Amino acids and Proteins
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
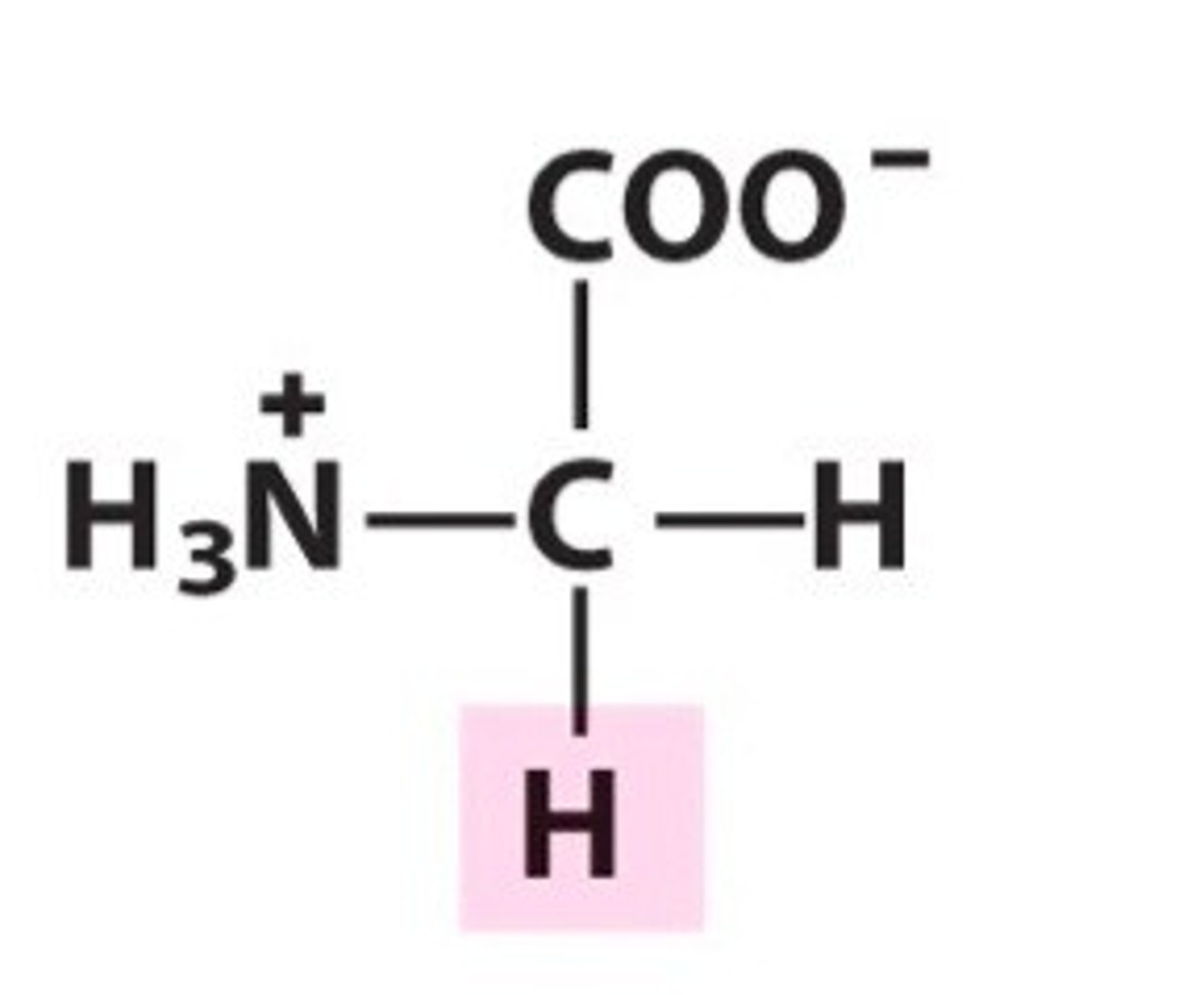
Glycine. Gly. Polar (up for debate)
Achiral and very small
Which amino acid may be found at tight turns in a protein due to its flexibility?
Glycine
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
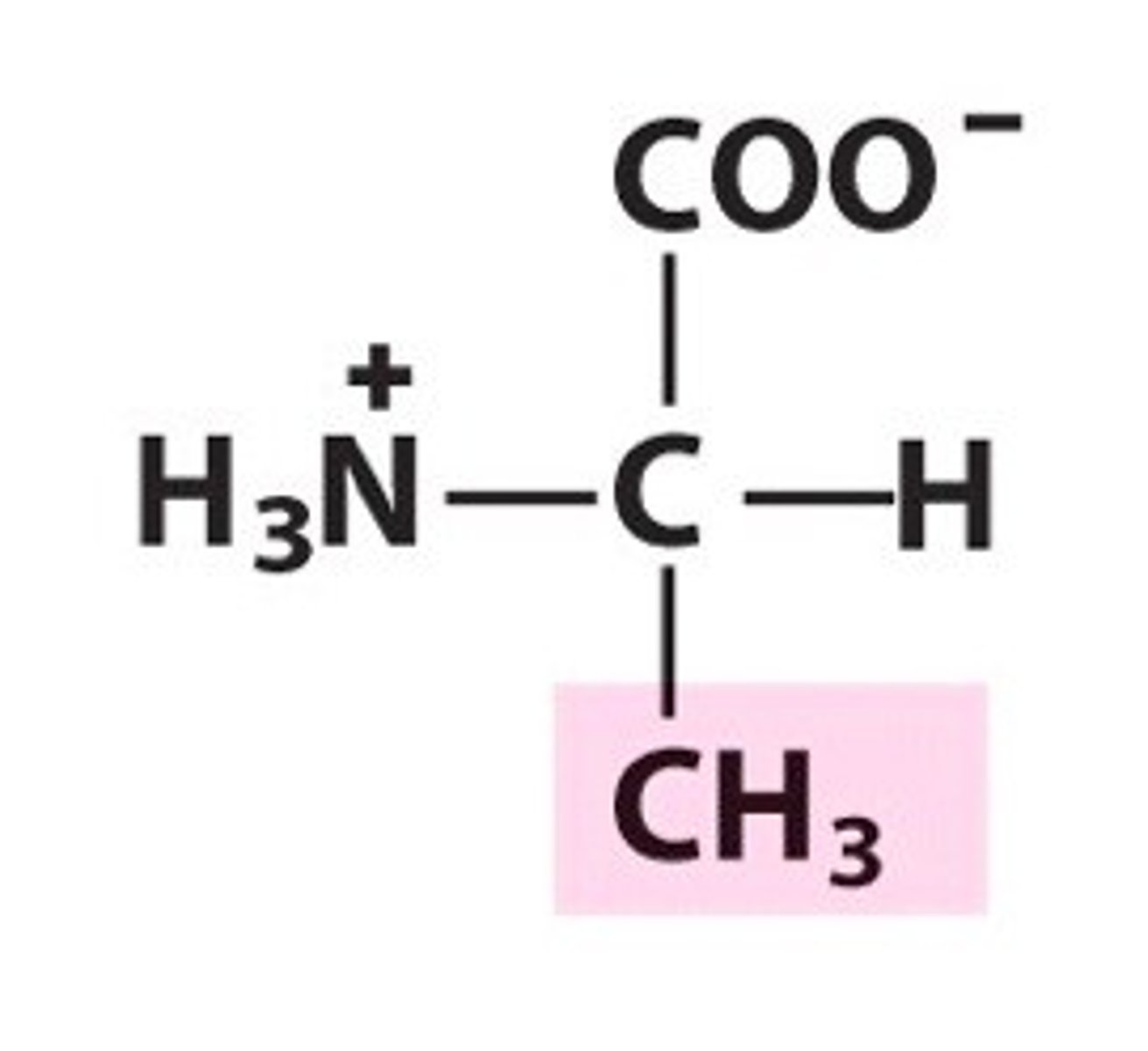
Alanine. Ala. Non-polar/hydrophobic
Would alanine or valine be more hydrophobic?
valine since it has a larger non-polar side chain
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
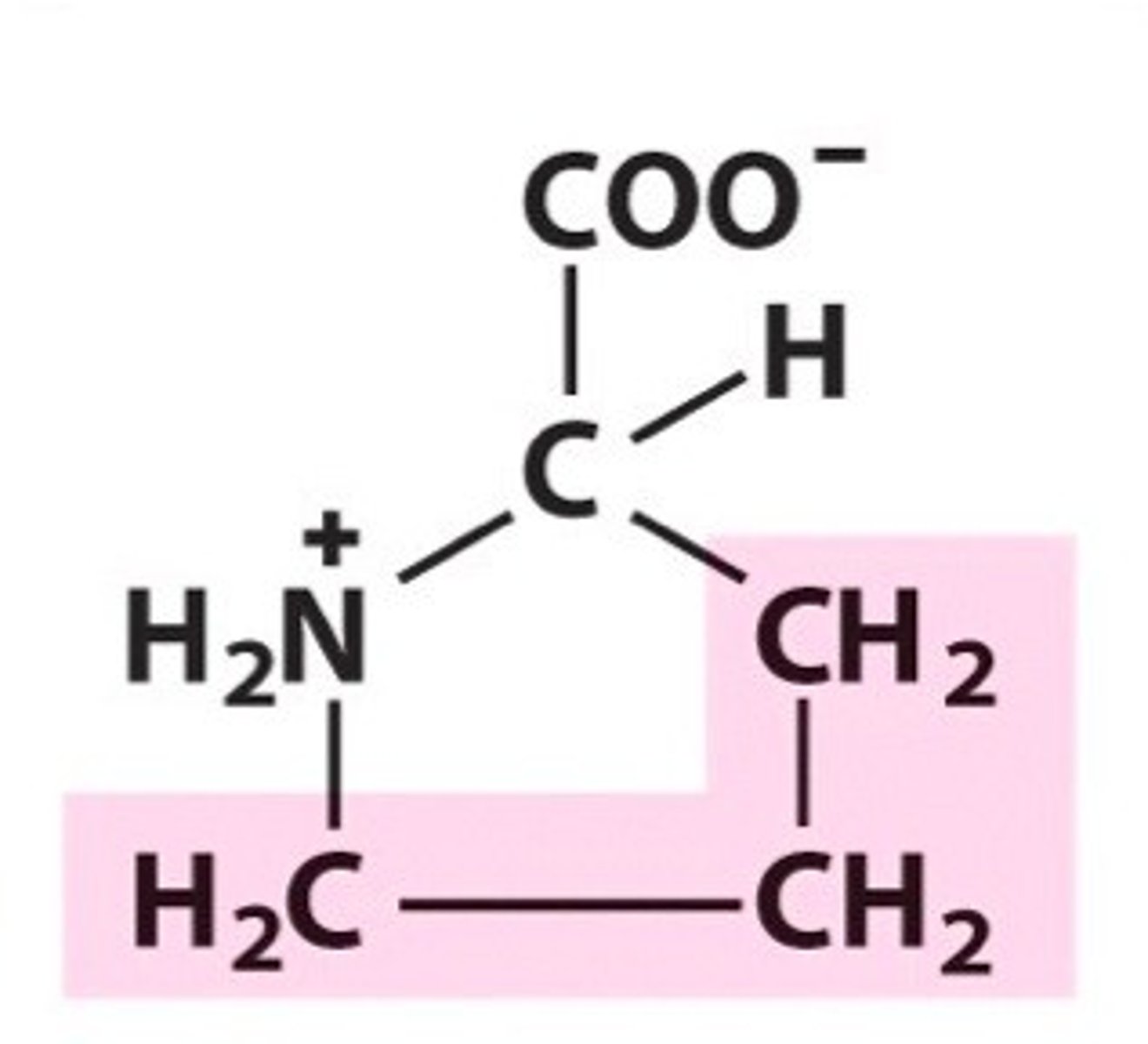
Proline. Pro. Non-polar/Hydrophobic.
