CDC Hymenolepiasis
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
[Hymenolepis diminuta] [Hymenolepis nana]
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Hymenolepiasis is caused by two cestodes (tapeworm) species, _________
Hymenolepis nana, Hymenolepis diminuta
Hymenolepis nana (the dwarf tapeworm, adults measuringmm in length)
15 to 40
Hymenolepis diminuta
rat tapeworm
Hymenolepis diminuta adults measuring ______ in length).
20 to 60 cm
Cestode of rodents infrequently seen in humans and frequently found in rodents.
Hymenolepis diminuta
Eggs of Hymenolepis nana are immediately infective when passed with the stool and cannot survive more than _______ in the
external environment
10 days
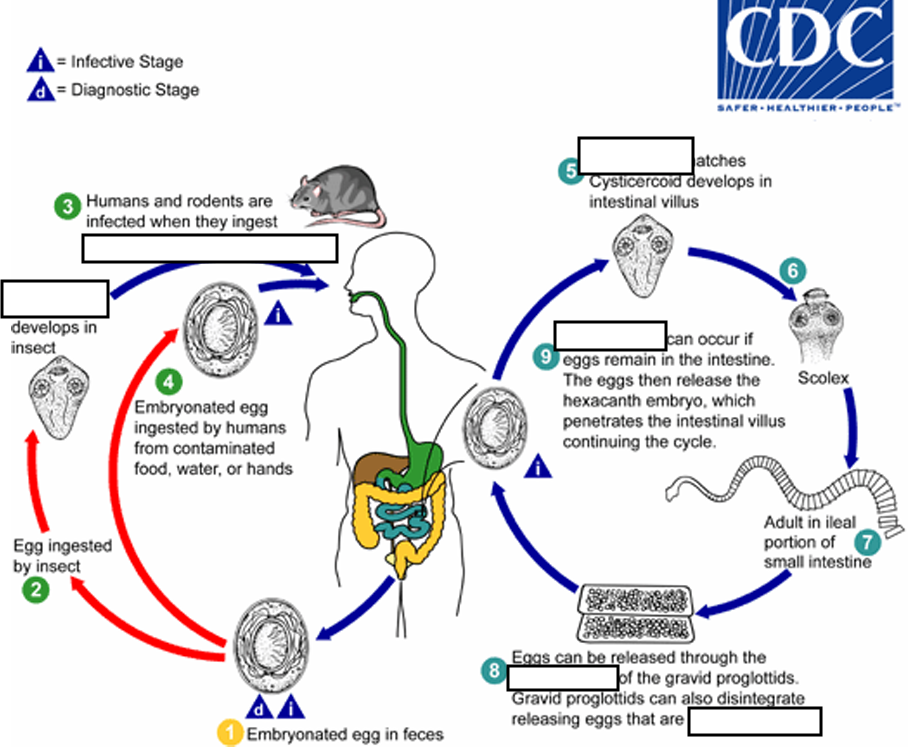
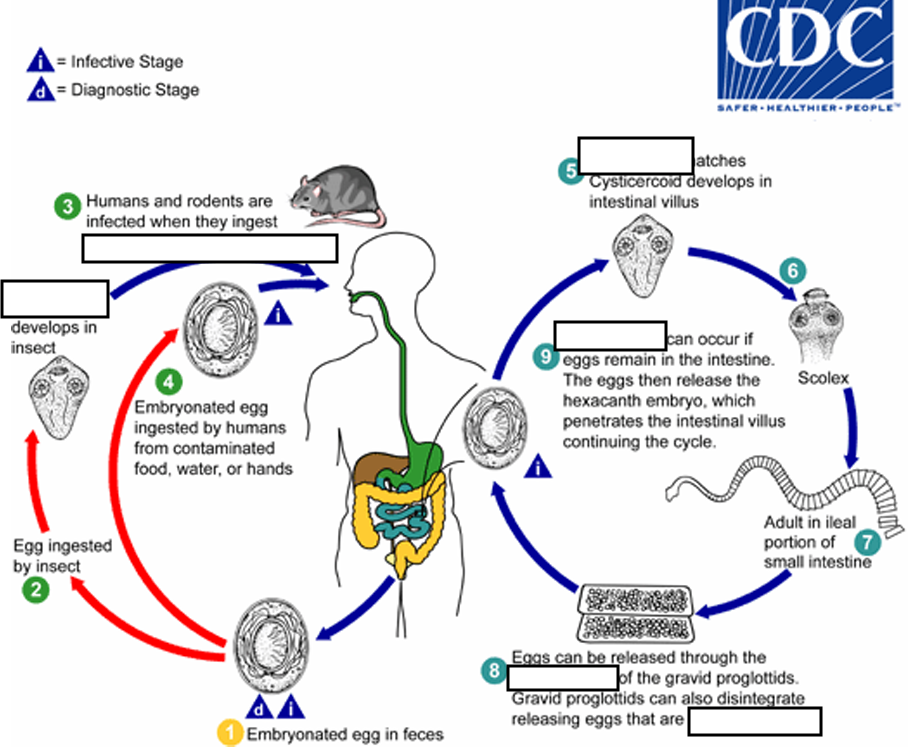
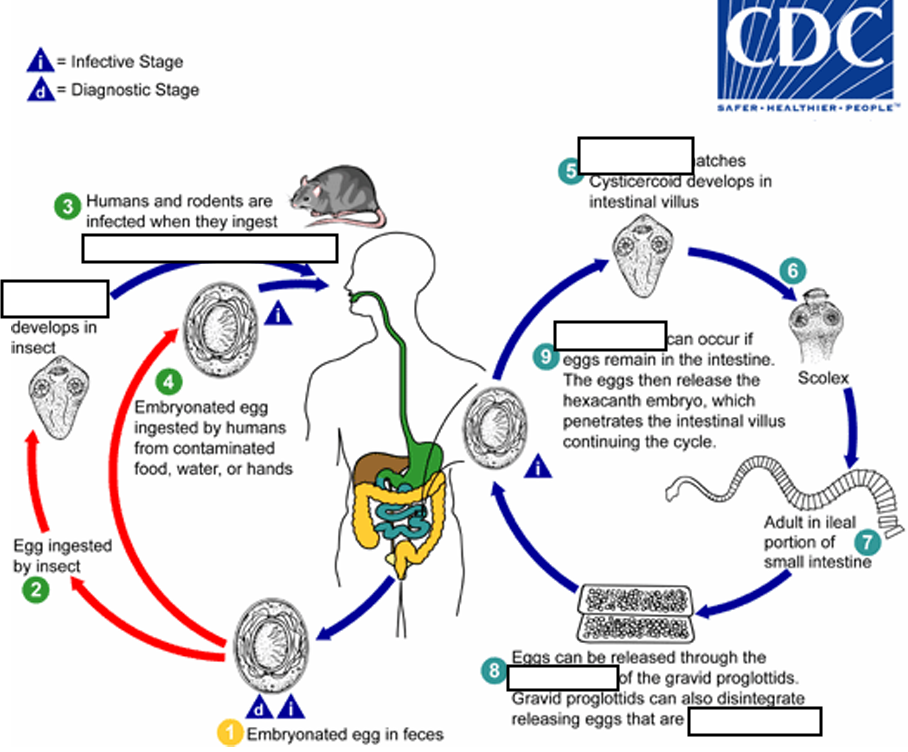
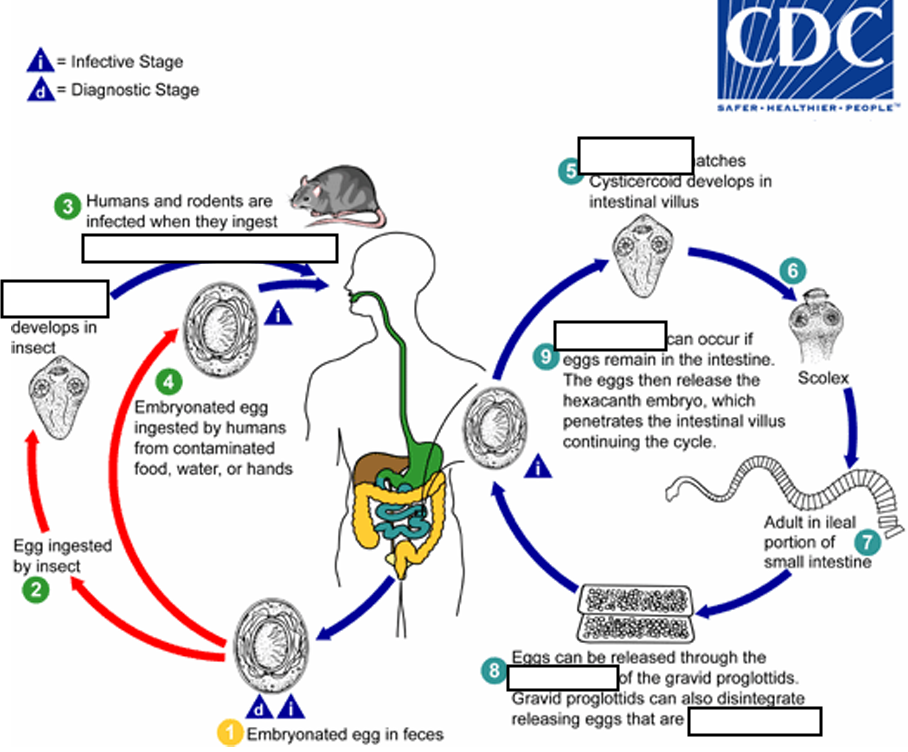
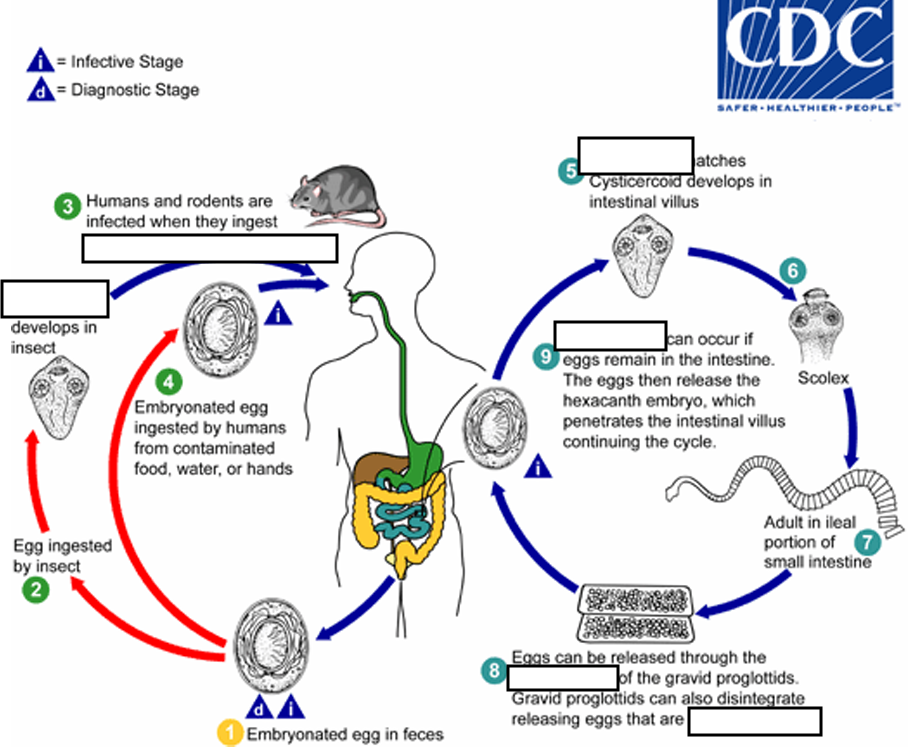
(1) Embryonated egg, (infective stage) when eggs are ingested by an arthropod intermediate host (2) (various species of ______ may serve as intermediate hosts), they develop into cysticercoids, which can infect humans or rodents upon ingestion
