GEOG 2020 Final Set 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:16 PM on 4/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
What is an SSP?
Shared socioeconomic pathway - a storyline for the future
2
New cards
What is SSP based on? (hint 4 things)
* Population projection
* Economic growth
* Technological trends
* Geopolitical trends
\
* Economic growth
* Technological trends
* Geopolitical trends
\

3
New cards
Define SSP 1
\*\*\*\* storylines that keep global warming under 2 degrees
\*\*\*\* storylines that keep global warming under 2 degrees
* Nations act immediately and aggressively to reduce their fossil fuel use
SSP 1-1.9
* faster emission reductions
* Faster carbon capture deployment
**Both**
* Strong economic growth
* Broad investments in education & healthcare
* Global standards of living increase
SSP 1-1.9
* faster emission reductions
* Faster carbon capture deployment
**Both**
* Strong economic growth
* Broad investments in education & healthcare
* Global standards of living increase
4
New cards
Describe SSP 2
\*\*\*\* Storylines where the future matches history of socio economic development
\*\*\*\* Storylines where the future matches history of socio economic development
* Nations don’t decline until 2050
* “roughly consistent” with nations’ 2030 climate pledges
* 2100 world has warmed by around 2.7°C
* “roughly consistent” with nations’ 2030 climate pledges
* 2100 world has warmed by around 2.7°C
5
New cards
Describe SSP 3
\*\*\*\*\* Dark Future
\*\*\*\*\* Dark Future
* Population is over 12 billion
* “Droughts and floods worsen considerably
* summertime Arctic sea ice vanishes
* once 50-year heat waves occur nearly 40 times more often
* 2100 - world has warmed by around 3.6°C
* “Droughts and floods worsen considerably
* summertime Arctic sea ice vanishes
* once 50-year heat waves occur nearly 40 times more often
* 2100 - world has warmed by around 3.6°C
6
New cards
Describe SSP 4
\*\*\*\*\*\* Inequality, A road divided
\*\*\*\*\*\* Inequality, A road divided
* Big disparities in economies, political power within and between countries
* High tech and low tech countries
* Social and political unrest
* Both low-carbon energy and policies in high income areas and high carbon fuels still used in stagnant economies.
* High tech and low tech countries
* Social and political unrest
* Both low-carbon energy and policies in high income areas and high carbon fuels still used in stagnant economies.
7
New cards
Describe SSP 5
\*\*\*\*\* Oil and gas intense economic growth future
\*\*\*\*\* Oil and gas intense economic growth future
* very rich,
* very equal, and
* very high tech
* “Earth is hellishly hot, but humans might be better equipped to adapt than they would be in the poor, highly unequal world beset by nationalism.”
* 2100 - world has warmed by around 4.4°C
* very equal, and
* very high tech
* “Earth is hellishly hot, but humans might be better equipped to adapt than they would be in the poor, highly unequal world beset by nationalism.”
* 2100 - world has warmed by around 4.4°C
8
New cards
What are the impacts of increased temps?