Cyclic but not aromatic.
Is the amino group primary, secondary or tertiary in proline?
secondary
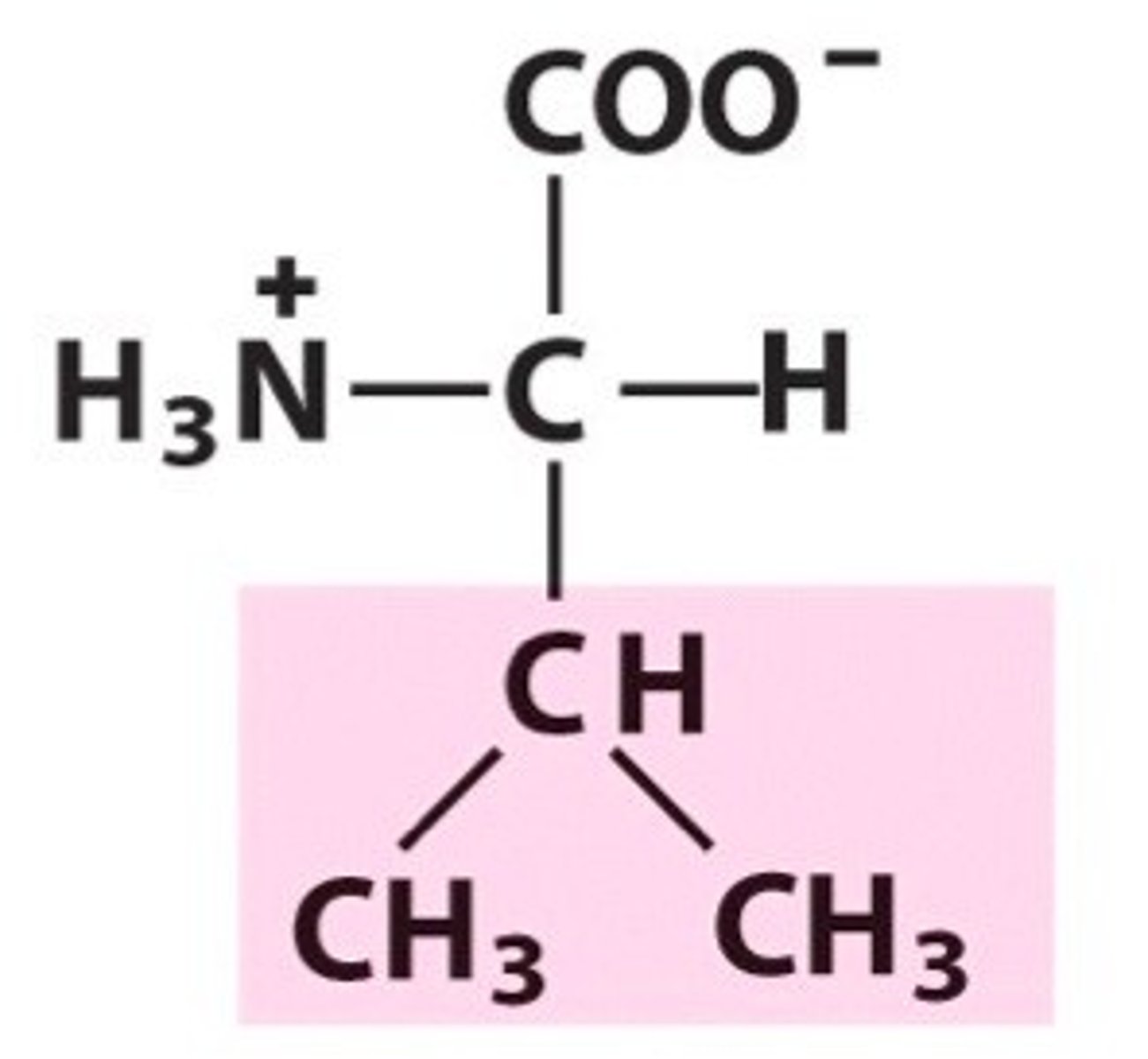
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
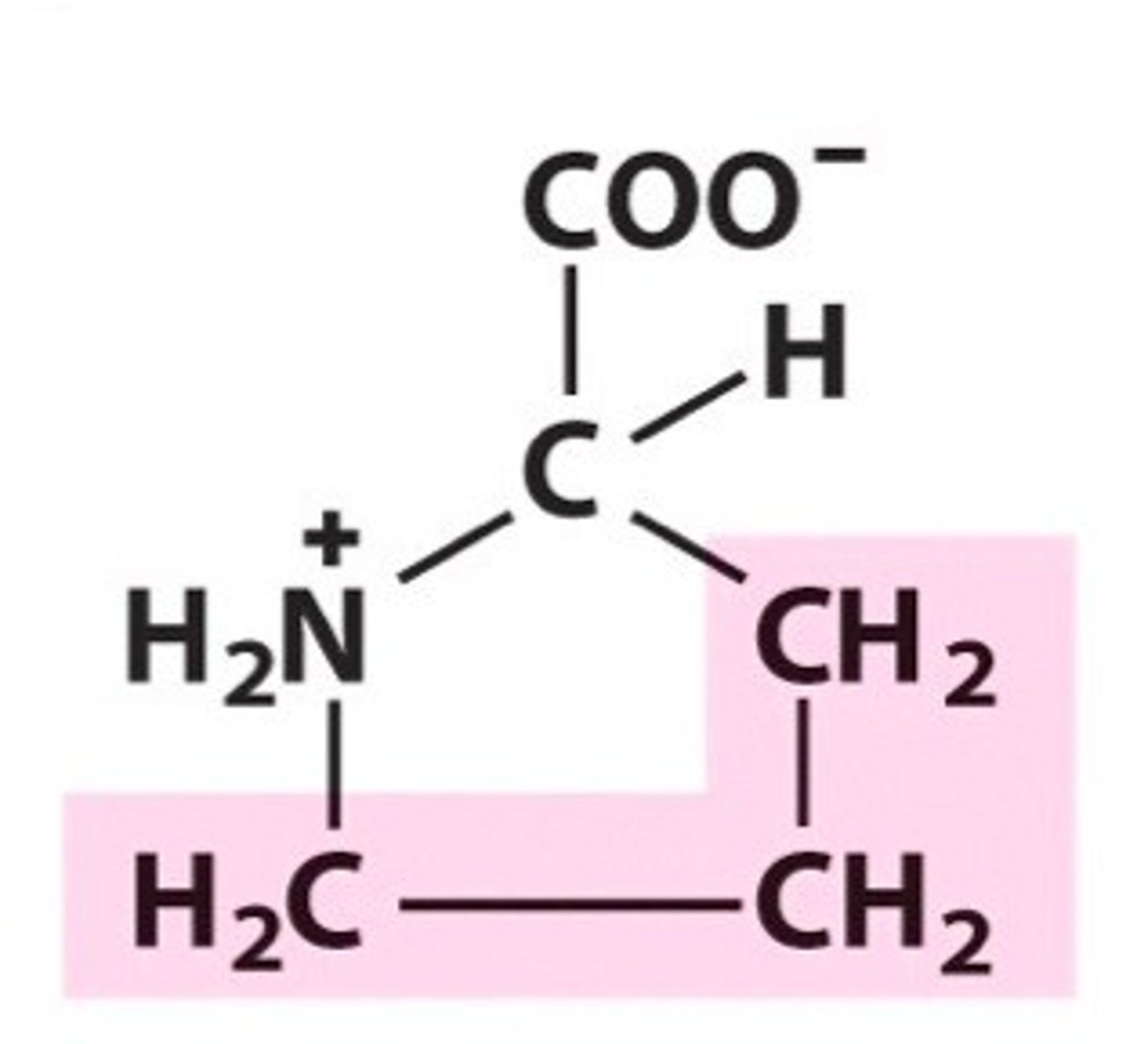
Valine. Val, Non-polar/hydrophobic
What are aliphatic amino side chains?
Aliphatic amino acids are non-polar and hydrophobic. contain only carbon and hydrogen.
