i love protein
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Enzymes are ____.
| a. | RNA molecules |
| b. | proteins |
| c. | DNA molecules |
| d. | transposable elements |
| e. | codons |
b
Every protein is assembled on a(n) ____ according to instructions copied from ____, using ____ as an intermediate.
| a. | mRNA; tRNA; DNA |
| b. | tRNA; mRNA; DNA |
| c. | ribosome; mRNA; tRNA |
| d. | tRNA; DNA; mRNA |
| e. | ribosome; DNA; mRNA |
e
Beadle and Tatum used nutritional mutants called ____ to study the relationship between genes and proteins in Neurospora.
| a. | transposons |
| b. | chaperones |
| c. | polysomes |
| d. | auxotrophs |
| e. | wild types |
d
Srb and Horowitz’s research led to the ____ hypothesis, which has since been modified to the ____ hypothesis.
| a. | one gene-one enzyme; one gene-one polypeptide |
| b. | one gene-one polypeptide; one gene-one enzyme |
| c. | one gene-one protein; one gene-one enzyme |
| d. | one gene-one polypeptide; one gene-one protein |
| e. | one gene-one enzyme; one gene-one protein |
a
Consider a mutant organism that is unable to make the amino acid arginine. Knowing that the metabolic pathway for arginine production is ornithine ® citrulline ® arginine, you test the ability of the mutant to grow in the presence of just one of these compounds. You find that the mutant can grow in the presence of arginine, but not in the presence of citrulline or ornithine. From this, you can conclude that the product of the mutant gene is most directly involved in the production of ____.
| a. | arginine from ornithine |
| b. | arginine from citrulline |
| c. | citrulline from ornithine |
| d. | ornithine from arginine |
| e. | citrulline from arginine |
b
The central dogma describes the flow of information of gene expression as ____.
| a. | DNA ® RNA ® protein |
| b. | RNA ® DNA |
| c. | RNA ® DNA ® protein |
| d. | protein ® DNA ® RNA |
| e. | DNA ® protein ® RNA |
a
The process of translation refers to the use of information encoded in ____ to make ____.
| a. | RNA; a complementary DNA copy |
| b. | DNA; a polypeptide |
| c. | DNA; a complementary RNA copy |
| d. | a polypeptide; RNA |
| e. | RNA; a polypeptide |
e
The process of translation refers to the use of information encoded in ____ to make ____.
| a. | RNA; a complementary DNA copy |
| b. | DNA; a polypeptide |
| c. | DNA; a complementary RNA copy |
| d. | a polypeptide; RNA |
| e. | RNA; a polypeptide |
e
Which bases are found in RNA?
| a. | adenine and uracil only |
| b. | adenine, thymine, and cytosine only |
| c. | adenine, uracil, and cytosine only |
| d. | adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine |
| e. | adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine |
d
Except for the stop codons, the codons in the genetic code specify which of the ____ amino acids will be added to a growing polypeptide chain.
| a. | 5 |
| b. | 64 |
| c. | 4 |
| d. | 20 |
| e. | 3 |
d
In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the start codon (or initiator codon) is ____, which codes for the amino acid ____.
| a. | UGA; proline |
| b. | UUU; phenylalanine |
| c. | AAA; lysine |
| d. | ACG; threonine |
| e. | AUG; methionine |
e
The genetic code is said to be degenerate because ____.
| a. | some codons that do not specify an amino acid |
| b. | most amino acids are represented by more than one codon |
| c. | the code varies considerably between different organisms |
| d. | the code is commaless, with no indicators of spaces between codons |
| e. | the code varies considerably between different cell types within a multicellular organism |
b
With minor exceptions, the genetic code ____.
| a. | is the same for all living organisms and viruses |
| b. | is specialized so that viruses use a different code than all living organisms |
| c. | differs between different organisms and viruses |
| d. | is the same for all viruses and for single-celled organisms, but is more complex in multicellular organisms |
| e. | has three versions: one for viruses, one for single-celled organisms, and one for multicellular organisms |
a
During transcription, ____.