beetles and fleas
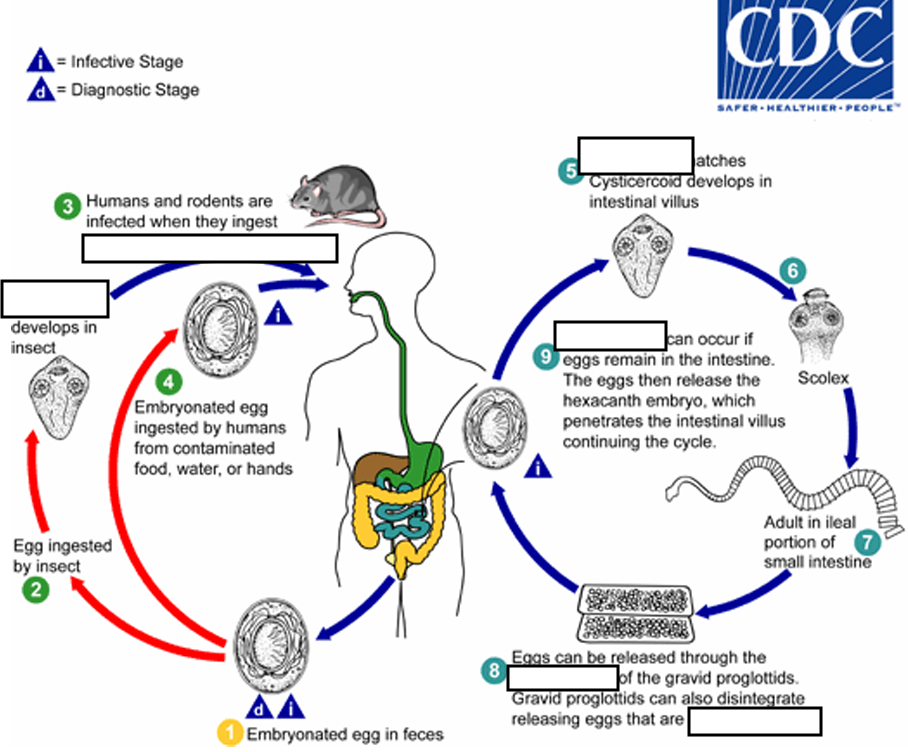
(2) they develop into_____, which can infect humans or rodents upon ingestion(they developed in insect)
cysticercoids
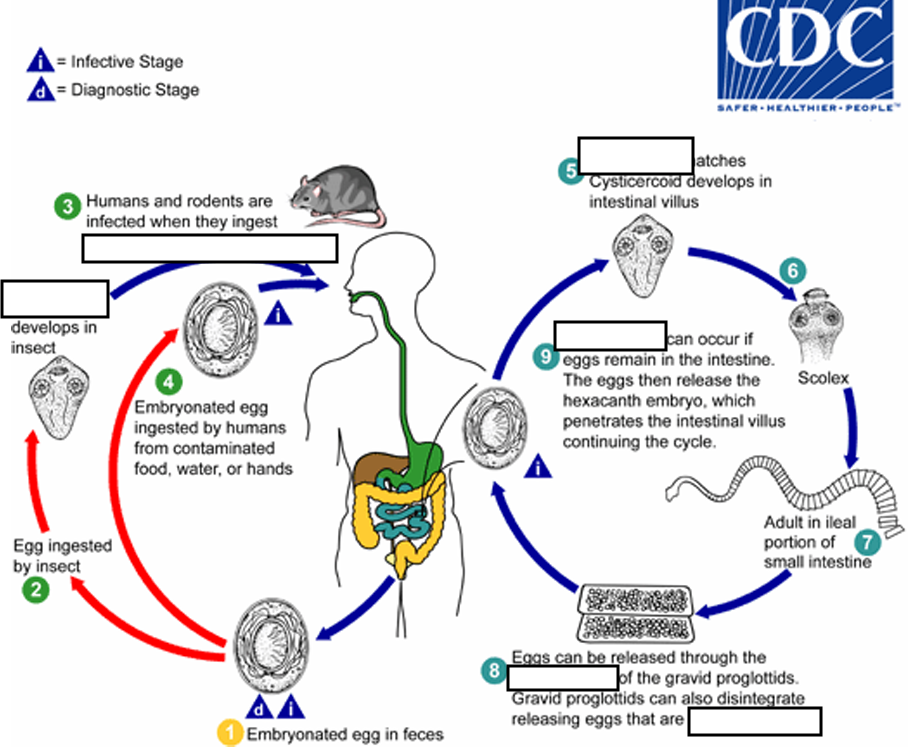
(3) develop into adults in the
small intestine
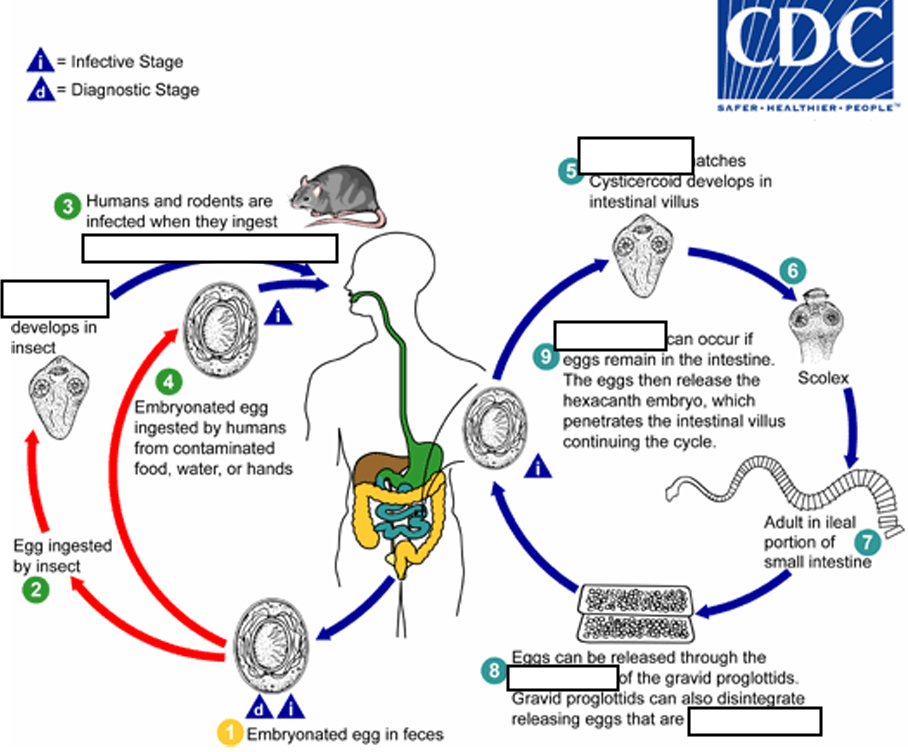
A morphologically identical variant, H. nana var. fraterna, infects rodents and uses arthropods as ______
intermediate hosts
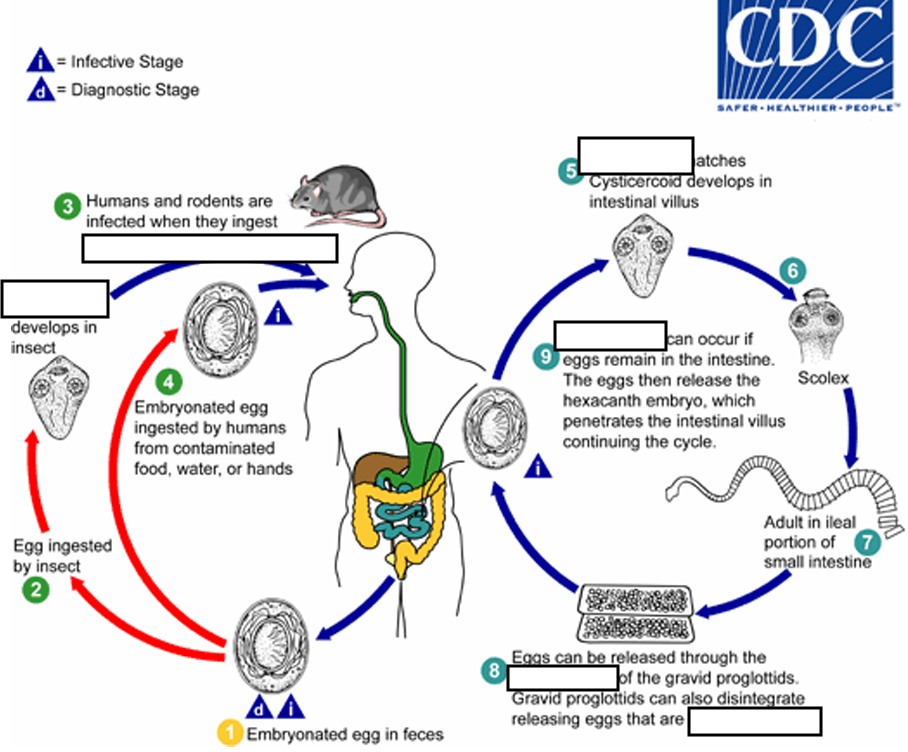
(4) When eggs are ingested (in contaminated food or water or from hands contaminated with feces), the
