APBio Unit 8 Ecology
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Population
a localized group of individuals of the same species that can interbreed, producing fertile offspring

Community
all the organisms that inhabit a particular area; as assemblage of populations of different species living close enough together for potential interaction

Ecosystem
all the organisms in a given area as well as the abiotic factors with which they interact

Biotic
pertaining to the living organisms in the environment

Abiotic
nonliving; referring to physical and chemical properties of an environment
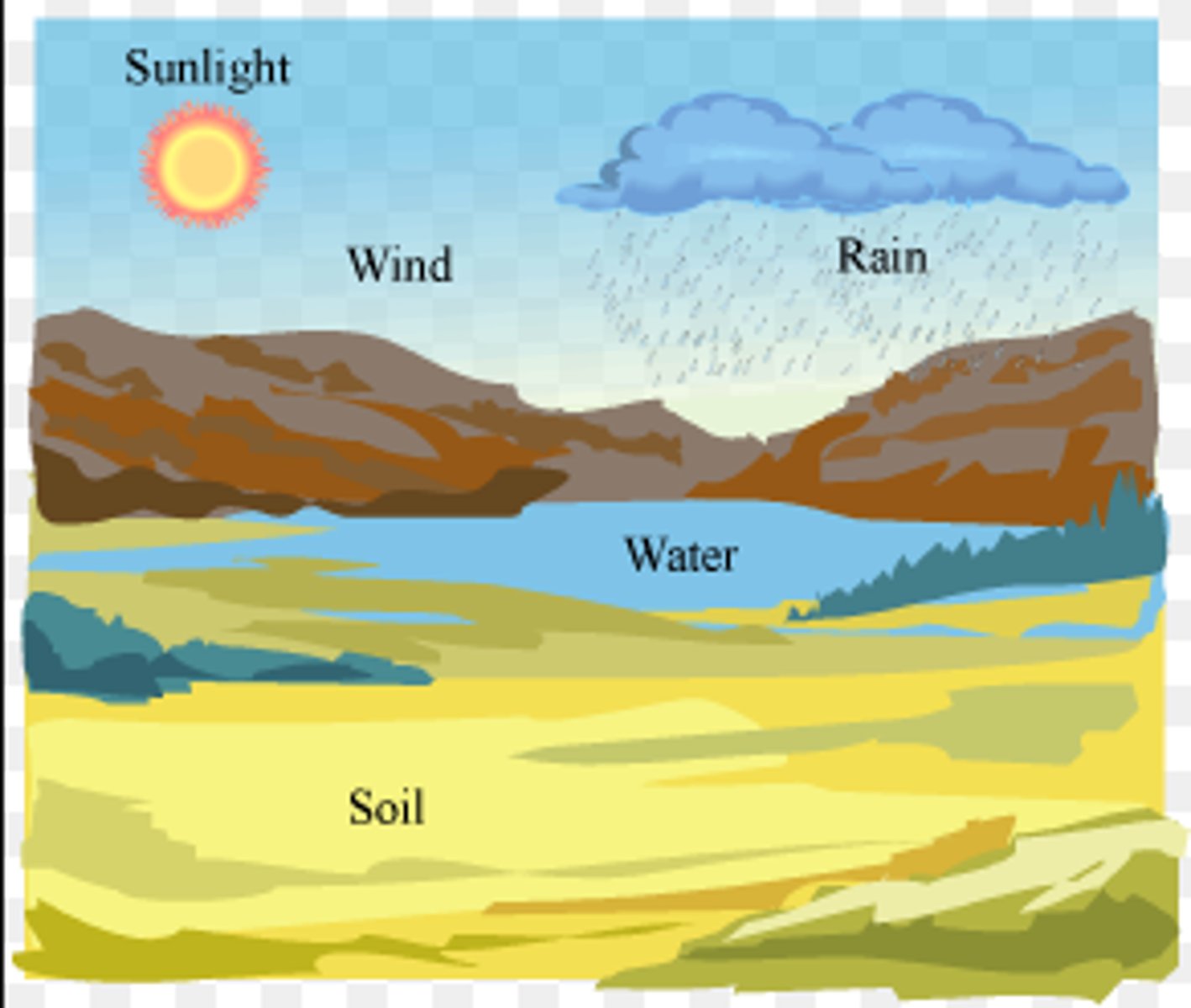
Biosphere
the entire portion of earth inhabited by life; the sum of all the planet's ecosystems
Niche
the sum of a species' use of the biotic and abiotic resources in its environment
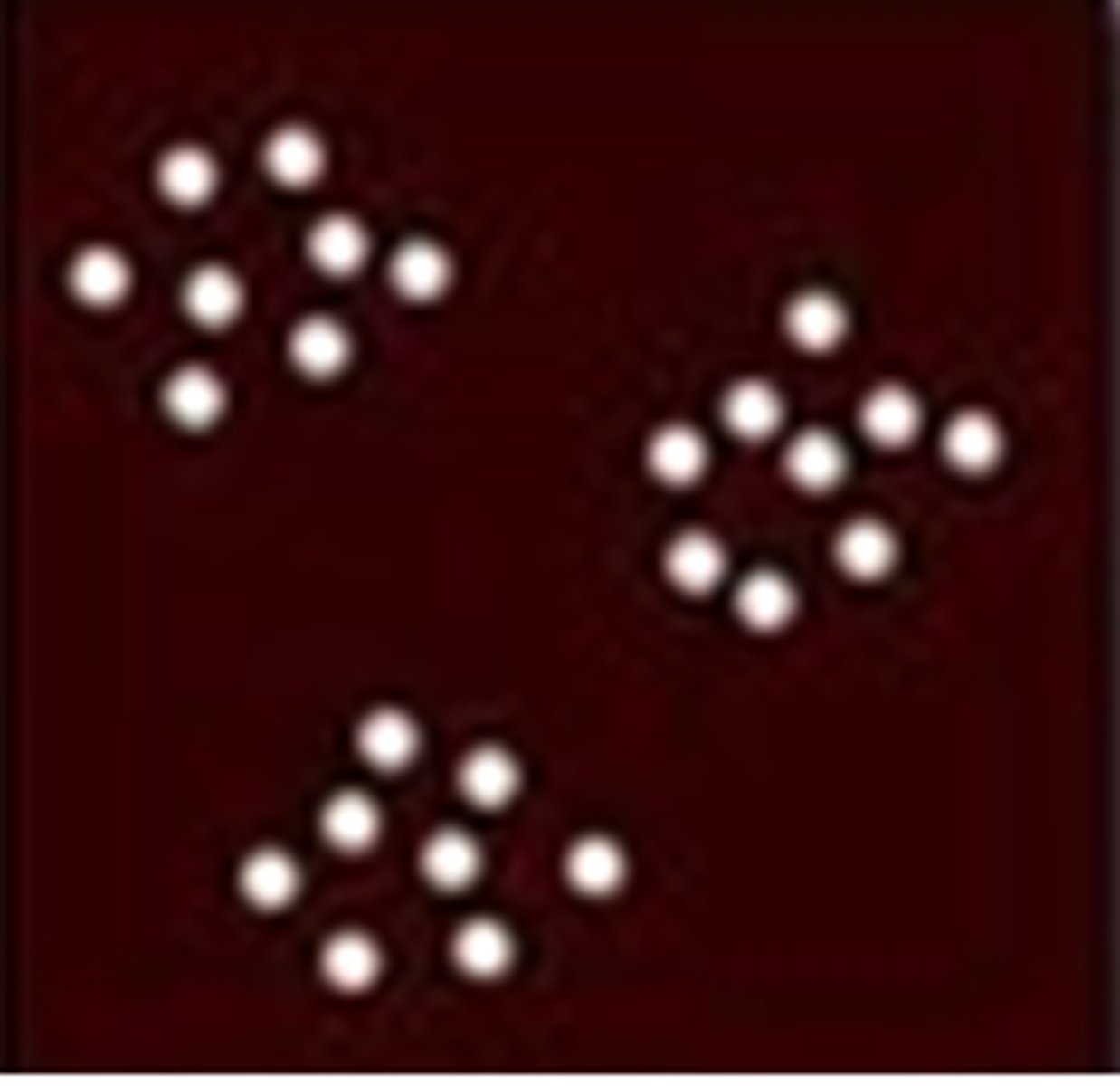
Clumped Distribution
individual aggregated patches, some organisms group together where food is abundant

Uniform Distribution
evenly spaced, some organisms maintain evenly distributed spacing to avoid aggressive interactions between neighbors
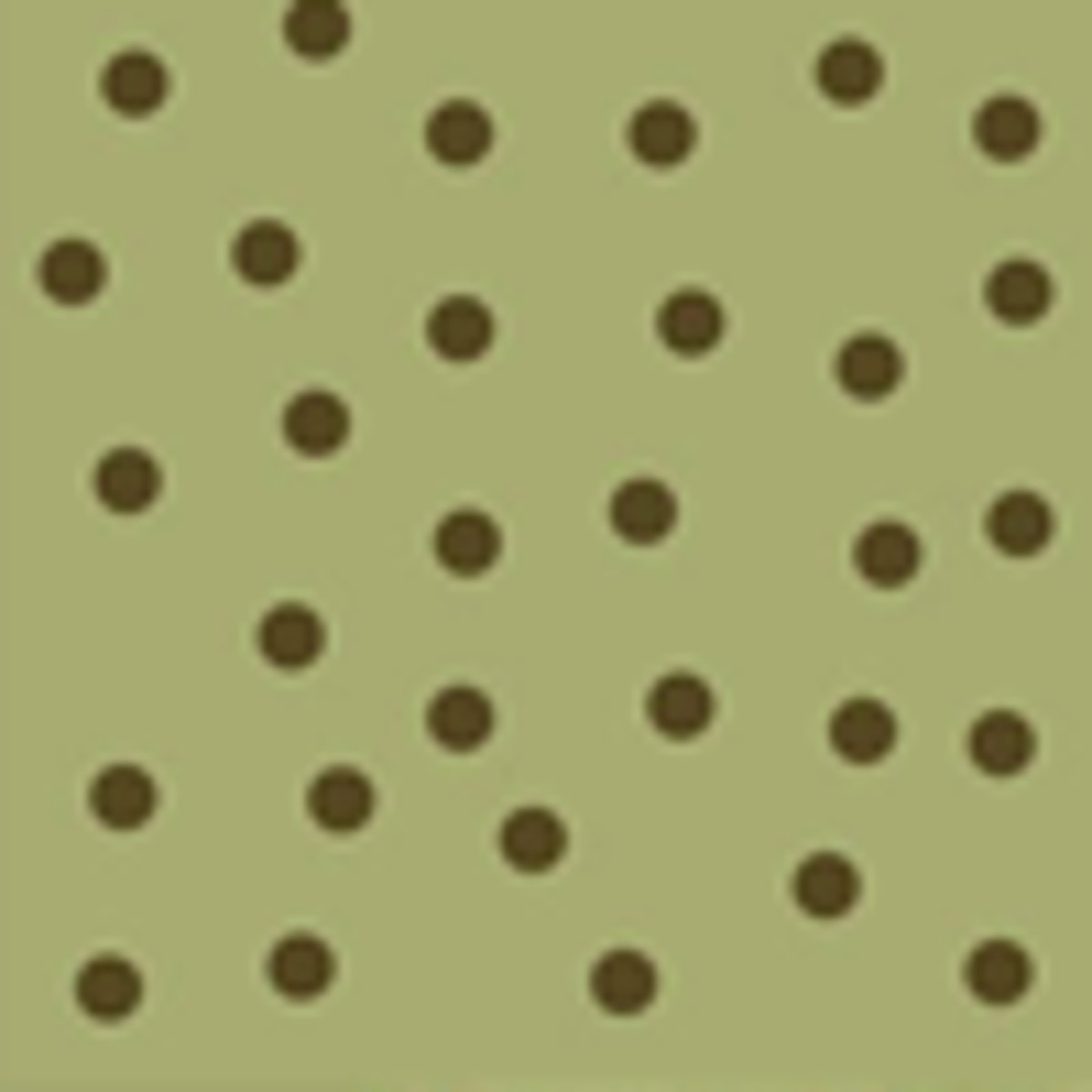

Random Distribution
unpredictable spacing, some plants grow in random groups if their seeds were windblown across an area

Population Ecology
the study of populations in relation to their environment, including environmental influences on populations, on population density and distribution, age structure, and variations in population size