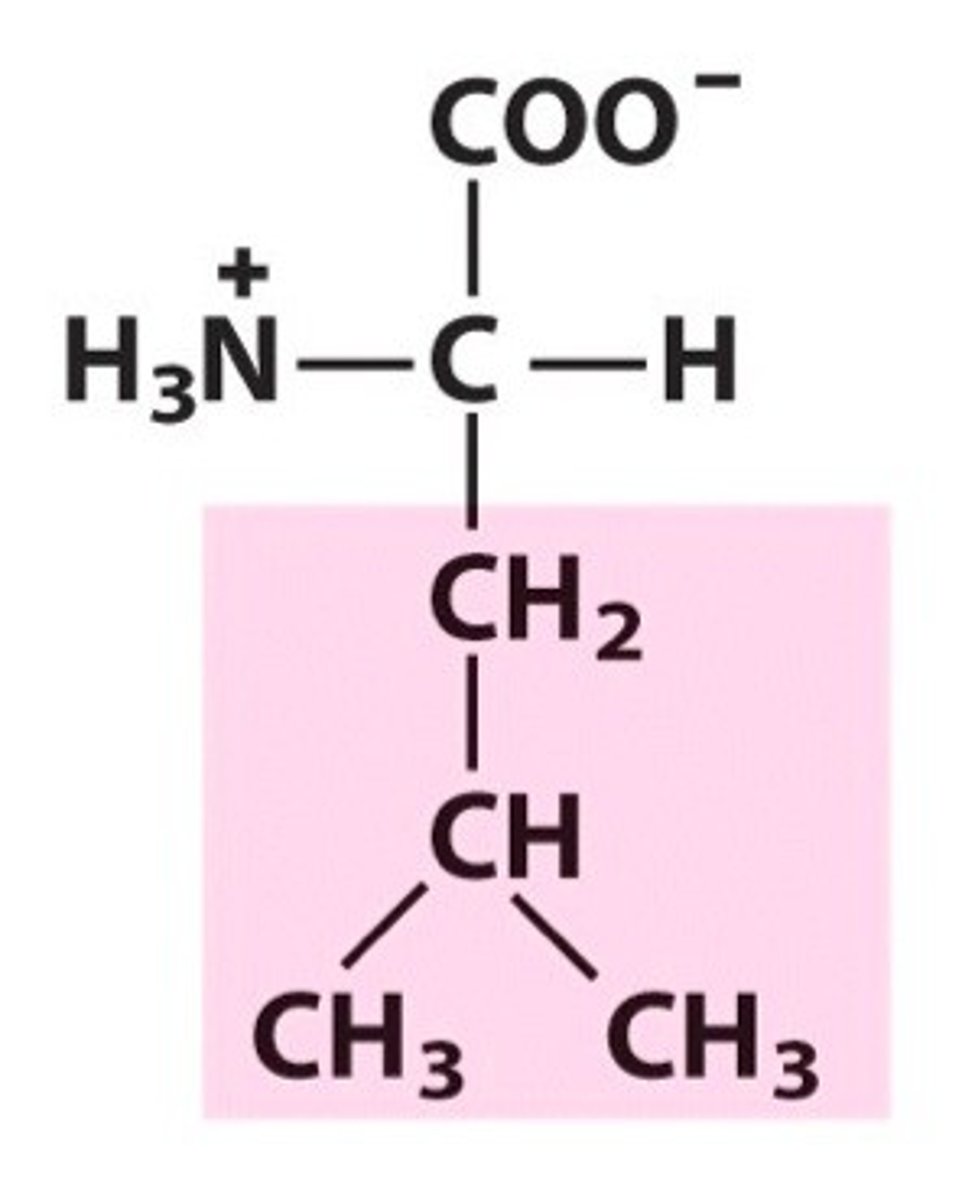
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Leucine. Leu. Hydrophobic/Non-polar
aliphatic
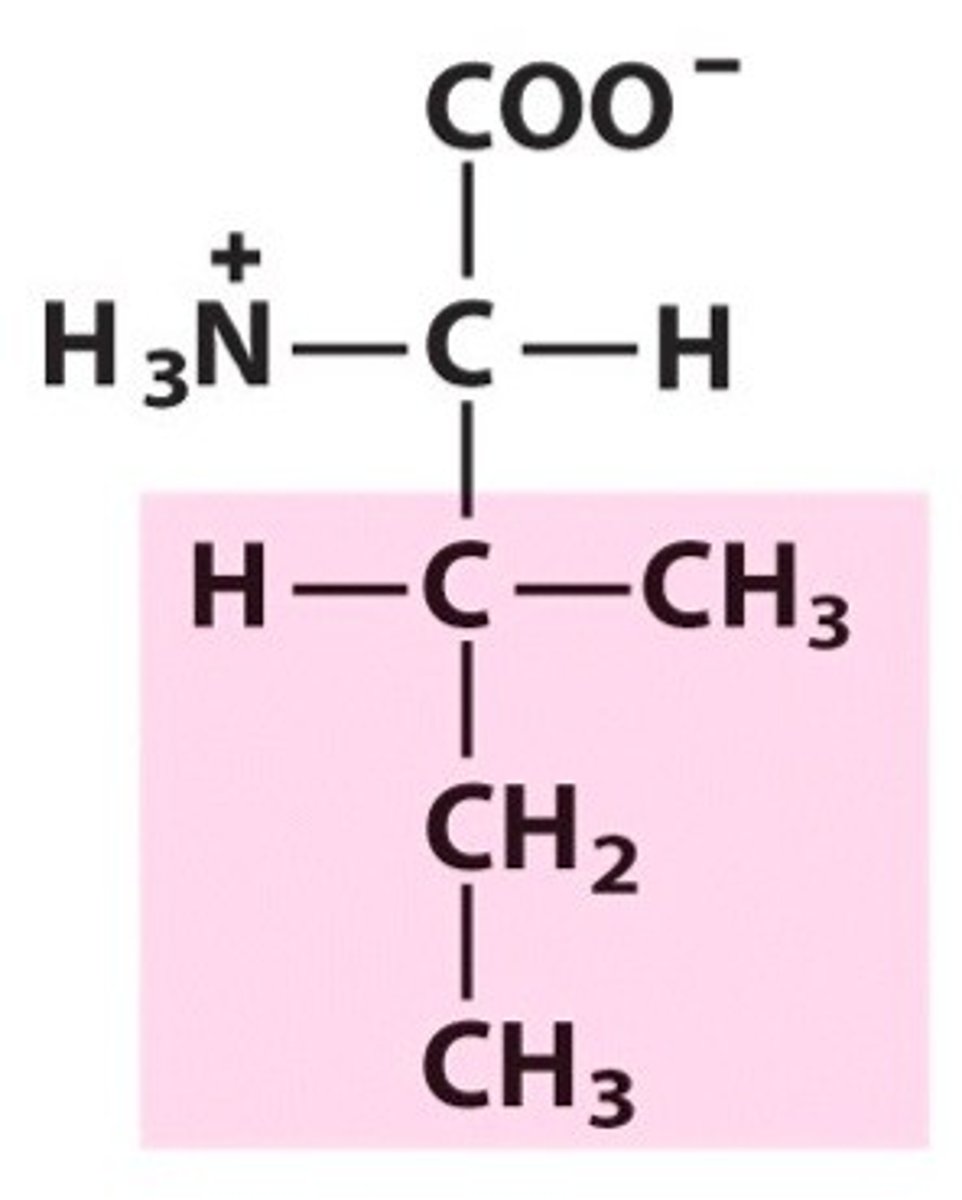
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Isoleucine. Ile. Hydrophobic/Non-polar
2 chiral carbons!
What are all the aromatic aminos?
Tryptophan, Histidine, Tyrosine, Phenylaline
Which 2 aminos have >1 chiral carbon
isoleucine and threonine
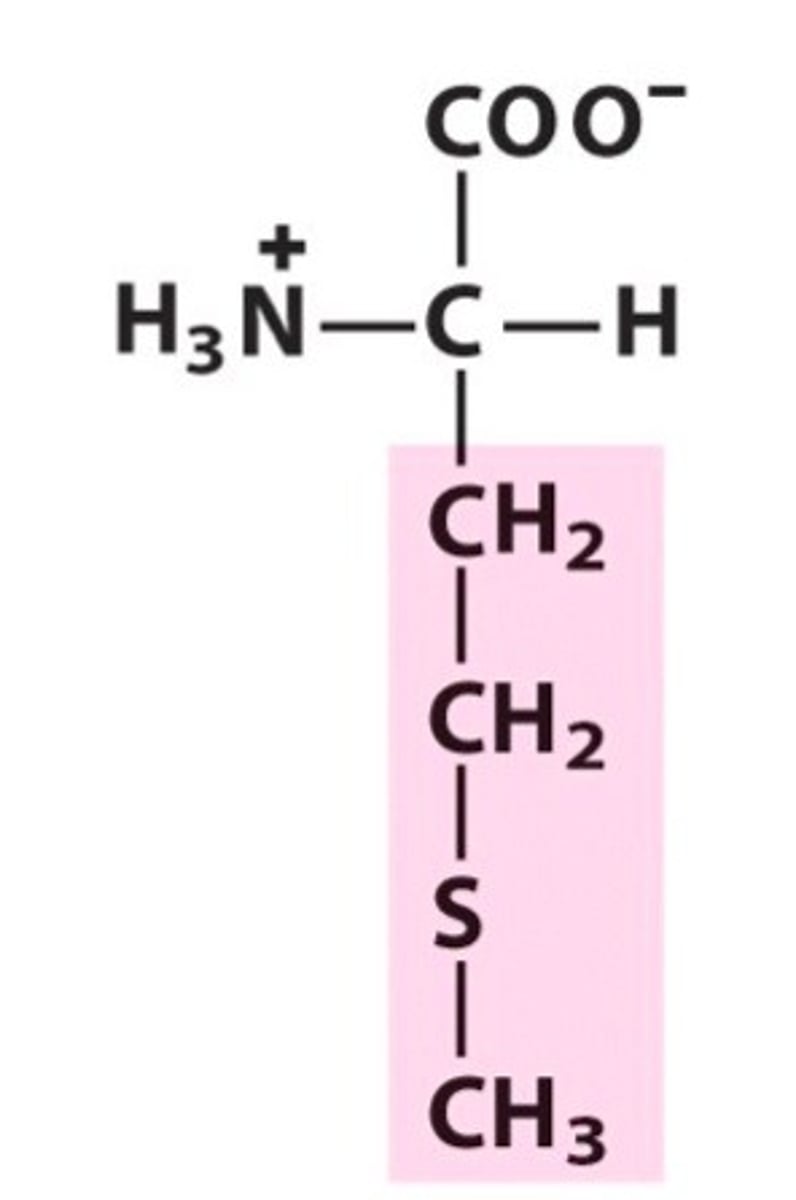
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Methionine. Met. Hydrophobic
even though sulfur is present (thioether), it is a non-polar side chain.
