Chemistry - Unit 13 - Acids and Bases
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Electrolytes
substance that conducts electricity because it has mobile charged particles.
EX; HCl, NaCl
What is conductive acids or bases
Both! They dissipate into ions (mobile, charge particles)
Higher acidity/lower pH = more conductive
Five important equations to do with OH and H and pH and pOH
pH = -log (H+)
pOH = -log (OH-)
H+ = 10^-pH
OH- = 10^-OH
pH + OH = 14
What can be explained by the Arrhenius theory
The behavior of many acids and bases
Describe the neutralization reaction
In a neutralization reaction and Arrhenius acid reacts with an Arrhenius base to produce water and a salt.
note that this is proved by the Arrhenius theory.
Hydronium =
Hydroxide =
H3O or H. Called H3O Becuase H is just one proton so it would attach to a H2O covalently
OH- , negatively charged
Steps to writing a neutralization reaction
1) write:
Acid + base —> water + salt
2) substitute the words for the compounds (OH- at the end and H+ at the beginning form the H2O, the other “spectator” ions come together to form the salt.
3) Criss cross charges for the salt
4) BALANCE THE EQUATION!!
What substance is always produced by a neutralization reaction?
Water
What is the process of titration
The process of adding measured volumes of an acid or a base of known concentration to an acid or a base of unknown concentration until neutralization occur occurs. The solution of known concentration is called the standard solution. Knowing the volumes of the acid and base used in titration, together with a known concentration of the standard solution, it is possible to calculate the concentration of the unknown solution.
Using : MOLARITY and the fact that neutralization happens with the same amount of OH and H. If we find the # moles of OH we know the # moles for H.
three equations used frequently in titration
Molarity = moles/volume
Moles= molarity x volume
Molarity H x volume acid = Molarity OH x volume base
OR
Ma x Va = Mb x Vb
Since the number of moles of H plus ions must equal the number of moles of OH minus ions, equating mole H and OH yields the following equation.
Molarity H times volume acid equals molarity OH times volume base.
pH 0-6
pH 7
pH 8-14
Acidic
more H3O than OH
Neutral (water)
equal H3O and OH
Basic
more OH than H3O
Increasing pH by 1 changes H concentration by…
A one-unit increase in pH means the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration decreases by a factor of ten.
H+ concentration and pH have inverse relation
And vice versa. Increasing pH means you are decreasing H+ because it’s getting more basic.
note: OH will increase x10 if pH increases by 1 (OH concentration is opposite of H trend)
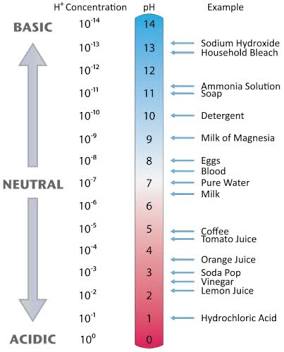
If you add a base…
If you add a acid…
Adding an acid to a solution will lower the pH, making it more acidic. Conversely, adding a base to a solution will raise the pH, making it more basic. This is because acids increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), while bases increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-)
What is the molarity of s substance with the pH of 0
1 M (high concentration of hydrogen meaning high acidity)
And alternative acid is defined as a proton, donor and alternative base is defined as a proton acceptor. All Arrhenius acids are also alternative acids alternative theory expands upon the Arrhenius concept by adding proton donors that are not an aqueous solutions.
Conjugate acid base pairs
Refers to the alternative theory
A pair of chemical formulas differing only by the presence of a hydrogen ion.
Forward : acid and base. Acid is donating, base is accepting.
These are valid reverse as well. Reverse would have different acid and different base.