more heat waves (illness and death)
energy costs for cooling
Agricultural pests and disease
drought and wildfire
permafrost and winter road thaw
energy costs for cooling
Agricultural pests and disease
drought and wildfire
permafrost and winter road thaw
9
New cards
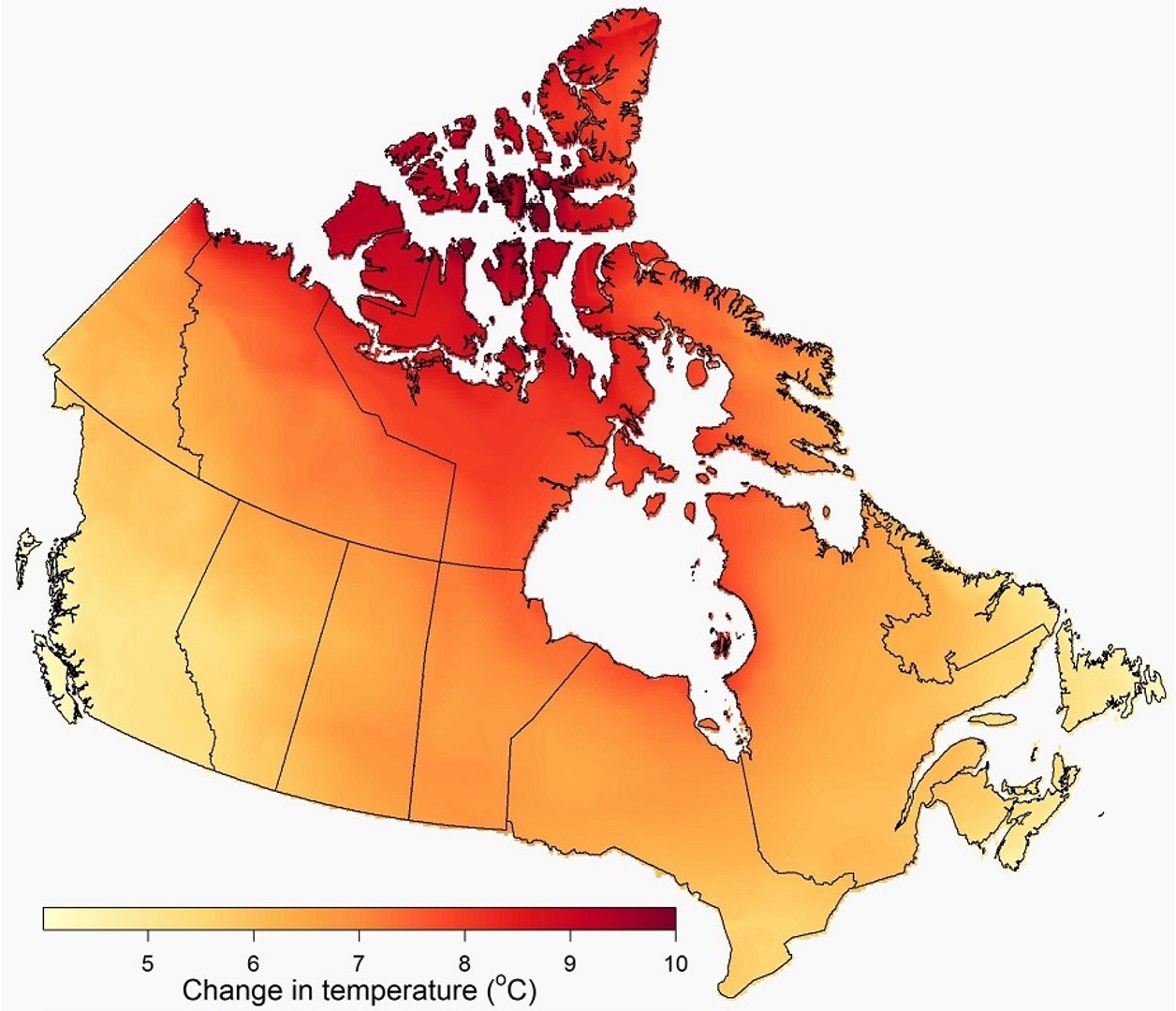
Temperature in 2100
Temperature changes range from around 4 to 10 degrees Celsius. The largest changes are seen in northern regions, particularly over the Arctic Archipelago, where changes are around 10 degrees Celsius. The smallest changes in Canada are seen on the southwest coast of British Columbia and the Atlantic provinces.
10
New cards
Precipitation in 2100.
There will be intensification of the water cycle and more water vapour in the atmosphere. What causes this?
There will be intensification of the water cycle and more water vapour in the atmosphere. What causes this?
Increased temp causes further warming because water vapour is a greenhouse gas.
