unit one: chemistry of life
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
form follows function
the subcomponents of a biological molecule and their sequence determines the properties of the molecule
polarity (water molecule)
oxygen is covalently bonded tot he 2 hydrogen atoms
covalent bond: electrons are shared
polar covalent bonds: is unequal sharing of electrons because O is electronegative
hydrogen bonding
when a hydrogen atom in a molecule makes a bond with F, O, or N in another molecule
creates an intermolecular force between the molecules
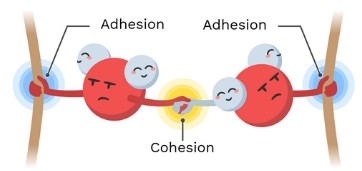
cohesion
when 2 of the same molecules form hydrogen bonds
ex: water x water
adhesion
when two different molecules form hydrogens bonds
ex. water x other
capillary action and transpiration
transpiration: when water moves up plants through the stems
leaves through the leaves as water vapor
the water holds together by cohesion, and clings to the xylem tubes by adhesion
surface tension
increased hydrogen bonding at the surface of the water
ex. can let water striders walk on water
can allow leaves tp float on water to allow for more photosynthesis
high specific heat
if water absorbs a lot of thermal energy before it changes states, then it can resist the changes in temp
ex. creates stable marine/land environment
high heat of vaporization allows for evaporative cooling while sweating
s tier solvent
solvent: dissolving agent
allows water based organisms to obtain key nutrients from enviroments
acts as a buffer
hydrophilic
likes water
polar, ions
cellulose, sugar, salt
blood
hydrophobic
repels water
nonpolar
oils and lipids
tails of the plasma membrane
expansion upon freezing
water molecules slow down when the temp decreases and the bonds between water molecules are more stable and spread out
forms a crytalline structure
floats because ice is less dense
creates a little blanket and traps in heat under the ice for organisms to survive
law of conservation of energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed
diversity of carbon
all macromolecules have it
can be chains, ring shaped, or branched
can have up to 4 bonding partners
carbohydrates
contain CHO
lipids
contain CHO(P)
NO TRUE MONOMERS
proteins
contain CHON (sometimes less)
nucleic acids
contains CHONP
dehydration synthesis
when 2 monomers link together (form covalent bonds)
an H is lost from one and an OH is lost from another
loses h2o to bind the monomers together
hydrolysis
add H to one monomer and OH to another to break them apart
carbohydrates (more detail)
monosaccharide —> disaccharide —> polysaccharide
monosaccharides: monomer like glucose and ribose
polysaccharides: long chain of monosaccharides like starch and cellulose
cellulose vs. starch
both are polysaccharides of carbohydrates
starch is made with α glucose monomers
cellulose is made with β glucose monomers
both have OH in different places!!!
storage vs. structural polysaccharides
storage (long chains)
plants: starch
animals: glycogen
structural (condensed)
cellulose and chitin for exoskeleton
lipids (detailed)
fats: triglycerides (store energy for long term) and adipose (insulation)
triglyceride: glycerol + 3 fatty acids
saturated, unsaturated, polyunsaturated fatty acids
steriods: cholesterol (creates plasma membrane) and hormones (chemical messengers)
phospholipids: lipid bilayer of plasma membrane
hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tails
lipid saturation
saturated
saturated with hydrogen
in animals
solid at room temp
butter, lard, etc.
unsaturated/polysaturated
have some double bond carbon that leads to kinks
in plants
liquid at room temp
corn oil, olive oil, etc
phospholipids
contains hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tails
has kinks in the tails
make the phospholipid bilayer
levels of protein structure
primary
amino acid sequence turns into a polypeptide chain
covalent peptide bonds link the amino acids together
always adds to the C TERMINUS, the carboxyl end
secondary
gains a 3d shape by hydrogen bonding
shapes are the alpha helix and beta plated sheet
tertiary
bonding between “R” groups of amino acids
hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, and van der Waal interactions are made !!
quaternary
2+ polypeptides bond together
only some proteins get to this level!!!
proteins (structure and function)
protein structure and function are sensitive to chemical and physical changes
unfold or denatures if the pH or temperature are not optimal
enzymatic proteins
acceleration of chemical reactions
defensive proteins
protection against disease
storage proteins
storage of amino acids
transport proteins
transport of substances
hormonal proteins
coordination of an organism’s activities
receptor proteins
response of cell to chemical stimuli
contractile and motor proteins
movement
structural proteins
support
nucleic acids (detailes)
store and transmit genetic info
purines (single ring0
adenine
guanine
pyrimidines (double ring)
cytosine
thymine
uracil
purines and pyrimidines bond together using hydrogen bonds!!
A = T/U
C triple bonded to G
3 bonds = more stability
DNA directionality
antiparallel: backbones run in opposite direction and don’t intersect!!!
build off 3’ exposed end in 5’ to 3’ direction
DNA & RNA
DNA
usually double stranded
AGCT
stores hereditary info
longer/larger
sugar: deoxyribose
RNA
usually single-stranded
AGCU
carry info from DNA to ribosomes
tRNA, rRNA, mRNA, RNAi
sugar: ribose