Core concepts of Biochemical Engg
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Biochemical engineering
It is the link between biological sciences and chemical engineering.
Biochemical engineering
This involves conducting biological processes on an industrial scale.
Biotechnology
This involves commercial techniques that use living organisms, or substances from those organisms, to make or modify a product.
Biotechnology
This also includes techniques used for the improvement of the characteristics of economically important plants and animals and for the development of microorganisms to act on the environment.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Biotechnology is one of the oldest chemical technologies.
Use of microorganisms to ferment beverage and food
Crossbreeding of plants and animals for better yields
What are two (2) examples of old biotechnology mentioned in the module?
Recombinant DNA
Cell fusion
What are two (2) examples of modern biotechnology mentioned in the module?
Recombinant DNA
(ADDITIONAL: This is also referred to as genetic engineering.)
MODERN BIOTECHNOLOGY. Determine what is being described below.
It allows the direct manipulation of genetic material of individual cells, which may be used to develop microorganisms that produce new products as well as useful organisms.
Cell fusion
MODERN BIOTECHNOLOGY. Determine what is being described below.
It is a process to form a single hybrid cell with nuclei and cytoplasm from two different types of cells in order to combine the desirable characteristics of the two.
Pharmaceuticals
Animal agriculture
Plant agriculture
Specialty chemicals
Environmental applications
Commodity chemicals
Bioelectronics
Enumerate the seven (7) areas where biotechnology can be applied.
Pharmaceuticals
APPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY. Determine which area is being described below.
The products or applications of this area include the following: antibiotics, antigens (stimulate antibody response), endorphin (neurotransmitter), gamma globulin (prevent infections), human growth hormone (treat children with dwarfism), human serum albumin (treat physical trauma), immune regulators, insulin, interferon (treat infection), interleukins (treat infectious disease or cancer), lymphokines (modulate immune reaction), monoclonal antibody (diagnostics or drug delivery), neuroactive peptides (mimic the body’s pain controlling peptides), tissue plasminogen activator (dissolve blood clots), vaccines.
Animal agriculture
APPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY. Determine which area is being described below.
The products or applications of this area include the following: development of disease-free seed stocks healthier, higher-yielding food animals.
Plant agriculture
APPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY. Determine which area is being described below.
The products or applications of this area include the following: transfer of stress-, herbicide-, or pest-resistance traits to crop species, development of plants with the increased abilities of photosynthesis or nitrogen fixation, development of biological insecticides, and non-ice nucleating bacterium.
Specialty chemicals
APPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY. Determine which area is being described below.
The products or applications of this area include the following: amino acids, enzymes, vitamins, lipids, hydroxylated aromatics, biopolymers.
Environmental applications
APPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY. Determine which area is being described below.
The products or applications of this area include the following: mineral leaching, metal concentration, pollution control, toxic waste degradation, and enhanced oil recovery.
Commodity chemicals
APPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY. Determine which area is being described below.
The products or applications of this area include the following: acetic acid, acetone, butanol, ethanol, and many other products from biomass conversion processes.
Bioelectronics
APPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY. Determine which area is being described below.
The products or applications of this area include the following: biosensors and biochips.
To obtain the best biological catalyst for a desired process.
To create the best possible environment for the catalyst to perform by designing the bioreactor and operating it in the most efficient way
To separate the desired products from the reaction mixture in the most economical way
Enumerate the roles of a biochemical engineer.
Mild reaction conditions
Specificity
Effectiveness
Renewable resources
Recombinant DNA technology
Enumerate the five (5) advantages of biochemical engineering mentioned in the module.
True
(ADDITIONAL: As a result of these conditions, the operation is less hazardous, and the manufacturing facilities are less complex, compared to typical chemical processes.)
TRUE OR FALSE. In biochemical engineering, the typical condition is at room temperature, atmospheric pressure, and fairly neutral to medium pH.
False
(EXPLANATION: Enzymes used are highly specific and catalyzes one or a small number of chemical reactions.)
TRUE OR FALSE. In biochemical engineering, enzymes used are not specific, so biochemical engineers have to choose between a variety of enzymes that can also catalyze a very wide range of reactions.
True
(ADDITIONAL: A small amount of enzyme is required to produce the desired effect.)