| a. | double-stranded RNA chains are produced |
| b. | the entire DNA molecule is copied to RNA |
| c. | primase creates an RNA primer to start the RNA strand |
| d. | only one of the two DNA strands acts as a template |
| e. | protein is made from RNA |
d
The ____ , located ____ of the transcription start point, is the site at which RNA polymerase associates with DNA to begin transcription.
| a. | promoter; upstream |
| b. | initiator; downstream |
| c. | initiator; upstream |
| d. | promoter; downstream |
| e. | intron; downstream |
a
The TATA box is a key element of the ____ of most eukaryotic protein-coding genes.
| a. | terminator |
| b. | coding region |
| c. | promoter |
| d. | transcription start point |
| e. | introns |
c
Proteins called transcription factors are involved in ____ of transcription.
| a. | both initiation and termination stages |
| b. | both initiation and elongation stages |
| c. | the termination stage |
| d. | the initiation stage |
| e. | the initiation, elongation, and termination stages |
d
During the elongation stage of transcription ____.
| a. | DNA nucleotides are added to the transcript |
| b. | the transcript grows in the 5'®3' direction |
| c. | transcription factors recruit RNA polymerase to the template strand |
| d. | the double helix remains single-stranded after being used as a template |
| e. | RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region |
b
Transcription is terminated in prokaryotes by ____.
| a. | generation of a stop codon |
| b. | transcription of an mRNA terminator sequence |
| c. | splicing introns out and pasting exons together |
| d. | generation of a guanine cap |
| e. | generation of a poly-A tail |
b
Protein-encoding genes in eukaryotes are transcribed by ____.
| a. | RNA polymerase I |
| b. | RNA polymerase II |
| c. | RNA polymerase III |
| d. | either RNA polymerase I or III |
| e. | either RNA polymerase II or III |
b
In an mRNA transcript, the 3' UTR refers to the region of the mRNA that is ____.
| a. | upstream from the start codon |
| b. | upstream from the site for initiation of transcription |
| c. | downstream from the stop codon |
| d. | the coding region |
| e. | downstream from the site for termination of transcription |
c
Pre-mRNA is found____.
| a. | only in prokaryotes |
| b. | in both the nucleus and cytoplasm of eukaryotes |
| c. | only in the cytoplasm of eukaryotes |
| d. | in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes |
| e. | only in the nucleus of eukaryotes |
e
Pre-mRNA is modified on its 5' end by ____.
| a. | exon shuffling |
| b. | the addition of a poly(A) tail |
| c. | mRNA splicing |
| d. | the addition of a guanine cap |
| e. | aminoacylation |
d
The cap on an mRNA transcript is the site where ____.
| a. | ribosomes attach at the start of translation |
| b. | the start codon is located |
| c. | translation is terminated |
| d. | the stop codon is covered until needed |
| e. | the mRNA is protected from attack by RNA-digesting enzymes. |
a
The poly(A) tail of an mRNA ____.
| a. | is where the start codon is located |
| b. | covers the stop codon until it is needed |
| c. | protects the mRNA from attack by RNA-digesting enzymes |
| d. | is where ribosomes attach at the start of translation |
| e. | is where translation terminates |
c
The regions retained in finished mRNA transcripts after pre-mRNA processing are called ____.
| a. | spliceosomes |
| b. | snRNPs |
| c. | exons |
| d. | domains |
| e. | introns |
c
The process of removing introns from mRNA and joining exons together occurs in a complex called the ____.
| a. | ribosome |
| b. | anticodon |
| c. | lariat |
| d. | polysome |
| e. | spliceosome |
e
Small ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs) are involved in ____.
| a. | mRNA splicing |
| b. | initiation of transcription |
| c. | aminoacylation of tRNA |
| d. | initiation of translation |
| e. | termination of translation |
a
In the process of mRNA splicing, the lariat structure is the ____.
| a. | splicing complex |
| b. | region where two exons are pasted together |
| c. | enzyme that cuts the pre-mRNA |
| d. | released intron |
| e. | region where two introns are pasted together |
d
The number of proteins humans can produce vastly exceeds the number of genes in the human genome. This is best explained by ____.