Birth Rate
rate of annual birth within a population
Death Rate
rate of annual death within a population
Sex Ratio
ratio of females to males within a population
Age Structure
the relative number of individuals of each age in a population
Immigration Rate
the rate of influx of new individuals INTO a population from other areas
Emigration Rate
the rate of movement of individuals OUT of a population
Carrying Capacity
the maximum population size that can be supported by the available resources, (symbolized by K)
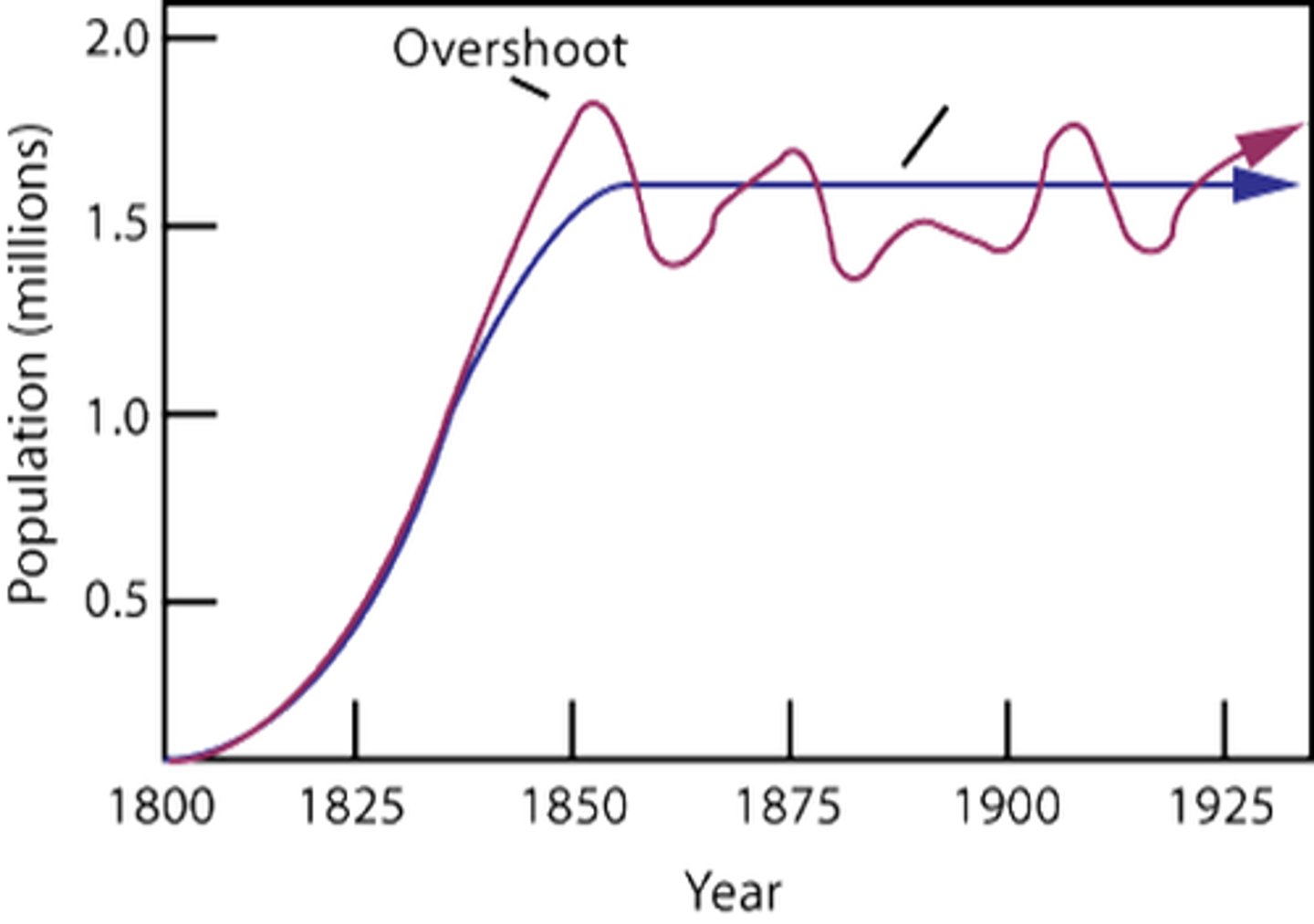
Density Dependent
any characteristic that varies according to an increase in population density
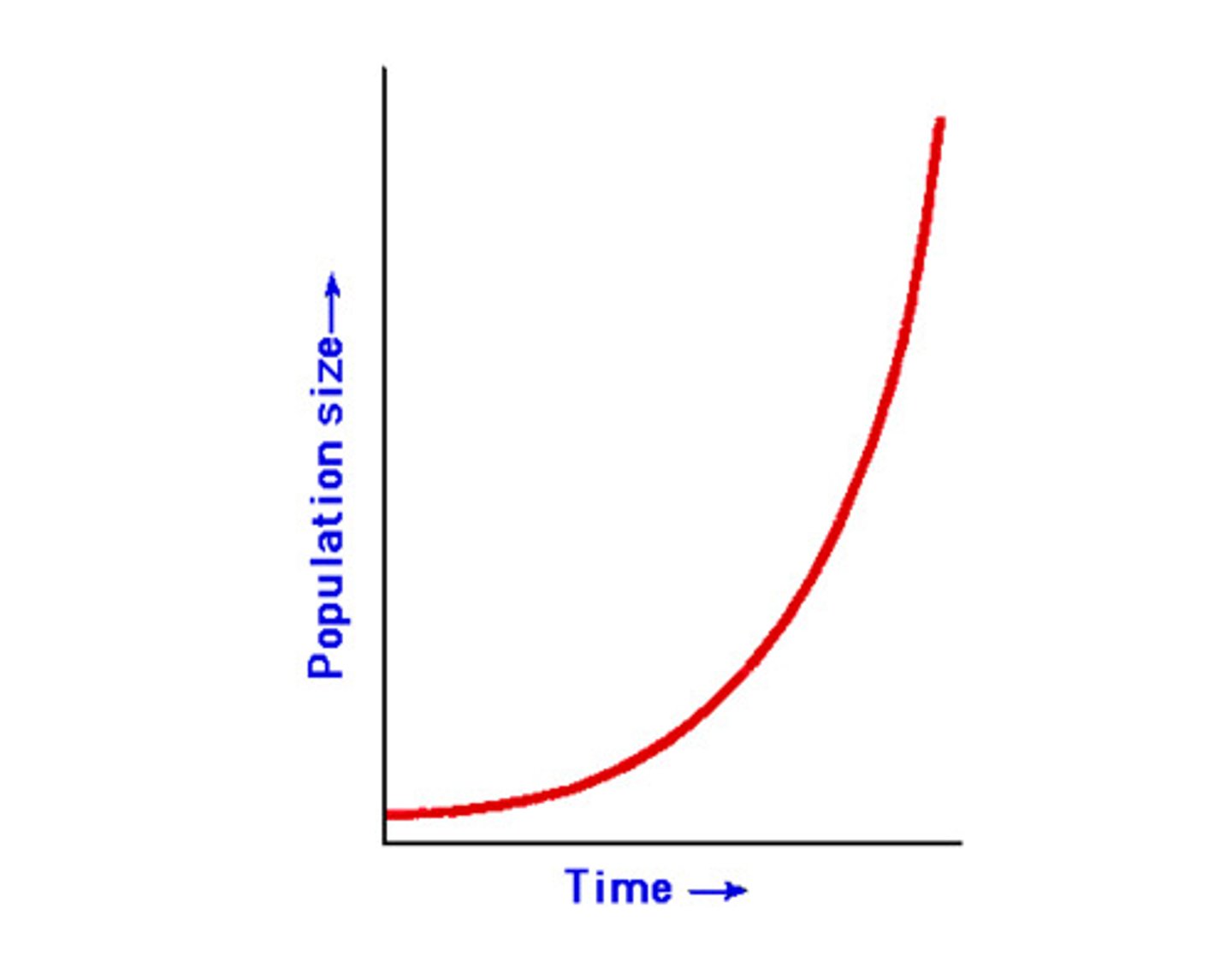
Exponential Growth
growth of a population in an ideal, unlimited environment, (represented by a J-Shaped curve when population size is plotted over time)
Logistical Growth
population growth that levels off as population size approaches carrying capacity
K-Selected
stabilize around carrying capacity, have fewer offspring later in life, mature later, live longer and invest more parental care
R-Selected
reside in unstable environment, have many offspring early in life, mature earlier, shorter life span, no parental care
Survivorship Curve
the plot of the proportion or numbers in a cohort still alive at each age
Type I Surivorship Curve
low death rates during early/middle life then increase among older age groups (humans)