TRUE OR FALSE. The rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is usually much faster than that of the same reaction when directed by non-biological catalysts.
Biomass
What is the major raw material in biochemical engineering processes?
Complex product mixtures
Dilute aqueous environments
Contamination
Variability
Enumerate the four (4) disadvantages of biochemical engineering mentioned in the module.
Plants
Animals
Microorganisms
Enumerate the three (3) sources of enzymes.
Multicellular
Eukaryotes are ___ living organisms.
Unicellular
Prokaryotes are ___ living organisms.
Animals and plants
Which two main groups are multicellular organisms divided into?
Eukaryotic cells
What type of cells do animals and plants have?
Algae
Protozoa
Fungi
Molds
Yeasts
Enumerate the five (5) types of unicellular protists listed in the module.
Unicellular prokaryote
What type of organism is bacteria classified as?
Prokaryotic cell
TWO BROAD CATEGORIES OF CELLS. Determine which is being described below.
It is found in two microbial group: bacteria and blue-green algae.
Prokaryotic cell
TWO BROAD CATEGORIES OF CELLS. Determine which is being described below.
This cell is small and simple, not compartmentalized by unit membrane systems.
Eukaryotic cell
TWO BROAD CATEGORIES OF CELLS. Determine which is being described below.
It is the unit structure in plants, animals, protozoa, fungi, and algae.
Eukaryotic cell
TWO BROAD CATEGORIES OF CELLS. Determine which is being described below.
It has internal unit membrane systems that segregate many of the functional components of the cell.
Cytoplasm, nuclear region
Prokaryotic cells have only two (2) structurally distinguishable internal regions. What are these two (2)?
Cytoplasm
In prokaryotic cells, it has grainy dark spots as a result of its content of ribosomes, which are composed of protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Ribosomes
In prokaryotic cells, the cytoplasm consists of ___, which are composed of protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA)
In prokaryotic cells, the cytoplasm consists of ribosomes, which are composed of ___ and ___.
Ribosome
In prokaryotic cells, it is the site of important biochemical reactions for protein synthesis.
Nuclear region
In prokaryotic cells, the ___ is of irregular shape, sharply segregated even though it is not bounded by a membrane.
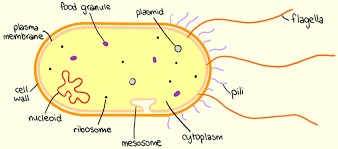
PROKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE.
PROKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE.
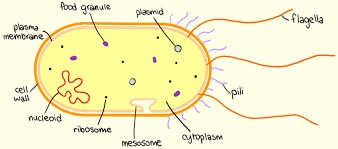
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
In prokaryotic cells, the nuclear region contains ___, which contains genetic information.
Cell wall; cell membrane
The prokaryotic cell is surrounded with a ___ and a ___.
Cell wall
(ADDITIONAL: The cell wall protects the cell from external influences.)
In prokaryotic cells, which is thicker: cell wall or cell membrane?
Cell membrane or cytoplasmic membrane
In prokaryotic cells, it is a selective barrier between the interior of the cell and the external environment.
DNA fragments and low molecular weight proteins
In prokaryotic cells, what are the largest known molecules known to cross their cell membrane?
True
TRUE OR FALSE. In prokaryotic cells, the cell membrane can be folded and extended into the cytoplasm or internal membranes.
Cell membrane
In prokaryotic cells, it serves as the surface onto which other cell substances attach and upon which many important cell functions take place.
False
(EXPLANATION: Eukaryotic cells are more complex and 1,000 to 10,000 times larger than prokaryotic cells.)
TRUE OR FALSE. Prokaryotic cells are more complex and 1,000 to 10,000 times larger than eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
In eukaryotic cells, it is surrounded by a double membrane with pores 40 to 70 micrometers wide, containing cytologically distinguishable chromosomes.
Nucleus
In eukaryotic cells, it controls hereditary properties and all vital activities of the cell.
False
(EXPLANATION: In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane.)
TRUE OR FALSE. In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus is surrounded by a single membrane.