______ contained in the eggs are released.
oncospheres
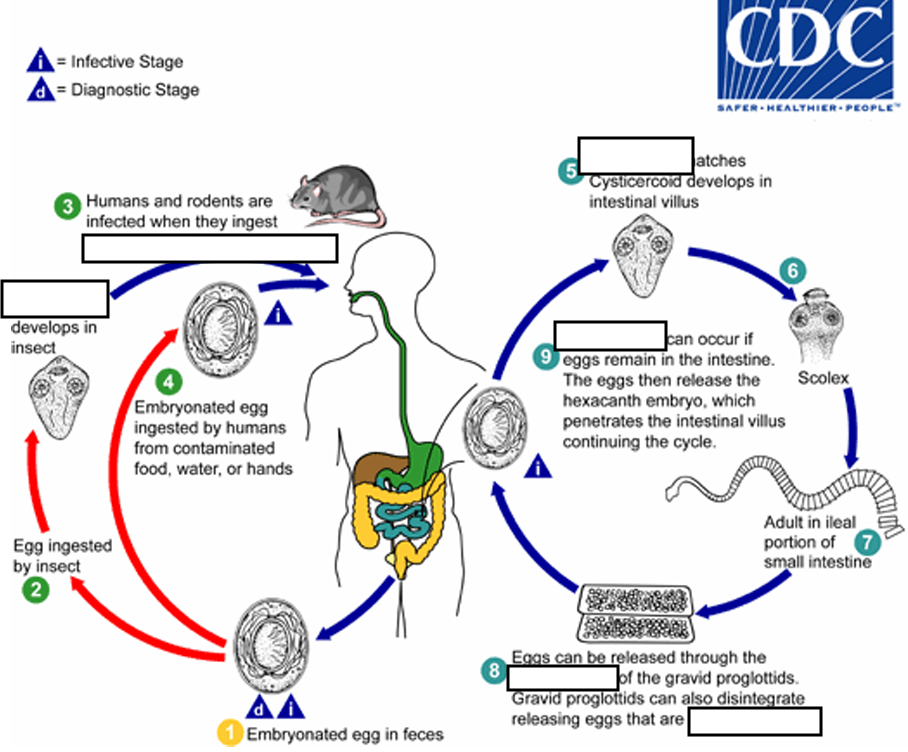
(4) The oncospheres (hexacanth larvae) penetrate the intestinal villus and ________
develop into cysticercoid larvae
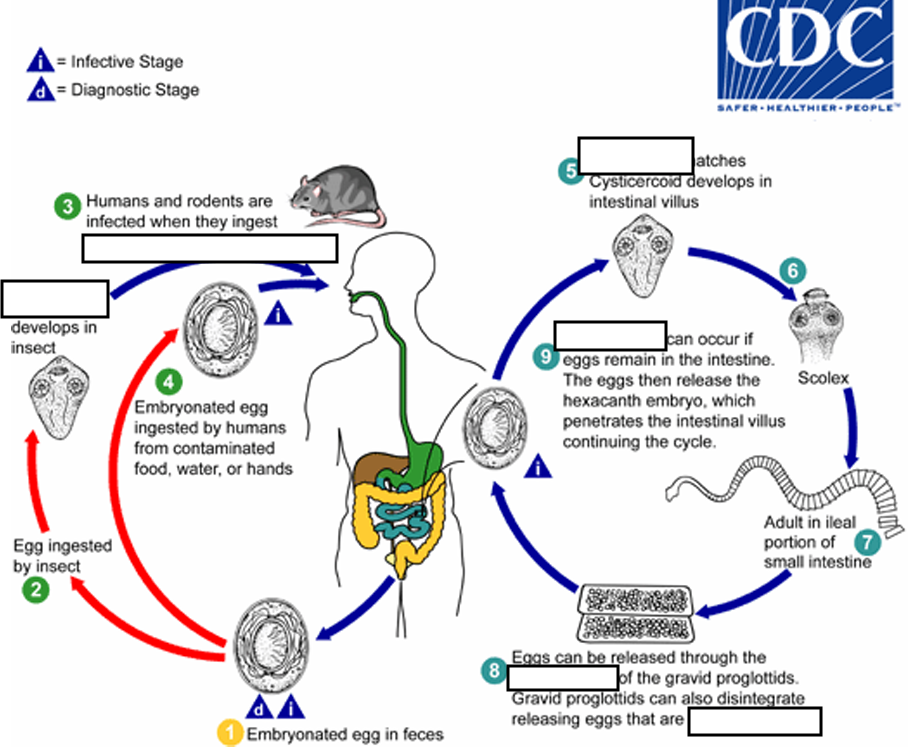
(5) Upon rupture of the villus, the cysticercoids return to the intestinal lumen, evaginate ( folds or pushes outward to form an extension, pouch, or tube.) their_____
scoleces (skolex)
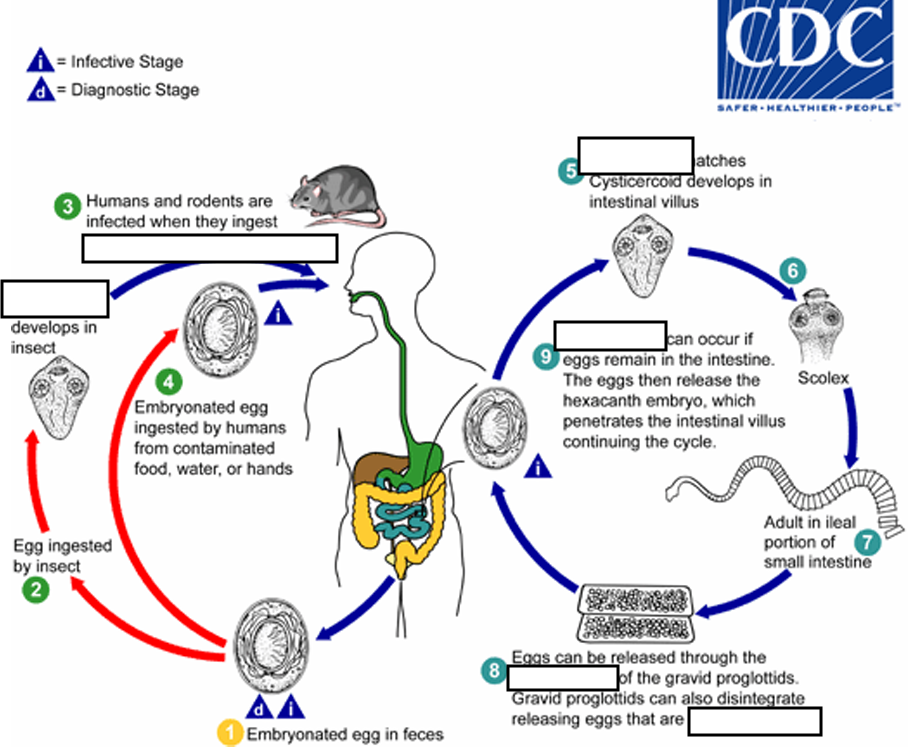
(6) attach to the intestinal mucosa and develop into adults that reside in the ileal portion of the small intestine producing _______
gravid proglottids