Unlikely to form H bonds.
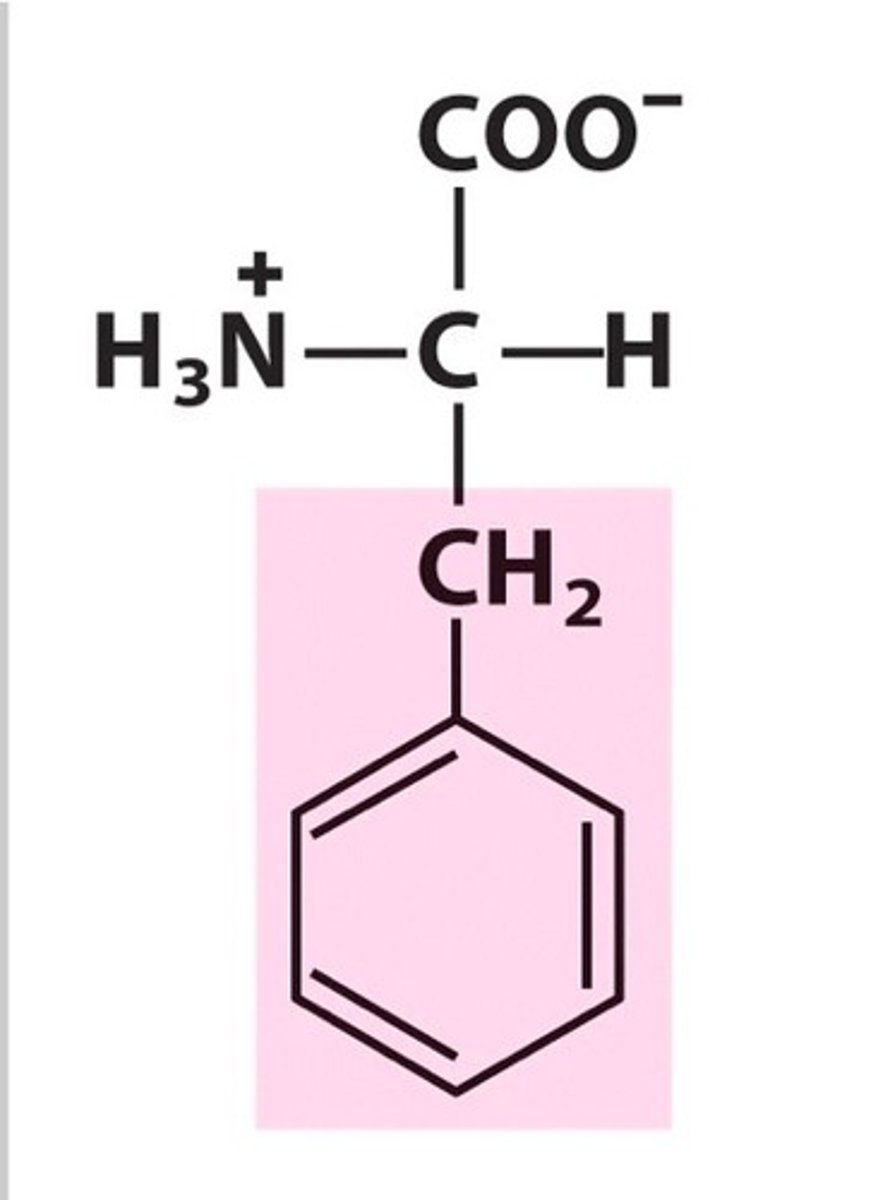
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Phenylalanine. Phe. Hydrophobic
Aromatic R group: absorbs UV very weakly at 280nm
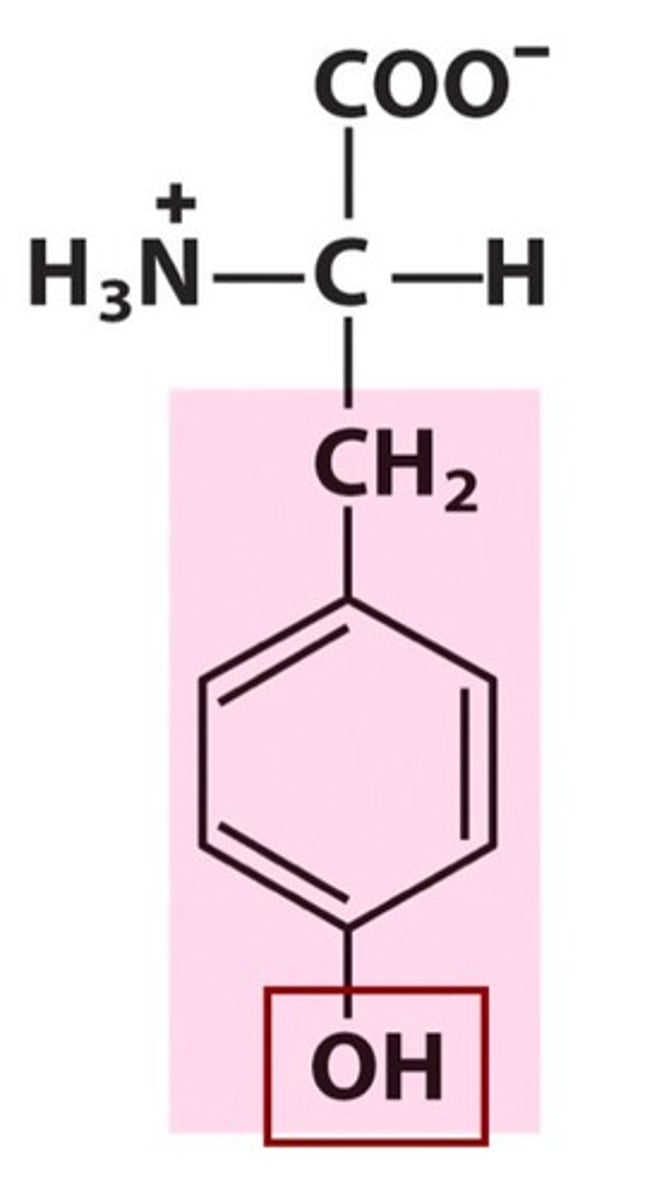
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Tyrosine. Tyr. Polar.
Can form H-bonds but also participate in hydrophobic interactions!!
Absorbs UV at 280nm
due to OH group, it can be phosphorylated
pKa = 10.5 therefore has H under biological conditions (negative charge at pH 14)
Which 7 aminos have ionizable R groups?
Glutamate, Aspartate, Lysine, Arginine, Tyrosine, Histidine, Cytsteine
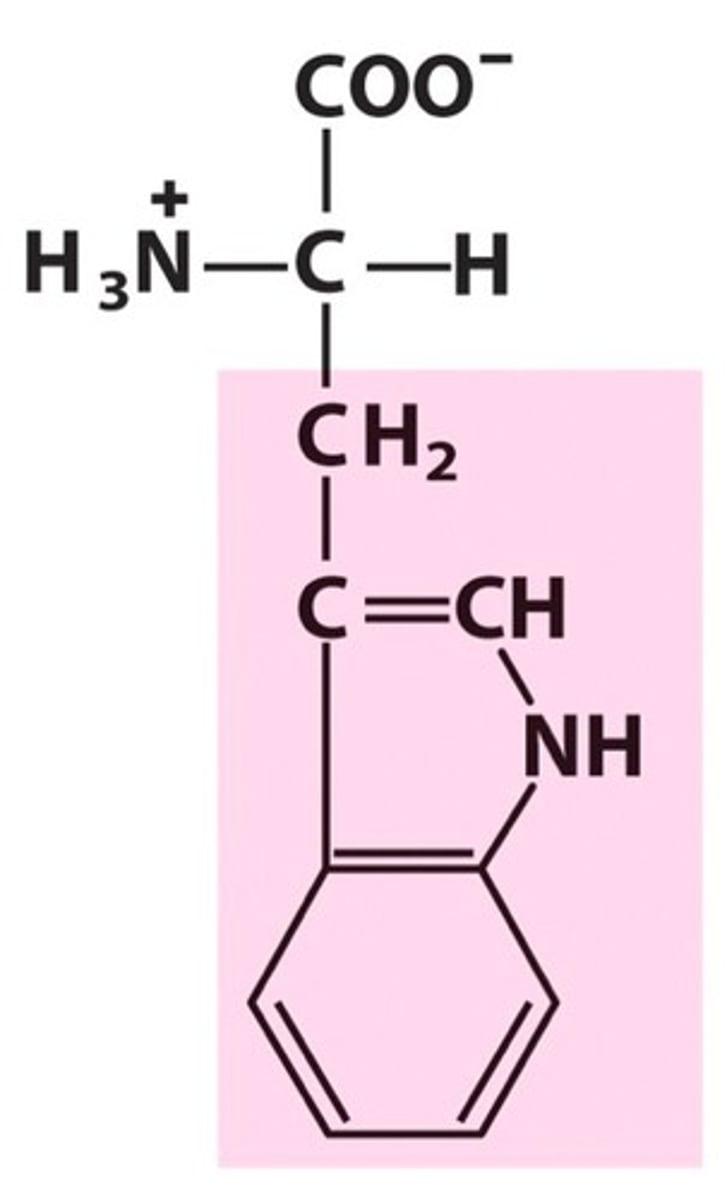
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Tryptophan. Trp. Hydrophobic.