Reverse: these different donors (acids) and bases (acceptors) you put “conjugate” in front of them
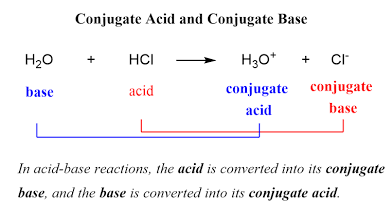
Two important parts of neutralization
SAME amount of OH and H
NEUTRAL = pH of 7
Definition for Arrhenius Acid
Acid releases/creates H+ in solution
A substance whose water solution contains the hydrogen ion as the only positive ion. For example, hydrochloric acid is classified as an Arrhenius acid because ionizes in water to form, hydrogen and chloride ions.
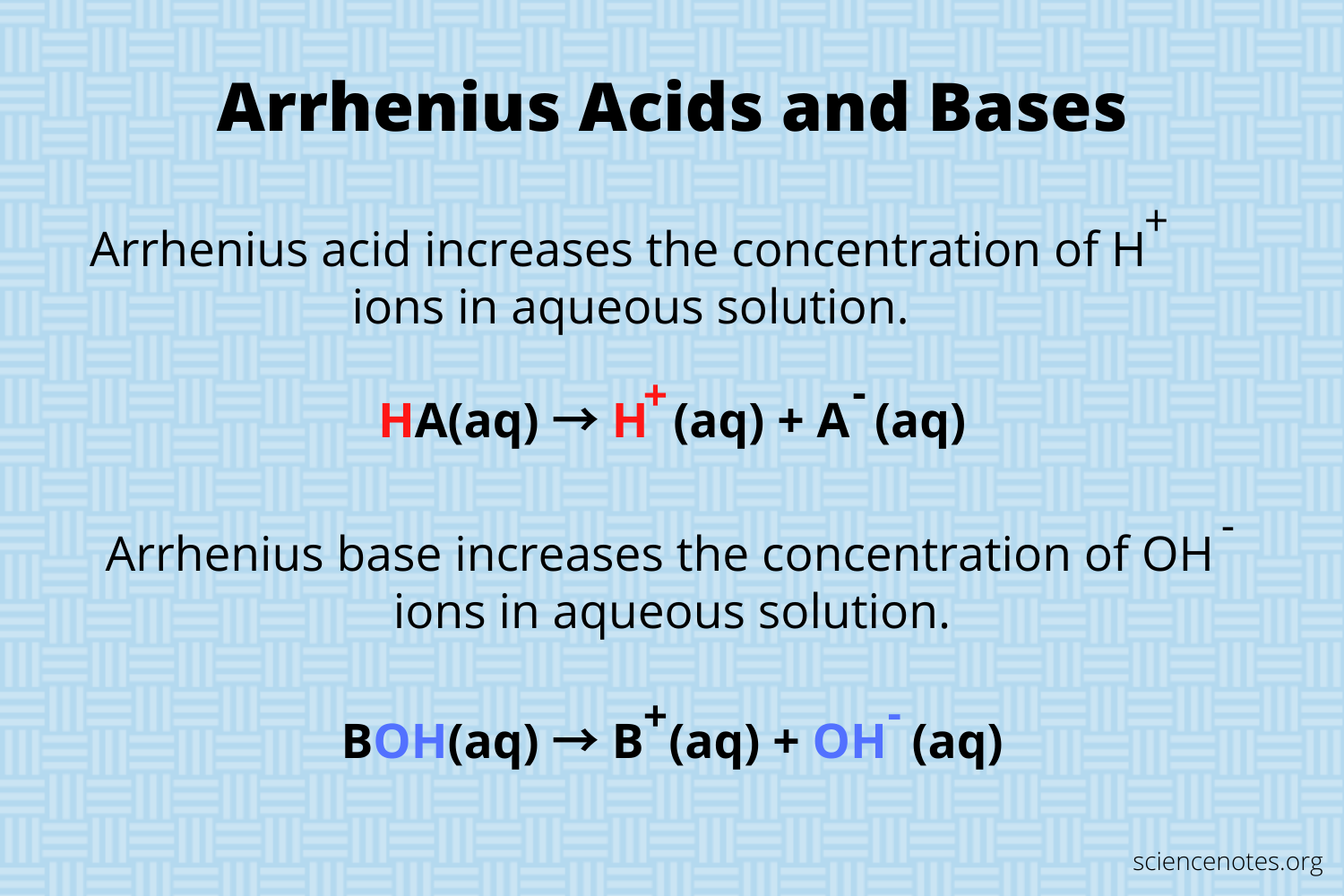
Definition for Arrhenius Base
Face releases/creates OH- in solution solution
The properties of bases are explained as the properties of hydroxide ion in solution. Each of Arrhenius base produces hydroxide ions were dissolved in water. The presence of the hydroxide ion makes the base and electrolyte. It is also the presence of a hydroxide ion that produces a slippery fear and bitter taste, with bases.