Type II Surviorship Curve
constant death rate over the organism's life span
Type III Surviorship Curve
very high death rates for the young and then declines for those few individuals that survive the early period (insects)
Symbiosis
an ecological relationship between organisms of two different species that live together in direct and intimate contact
Commensalism
a symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits but the other is neither helped nor harmed
Mutualism
a symbiotic relationship in which both participants benefit
Parasitism
a symbiotic relationship in which one organism (the parasite) benefits at the expense of another (the host) by living either within or on its host
Intraspecific Competition
interactions between the same species competing for resources
Interspecific Competition
competition for resources between individuals of two or more species when resources are in short supply
Predation
an interaction between species in which one species (the predator) eats the other (the prey)
Aposematic Coloration
the bright coloration of animals with effective physical or chemical defenses that acts as a warning to predators
Batesian Mimicry
a type of mimicry in which a harmless species look like a species that is poisonous or harmful to predators
Cryptic Coloration
camouflage that makes a potential prey difficult to spot against its background
Mullerian Mimicry
a mutual mimicry by two unpalatable species
Pioneer Species
the first species to colonize previously disrupted or damaged ecosystems, beginning a chain of ecological succession that ultimately leads to a more biodiverse steady-state ecosystem
Climax Community
in a community of organisms in a specific area where ecological succession has reached a steady state
Succession
the process by which the structure of a biological community evolves over time
Primary Succession
a type of ecological succession that occurs in an area where there were originally no organisms present and where soil has not yet formed
Secondary Succession
a type of succession that occurs where an existing community has been cleared by some disturbance that leaves the soil or substance intact
Herbivore
an animal that eats mainly plants or algae
Carnivore
an animal that mainly eats other animals
Detritivore
a consumer that derives its energy and nutrients from nonliving organic material such as corpses, fallen plant material, and the wastes of living organism (a decomposer)
Food Chain
the pathway along which food energy is transferred from trophic level to trophic level, beginning with producers
Food Web
the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem
Trophic Levels
the positions organisms occupy in a food chain
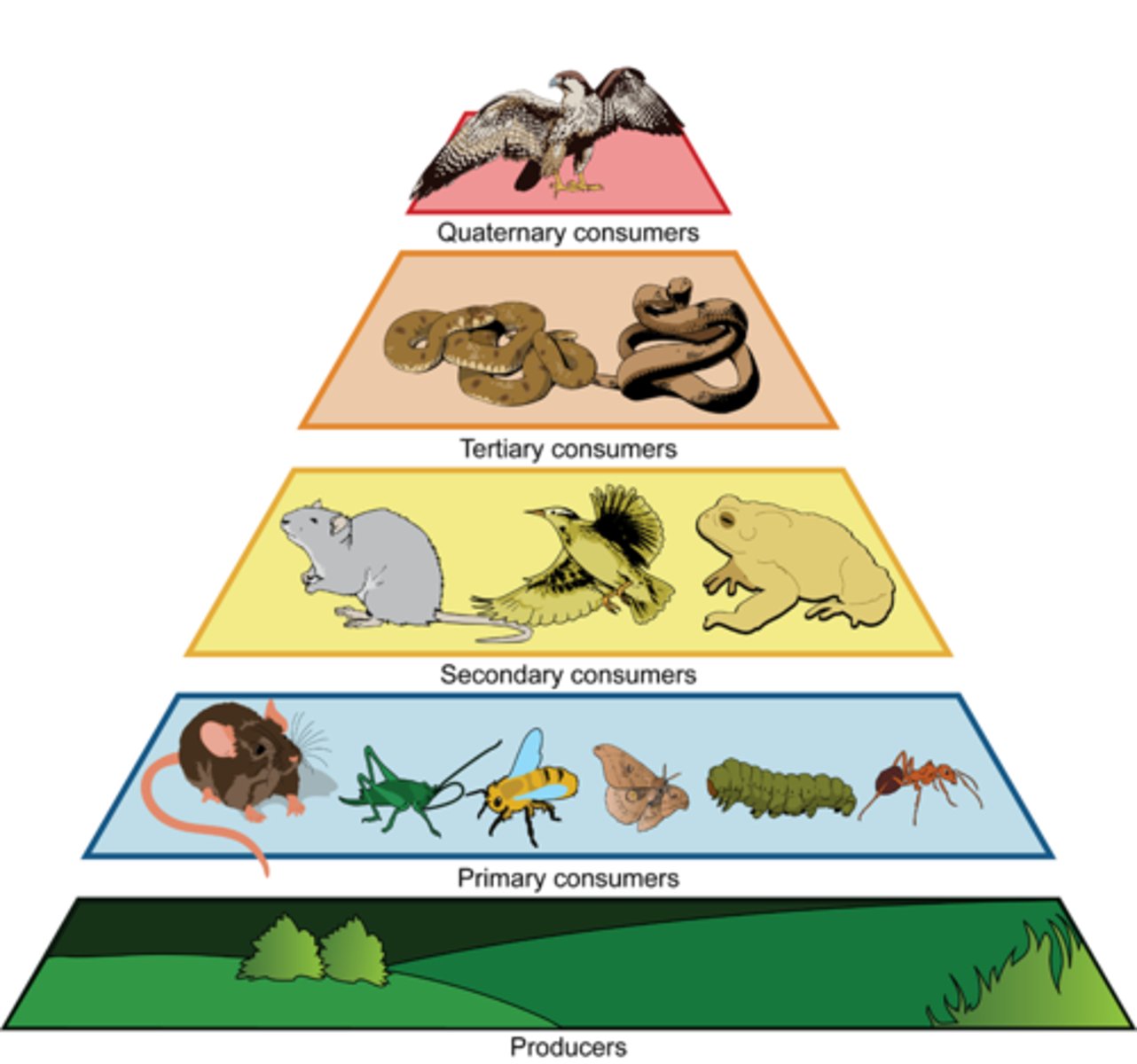
Secondary Consumer
a carnivore that eats herbivores
Primary Consumer
a herbivore; an organism that eats plants or other autotrophs
Biogeochemical Cycles