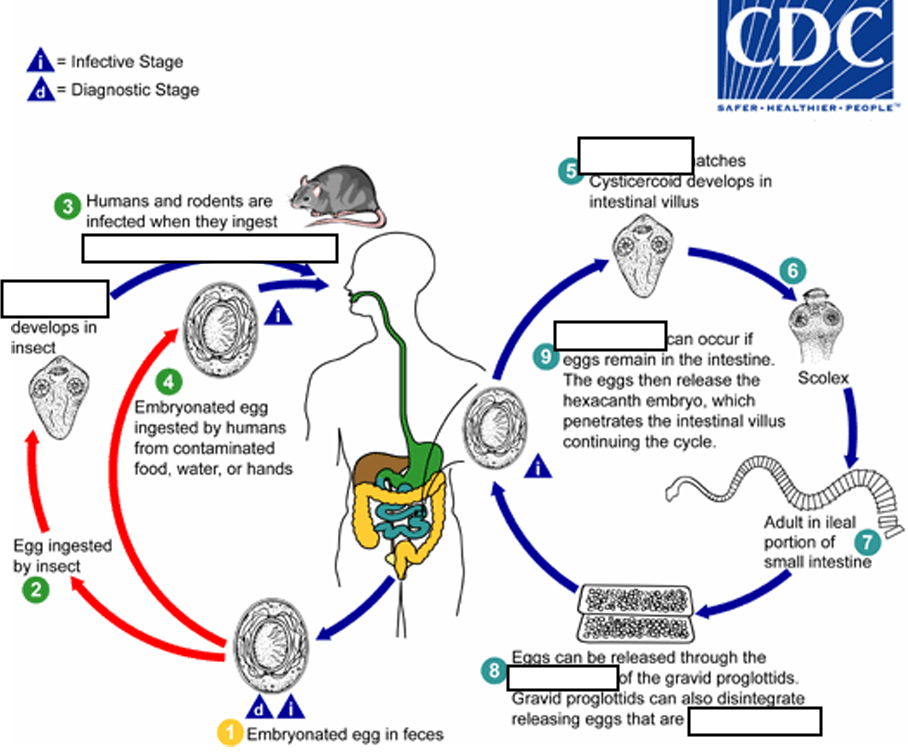
(7) Eggs are passed in the stool when released from proglottids through its ______or when proglottids disintegrate in the small intestine
genital atrium
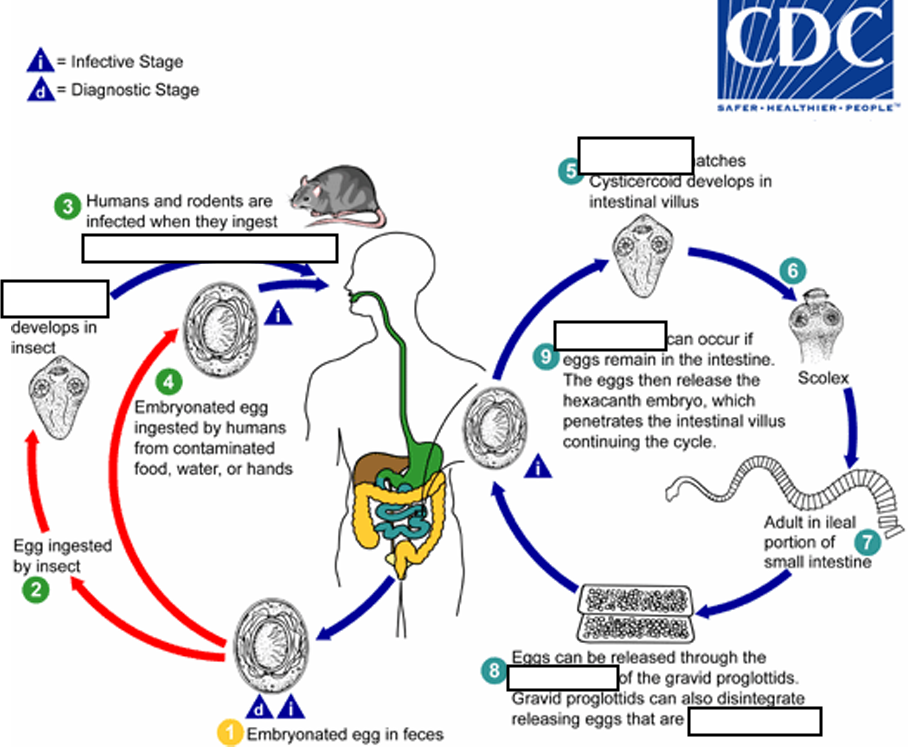
(8) An alternate mode of infection consists of internal autoinfection, where the eggs release their ______, which
penetrates the villus continuing the infective cycle without passage through the external environment
hexacanth embryo
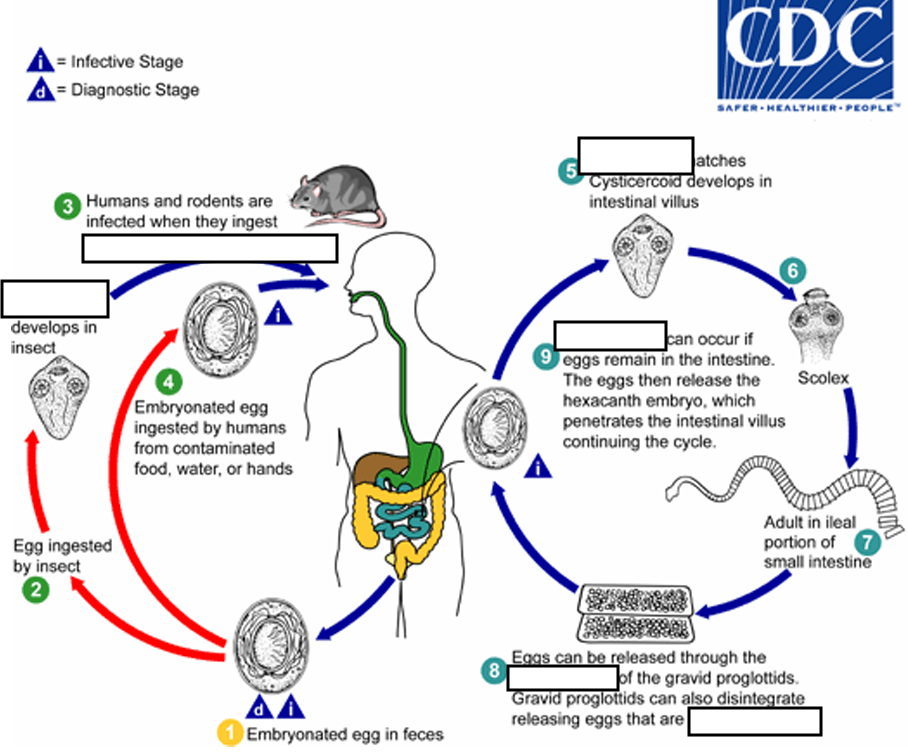
(9) The life span of adult worms is _____, but internal autoinfection allows the infection to persist for years.
