Lecture 19 - Management of Patient and Personnel Dose in Diagnostic X-Rays and Radiation Therapy
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 243 - Radiation Safety
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What can poor communication with the patient cause
repeat exposures, improper treatment and increased patient uneasiness
ways to reduce patient exposure to radiation
use proper immobilization, adequate filtration, shielding, motion reduction, etc
consequences of blurred x-ray images
examination needs to be repated, causing additional exposure
or improper dose delivery with radiation therapy
how to reduce patient motion
motion reduction techniques or immobilization
two types of patient motion
voluntary motion
involuntary motion
why is protective shielding needed
to minimize radiation exposure to patients and healthcare personnel.
what areas of the body should be shielded
lens of eye
breasts
reproductive organs
thyroid gland
female reproductive organs receive about _____ exposure after pelvic irradiation than men
3x more
if an x-ray machine doesnt have automatic exposure control, what should it have?
a standardized technique chart
____ kVp and ____ exposure time reduces patient dose
higher kVp, lower mAs
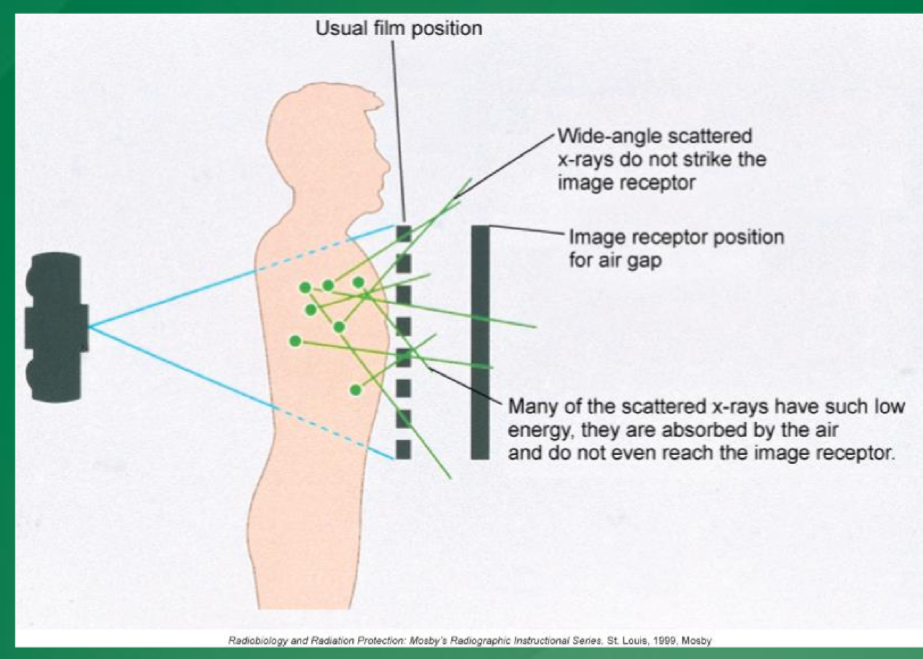
What is the air gap technique
A method to reduce patient dose in radiography by increasing the distance between the patient and the image receptor, which minimizes scatter radiation.
Consequences of repeat images
include increased patient exposure to radiation and potential delays in diagnosis.
double dose
3 examples of uneccessary radiologic proceures
CXR for admission to hospital
CXR for preemployment physical
CXR for routine health checkup
what type of dosimeters are used to directly measure skin dose
thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLDs)
why is ESE (entrance skin exposure) the most reported dose
simplest to determine
if a patient is pregnant but needs an x-ray, what do you do
Assess risks and benefits, consult a physician, and use shielding when possible.
consult the RSO
most medical procedures result in fetal doses less than
0.01 Gy
what should you do if patient who is unknowingly pregnant is irradiated
Monitor fetal exposure and evaluate potential risks; consult with a specialist for further guidance.
figure out as much of the informtion on the x-ray exam as possivle
contact RSO
determine EqD
how often should women 50-69 be screened with mammos
every 2-3 years to detect breast cancer early.
what CT scan gives the highest dose
multi slice spiral CT scanners with small slice thicknesses
is there more or less scattered radiation in CT
less
due to tight beam collimation
what is the risk of cancer from a dose from a CT scanner
The risk of cancer from a dose from a CT scanner varies but is generally considered low. It is estimated that the lifetime risk of developing cancer increases by about 0.1% for each CT scan.

