Lecture 21: Metabolic Diversity of Microorganisms in Brock Biology
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What are the foundational principles of metabolic diversity in microorganisms? (3 answers)
All microbes must conserve energy, need reducing power, and achieve redox balance.
How do microorganisms conserve energy?
By converting chemical or light energy into ATP through coupling electron flow to ATP synthesis.
What is the role of electron flow in microbial metabolism?
it consists of redox reactions for ATP synthesis through substrate-level, oxidative, or photophosphorylation.
What distinguishes respiration from fermentation?
Respiration requires an external electron acceptor and generates ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, while fermentation does not.
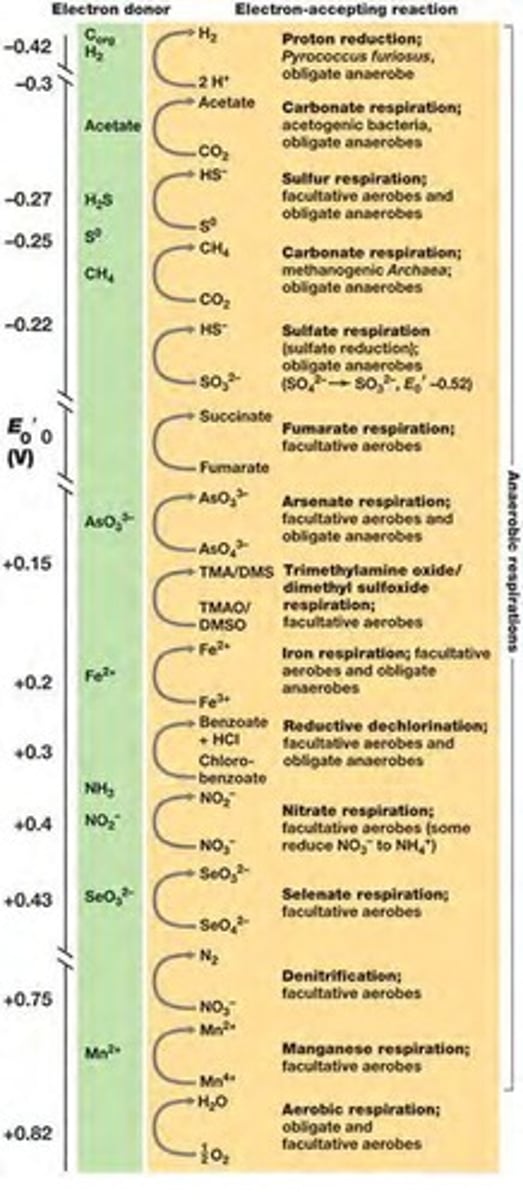
How is ATP generated during respiration?
by oxidative phosphorylation from electron transport, creating a proton motive force (pmf) which ATP synthase harnesses to produce ATP.
What are chemolithotrophs?
organisms that use inorganic electron donors for respiration.
Anaerobic respirations use:
electron acceptors other than O2
Why does anaerobic respiration yield less energy than aerobic respiration?
because the O2/H2O couple is the most electropositive, allowing aerobic organisms to conserve more energy.
What factors contribute to the prevalence of anoxic habitats?
Because O2 is rapidly consumed and poorly water-soluble.
What is the significance of redox balance in microbial metabolism?
regenerating oxidized electron carriers with an external electron acceptor.
How is diversity driven by modularity of metabolic reactions? (2 answers)
- Formation of new pathways from horizontal transfer
- Modification of enzymes and pathways
What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a method of generating ATP by transferring a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
the process of generating ATP using the energy from electron transport chains.
What is photophosphorylation?
the generation of ATP from light energy.
What is the importance of reducing power in microbial metabolism?
Cells need it for biosynthesis
_______ organisms typically outcompete ________ organisms because they conserve more energy.
Aerobic; anaerobic
What are assimilative processes?
reduce inorganic molecules into cells, consuming energy (ATP and reducing power) to acquire materials for biosynthesis.
What is the most important assimilative process?
CO2 fixation.
What are dissimilative processes?