4 to 6 weeks
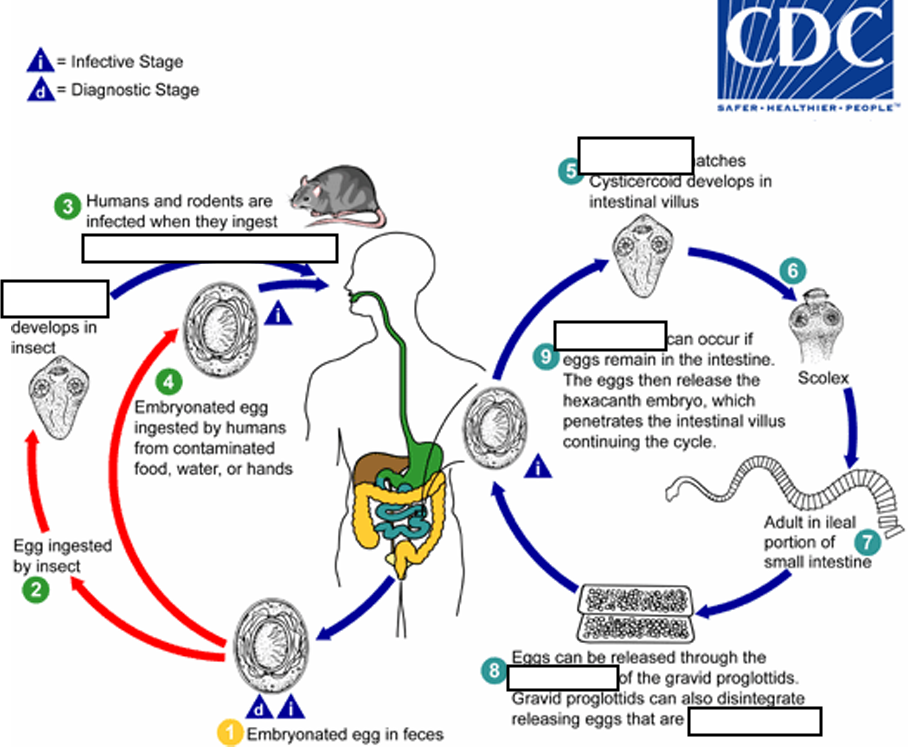
_____ Developed in insect
Cysticercoid
(3)
cysticercoid-infected arthropods.
(5)
Oncosphere
(8)
genital atrium, passed in stool
(9)
autoinfection
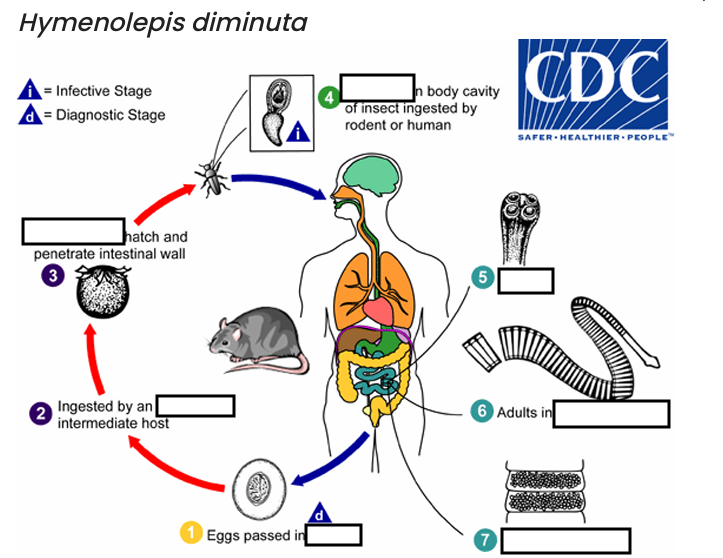
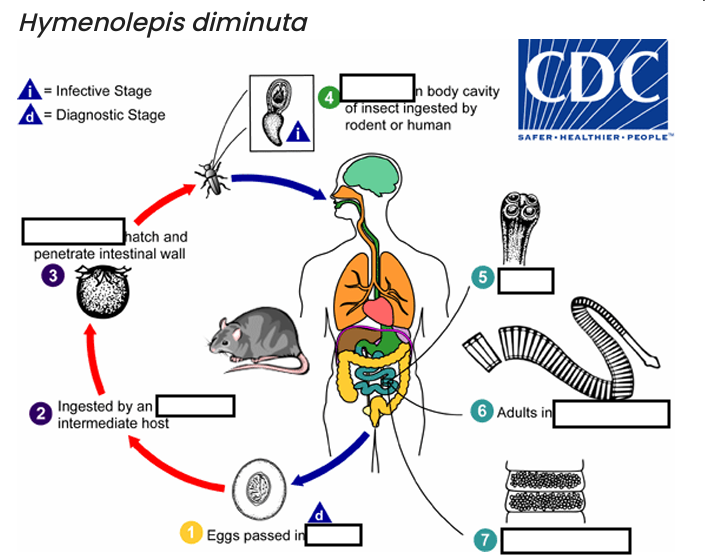
ingested by an intermediate host (various___________)
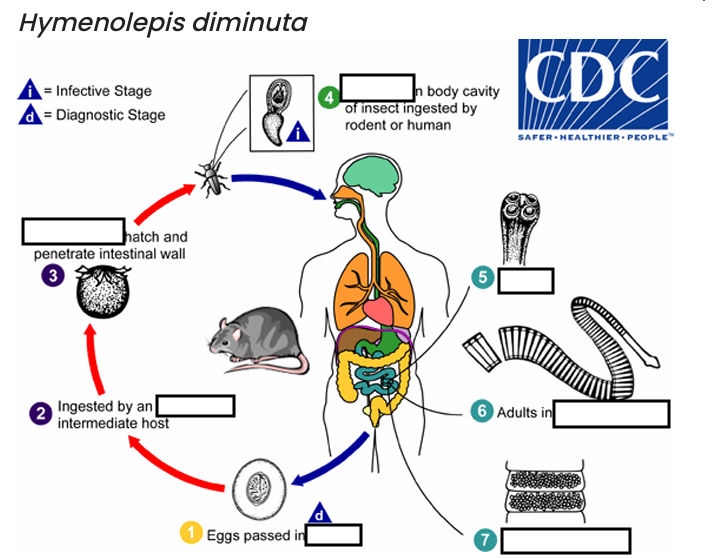
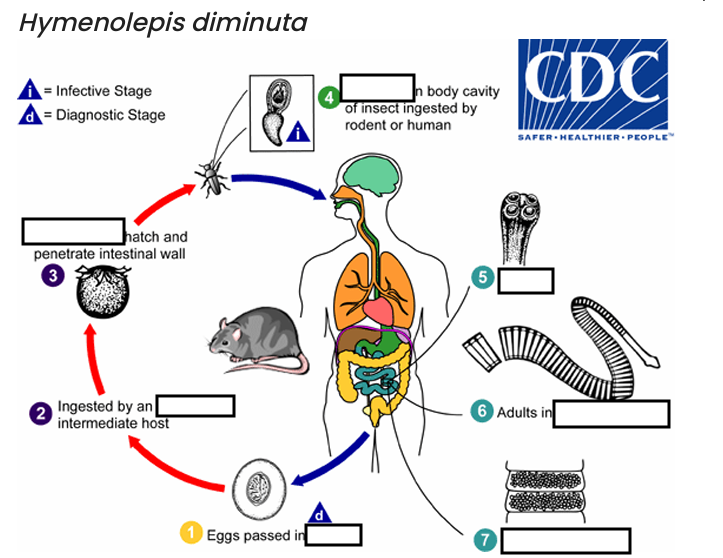
hosts for H. diminuta.