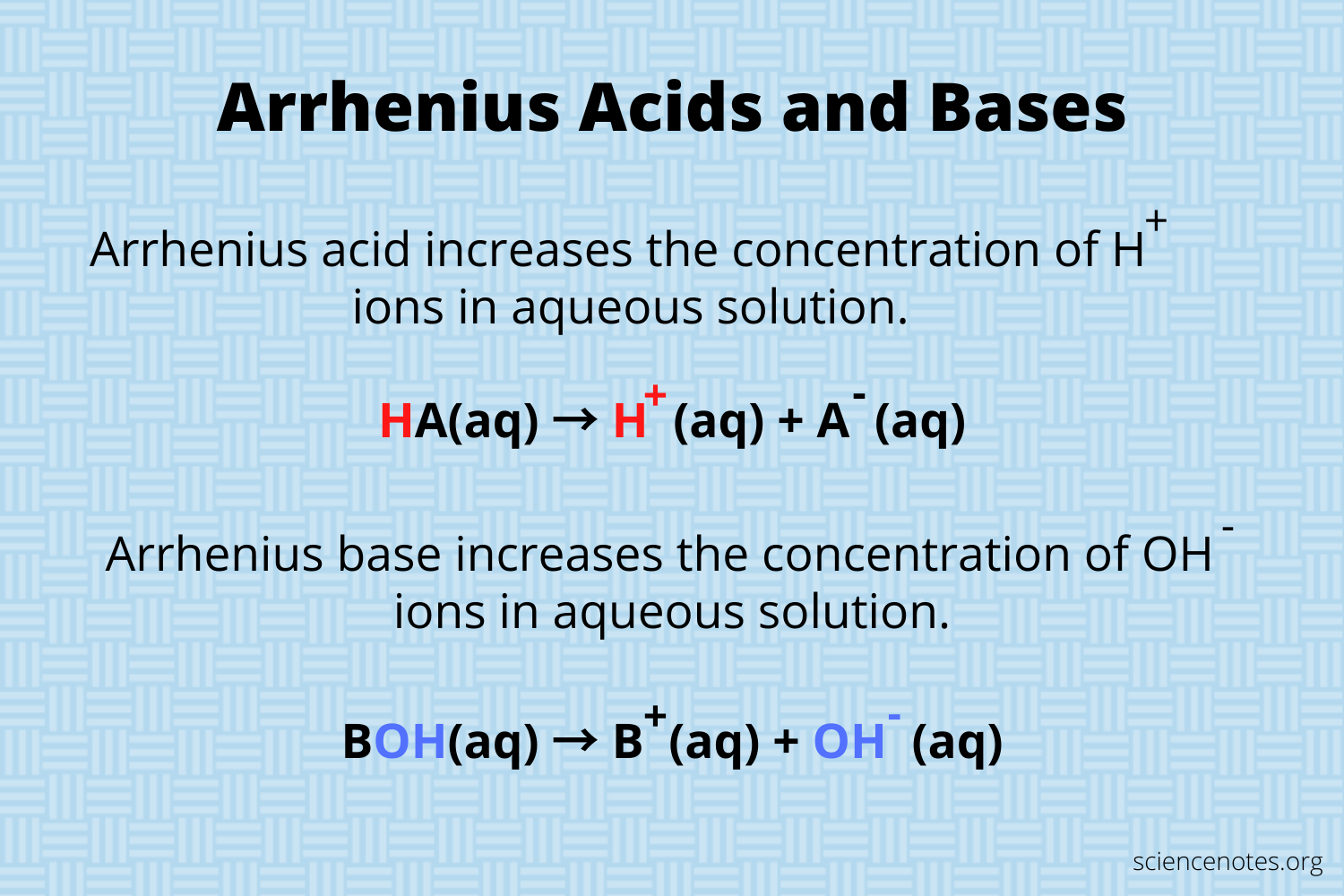
What is the Arrhenius definition for acid and bases? (Broad)
Acids and bases differ based on what ions are released in aqueous solutions.