Processes that conserve energy, where electron acceptors are reduced and excreted, and are part of anaerobic respiration.
What types of organisms can assimilate CO2 into cell material?
Autotrophs
What is the Calvin Cycle?
The most widespread pathway for CO2 fixation, used by all oxygenic phototrophs, most purple bacteria, and most aerobic chemolithotrophic bacteria.
What is the key enzyme in the Calvin Cycle?
RubisCO.
What effect does O2 have on CO2 in the Calvin Cycle?
O2 acts as a competitive inhibitor of CO2, causing photorespiration.
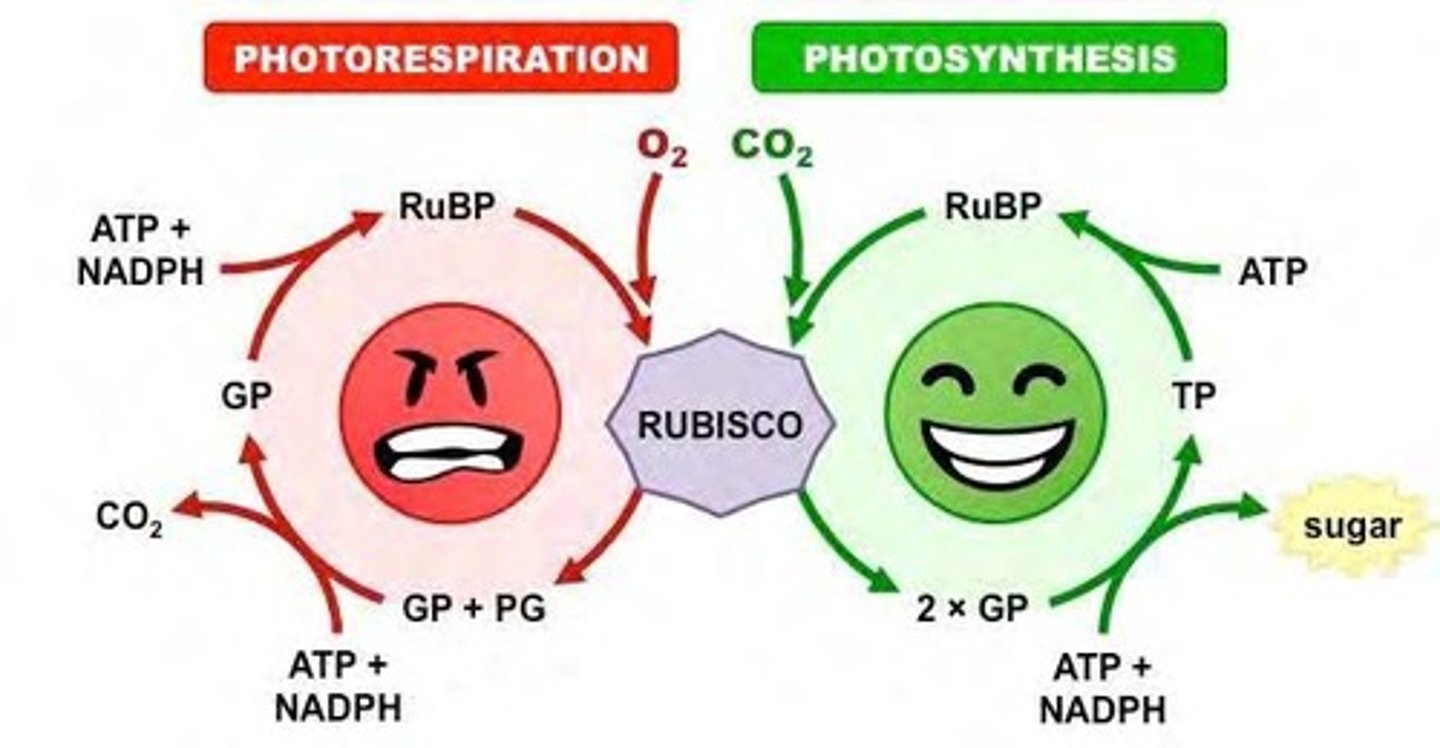
What are carboxysomes?