who is more radiosensitive, adults or children
Children are more radiosensitive than adults due to their rapidly dividing cells and greater susceptibility to radiation effects.
CT scans early in life increase cancer incidence in adults
are men or women more radiosensitive
Women are generally more radiosensitive than men due to biological differences in tissue composition and hormone levels.
what is the image gently campaign

three categories of radiation in an x-ray room
primary
scatter
leakage
scatter and leakage radiation are known together as
secondary radiation
imaging procedures that have increased risk of exposure to radiographers

EfD does not include
personal medical exposure and natural background exposure
annual occupational EfD
50 mSv
three basic principles of ALARA
time
distance
shielding
what is the major source of scattered radiation to the radiographer
the patient
via compton interactions
where should a radiographer stand if he needs to be in the x-ray
90 degrees from primary x-ray beam

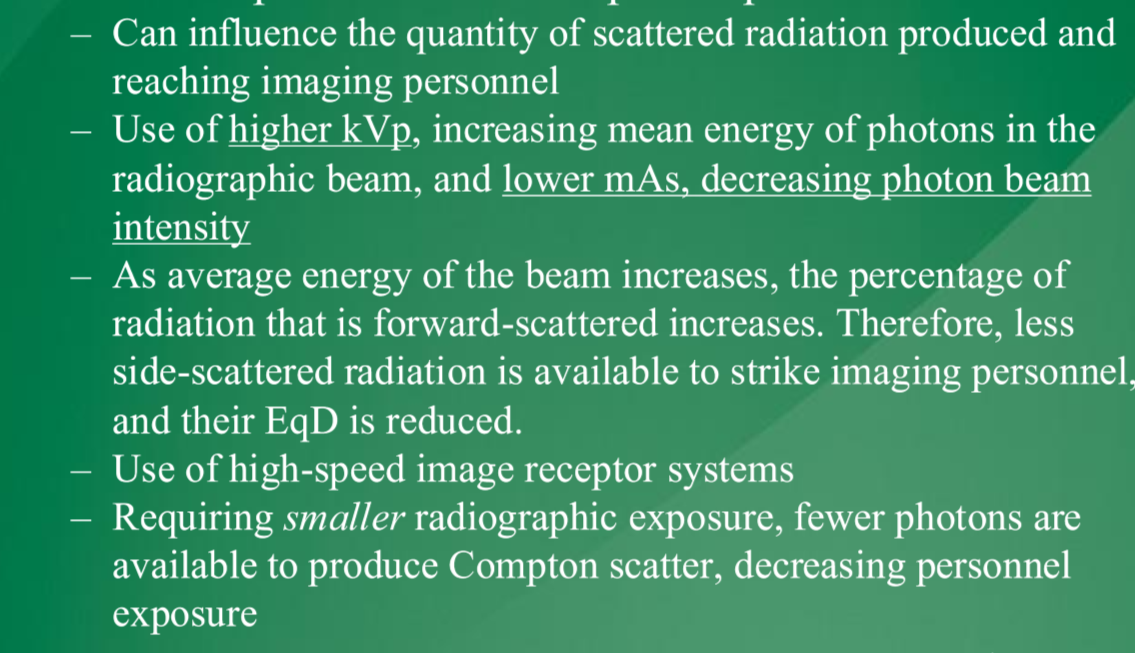
technical parameters that impact exposure
Effectiveness of shielding material depends on what 3 things
atomic number
density
thickness
purpose of primary protective barriers
prevent direct unscattered radiation from reaching personnel
purpose of secondary protective barrier
protect against leakage and scatter radiation
ensure maxmimal protection for personnel
can have observation window made out of lead
what can lead-acrylic overhead barriers be used for
to provide open view during special procedures
0.5 mm lead equivalent protection
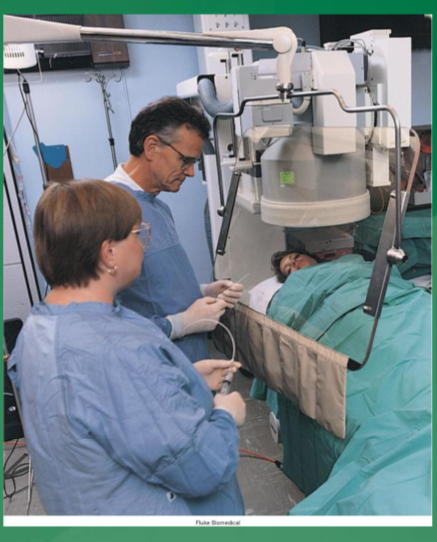