In summary; this broad definition, classifies, acids, and bases on what they Release. If a compound releases or creates each in a solution, it will be classified as an Arrhenius acid if a compound releases or creates OH in a solution it is classified as an Arrhenius base.
Alternative (Bronsted) Theory
Acids and bases differ based on how they interact with H+
Acids give/donate an H+ ion
Bases accept/receive an H+ ion
Alternative/Bronsted acid
Acids give/donate an H ion
Alternative/Bronsted base
Basis except/receive H+ ion
Arrhenius versus bronsted theory
Arrhenius = H+ means acid, OH- means base
Bronsted = proton donors and receptors, increasing concept to any reaction involving proton transfer not just water
Amphoteric
Water can act to both as an alternative base and a base
Can accept and donate a proton.
Biggest example is water or H2O
Auto ionization of water
When water spontaneously separates into H3O- And OH-
This only happens once for every 10 million water molecules
Will always produce equal amounts of each H3O and OH as water is a neutral substance
Is H2O an acid or a base?
Trick question; it’s both!
Water is one of the Biggest examples of amphoteric. Where it can act as an alternative asset and base, therefore or in other words, it can accept and donate a proton.
What is pH?
Stands for power of hydrogen and is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen in a substance or compound
What is pOH?
Power of oxygen hydroxide or other words, the Measure of the concentration of oxygen hydroxide in a substance or compound.
What are the ranges for an acidic, neutral, and basic solution? (pH)
Basic is any substance or compound with a pH of over seven
Acidic is any substance or compound with a PH of under seven
Neutral is any substance or compound with a pH of exactly 7
Water/H2O
Overall trend; Lower number means it’s more acidic higher number means it’s more basic
What is the relationship between pH And pOH?
pH+pOH= 14
What is the relationship between the strength of the acid and the strength of the conjugate base?
Conjugate base is what is left after an acid gives up a proton. The stronger, the acid, the weaker, the conjugate base. The weaker, the acid, the stronger, the conjugate base.
A.k.a.; the relationship between the strength of the acid and the strength of the conjugate base is Inverse. If one is more strong, the other is a weak if the other is weak, the other is strong.
How can you calculate pH? (Log)
-Log(H+)
H+ —> concentration of hydrogen (followed by “M”)
How can you calculate pOH? (Log)
-log(OH-)
OH- —> Concentration of OH followed by M
How to find concentration of hydrogen/“H+” from pH?
H+ = 10^-pH
Concentration of hydrogen is always written before an M
How to find the concentration of oxygen hydroxide from pOH?
OH- = 10^-pOH
Oxygen hydroxide, the concentration is always written, followed by M
In terms of the Bronsted acid and base theory what is the acceptor and what is the donor?
The donor of the hydrogen proton is the acid
The acceptor of the hydrogen proton is the base
In other words; what gains the hydrogen proton is the base and what loses the hydrogen proton is the acid
When the concentration of hydrogen ions increases, does pH increase or decrease?
They have an inverse relationship because when hydrogen ions increase pH will decrease indicating a more acidic compound or solution. With the same logic, if the concentration of hydrogen ions decreases PHO increase because an increased pH means that the solution is more basic.
What is hydronium?