Proteinaceous microcompartments containing RubisCO (protect it from O2)
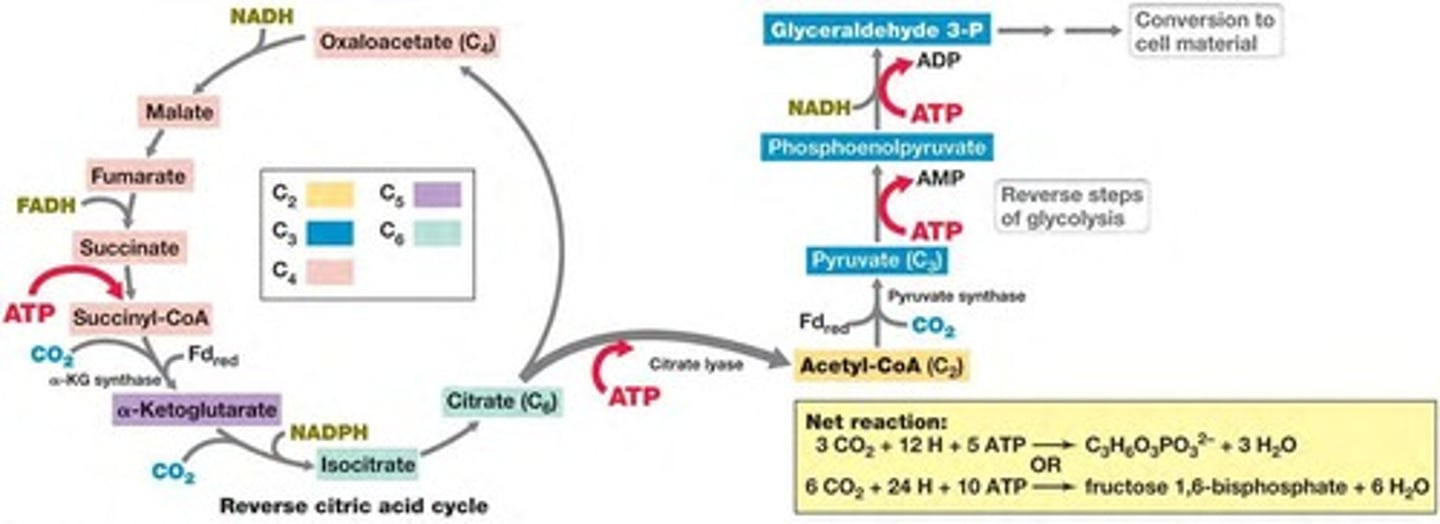
What is the Reverse Citric Acid Cycle?
Also called the reductive TCA cycle, reduces CO2 by reversing steps in the citric acid cycle.
- Used by green sulfur bacteria and many anaerobic or microaerophilic chemolithotrophic bacteria
What pathway do green nonsulfur bacteria use to fix CO2?
The 3-hydroxypropionate bi-cycle to fix CO2 into pyruvate.
What pathway do chemolithotrophic Archaea use?
3-hydroxypropionate and dicarboxylate (both 4-hydroxybutyrate cycle)
What is the most efficient CO2 fixation pathway and what is it used by?
Reductive acetyl-coenzyme A pathway; some obligate anaerobic bacteria and Archaea
What is the relationship between mixotrophs and their environment?
Can perform both heterotrophy and autotrophy depending on environmental conditions.
How do dissimilative processes differ from assimilative processes?
Dissimilative processes conserve energy, while assimilative processes consume energy to acquire materials.
What type of respiration are dissimilative reductions part of?
Anaerobic respiration.
Which organisms primarily utilize the Calvin Cycle?
Oxygenic phototrophs such as cyanobacteria, algae, and plants.
What is the primary function of RubisCO in the Calvin Cycle?
To catalyze the fixation of CO2.
What is the impact of photorespiration on photosynthesis?
It reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis by competing with the fixation of CO2.
What is the importance of diverse pathways in CO2 fixation?