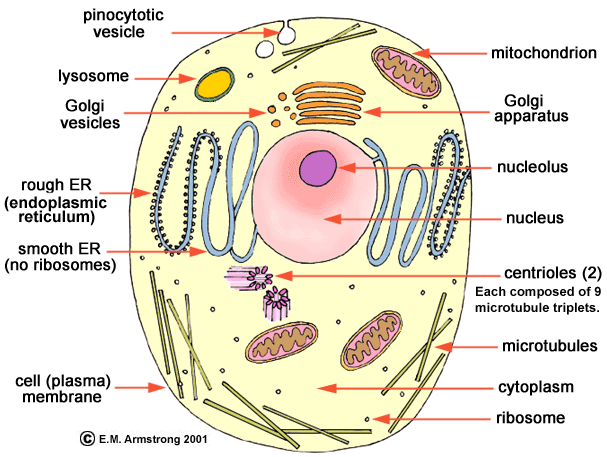
EXAMPLE OF AN EUKARYOTIC CELL.
EXAMPLE OF AN EUKARYOTIC CELL.
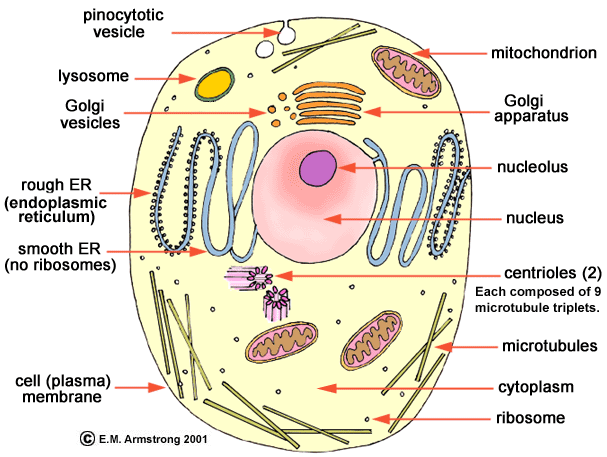
Chromosomes
In eukaryotic cells, these are long and threadlike bodies and are found in the nuclei of cells, which contains the genes arranged in linear sequence.
True
(ADDITIONAL: In both cells, the cytoplasm contains ribosomes, which are involved in continuous reactions to synthesize cell materials.)
TRUE OR FALSE. Cytoplasm is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Endoplasmic reticulum
In eukaryotic cells, the ribosomes is especially concentrated along the rough surface of the ___.
Mitochondria
In eukaryotic cells, it contains the electron transport enzymes that utilize oxygen in the process of energy generation.
Vacuole and lysosomes
In eukaryotic cells, these are organelles that serve to isolate various chemical reactions in a cell.
High molecular weight polymeric compounds (Proteins, nucleic acid, polysaccharides, lipids, and other storage materials)
Inorganic salts
Metabolic intermediates (pyruvate, acetate)
Vitamins
Cells are composed of (4):
50% carbon
20% oxygen
14% nitrogen
8% hydrogen
3% phosphorus
1% sulfur
small amounts of K, Na, Ca, Mg, Cl, vitamins
Typical cells are composed of elements such as (7):
True
(EXPLANATION: Cellular macromolecules like proteins and nucleic acids can only carry out their specific biological functions when they are folded or arranged into the correct three-dimensional shape. If this structure is altered (misfolded or denatured), they lose their function.)
TRUE OR FALSE. The cellular macromolecules are functional only when in the proper three-dimensional configuration.
READ.
Each macromolecule is part of an intracellular organelle and functions in its unique microenvironment.
Information transfer from one organelle to another (ex.: from nucleus to ribosomes) is mediated by special molecules (ex.: messenger RNA).
Most of the enzymes and metabolic intermediates are present in cytoplasm. However, other organelles, such as mitochondria, contain enzymes and other metabolites.
READ.
Each macromolecule is part of an intracellular organelle and functions in its unique microenvironment.
Information transfer from one organelle to another (ex.: from nucleus to ribosomes) is mediated by special molecules (ex.: messenger RNA).
Most of the enzymes and metabolic intermediates are present in cytoplasm. However, other organelles, such as mitochondria, contain enzymes and other metabolites.
False
(EXPLANATION: These reactions are interrelated and are controlled in a complicated fashion. These reactions are also called as metabolic pathways.)