H3O, positively charged ions formed when a hydrogen ion (H+) binds to a water molecule (H2O) in aqueous solution. Essentially, a proton (H+) from an acid molecule joins with a water molecule to create the hydronium ion
What is a neutralization reaction
When an Arrhenius acid and Arrhenius base combine to form a salt and water
The concentration of H+ and OH- is EQUAL because this would be enough to for, H2O (neutral)
essentially a double replacement reaction with acids and bases
What does adding an acid do to the pH of a solution and why?
What does adding a base do to the pH of a solution and why?
1) DECREASES the pH becuase the solution is getting more acidic, more acidic means lower pH
2) INCREASES the pH because the solution is getting more basic, more basic means higher pH
What does a neutralization reaction produce?
A salt and water
Properties of acids
Solutions of acids have sour taste
AQ solutions of acids conduct an electric current
Substances that conduct an electric current are called electrolytes
Ability to conduct electricity is dependent on concentration (number) of ions in a solution
Acids react with bases to form a water and salt
neutralization reaction
Acids react with certain metals to produce hydrogen gas
Acids cause acid-base indicators to change color
What is an electrolyte?
Substances that conduct an electric currents are called electrolytes. The ability of a solution to conduct an electric current is dependent on the concentration or number of ions in the solution. That is, the greater the concentration of ions in solution, the greater the electrical conductivity. If a solution of an acid is a good conductor of electricity, it is strong acid. If such a solution in a poor conductor, it is teamed a weak acid.
If a solution of an acid is a good conductor of electricity, it is an ____ acid. If such a solution in a poor conductor, it is teamed an ____ acid.
Strong
Weak
Characteristic properties of bases
Bases have a bitter taste
Slippery or soapy feeling
Conducts electric current
React with acids to produce a water and salt (neutralization reaction)
Cause acid-base indicators to change color
Hydronium ion
Chemists believe that this proton (Hydrogen) Cannot exist in a water solution as an isolated proton. The positively charged proton is attracted to an unshaded pair of electrons in the water molecule. The proton covalently Bonds with the water forming H30 plus, the hydronium ion. Acid dissolve in water and react to produce hydronium and negative ions.