To allow different organisms to adapt to various environmental conditions and utilize CO2 effectively.
What are the four pathways of CO2 fixation used by chemolithotrophic Archaea?
1. 3-hydroxypropionate/4-hydroxybutyrate cycle 2. dicarboxylate/4-hydroxybutyrate cycle 3. Bicarbonate and/or CO2 reduced to acetyl-CoA 4. Reductive acetyl-coenzyme A pathway.
In which organisms did photosynthesis originate?
Photosynthesis originated in Bacteria.
What is the electron donor in oxygenic photosynthesis?
Water is the electron donor in oxygenic photosynthesis, with oxygen as a waste product.
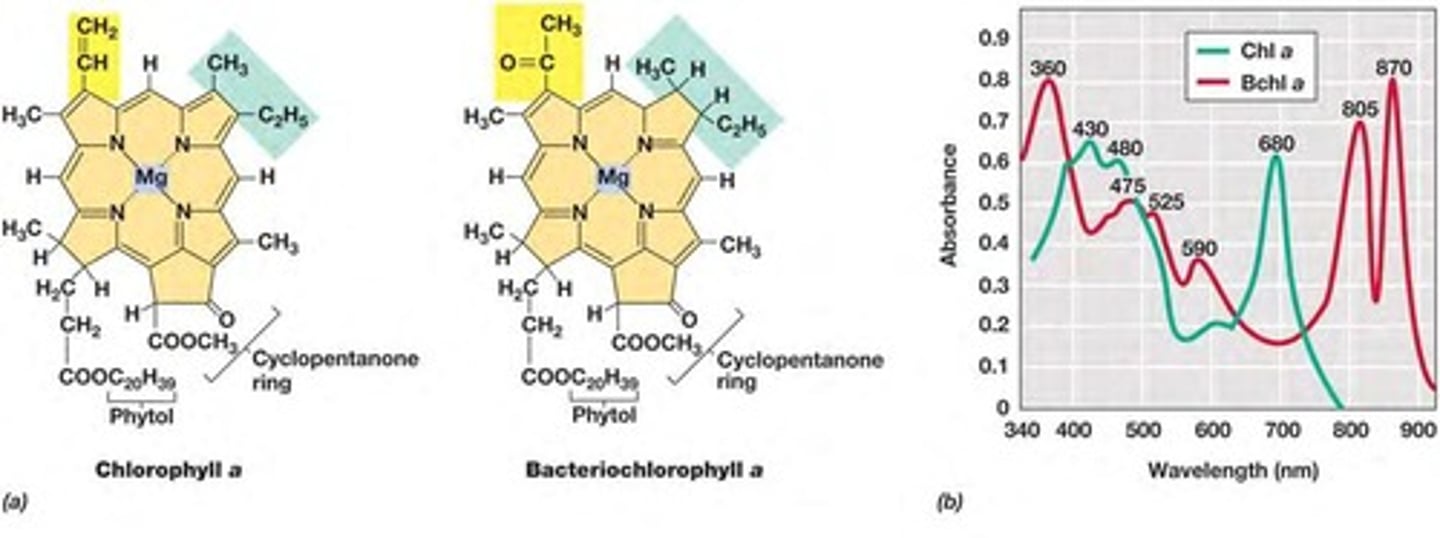
What types of organisms utilize bacteriochlorophylls?
anoxygenic phototrophs.
Why is chlorophyll a green in color?
Chlorophyll a transmits green light and absorbs red and blue light.
___________ _ is the principal chlorophyll of oxygenic photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll A
Several structurally different chlorophylls exist with a distinct __________ ________
Absorption spectrum
What is the ecological importance of pigment diversity in phototrophs?
Allows different phototrophs to absorb different wavelengths and coexisterm-52t in same habitat
What are the two main types of pigments involved in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll/bacteriochlorophyll
___________ contains magnesium at its center, while ___________________ is found in anoxygenic phototrophs.
Chlorophyll; bacteriochlorophyll
What is the significance of the reductive acetyl-CoA pathway in anaerobic organisms?
it's the most efficient CO2 fixation pathway for obligate anaerobic Bacteria and Archaea.