any of the various chemical cycles, which involve both biotic and abiotic components of ecosystems
Carbon Cycle
forming the framework of organic molecules, photosynthesis & cellular respiration circulate this nutrient
Phosphorus Cycle
cycling of this nutrient through geologic processes such as erosion and sedimentation
Nitrogen Cycle
this nutrient is converted to compounds that can be assimilated by plants then returned in gas form to the atmosphere; all processes rely on bacteria
Nitrogen Fixation
the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia
Water Cycle
this nutrient cycle involves evaporation from the earth & transpiration from plants and falls then by precipitation back down to the earth to begin the cycle again
Age Structure Diagrams
a visual representation of the relative number of individuals of each age in a population
Competitive Exclusion Principle
the concept that when populations of two similar species compete for the same limited resources, one population will use the resources more efficiently and have a reproductive advantage that will eventually lead to the elimination of the other population
Resource Partitioning
the division of environmental resources by coexisting species such that the niche of each species differs by one or more significant factors from the niches of all the coexisting species
Zero Population Growth (ZPG)
a period of stability in population size, when the per capita birth rate and death rate are equal
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
the total primary production of an ecosystem
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
the gross primary production of an ecosystem minus the energy used by the producers for respiration
Keystone Species
a species that is not necessarily abundant in a community yet experts strong control on community structure by the nature of its ecological role or niche
Bottom-up Model
a model of community organization in which mineral nutrients influence community organization by controlling plant or phytoplankton numbers, which in turn control herbivores, which in turn control predator numbers
Top-down Model
a model of community organization in which predation influences community organization by controlling herbivore numbers, which in turn control plant or phytoplankton numbers, which in turn control nutrient levels; also called the trophic cascade model
Biological Magnification
a process in which retained substances become more concentrated at each high trophic level in a food chain
Decomposers
organisms that absorb nutrients from nonliving organic material such as corpses, fallen plant material, the wastes of living organisms and converts them into inorganic forms; a detritivore
Eutrophication
a process by which nutrients, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, become highly concentrated in a body of water, leading to increased growth of organisms such as algae or cyanobacteria
Fundamental Niche
the niche potentially occupied by that species
Realized Niche
the portion of the fundamental niche that a species actually occupies in the environment
Invasive Species
a species often introduced by humans, that takes hold outside its native range
Altruism
behavior that increases fitness of another individual but decreases their own fitness
Kin selection
enhancing the reproductive success of one's relatives
Classical conditioning
association between neutral stimulus and natural response (ex: dogs salivating to sound of bell ringing)
Operant conditioning
trial and error learning; making associations between behavior and a reward or punishment
Communication
tactile, visual, auditory and chemical means of relaying messages to other members of ones species
Taxis
directed movement towards or away from a stimulus
Kinesis
movement in response to a stimulus that is not directional
Fixed Action Pattern
a sequence of unlearned actions that are unchangable and often carried to completion
Density dependent factor
factor that affects population based on size (disease, predation etc)
Density independent factor
factor that affect population regardless of size (weather, humans etc)
Species diversity
variety of organisms in a community
Species richness
the number of different species in a community
Relative abundance
evenness of distribution of individuals among species in a community