\
\
11
New cards
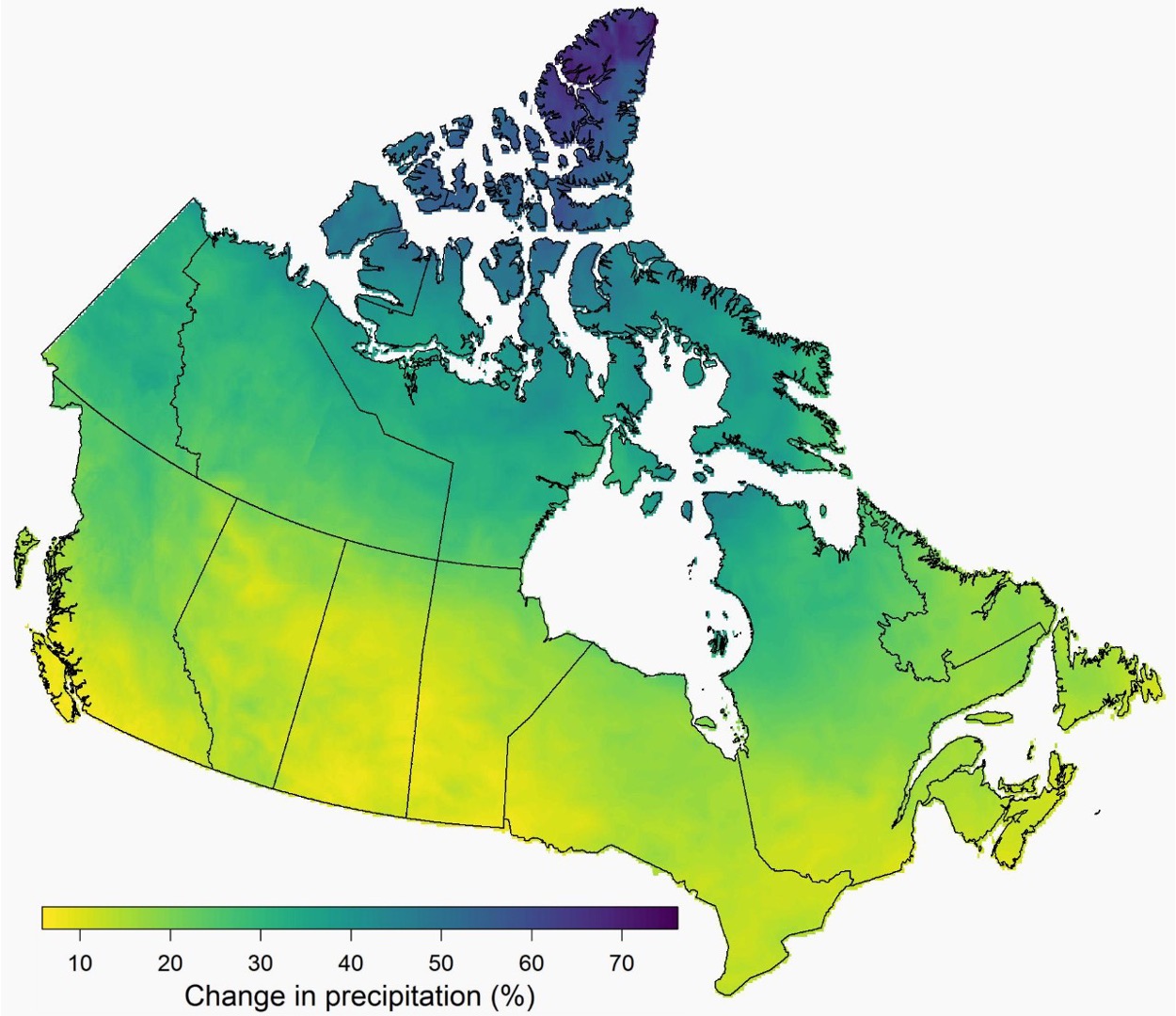
Precipitation in 2100 - see other side
•Precipitation increases range from around 8% to over 70%.
•The largest increases are seen in northern regions, particularly over Elsmere Island where increases are over 70%.
•The smallest changes are seen in the Prairies as well as the southwest coast of British Columbia.
•Timing of precipitation unknown
•Offset by evaporation causing drought in some areas
•The largest increases are seen in northern regions, particularly over Elsmere Island where increases are over 70%.
•The smallest changes are seen in the Prairies as well as the southwest coast of British Columbia.
