Cellular Innate Immunity: Inflammation and Sickness
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is inflammation? Is it beneficial or not?
Complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli between many cells, organs, and microenvironment
Beneficial: eliminate pathogens and control injury
What is purpose of inflammation?
Eliminate pathogen, trigger acquired immunity and systemic responses, minimize/ control injury
What types of events trigger inflammation?
Infections, trauma, physical/chemical injury, tissue necrosis, immune reactions
List the main pro-inflammatory cytokines that trigger acute inflammation?
IL1, IL6, TNF
What are the roles of histamine, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins in inflammation?
Lipid mediators (prostaglandins)-fever
Modified amino acid (histamine)- hypersensitivity response
Lekotrienes - lipid mediators
What are chemokines and their roles in inflammation
Proteins released by immune and non-immune cells to attract immune cells to the inflammatory sites
What are the steps involved in accumulation of neutrophils at the site of injury?
Neutrophils extravasion (rolling → adherence → emigration → blood flow → chemotaxis (attracted)
List the cardinal signs of inflammation. What is the mechanism leading to each of those cardinal signs?
Redness: increased blood flow
Heat: increased blood flow
Swelling: increased vascular permeability + neutrophil emigration
Pain: nerve damage + vasoactive molecules
Loss of function: pain and neurological reflex
What are the local effects of inflammation?
increased blood flow
Vascular permeability
Increased expression of cell adhesion cells
Inflammatory cytokine production
What is the role of the complement system in inflammation?
Releases anaphaelaxins (C5a and C3a)
What are acute phase proteins and what do they do?
Produced by liver and activates other processes to eliminate pathogen
Increased inflammatory response
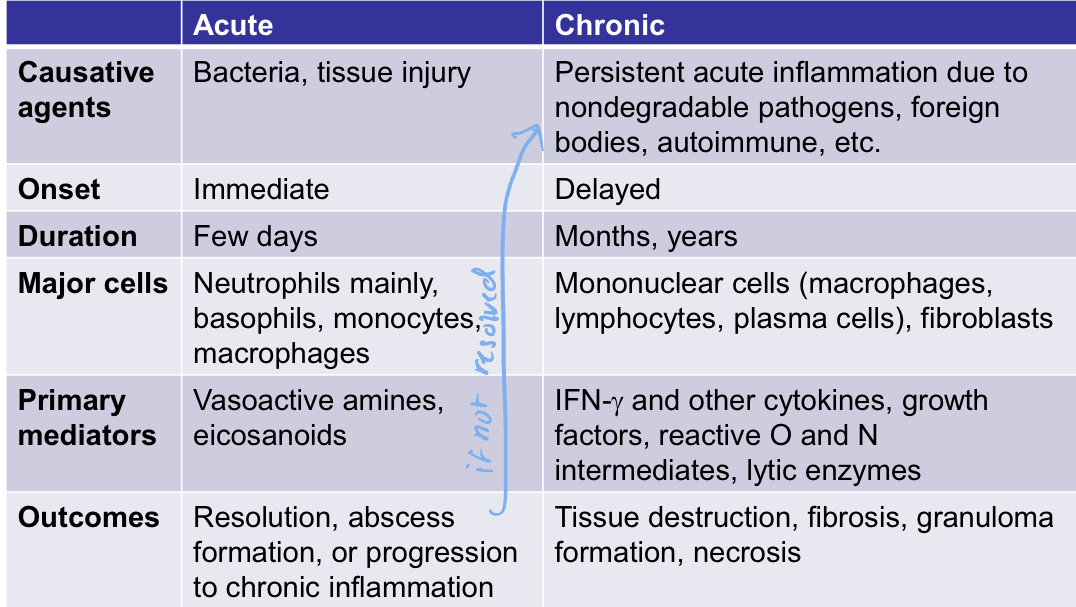
How are acute and chronic inflammation different?