TRUE OR FALSE. A living cell can be visualized as a very complex reactor in which more than 2,000 reactions take place. These reactions are not related with each other.
Proteins
These are the most abundant organic molecules in living cells.
40% to 70%
Proteins are ___ to ___ of the cells’ dry weight.
Proteins
These are polymers built from animo acid monomers.
READ.
Proteins have typical molecular weights of 6,000 to several hundred thousand.
Proteins can be structural, catalytic, transport, regulatory, or protective.
READ.
Proteins have typical molecular weights of 6,000 to several hundred thousand.
Proteins can be structural, catalytic, transport, regulatory, or protective.
Amino acids
These are the building blocks of proteins.
20 common amino acids
How many common amino acids are there?
R-group attached to the alpha-carbon
Amino acids are named on the basis of the ___.
READ
Amino acids are optically active and occur in two isomeric forms.
Amino acids contain at least one carboxyl group and one alpha-amino group. They differ from each other in the structure of their R groups or side chains.
READ
Amino acids are optically active and occur in two isomeric forms.
Amino acids contain at least one carboxyl group and one alpha-amino group. They differ from each other in the structure of their R groups or side chains.
False
(EXPLANATION: Only L-amino acids are found in proteins.)
TRUE OR FALSE. Only D-amino acids are found in proteins.
READ.
At low pH, the acidic group is neutral.
At high pH, the acidic group is negatively charged.
At intermediate pH, an amino acid has positively and negatively charged groups.
READ.
At low pH, the acidic group is neutral.
At high pH, the acidic group is negatively charged.