•Timing of precipitation unknown
•Offset by evaporation causing drought in some areas
12
New cards
Sea Ice - if nothing changes and global warming cannot be stopped what will happen in the Arctic?
Recent studies show the arctic will be ice-free in the summer by 2050 (or as early as 2035)
13
New cards
What are the impacts of precipitation?
landslides and flooding due to:
more frequent and intense rainfalls, such as downpours from thunderstorms
more instances of rain failing on snow
new storm patterns
more frequent and intense rainfalls, such as downpours from thunderstorms
more instances of rain failing on snow
new storm patterns
14
New cards
Albedo Effects - Imagine that you are observing our warming planet over the next century from space. Describe 5 different changes involving albedo that you anticipate being able to observe visually that would in turn impact the rate of warming.
1. Snow and ice changes
2. Vegetation cover
3. Aerosols (sea salts, forest fires, sulphur dioxide, nitrous dioxide
1. Clouds
2. Sea Level Change
\
\
15
New cards
What is an albedo feedback?
A process of warming that causes a change that further impacts that process.
Amplifying (positive feedback)
“Warming” causes “A change in albedo”
\
Amplifying (positive feedback)
“Warming” causes “A change in albedo”
\

16
New cards

Visual cue card
17
New cards
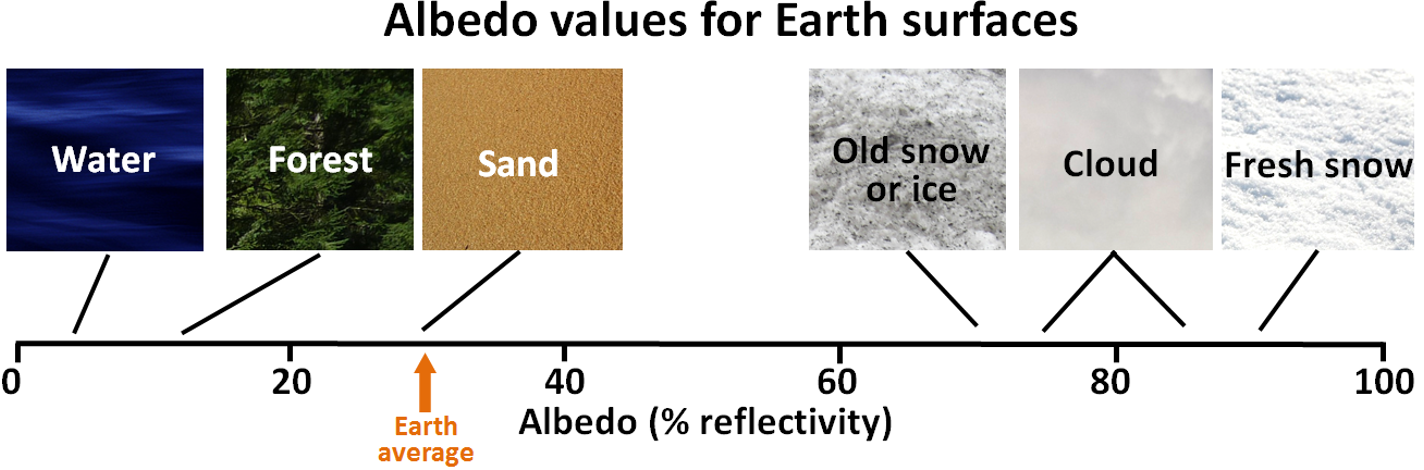
What are the albedo values for Earth surfaces?
\
EARTH’S REFLECTIVITY = 30%
EARTH’S REFLECTIVITY = 30%
18
New cards
True or false?
Does an increase in the amount of ocean surface increase albedo?
Does an increase in the amount of ocean surface increase albedo?
False - it decreases albedo
•AMOUNT OF OCEAN SURFACE INCREASE = DECREASE ALBEDO
For more info! :)
•AMOUNT OF DESERT INCREASE = INCREASE ALBEDO
•AMOUNT OF TUNDRA DECREASE = DECREASE IN ALBEDO
•AMOUNT OF OCEAN SURFACE INCREASE = DECREASE ALBEDO
For more info! :)
•AMOUNT OF DESERT INCREASE = INCREASE ALBEDO
•AMOUNT OF TUNDRA DECREASE = DECREASE IN ALBEDO
19
New cards
Aerosols - name them
Wildfire
volcanic gases and ash
seasalts
mineral dust
anthropogenic soot
**Challenge yourself -**
Generally, aerosols cool.