| a. | aminoacylation |
| b. | exon shuffling |
| c. | the wobble hypothesis |
| d. | degeneracy |
| e. | alternative splicing |
e
The pre-mRNA transcript of mammalian α-tropomyosin undergoes ____ to produce different mRNAs in smooth and striated muscles.
| a. | aminoacylation |
| b. | alternative splicing |
| c. | polyadenylation |
| d. | degeneracy |
| e. | exon shuffling |
b
In which process are existing protein regions or domains mixed in novel combinations to produce new proteins?
| a. | alternative splicing |
| b. | degeneracy |
| c. | exon shuffling |
| d. | the wobble hypothesis |
| e. | aminoacylation |
c
For most eukaryotic genes, translation begins in the____.
| a. | cytosol |
| b. | nucleolus |
| c. | nucleus |
| d. | mitochondria |
| e. | Golgi apparatus |
a
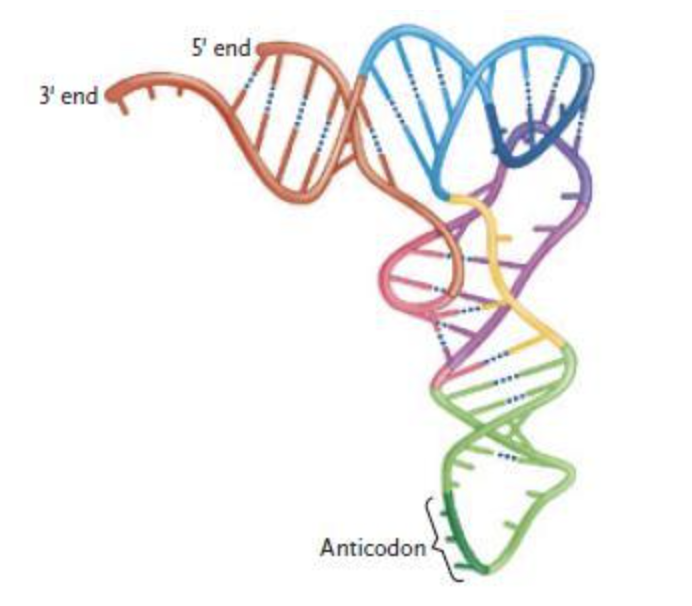
The structure in the figure above represents a molecule of ____.
| a. | pre-mRNA |
| b. | tRNA |
| c. | snRNA |
| d. | mRNA |
| e. | rRNA |
b
The region in a tRNA molecule that base-pairs with mRNA during translation is the ____.
| a. | anticodon |
| b. | aminoacylation site |
| c. | TATA box |
| d. | cloverleaf |
| e. | reading frame |
a
The complete set of 61 sense codons can be read by fewer than 61 distinct tRNA molecules according to ____.
| a. | alternative splicing |
| b. | degeneracy |
| c. | exon shuffling |
| d. | the wobble hypothesis |
| e. | aminoacylation |
d
The process of linking the correct amino acid to a tRNA molecule is catalyzed by ____.
| a. | the tRNA itself |
| b. | RNA polymerase |
| c. | an mRNA |
| d. | the ribosome |
| e. | an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase |
e
A ribosome consists of ____.
| a. | two small subunits |
| b. | two large subunits |
| c. | three subunits of different size |
| d. | rRNA and ribosomal proteins |
| e. | tRNA and ribosomal proteins |
d
The formation of peptide bonds during translation is catalyzed by ____ found in the ____.
| a. | RNA polymerase; large ribosomal subunit |
| b. | peptidyl transferase; small ribosomal subunit |
| c. | peptidyl transferase; large ribosomal subunit |
| d. | aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; small ribosomal subunit |
| e. | aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; tRNA |
c
The antibiotics streptomycin and erythromycin work by inhibiting the function of ____ in bacteria but not eukaryotes.
| a. | RNA polymerases |
| b. | aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases |
| c. | spliceosomes |
| d. | DNA polymerases |
| e. | ribosomes |
e
At the start of translation, the initiator tRNA pairs with the start codon at the ____ of the ribosome.