What is the purpose of photocomplexes?
They store chlorophyl/bacteriochlorophyll
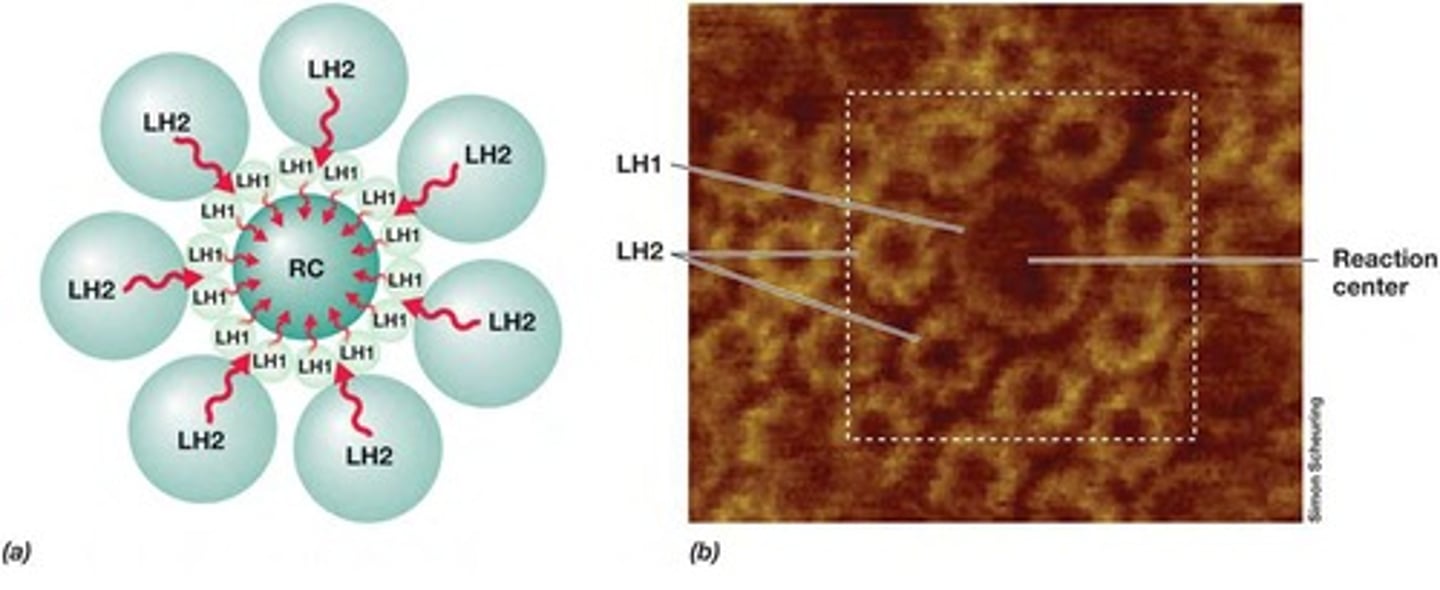
What are the antenna pigments and what do they do?
Large number of chlorophylls; they funnel light energy to reaction centers.
What are reaction centers in photosynthesis?
They contain pigments and participate directly in energy conservation.
How do prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes in terms of photosynthetic membranes?
Prokaryotes have pigments integrated into internal invaginations of the cytoplasmic membrane
Where are pigments integrated in purple bacteria?
Chromatophores and lamellae
Where are pigments integrated in cyanobacteria?
Thylakoids
What are chlorosomes and where are they found?
Structures that capture low light intensities; found in green sulfur bacteria, green nonsulfur bacteria, and phototrophic Acidobacteria (all anoxygenic)
What is the primary function of carotenoids in photosynthesis?
serve as photoprotective agents, quenching toxic oxygen species and preventing dangerous photooxidation.
What colors do carotenoids typically exhibit?
Yellow, red, brown, or green.
What are the three types of phycobiliproteins?