What is one trick for pH 7 and pH 1
pH 7 - 7 zeroes (including first) 0.0000001 M
pH 1 - 1 zero - 0.1 M
Endpoint
The point when enough acid or base is added to a solution to observe a permanent color change
Equivalence point
When moles of H+ = moles OH- in an acid base reaction (neutralization) reaching the endpoint with phenophalien is a good sign the solution is at/very near the equivalence point (colorless —> pink)
Steps to completing titration equation (neutralization) not using exact equation
1) convert to liters
2)write out the balanced equation. If the ratio acids to bases is NOT 1:1 we divide at the end.
3) find the number of moles using the molarity (concentration) and volume of the KNOWN base or acid
4) Becuase pH is 7 (neutralization) the amount of H is the same as OH (moles) so we use the same number and divide by the volume of the other to find the number of moles of the other unknown base or acid
5) now the ratio comes into play what do you need to multiply to get to the unknown acid or base? Ex: if the ratio is 1:2 you multiply by two. We do the same for the moles we found
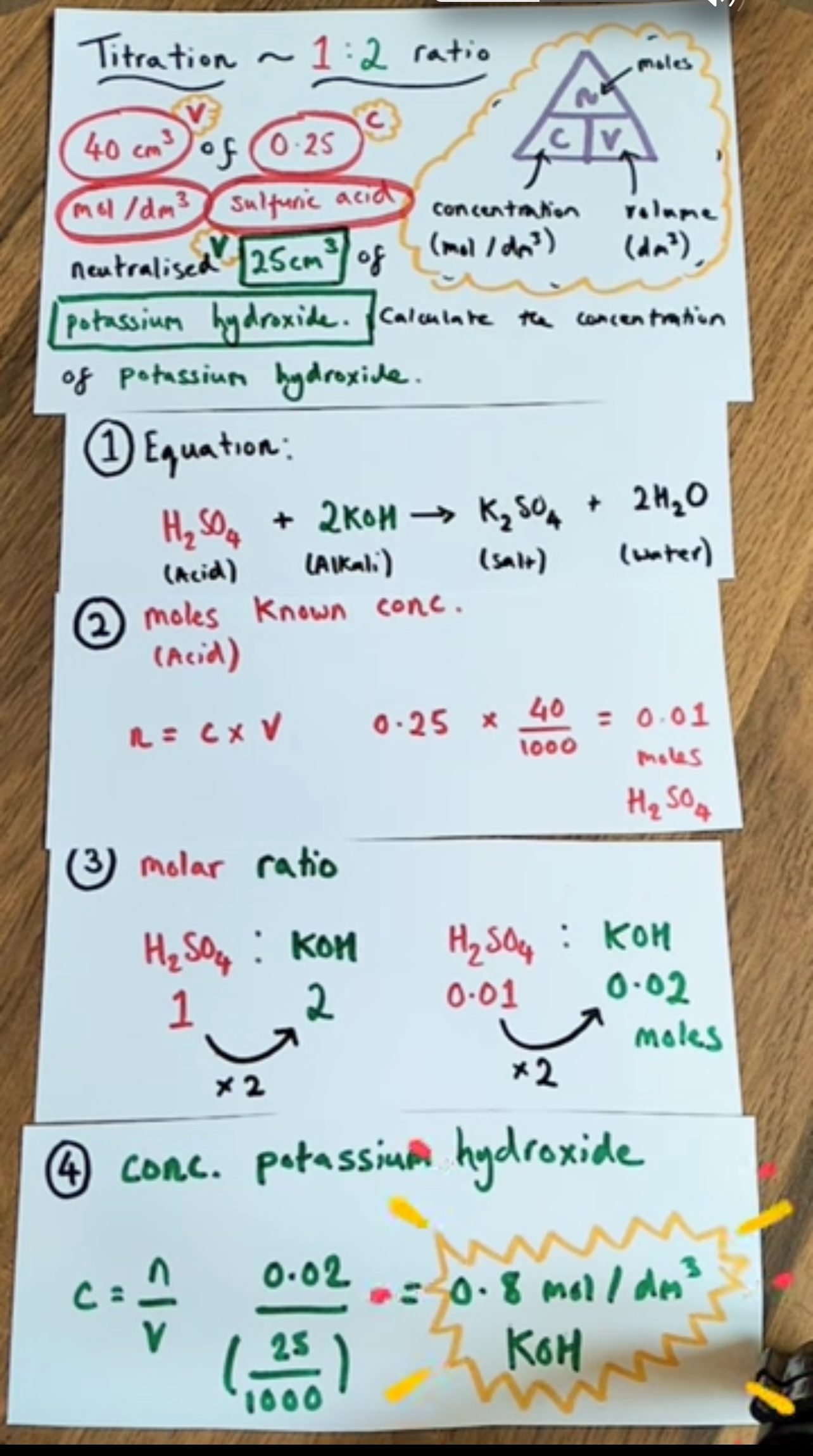
What is the equation for titration and why does it work?
M1V1 = M2V2 because multiplying molarity (m/l)xliters gets the number of moles and in neutralization the number of moles is the same for OH and H
How to identify a strong base and a strong acid?
Strong acid = higher concentration of H
Strong base = cation from group 1 or group 2
How to identify electrolytes from their compounds
To distinguish between electrolytes and nonelectrolytes, consider their ability to conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Electrolytes, typically ionic compounds, dissociate into ions, allowing the solution to conduct electricity. Nonelectrolytes, usually molecular compounds, do not dissociate into ions and therefore do not conduct electricity.
Look for ionic compounds - one metal, one nonmetal
Electrolytes AQ
What are the steps to completing a titration problem using equation ?
1) M1V1 = M2V2 because molarity times volume cancels liters and leaves you with # moles
2) convert to liters
3) before solving: write a balanced equation. If the mole ratio acids to bases is NOT 1:1 then you add the ratio number in front of the M1V1 and the other in front of the M2V2.
4) distribute this number via multiplication
5) divide to get the missing variable alone