| a. | A (aminoacyl) site |
| b. | promoter |
| c. | P (peptidyl) site |
| d. | ribosomal binding site |
| e. | E (exit) site |
c
Which region(s) of the ribosome accept(s) charged tRNA molecules during the elongation phase of translation?
| a. | the A site |
| b. | the A site or the E site |
| c. | the P site |
| d. | the P site or the E site |
| e. | the E site |
a
Energy for the three stages of translation is directly provided by ____.
| a. | sugars |
| b. | ATP |
| c. | GTP |
| d. | dNTP |
| e. | fats |
c
Initiation factors are ____ that assist in the initiation of transcription.
| a. | mRNAs |
| b. | proteins |
| c. | tRNAs |
| d. | amino acids |
| e. | snRNPs |
b
The ribosome binding site in an mRNA transcript is located ____ and is where ____.
| a. | at the start codon; the large ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA-tRNA complex in prokaryotes |
| b. | just upstream of the start codon; the large ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA in eukaryotes |
| c. | at the start codon; the small ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA-tRNA complex in eukaryotes |
| d. | on aminoacyl-tRNA; the large ribosomal subunit binds to tRNA in prokaryotes |
| e. | just upstream of the start codon; the small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA in prokaryotes |
e
The reading frame for translation is established by ____.
| a. | removal of the cap from mRNA |
| b. | pairing of initiator tRNA with the start codon |
| c. | the first base in the mRNA molecule |
| d. | the ribosome binding site |
| e. | the poly(A) tail |
b
During translation, mRNA is read in the ____ direction and the polypeptide is assembled from the ____.
| a. | 5¢®3¢; N-terminal end to the C-terminal end |
| b. | 5¢®3¢; C-terminal end to the N-terminal end |
| c. | 3¢®5¢; N-terminal end to the C-terminal end |
| d. | 3¢®5¢; C-terminal end to the N-terminal end |
| e. | 5¢®5¢; N-terminal end to the C-terminal end |
a
Relative to the mRNA, which of the following moves during translocation?
| a. | attached tRNAs and the ribosome |
| b. | attached tRNAs and the polypeptide chain |
| c. | the ribosome only |
| d. | the ribosome and the polypeptide chain |
| e. | the polypeptide chain only |
c
During translation, tRNAs bind to mRNA through ____.
| a. | ionic bonds |
| b. | van der Waals forces |
| c. | nonpolar covalent bonds |
| d. | hydrogen bonds |
| e. | polar covalent bonds |
d
Translation ends when a stop codon in the ____ site allows a ____ to bind there.
| a. | P; release factor |
| b. | A; terminator tRNA |
| c. | E; terminator tRNA |
| d. | A; release factor |
| e. | P; terminator tRNA |
d
A polysome is ____.
| a. | the combination of a large and a small ribosomal subunit |
| b. | the complex where mRNA splicing occurs |
| c. | the promoter assembly at the site of transcription initiation |
| d. | an mRNA transcript to which multiple ribosomes are attached |
| e. | the complex that adds a poly(A) tail onto an mRNA |
d
Helper proteins that assist in protein folding are called ____.
| a. | snRNPs |
| b. | chaperones |
| c. | ribosomes |
| d. | spliceosomes |
| e. | polysomes |
b
The first part of a new polypeptide chain being produced in a eukaryotic cell has a signal peptide. Translation of this polypeptide ____.
| a. | occurs on a free ribosome in the cytosol |
| b. | begins on a free ribosome in the cytosol and is completed on the rough ER |
| c. | occurs in the Golgi apparatus |
| d. | begins on the rough ER and is completed in the Golgi apparatus |
| e. | occurs on the rough ER |
b
Proteins that function in the cytosol are synthesized ____.
| a. | on free ribosomes in the cytosol |
| b. | on the rough ER before being transported to the cytosol |
| c. | in the Golgi apparatus |
| d. | on the rough ER before being transported to the Golgi apparatus |
| e. | in the nucleus before being transported to the cytosol |
a
If a codon in the mRNA is 5’-ACG-3’, then the anticodon of the proper tRNA will be ____.