More aerosols = more nuclei= smaller droplets = increased droplet concentrations = higher albedo = cooling
Which ones cool?
Which ones heat?
Which ones are it depends?
volcanic gases and ash
seasalts
mineral dust
anthropogenic soot
**Challenge yourself -**
Generally, aerosols cool.
More aerosols = more nuclei= smaller droplets = increased droplet concentrations = higher albedo = cooling
Which ones cool?
Which ones heat?
Which ones are it depends?
20
New cards
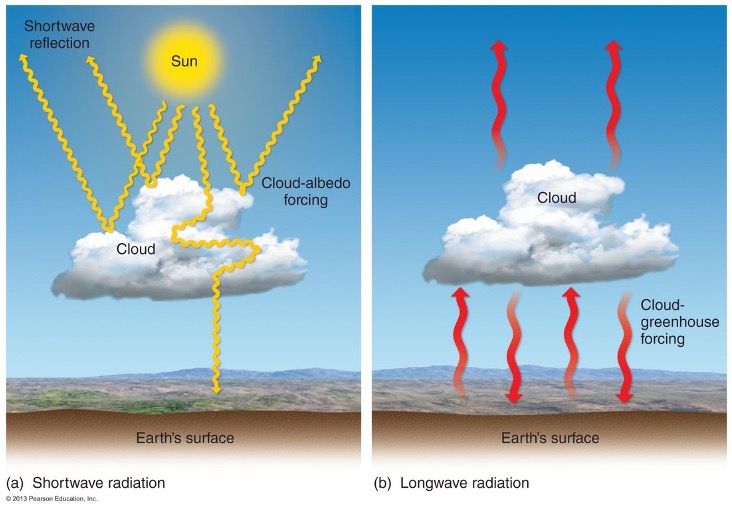
Why care about clouds? hint - think what they do
•HIGHER ALBEDO THAN EARTH’S SURFACE (MOSTLY)
•THEY TRAP HEAT (COMPOSED OF GREENHOUSE GASES)
•THEY TRAP HEAT (COMPOSED OF GREENHOUSE GASES)
21
New cards
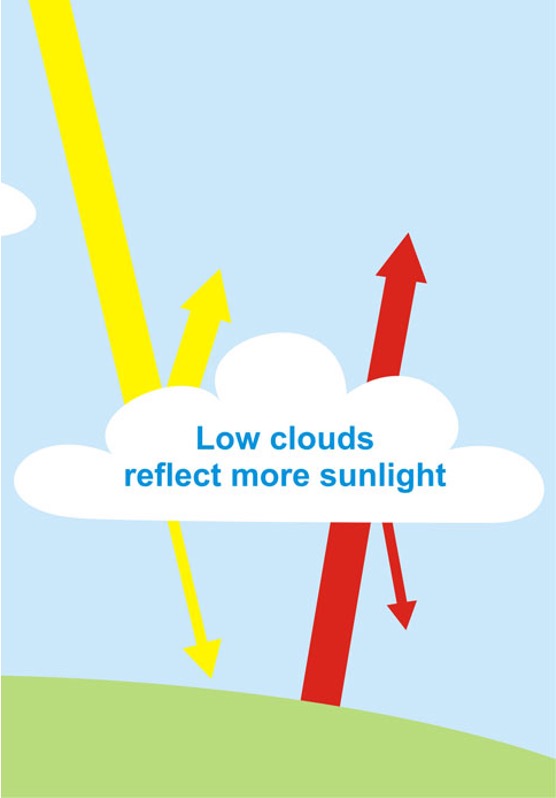
True or false?
Low clouds reflect more sunlight
Low clouds reflect more sunlight
True - Thick low clouds are more light coloured and the clouds are more reflective of sunlight, thereby cooling the earth.