At intermediate pH, an amino acid has positively and negatively charged groups.
Zwitterion
At intermediate pH, an amino acid is referred to as ___.
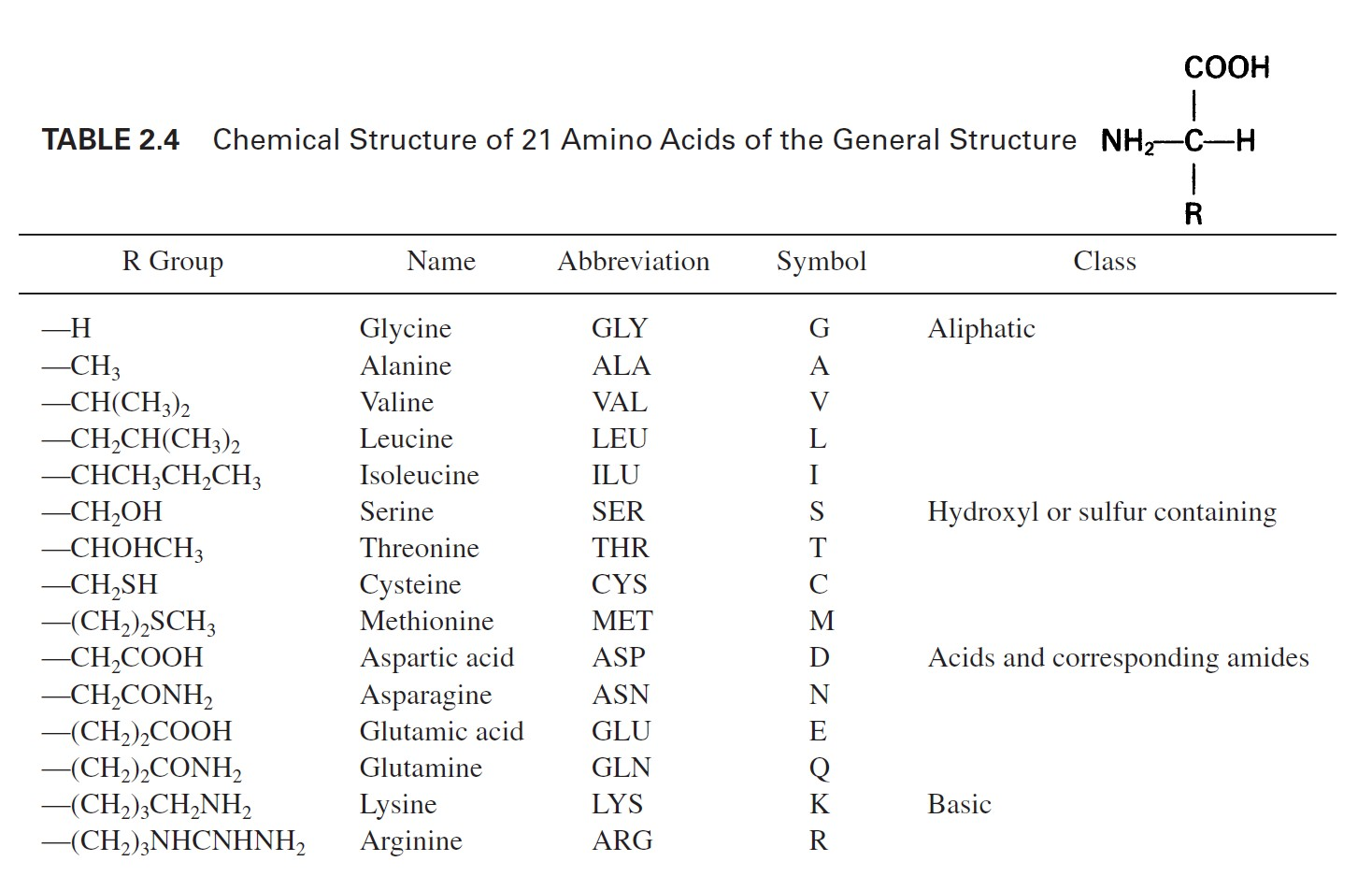
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
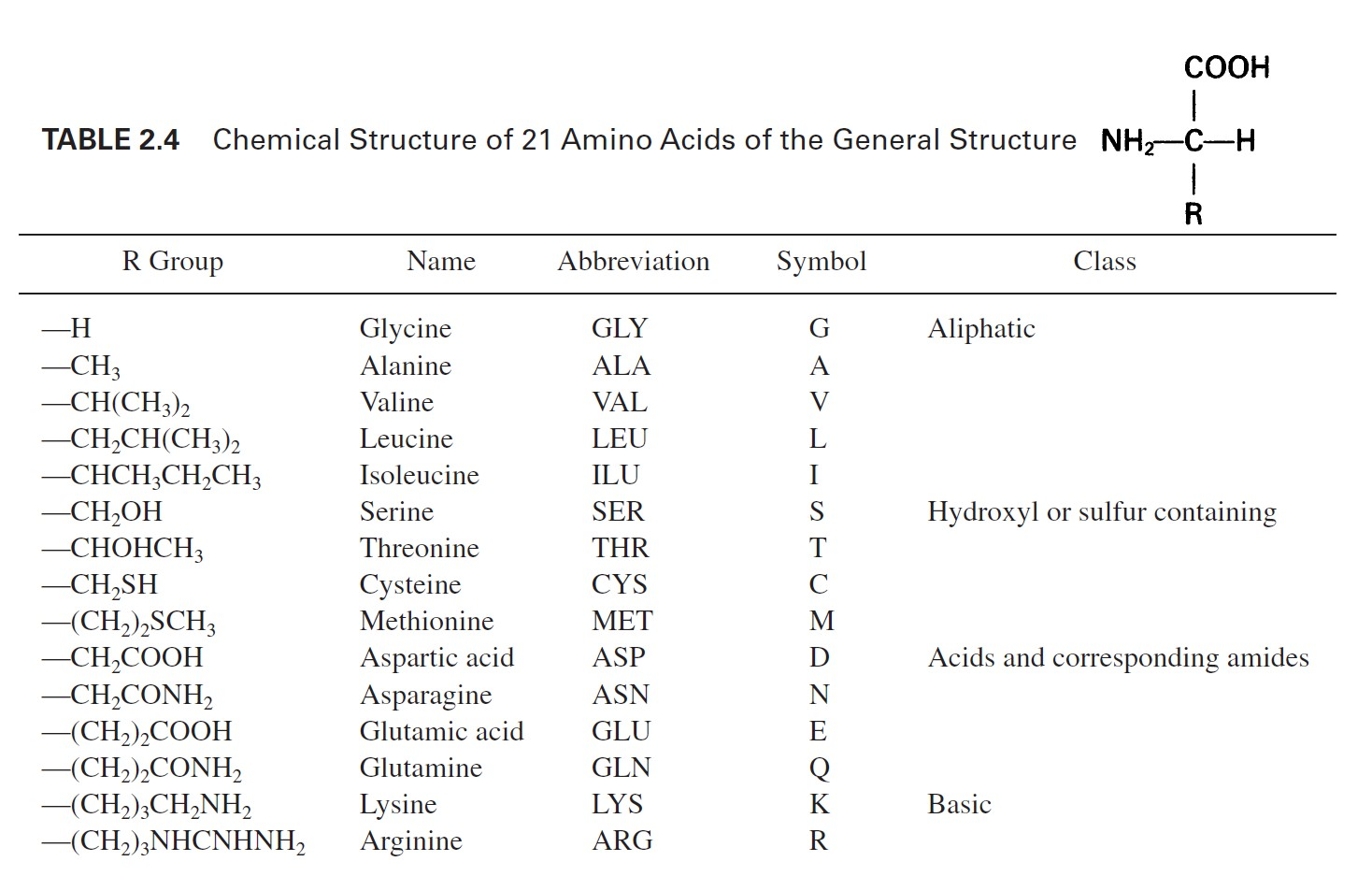
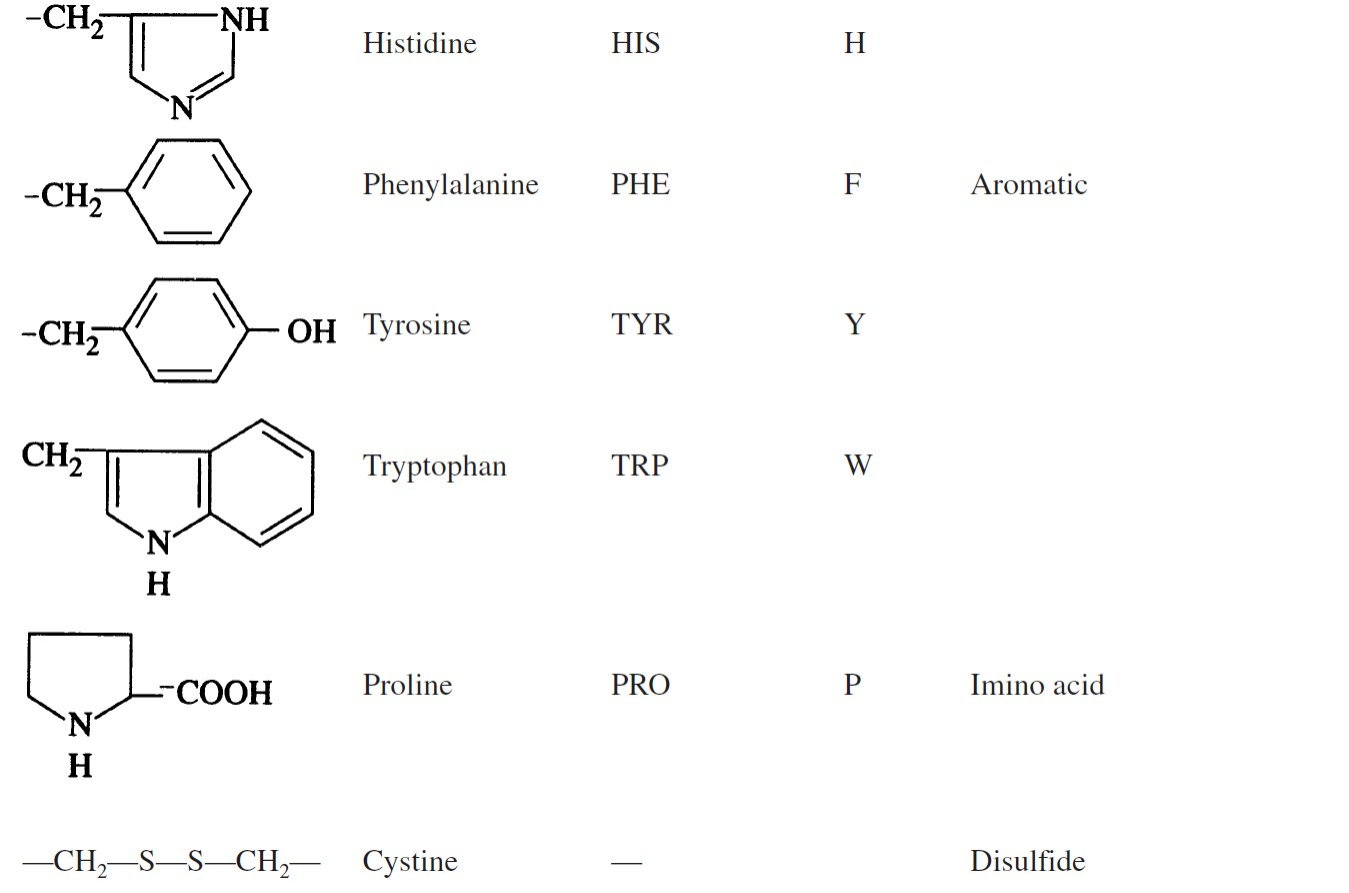
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
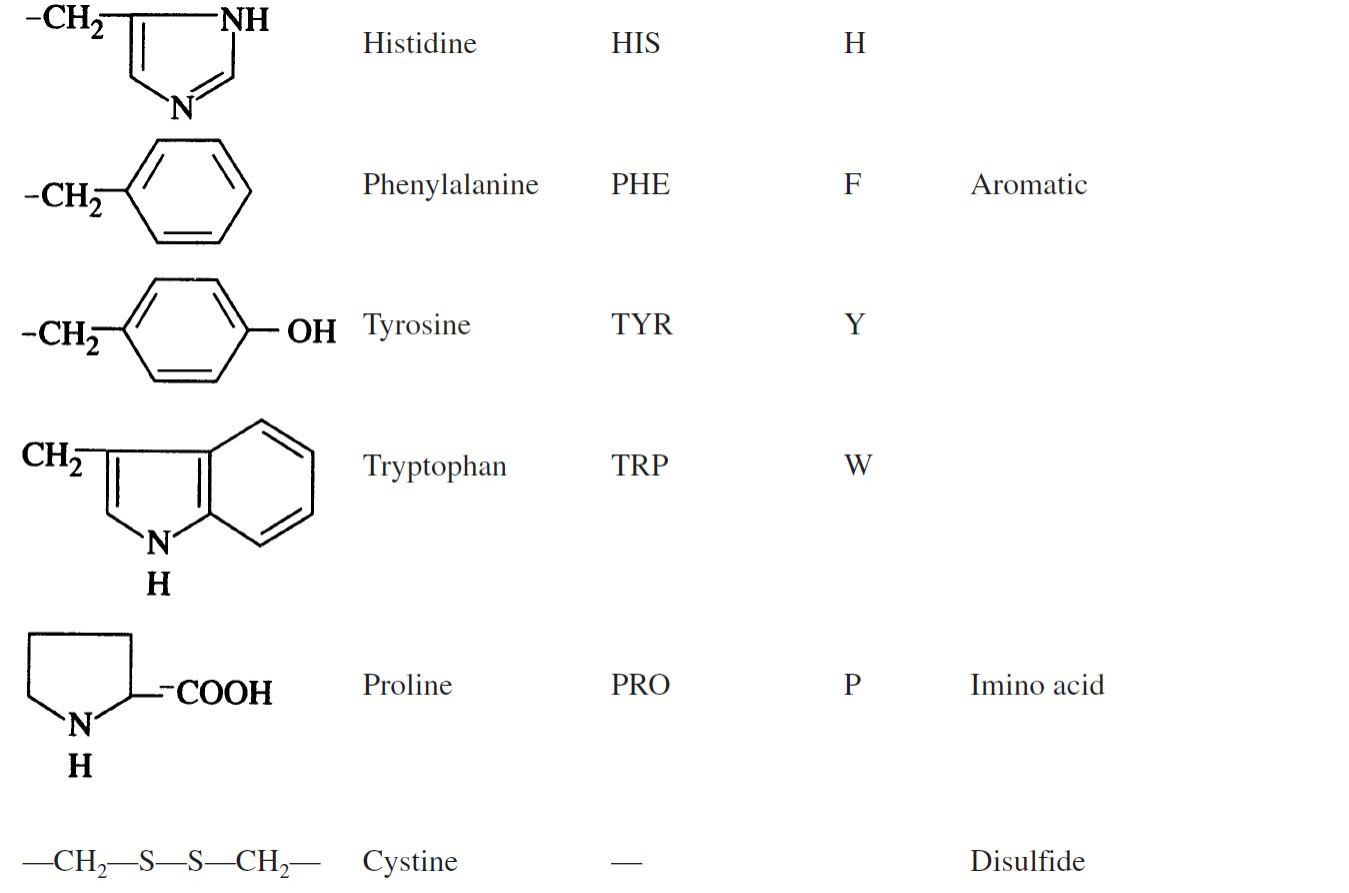
Isoelectric point
(ADDITIONAL: At its isoelectric point, an amino acid does not migrate under the influence of an electric field.)
