non-metal
cation
what is formed when a non-metal accepts an electron
anion
what is a dative bond
a bond where both of the shared electrons come from one atom
what are coordination complexes
compounds consisting of a coordination centre (usually a metal ion) surrounded by molecules (ligands) capable of coordinating with the central atom through dative bonding.
what are ligands
molecules that can bond to a central metal atom through dative bonding
what are examples of ligands
ammonia, water, chloride ions
what is the coordination number
total number of ligands attached to central metal, determines the geometry of the complex
coordination number 2 shape
linear
coordination number 4 shape
tetrahedral
coordination number 6 shape
octahedral
what is a chelating agent
a ligand capable of forming more than 1 coordinate bond
what is the complex called when the ligand forms more than 1 coordinate bond
chelate
what is conjugation
the ability of electrons in a system of double bonds to spread over the whole system, rather than staying localised on a specific double bond
what does conjugation do
increase stability
example of conjugated system
alternating single double bonds or aromatics
what is resonance
a method of describing the delocalised electrons in molecules where bonding cannot be rationalised by Lewis structures
examples of resonance structures
peptide bond (no free rotation around C-N)
carbonate ion
benzene
what is homolytic fission
the process where a bond is broken evenly and each atom gains one electron - forms radicals
what is heterolytic fission
the process where a bond is broken unevenly and one atom gains both electrons - forms opposite ions
what is the VSEPR theory based on
electrons repel each other and place themselves as far away as possible to maximise separation
what do non-bonding pairs do in VSEPR
repel each other more, which can distort expected geometry
what is steric number
the sum of the atoms attached to central atom and the number of lone pairs
shape and bond angle for steric number 2
linear - 180
shapes and bond angles for steric number 3
0 lone pairs - trigonal planar - 120
1 lone pair - angular - >120
shapes and bond angles for steric number 4
0 lone pairs - tetrahedral - 109
1 lone pair - trigonal pyramidal - <1109
2 lone pairs - angular - <<109
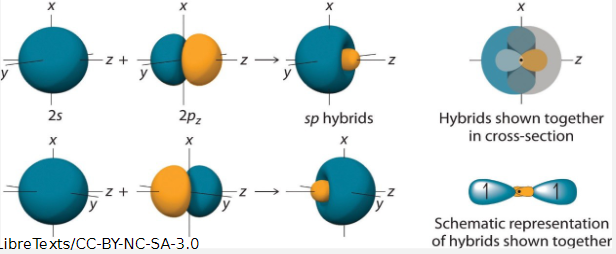
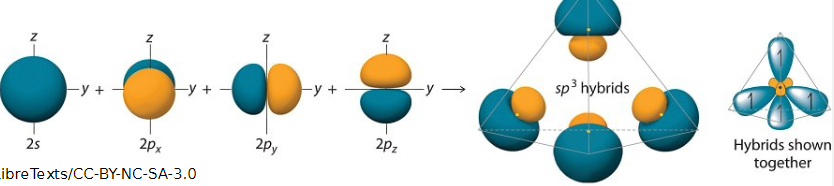
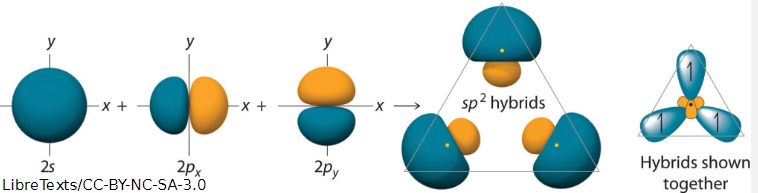
what is hybridisation
the mixing of atomic orbitals which combine to form a new set of degenerate hybrid orbitals
3 sets of carbon hybrid orbitals
sp3, sp2, sp
what shape does sp3 form
tetrahedral
what shape does sp2 form
trigonal planar
what shape does sp form
linear