The cysticercoid larvae persist through the arthropod’s morphogenesis to adulthood. H. diminuta infection is acquired by the mammalian host after______________ carrying the cysticercoid larvae

accidentally infected through the ingestion of insects in___________, or other food items, and directly from the environment
(e.g., oral exploration of the environment by children).
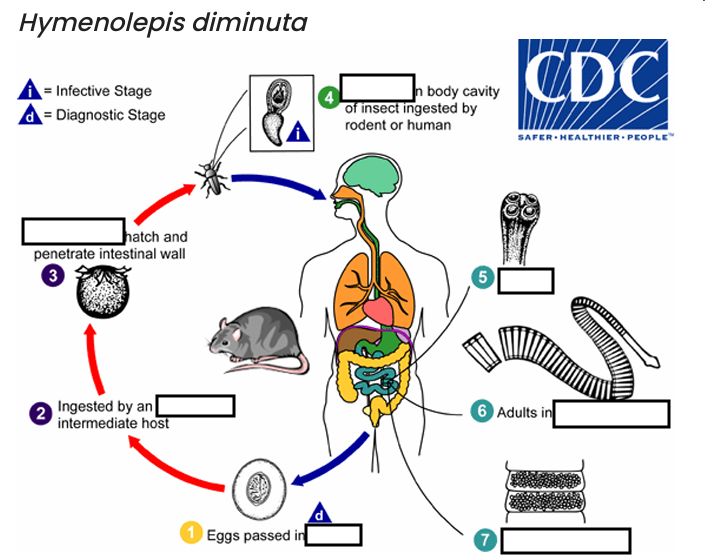
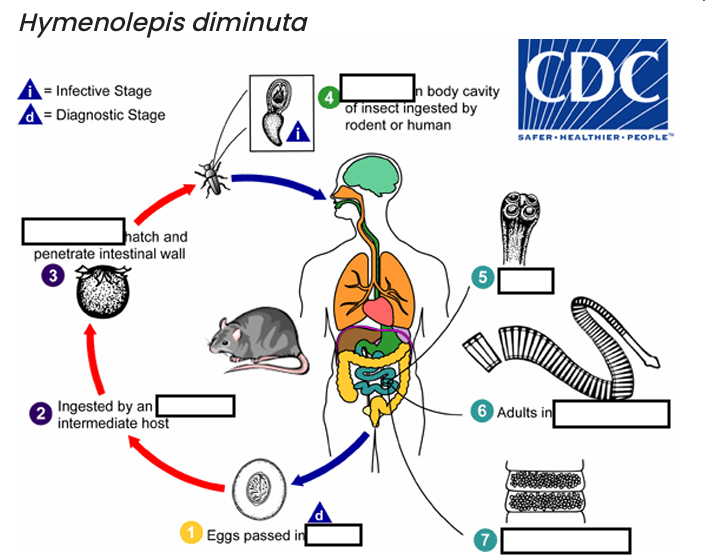
occurs shortly after the cysticercoid larvae are released.
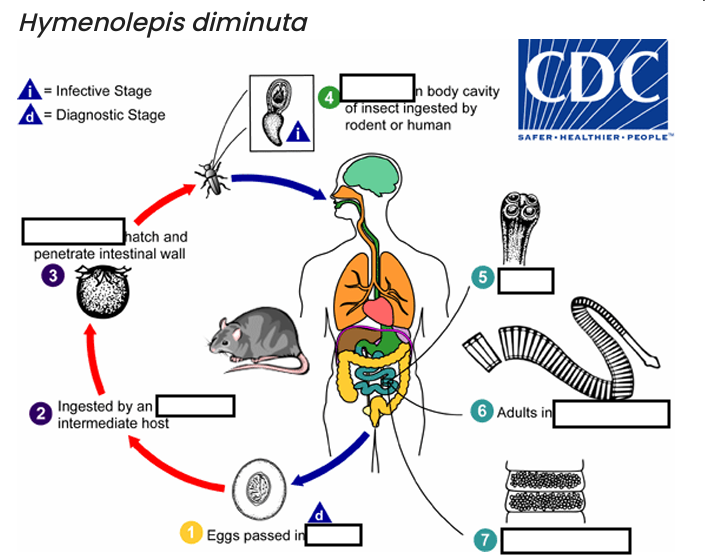

host’s feces
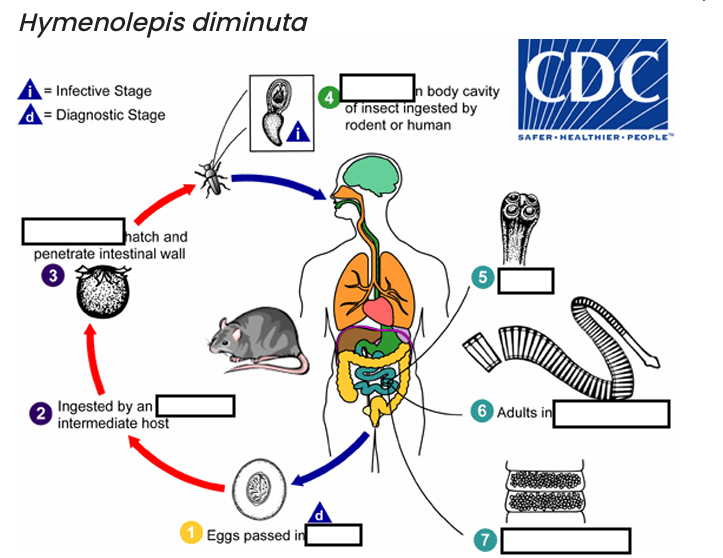
(1) diagnostic stage
feces