The three types of phycobiliproteins are phycoerythrin (red), phycocyanin (blue), and allophycocyanin.
What are phycobiliproteins and their role in photosynthesis?
main light-harvesting systems of cyanobacteria and red algae chloroplasts, consisting of bilins bound to proteins.
What do red phycoerythrin, blue phycocyanin, and allophycocyanin absorb?
Red phycoerythrin absorbs ~550nm and blue phycocyanin absorbs ~620nm, and allophycocyanin absorbs ~650nm.
What are phycobilisomes?
Aggregated phycobiliproteins
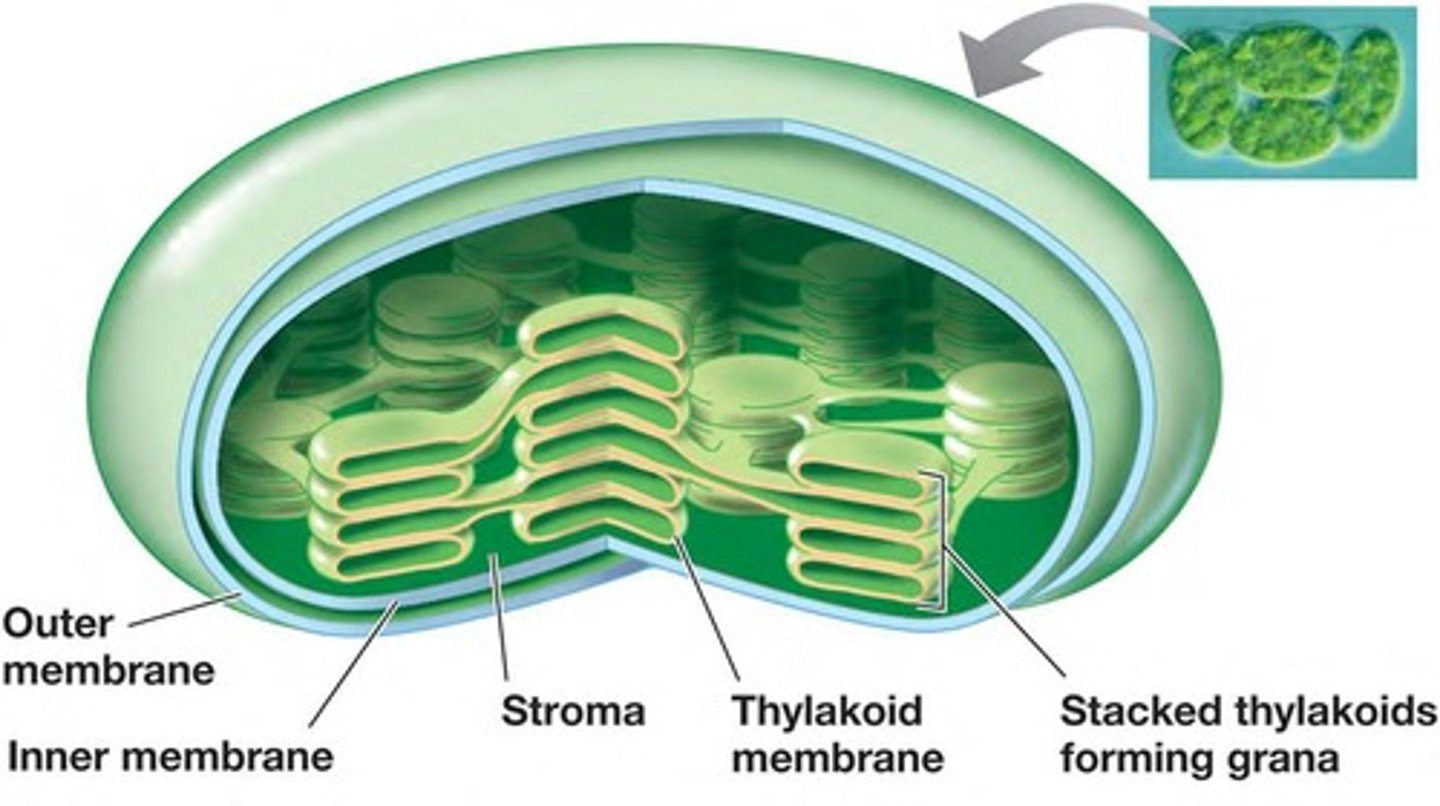
What is the function of thylakoids in chloroplasts?