Biggest and bulkiest side chain. Hydrophobic but can form an H bond.
Heterocyclic and Absorbs UV Strongly at 280nm
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
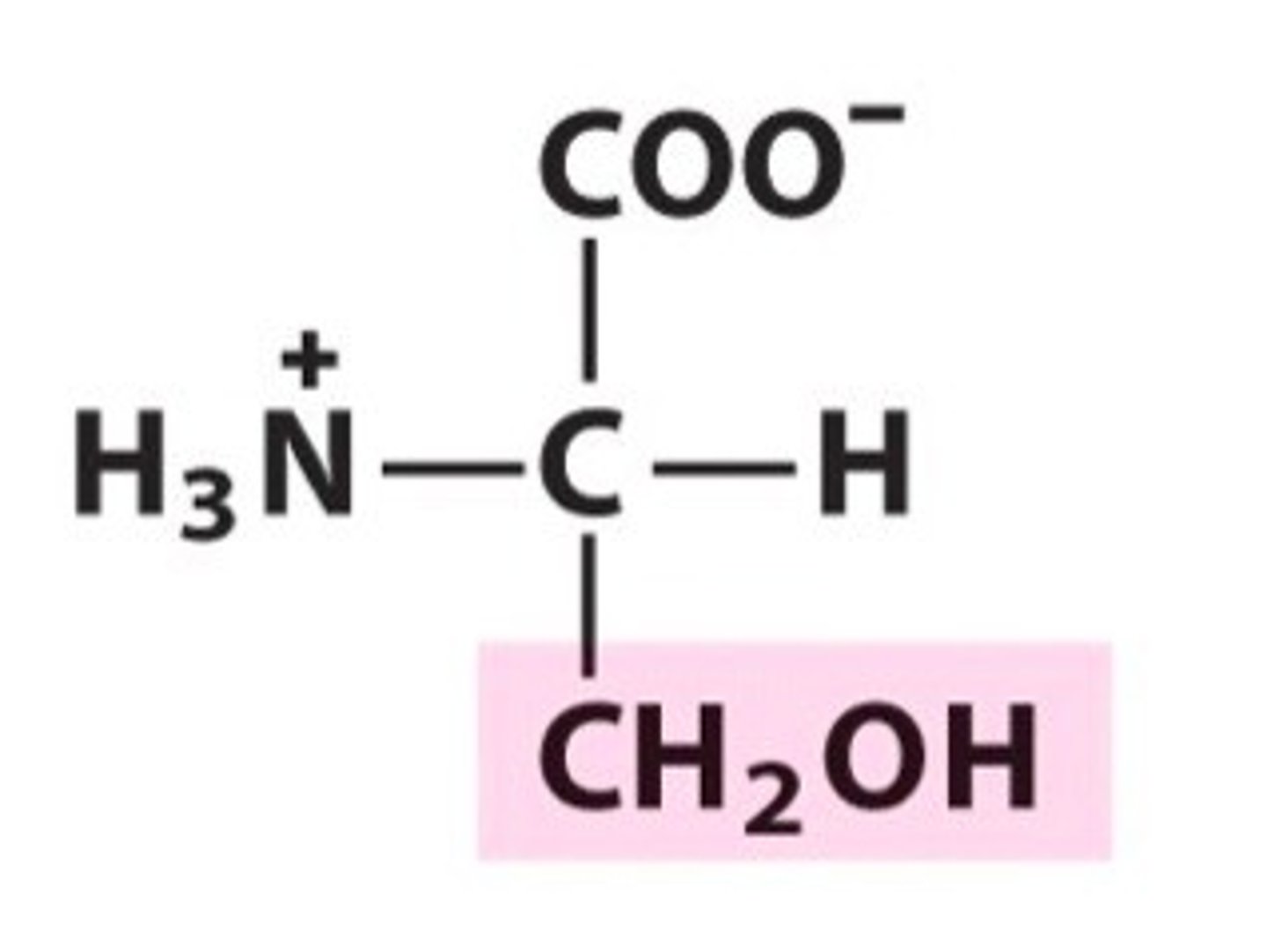
special features?
Serine. Ser. Polar
Can be phosphorylated due to OH group.
Participates in H bonding.
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
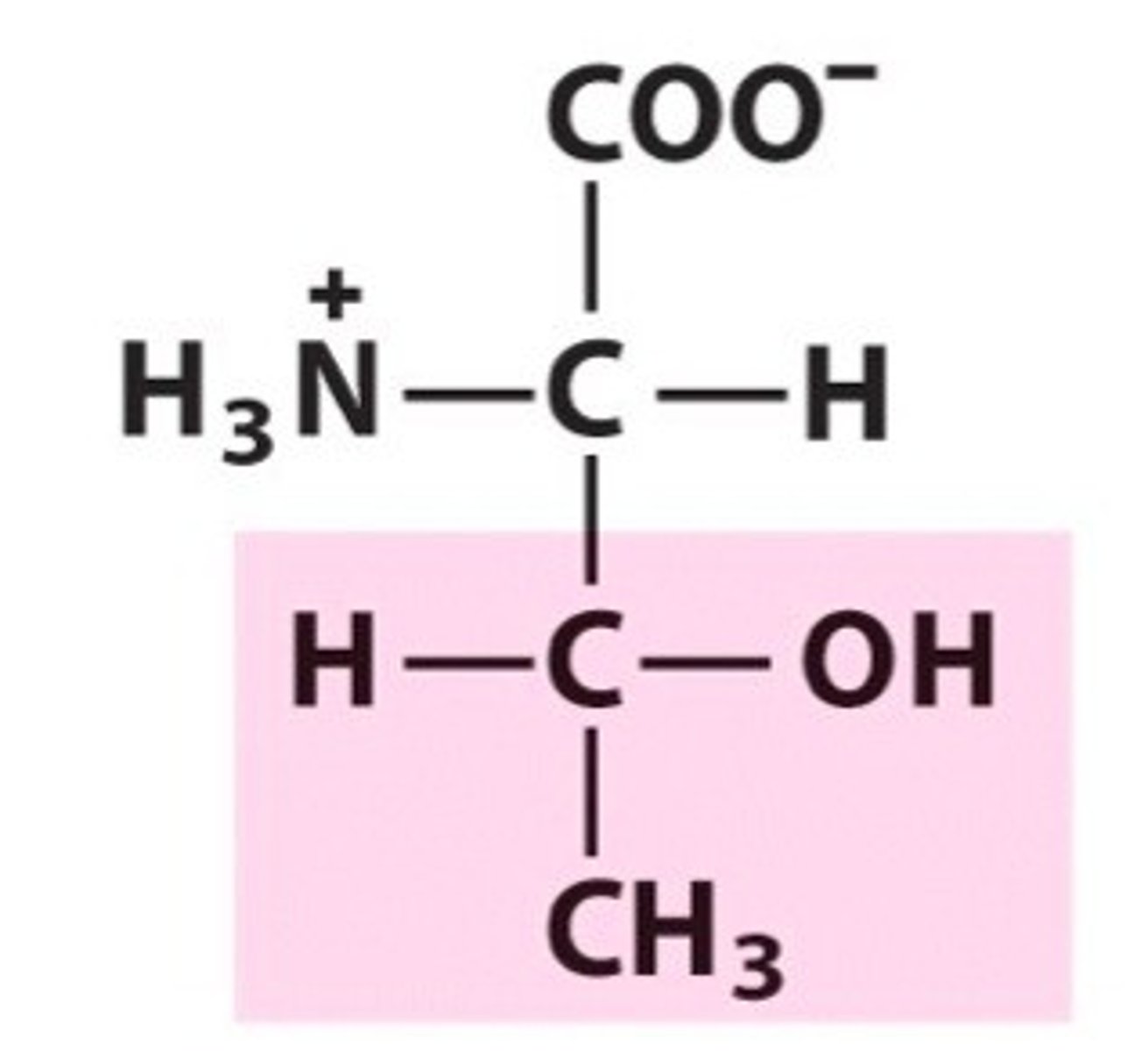
Threonine. Thr. Polar
2 chiral carbons!