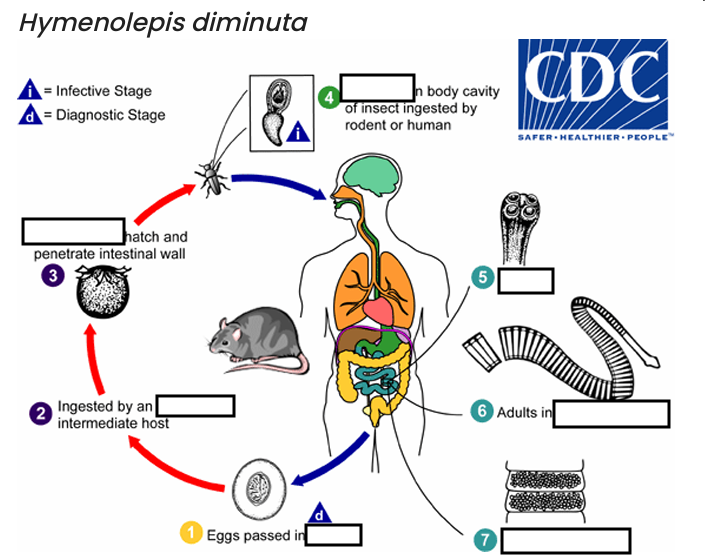
(2)
arthropod
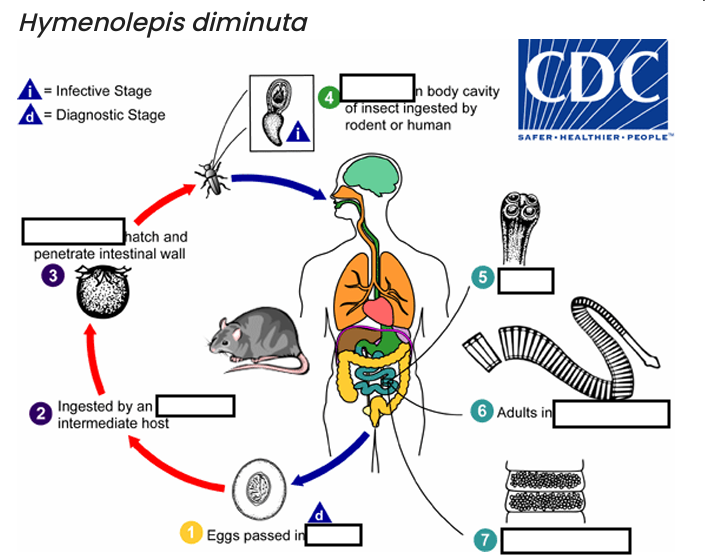
(3)
oncospheres
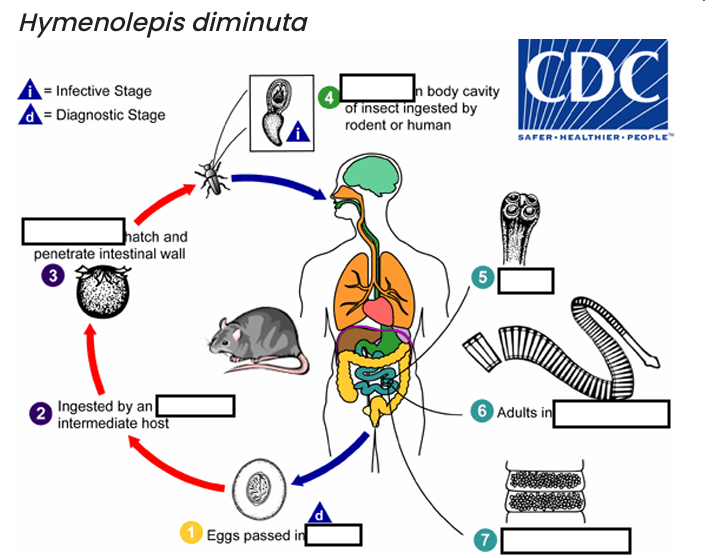
(4) Infective Stage
cysticerci
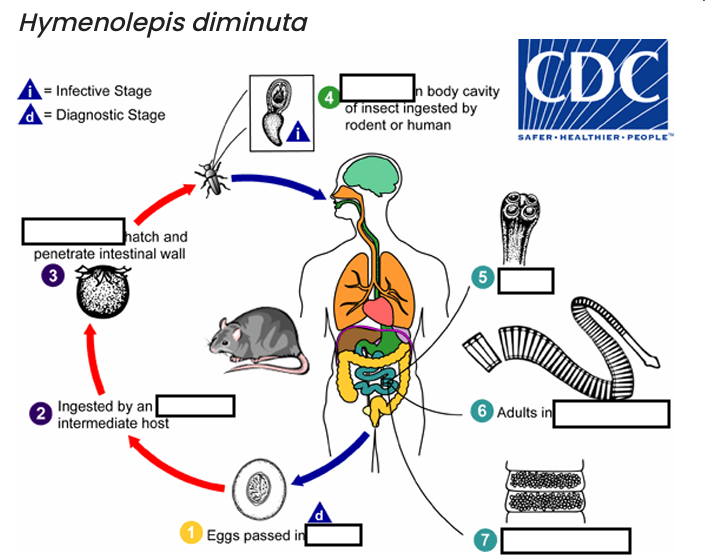
(5)
scolex
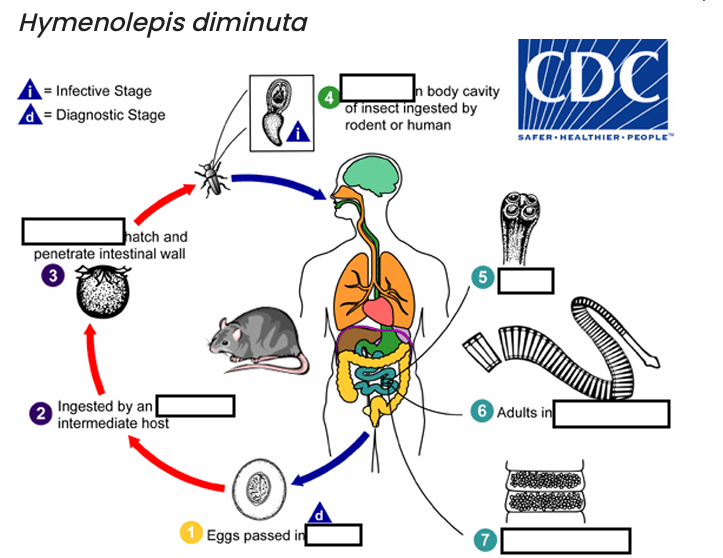
(6)
small intestine
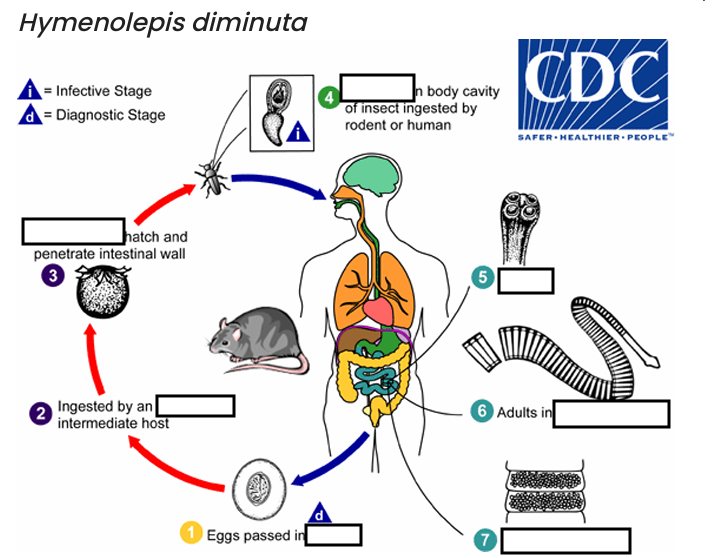
(7)
gravid proglottids
Hymenolepis nana is the most _______________, and is encountered worldwide. In temperate areas its incidence is higher in children and institutionalized groups. Hymenolepis diminuta, while less frequent, has been reported from various areas of the world
common cause of all cestode infections

Scolex of H. nana