Thylakoids are membrane systems where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur.
What type of bacteria use reduced sulfur compounds as electron donors?
Colorless sulfur bacteria
What is the final oxidation product of reduced sulfur compounds?
usually sulfate (SO4^2-).
What is one consequence of sulfur oxidation in the environment?
Acidifies the surroundings with the production of hydrogen ions (H+)
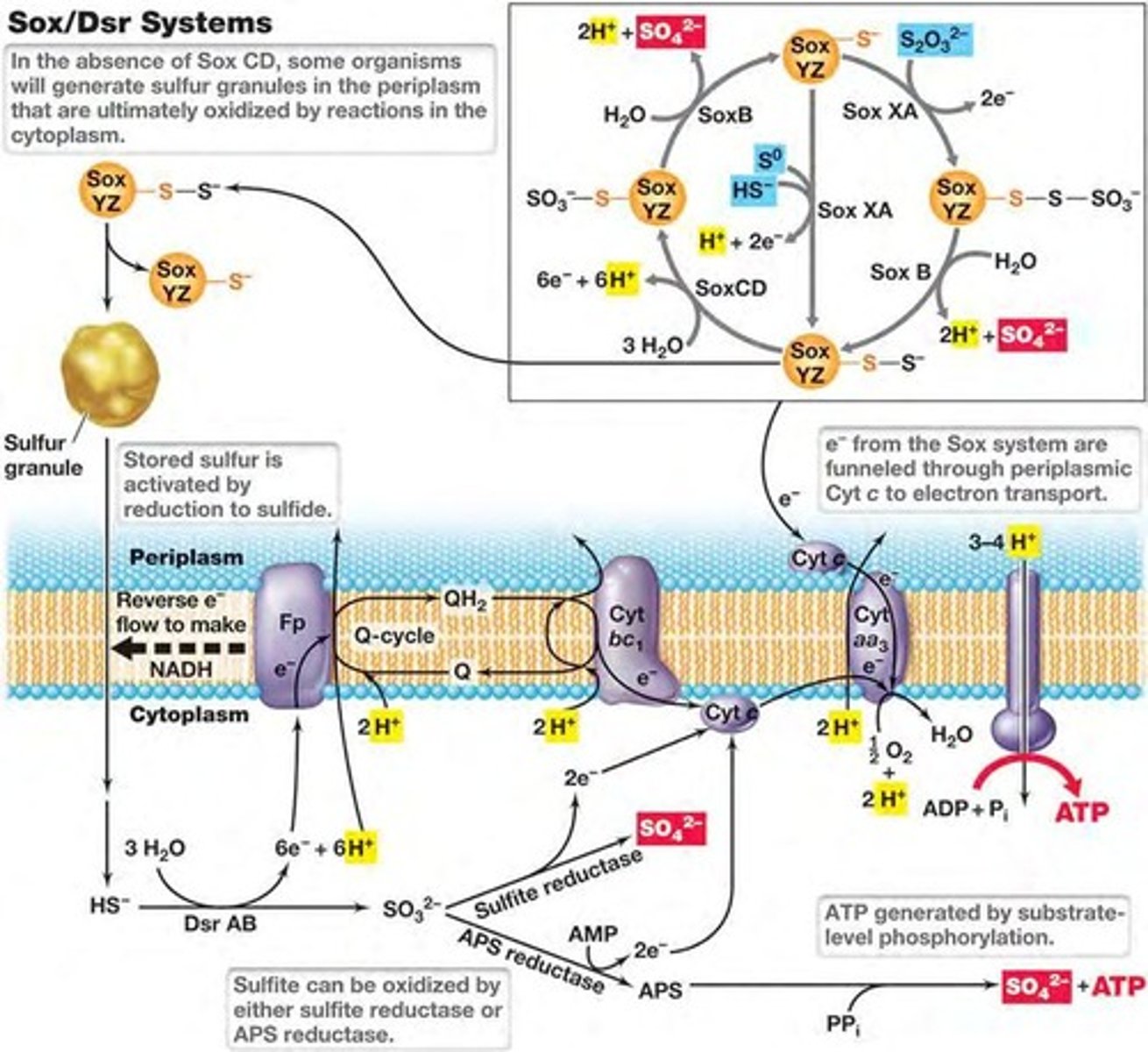
What is the Sox (sulfur oxidation) system in sulfur oxidation?