| a. | 5’-UGC-3’ |
| b. | 5’-CGU-3’ |
| c. | 5’-CGT-3’ |
| d. | 5’-TGC-3’ |
| e. | 5’-GCA-3’ |
b
The routing of proteins to their final destinations in eukaryotic cells is ____.
| a. | essentially random |
| b. | based on transcription factors |
| c. | controlled by the type of ribosome used |
| d. | directed by signals that are part of the proteins |
| e. | primarily determined by mRNA splicing |
d
Substitution of one base pair for another in the coding region of a gene can result in a ____ mutation where the changed codon still specifies the same amino acid.
| a. | missense |
| b. | chromosomal |
| c. | frameshift |
| d. | silent |
| e. | nonsense |
d
Substitution of one base pair for another in a coding region of a gene can result in a ____ mutation where the changed codon specifies a different amino acid.
| a. | missense |
| b. | chromosomal |
| c. | frameshift |
| d. | silent |
| e. | nonsense |
a
Substitution of one base pair for another in a coding region of a gene can result in a ____ mutation where a codon specifying an amino acid is changed to a stop codon.
| a. | missense |
| b. | chromosomal |
| c. | frameshift |
| d. | silent |
| e. | nonsense |
e
Insertion of two bases into the coding region of a gene just after the start codon of a gene will result in a ____ mutation.
| a. | missense |
| b. | chromosomal |
| c. | frameshift |
| d. | silent |
| e. | nonsense |
c
Mutagenesis ____.
| a. | is an example of spontaneous mutation |
| b. | acts directly on proteins by causing them to unfold |
| c. | occurs due to a single mRNA being translated by too many ribosomes simultaneously |
| d. | is the production of mutations in a laboratory by exposure of a living organism to a mutagen |
| e. | occurs when errors made by DNA polymerase are not repaired |
d
Segments of DNA that can move from one place to another within a cell’s genome are called ____.
| a. | target sites |
| b. | transposases |
| c. | transposable elements |
| d. | replicative factors |
| e. | release factors |
c
DNA transposons move using a(n) ____ intermediate while retrotransposons move using a(n) ____ intermediate.
| a. | RNA; DNA |
| b. | DNA; protein |
| c. | DNA; snRNP |
| d. | DNA; RNA |
| e. | RNA; protein |
d
The two major types of bacterial transposable elements are ____.
| a. | DNA transposons and transposases |
| b. | DNA transposons and retrotransposons |
| c. | insertion sequences and retrotransposons |
| d. | transposons and transposases |
| e. | insertion sequences and transposons |
e
Noller’s research with ribosomes showed that the site of peptide bond formation is located on ____.
| a. | the tRNA molecules |
| b. | ribosomal DNA |
| c. | proteins of the small ribosomal subunit |
| d. | ribosomal RNA |
| e. | proteins of the large ribosomal subunit |
d
A gene being transcribed uses transcription factors to recruit RNA polymerase II to the DNA at the promoter region. After the polymerase is recruited, transcription elongation occurs, and nucleotides are added to the transcript in the 5¢®3¢ direction. How do you know that the gene being transcribed is not a prokaryotic gene?
| a. | In prokaryotes, the promoter comes after the transcription unit. |
| b. | Prokaryotes do not have promoters. |
| c. | In prokaryotes, nucleotides are added to the transcript in the 3¢®5¢ direction. |
| d. | Prokaryotes use ribosomes rather than RNA polymerase to transcribe genes. |
| e. | Prokaryotes do not use transcription factors to recruit RNA polymerase to the DNA. |
e
See the provided genetic code table. A change in a single base pair could cause which missense mutation?
| a. | glutamic acid to threonine |
| b. | glycine to proline |
| c. | threonine to glutamine |
| d. | glutamic acid to methionine |
| e. | valine to methionine |
e
Which process occurs in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell?
| a. | translation |
| b. | DNA replication and transcription |
| c. | transcription |
| d. | DNA replication |
| e. | translation and transcription |
a