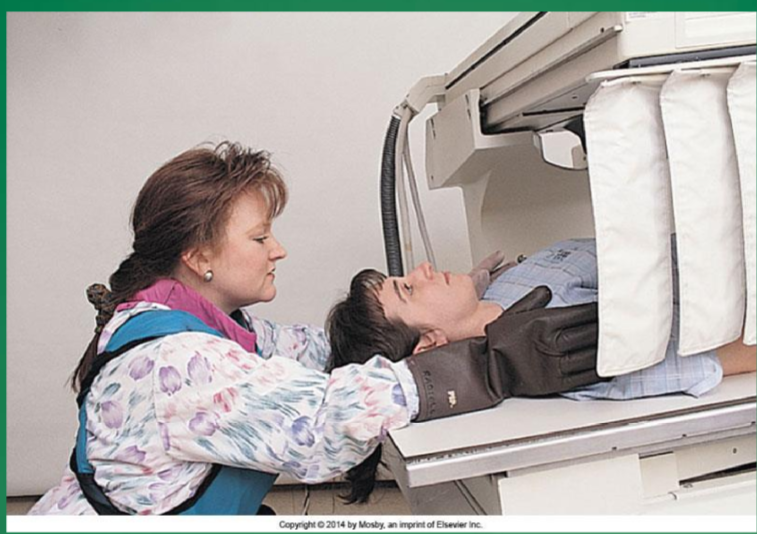
when are lead gloves used
if the patient needs to be restrained during imaging
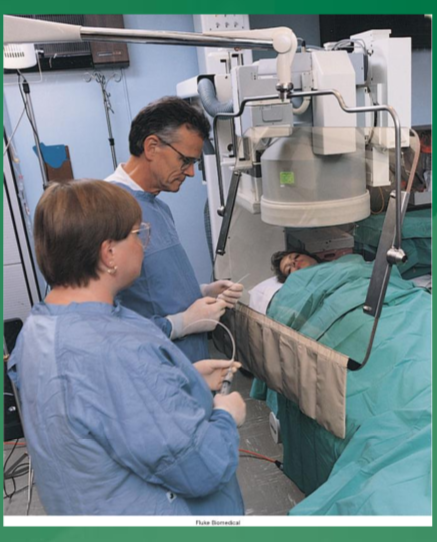

when are thyroid shields used
during fluoroscopy
protective eyeglasses
used to reduce scatter radiation to lens of eye
what is the protective tube housing on x-ray machines used for

what is a spot film device used for ?
minimize exposure to technologists during fluoroscopy
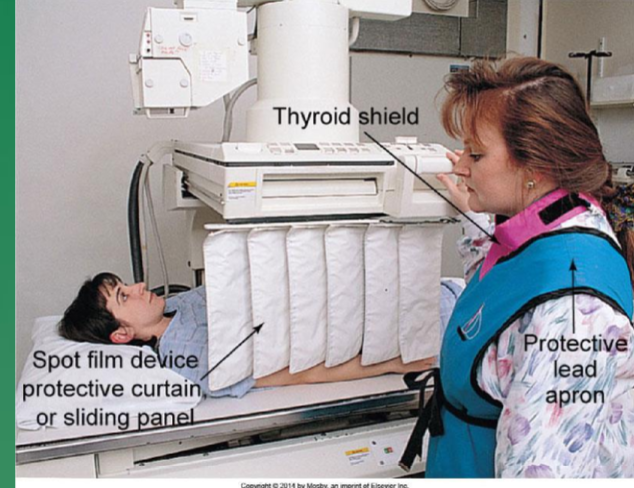
what is a bucky slot
protects radiographer at gonadal level
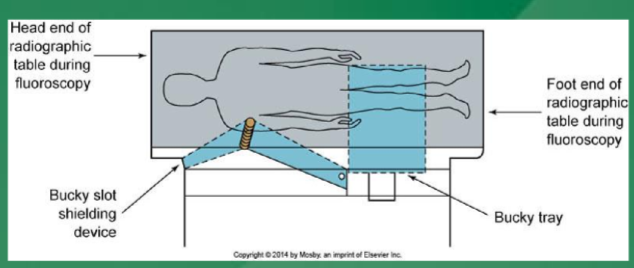
which imaging procedures result in technologist receiving highest dose

where is the safestly place to position C-arm fluoroscope
x-ray tube of arm under table and image intensifer over the table
ways to minimize exposure during c-arm fluoroscopy

ways to reduce dose in interventional procedures

where should the radiographer stand during the procedure
90 degrees from beam

are pregnant radiographers permitted to assist in holding patient during treatment
no, never
protocol for pregnant radiographers
see last 5 slides
essentially try to minimize dose as much as possible
how much lead must be in the doors to x-ray rooms
at least 0.8 mm