Can be phosphorylated
H-bonds as donor and acceptor
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
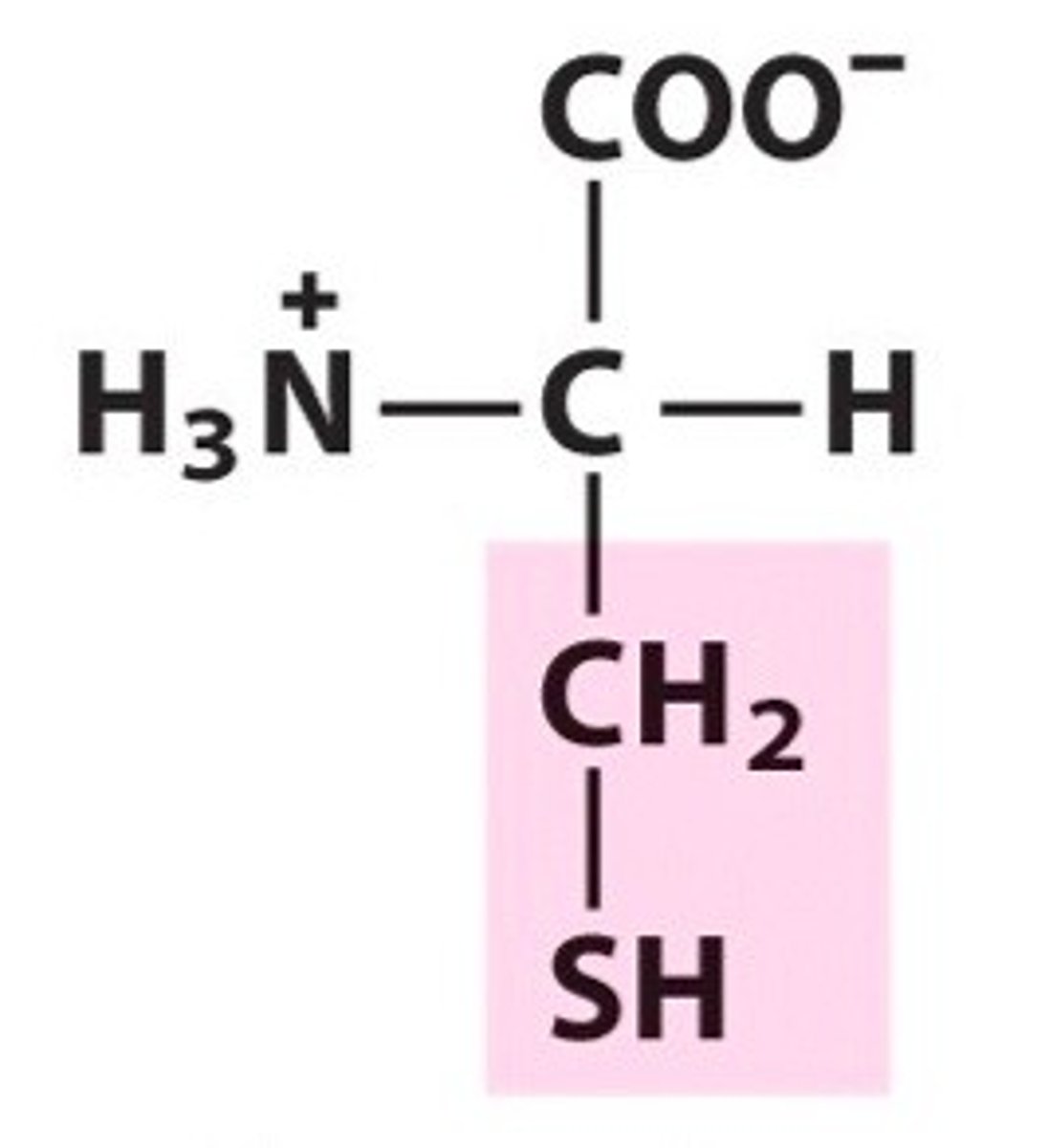
Cysteine. Cys. Polar.
Can form disulphide bridges/bonds with other Cys.
Can form H-bonds but doesn't act as an acceptor
pKa = 8.5 can give up H at pH 14
What are the necessary conditions to form a disulphide bridge and where can this occur?
Two Cys residues must be close enough to form a bond
Oxidizing environment such as the mitochondria or the extracellular fluid
If S-S bonds are formed in an oxidizing environment, what breaks a disulphide bond?
A reducing env.
What is Cystine? Is it polar or hydrophobic?
Two cysteine side chains interacting in a disulphide bond.
Relatively hydrophobic (S-S bond not S-H)
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
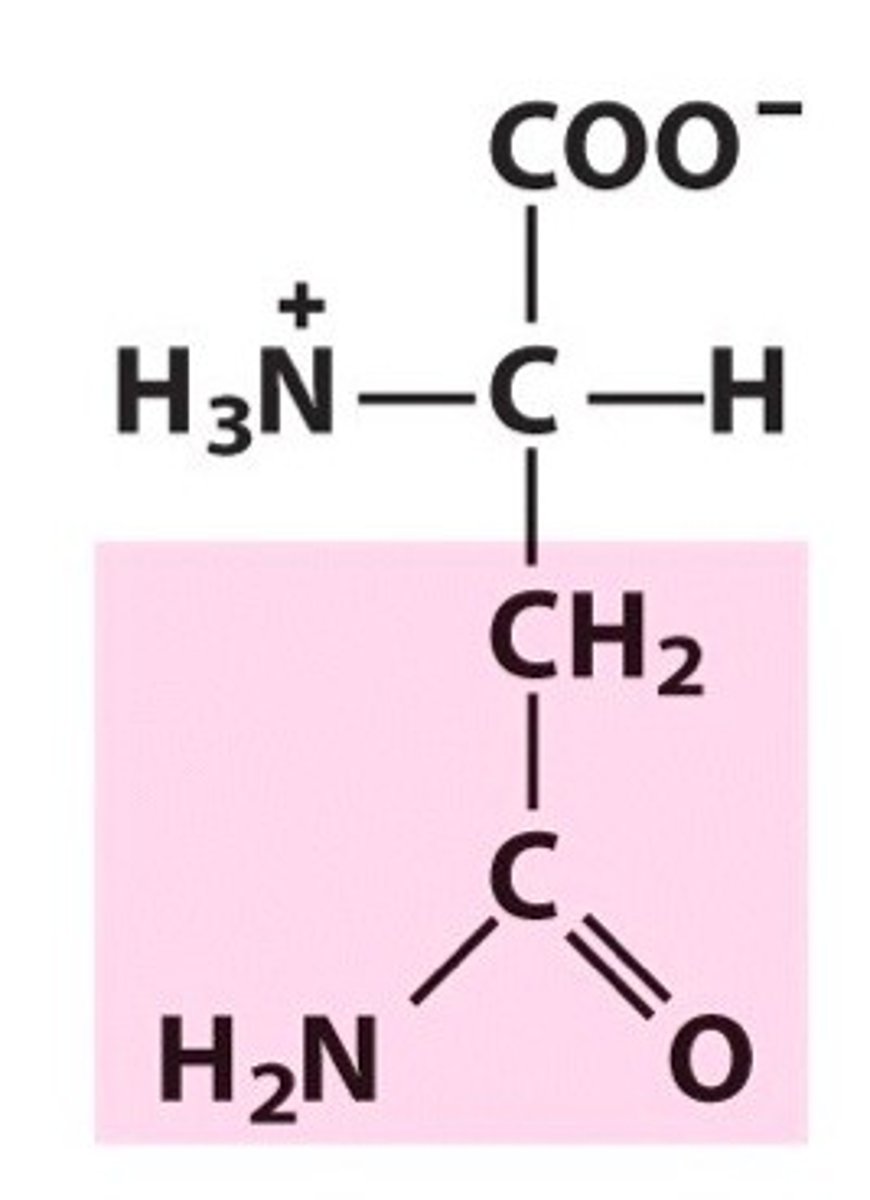
Asparagine. Asn. Polar.
Amide group and forms hydrogen bonds (O acceptor, N donor)
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
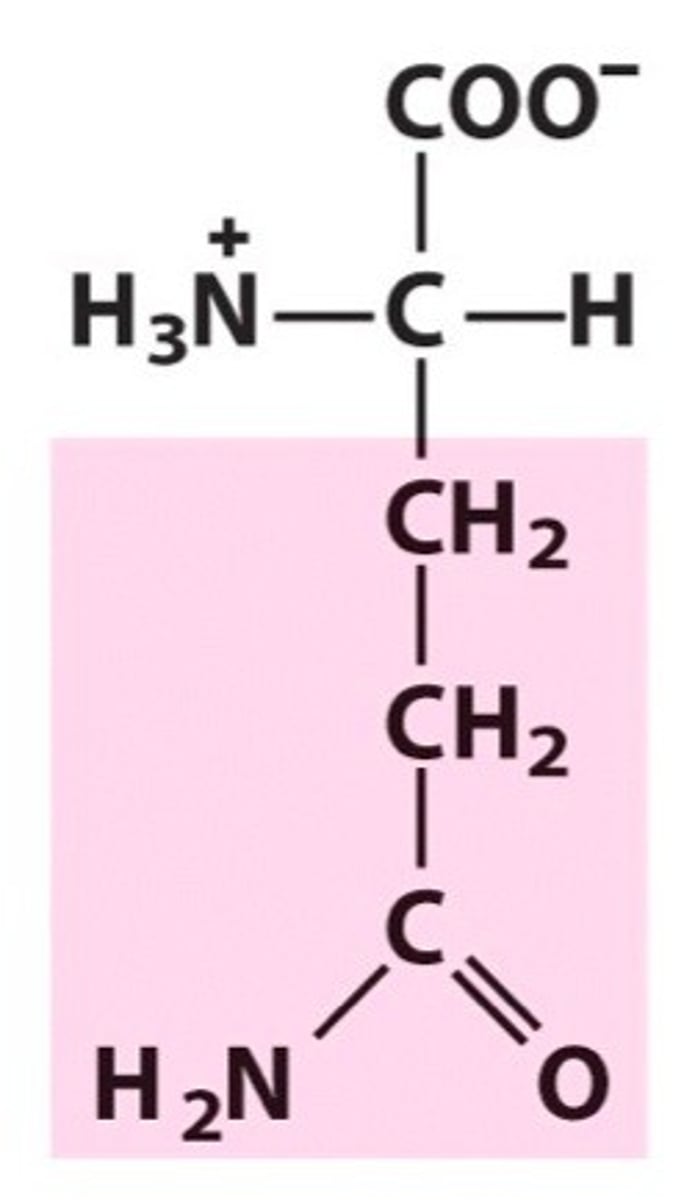
Glutamine. Gln. Polar
Amide group, forms H-bonds
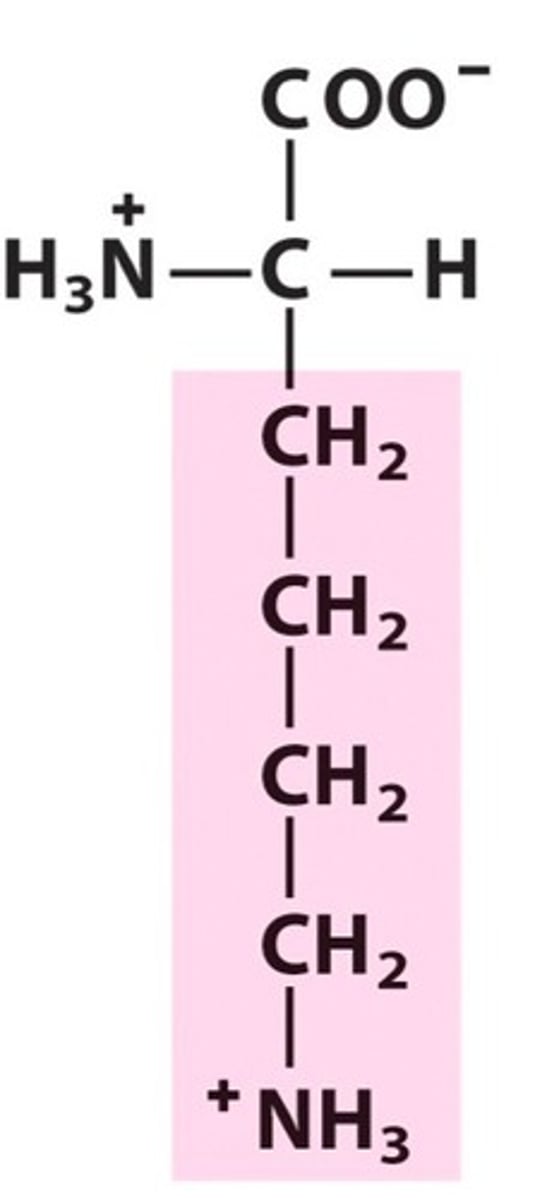
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Lysine. Lys. Charged.