\
\
22
New cards
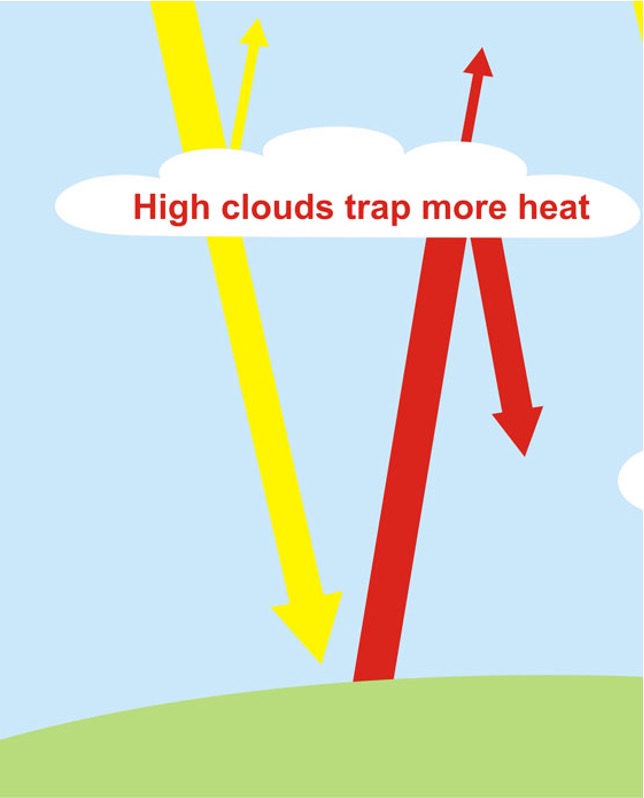
True or false?
High clouds trap less heat
High clouds trap less heat
False - high clouds trap more heat. They allow light through but are slow to release heat into space, thereby causing more warming.
\
\
23
New cards
How does the Earth’s atmosphere work like a blanket?
The Earth’s atmosphere works like a blanket that traps heat and keeps the planet warm enough to support life. However, greenhouse gas emissions produced by humans have “thickened” this blanket by adding additional heat trapping gases into the atmosphere. Since the industrial period, increased consumption of natural resources and the burning of fossil fuels (such as coal, oil and natural gas) have increased the emission of these gases and their concentrations in the atmosphere.
24
New cards
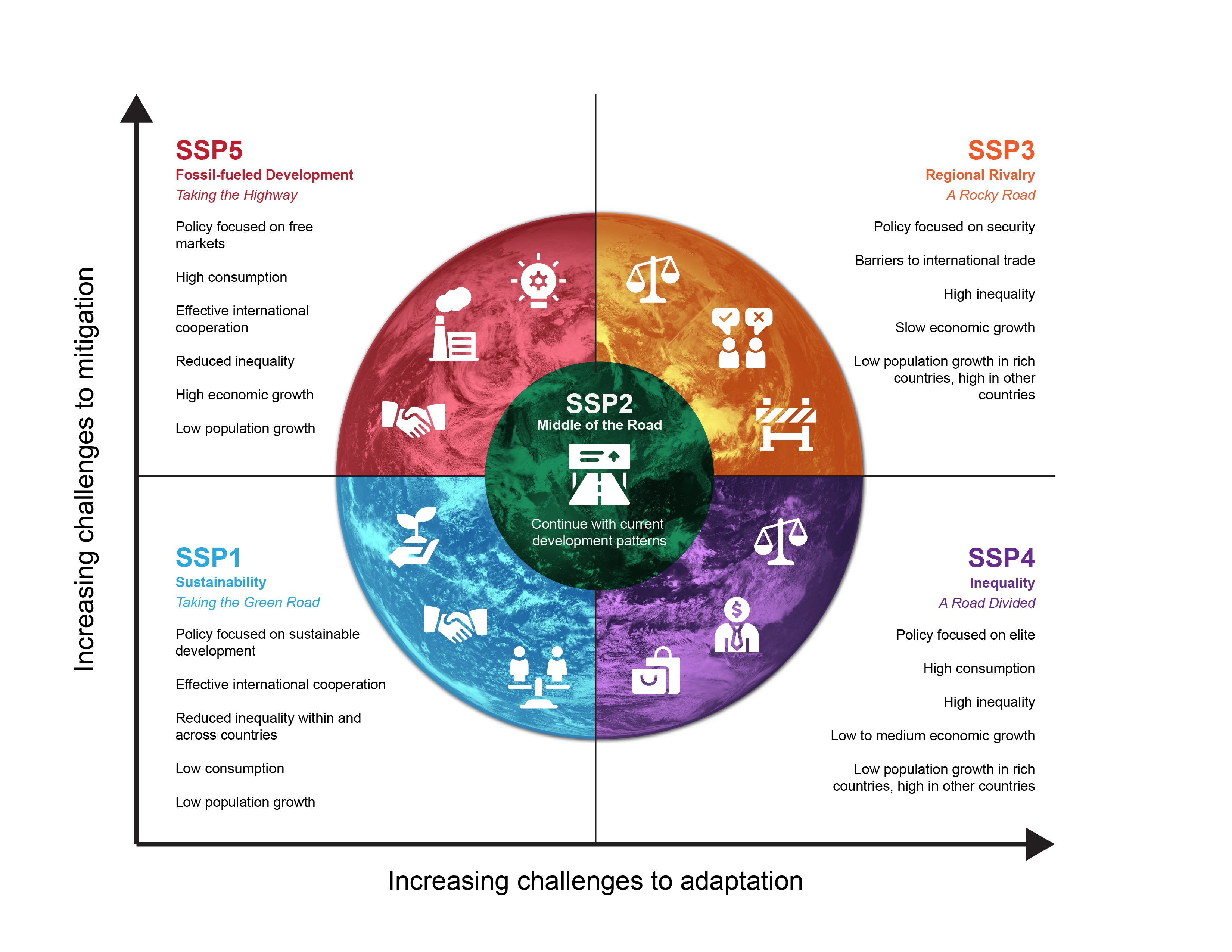
Study and learn the SSPs :)
25
New cards
What is the Kopek system based on?
\
\
Based on the assumption that vegetation type is closely linked to climate (especially temperature and precipitation)
26
New cards
What is the nature of codes in the Koppen system?
Capital letter - relates to category
Goes from A - E
Goes from warm to cool except B’s – arid and semi arid
Goes from A - E
Goes from warm to cool except B’s – arid and semi arid
27
New cards
Koppen System - What does A, B, C, D and E mean?
A - Tropical
B - Desert and Steppe climates
C - Mid-Latitude Meso-thermal climates
D - Mid-Latitide Micro-thermal climates
E - Polar Climates