It oxidizes reduced sulfur compounds directly to sulfate (likely transferred by horizontal gene flow)
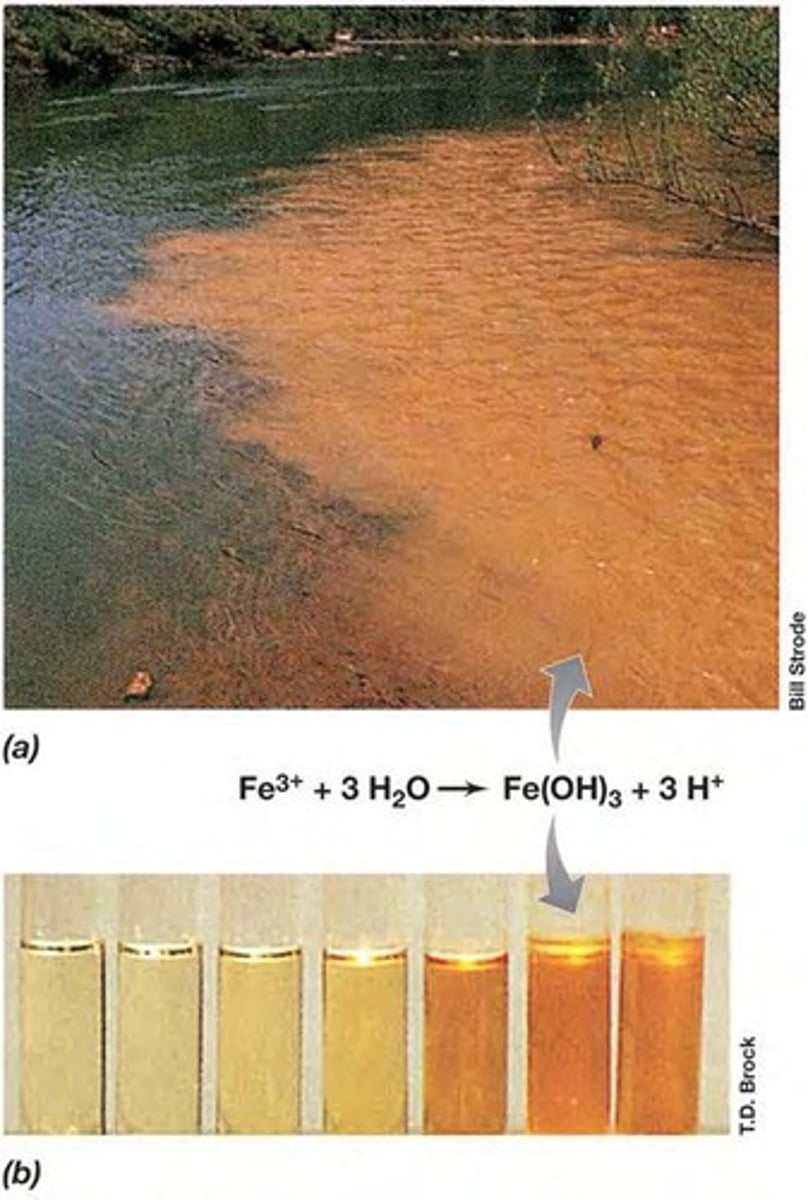
What happens to ferric hydroxide in water?
Ferric hydroxide precipitates in water, driving down the pH.