Positive charge from NH3 at pH 7
pKa = 10.5 therefore neutral/loses H at pH 14. Basic amino acid
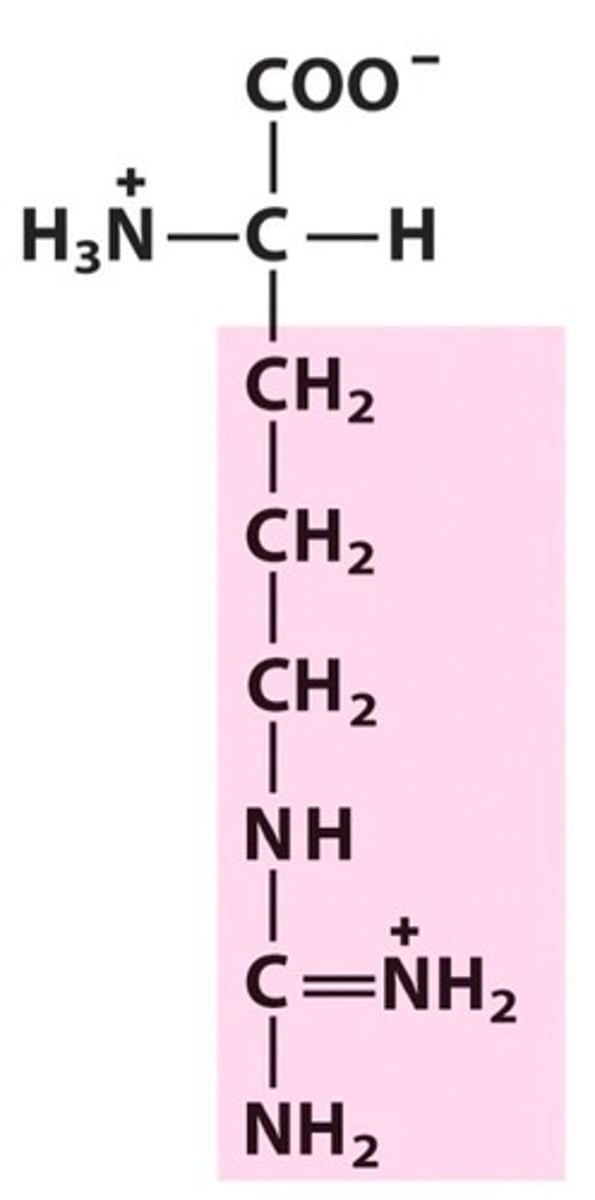
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Arginine
Basic and charged, but never deprotonated under biological conditions
pKa = 12.5
H bond donor only!
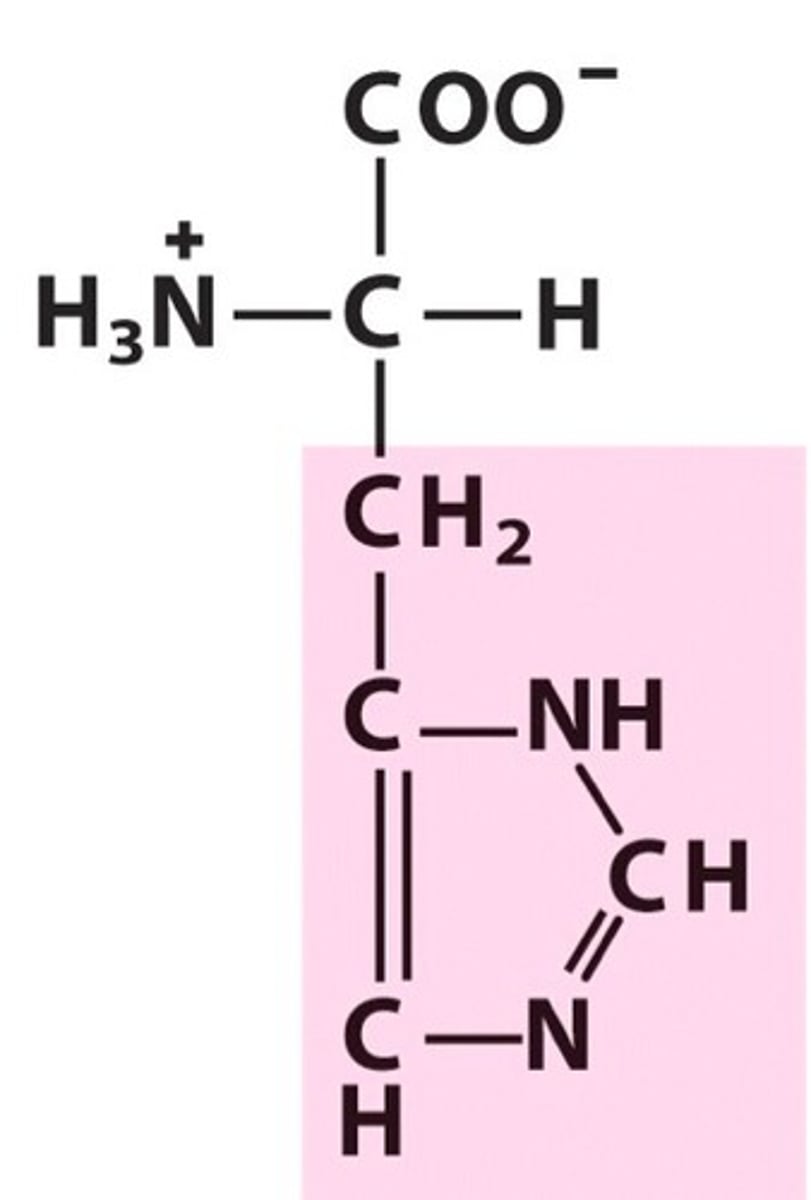
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Histidine. His. Polar
Aromatic - abs weakly at 280nm
pKa = 6 therefore neutral at 7 but becomes protonated at pH 1 with a positive charge!
Histidine can act as an acid or a base in reactions and also participates in H-bonding.
At pH 10 and 1 is histidine protonated or not? what is its pKa
pKa = 6 therefore;
10 = deprotonated
1 = protonated
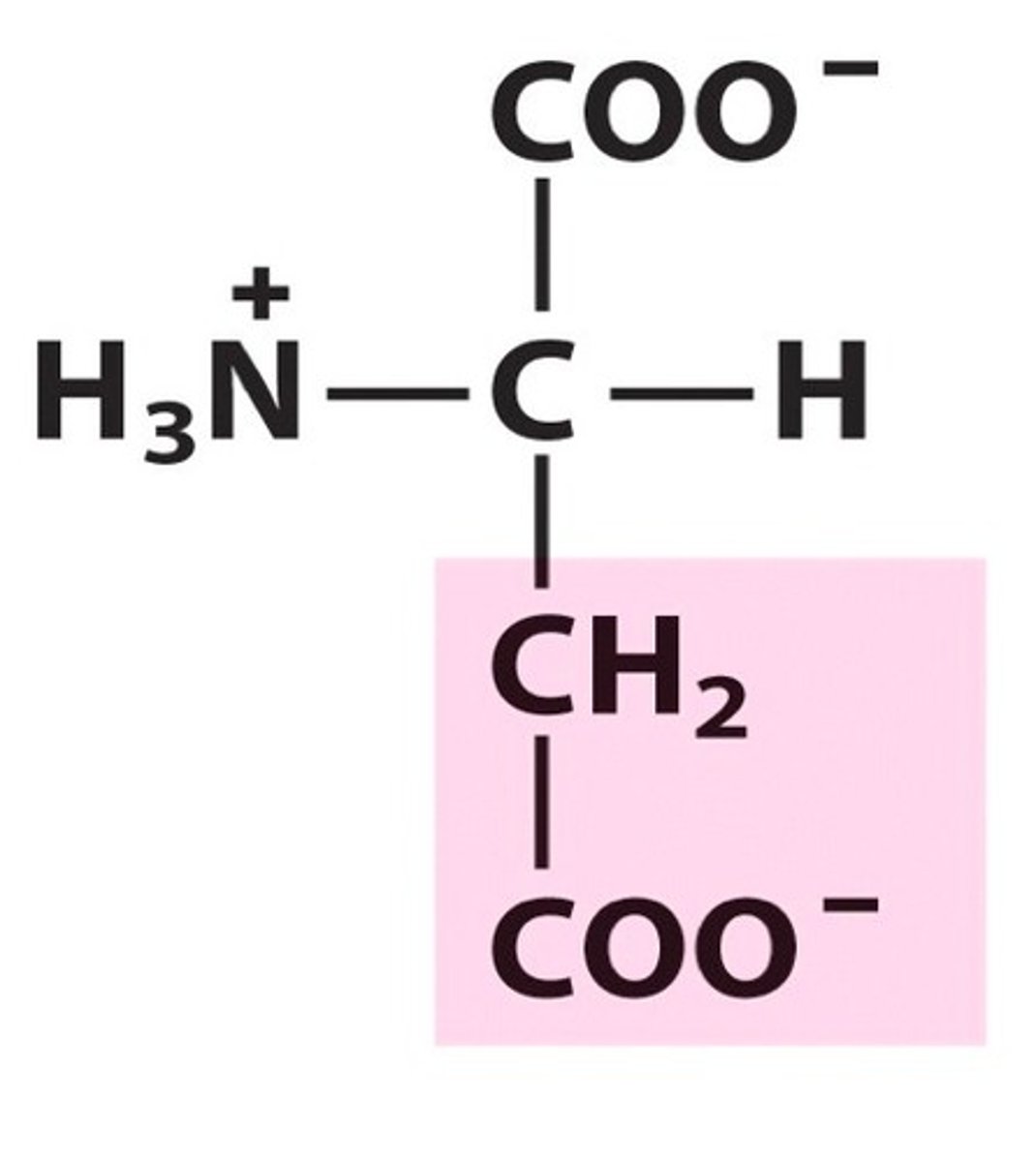
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Aspartate. Asp. Charged
acidic amino acid. pKa = 4.0
Negative charge at pH = 7 but called aspartic acid at pH 1 since it becomes protonated
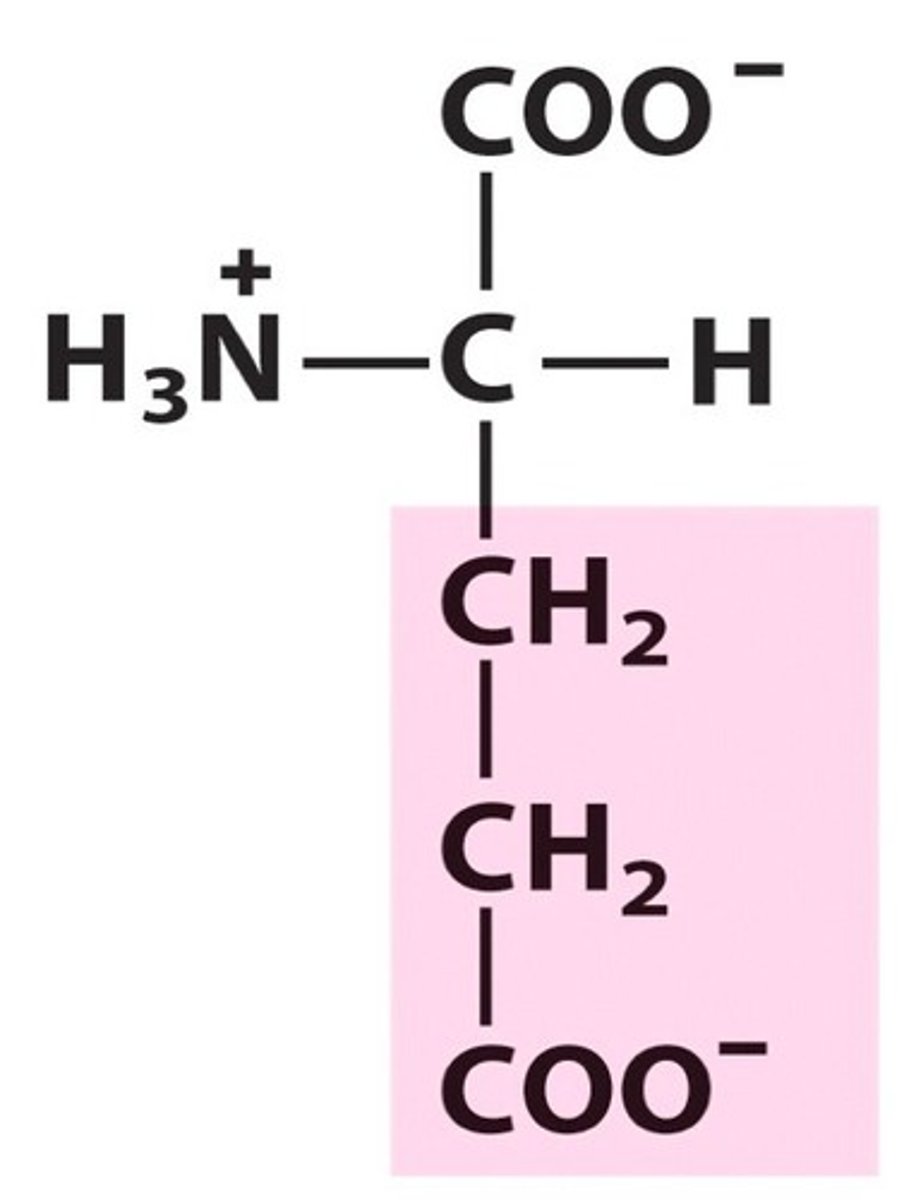
Negatively Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Glutamate. Glu. Charged.
pKa = 4: Negative at pH 7
acidic amino acid
called glutamic acid at pH 1 since becomes protonated
What will happen to the pH of water (pH 7)
if the fully deprotonated form of lysine is
dissolved in it?
pH will increase
What will happen to the pH of water (pH 7)
if the fully protonated form of lysine is dissolved in it?
it will decrease because the H from the carboxyl side chain will be given up.
what is a zwitterion? at what pH is a free generic amino acid a zwitterion?
A molecule containing an even # of positive and negative charged groups. At pH 7 a generic aa is a zwitterion.
At what pH does a free generic amino acid have a positive charge? Negative charge?
negative and pH 14 an d positive at pH 1
In all cases, a protein’s function is determined
by its _______.
Structure
What do proteins do? Name 5 functions
Structure
Transport
catalysis
movement/contraction
communication
What is pH and what is pKa? What do their high and low values mean?
pH is a measure of the concentration of H+ in solution while pKa measures the strength of an acid
At a pH above pKa, the acid exists predominately as?
The conjugate base/deprotonated form
At a pH below pKa, the acid exists predominately as?
The protonated form
When pH = pKa, what is true?
The concentration of HA = the Concentration of A-
What are the pHs of the following groups?
SH-
OH-
COOH
NH3
SH = 9
NH3+ = 9.5
COOH = 2 to 5
OH = highly variable
what is a chiral carbon? what are sterioisomers?
a carbon with 4 different groups attached. Stereoisomers = molecules with the same chemical formula and connectivity, but with different 3D arrangments of atoms
What is the major chiral carbon in 19/20 amino acids?
the alpha carbon
How are amino acids classified vs what are their properties?
Classification is based on Side chain but properties can be different.
What will happen to the pH of water (pH 7) if aspartate is added to it?
nothing
What are the characteristics of a peptide bond?
Rigid, planar, partial double bonds, polar
it is an amide/covalent bond, abs UV at 230 nm, neutral
made in a condensation rxn
Why cant a peptide bond rotate? Which bonds in the backbone can rotate?
It has partial double bond character due to electron resonance
The bonds to the alpha carbon can rotate (Ca-N and C-Ca). However, they are limited by steric hindrance..
What is the directionality of polypeptides and peptide bonds?
polypeptides run N to C and Peptide bonds are C to N
Define Polypeptide and Protein
A polypeptide is a long chain of amino acids, usually natural