The pH value at which amino acids have no net charge is called the ___.
Structural proteins
Catalytic proteins
Transport proteins
Regulatory proteins
Protective proteins
Enumerate the five (5) functions of proteins mentioned in the module.
Structural proteins
FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS. Determine which of the functions are being described below.
Glycoproteins, collagen, keratin
Catalytic proteins
FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS. Determine which of the functions are being described below.
Enzymes
Protective proteins
FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS. Determine which of the functions are being described below.
Antibodies, thrombin
Regulatory proteins
FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS. Determine which of the functions are being described below.
Hormones (insulin, growth hormone)
Transport proteins
FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS. Determine which of the functions are being described below.
Hemoglobin, serum albumin
Enzymes
These represent the largest class of proteins.
Globular proteins
(ADDITIONAL: A globular protein is a protein whose polypeptide chains fold into a compact, roughly spherical shape, making it generally soluble in water.)
Most enzymes are ___.
Enzymes
They are highly specific in their function and have extraordinary catalytic power.
READ.
Over 2,000 different kinds of enzymes are known.
Each enzyme’s molecule contains an active site to which its specific substrate is bound during catalysis.
Some enzymes are regulated and are called regulatory enzymes.
READ.
Over 2,000 different kinds of enzymes are known.
Each enzyme’s molecule contains an active site to which its specific substrate is bound during catalysis.
Some enzymes are regulated and are called regulatory enzymes.
Peptides
They contain two or more amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Polypeptides
They usually contain fewer than 50 amino acids.
READ.
The peptide bond is planar.
Larger amino acid chains are called proteins.
Many proteins contain organic and/or inorganic components other than amino acids. These components are called prosthetic groups.
READ.
The peptide bond is planar.
Larger amino acid chains are called proteins.
Many proteins contain organic and/or inorganic components other than amino acids. These components are called prosthetic groups.
Conjugated proteins
(ADDITIONAL: Prosthetic groups are tightly bound, non-protein components of a protein.)
Proteins containing prosthetic groups are called ___.
Hemoglobin
It is an example of a conjugated protein and has four heme groups, which are iron-containing organometallic complexes.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. The sequence of amino acids dictates the structure of the protein.
Primary structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
Enumerate the four (4) levels of structure of amino acids.
Primary structure
LEVELS OF STRUCTURE. Determine what is being described below.
It is the linear sequence of amino acids in the protein.
READ.
In the primary structure of amino acids in the protein,
The unique arrangement of the amino acids determines the three-dimensional structure and hence the function of the protein.
Only the 1st and last residue have amino or carboxylic acid groups.
READ.
In the primary structure of amino acids in the protein,
The unique arrangement of the amino acids determines the three-dimensional structure and hence the function of the protein.
Only the 1st and last residue have amino or carboxylic acid groups.
False
(EXPLANATION: A protein sequence is written in the N-C direction.)
TRUE OR FALSE. A protein sequence is written in the C-N direction.
N-terminus and C-terminus
(ADDITIONAL: The N-terminus (amino-terminus) is the end with a free amino group, while the C-terminus (carboxyl-terminus) is the end with a free carboxyl group.)
These refer to the two ends of a polypeptide or protein chain.
Secondary structure
LEVELS OF STRUCTURE. Determine what is being described below.
It is the extension of the chain as a result of hydrogen bonding between residue not too far apart.