* All climates with the exception of “B” climates are based on temperature.
B - Desert and Steppe climates
C - Mid-Latitude Meso-thermal climates
D - Mid-Latitide Micro-thermal climates
E - Polar Climates
* All climates with the exception of “B” climates are based on temperature.
28
New cards
What are the average temps for A, C, D, E in the Koppen system
A - nice and warm - 18C average annual temp
C - average temp of warmest month is more than 10C and avg temp of collect month is less than 18C and greater or equal to -3C
D - average temp of warmest month is greater than 10C and the temp of the coldest month is greater than or equal to -3C
E - average temp of warmest month greater than 10C
C - average temp of warmest month is more than 10C and avg temp of collect month is less than 18C and greater or equal to -3C
D - average temp of warmest month is greater than 10C and the temp of the coldest month is greater than or equal to -3C
E - average temp of warmest month greater than 10C
29
New cards
What is unique about B in the Koppen system?
Based on potential evaporation, precipitation and temperature.
to be considered a B climate the average annual precipitation must fall below a threshold value (Pt)
Whether neither half of year has a greater or equal to 70% of precipitation:
Pt = 20T + 140
Note T = average annual temperature C
to be considered a B climate the average annual precipitation must fall below a threshold value (Pt)
Whether neither half of year has a greater or equal to 70% of precipitation:
Pt = 20T + 140
Note T = average annual temperature C