A protein is one or more polypeptides with biological function
What is van der Waals contact in the context of an alpha helix
The atoms on the inside of an alpha helix are said to be in van der Waals contact since they are closely packed to minimize empty space.
Differentiate globular and fibrous tertiary structure
Fibrous = elongated filament, basically insoluble in aqueous solutions
Globular = hydrophobic interior, and normally hydrophilic side chains at the surface. soluble and compact
Define domains and motifs. Give an example of a motif.
A domain is segment of a polypeptide that folds into a single structural unit with a hydrophobic interior. It can often have independent function.
Motifs = a short region of a polypeptide with a recognisable 3D shape. It usually involves a common arrangement of secondary structures. Specific conserved function.
Example = The zinc finger motif
why are b-sheets not sequential? do antiparallel or parallel sheets have longer loops?
Strands are linked by loops which breaks up the sequence of amino acids involved in the sheet.
Parallel sheets have longer loops.
Define secondary structure. What about tertiary?
2 = the local arrangement/folding of a polypeptide backbone
3 = the arrangement of all the atoms in a single polypeptide
R groups and backbone
Where can polar and charged side chains be found in a protein?
they can typically be found at the surface but may be found in the interior if they are taking part in a hydrogen bond or a salt bridge (charged only)
what is the primary structure of proteins? What is the major stabilising force?
Sequence of amino acid residues and the force is peptide bonds
What atoms make up the backbone of a polypeptide?
The backbone of a polypeptide includes the
alpha carbon atoms and those atoms involved in the peptide bond
What limits rotation of the backbone?
steric hindrance from bulky R groups and Carbonyl oxygens
What determines the 3D structure of a protein?
Primary structure determines the 3-D structure. Specifically where the hydrophobic amino acid residues are located influences folding.
Can the alpha carbon participate in H-bonding?
No
what is regular vs irregular secondary structure?
Regular structures form independently of the amino acid residues in the polypeptide. They include alpha helices and beta pleated sheets.
Irregular structure includes loops which do depend on the amino acid residues present.
What is the major stabilizing force in secondary structure?
Hydrogen bonds between atoms in the peptide bond
What drives the formation of tertiary structure/what is the major stabilising force? What are the supplemental forces?
The major stabilising force is The Hydrophobic effect / hydrophobic interactions
Supplementary =
H bonds (between R groups and unused backbone groups)
Salt bridges (charged aminos and N and C terminals)
Disulphide bridges
What is the H bonding pattern in an alpha helix? Which groups cannot H-bond in this way?
A carbonyl group H-bonds with a N-H group 4 residues downstream.
the 1st 4 carbonyls at the C-terminus cannot Hydrogen bond since there are no N-H groups far enough downstream.
the 1st 4 N-H at the N-terminus cannot Hydrogen bond since there are no carbonyls far enough upstream.
In what 2 scenarios would hydrophobic side chains be found on the surface of a protein?
For a membrane protein and for polypeptides with quaternary struture.
Why do loops tend to be located at the surface and regular structure in the center?
Residues in loops are more available for H bonding while in helices and sheets, many of the groups that can hydrogen bond are already doing so.