OCTH 236 Midterm 1: TBI, SCI, movement disorders, CN
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Damage to brain tissue casused by an external mechanical force with resultant loss of conciousness, posttraumatic amnesia, and skull fracture or objectuive neurological findings that can be attributed to the trauamtic event by radiological findingsm physical, or mental status exam
TBI stats
Underreported; Don't include Er visits that didn't result in admission to hospital
80% are mild
-most common among men
Causes of TBI
Falls are majority (47%)
-most common in older adults
-intentional self hard is leading cause of TBI related deaths
Demographic disparities of TBI
More common among men
Natives- higher rates of hospitalization/death (higher crashes, substance abuse, suicide, less access to care)
POC- less likely to receive follow up care=poorer outcomes
Low income- less likely to receive surgery/services/die in hospital
Rural- more likely to die from TBI/less access to specialized care
What are the different types of brain injuries?
Severe TBI: open/closed
Non traumatic brain injury
Open Head Injury (OHI)
An injury to the brain caused by a foreign object entering the skull; causes may include firearm injuries or being struck with sharp object
-There is penetration to the skill
Closed Head Injury (CHI)
An injury to the brain caused by movement of the brain within the skull; causes may include falls, MVC, or being struck by or w an object
-there is NO penetration to the skull
non-traumatic brain injury
damage to the brain caused by internal factors, such as depletion of oxygen (carbon monoxide or anoxia), exposure to toxins, drug overdose or chronic substance use
Guidelines for management TBI
Absence of increased ICP
Steroids are not recommended to reduce ICP
Prophylactic are not recommended for preventing seizures
Hypotension/hypoxia must be monitored/corrected immediately
>40 yrs/GCS 3-8/hematomas: ICP monitoring is appropriate
If ICP exceeds values, treatment should be initiated to lower it
Surgical interventions for TBI
Removal of objects (bulletin/debris)
Evacuation of hematoma
Tumor removal
Bone flap
Predictor outcomes of TBI
Immediate
Autonomic functions (pulse, RR, temp, Bl press, diaphoresis)
Consciousness (arousal, cognition, length of coma)
Motor functions (reflexes, voluntary mov, abnormal postures)
Pupillary response
Ocular movements (pupil size, shape, light)
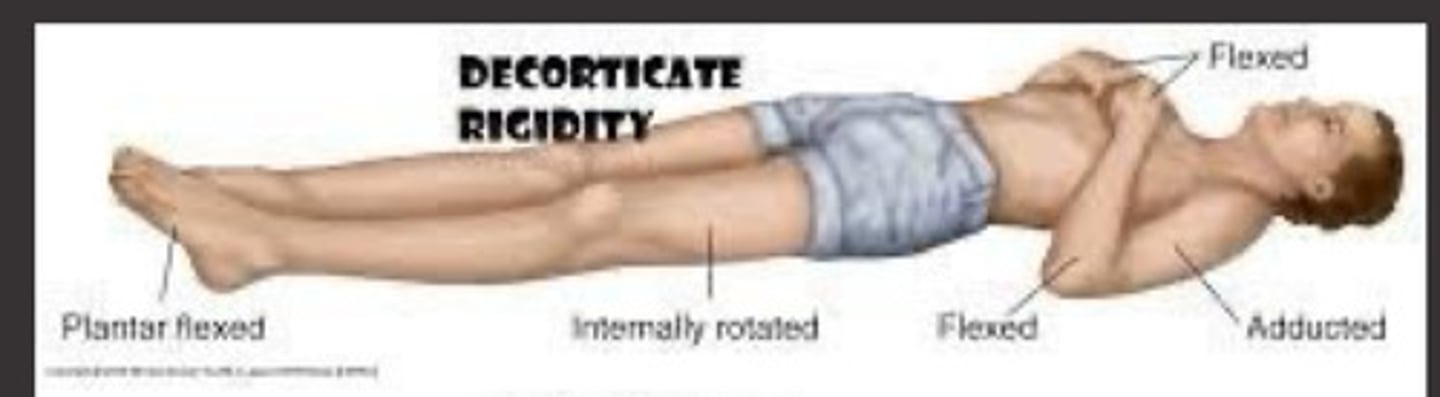
Decorticate posturing
UE in a spastic, flexed position, Int rot and adduction
LE spastic extended, Int rot and adduction
Cerebral hemisphere, internal capsule, above superior colliculus
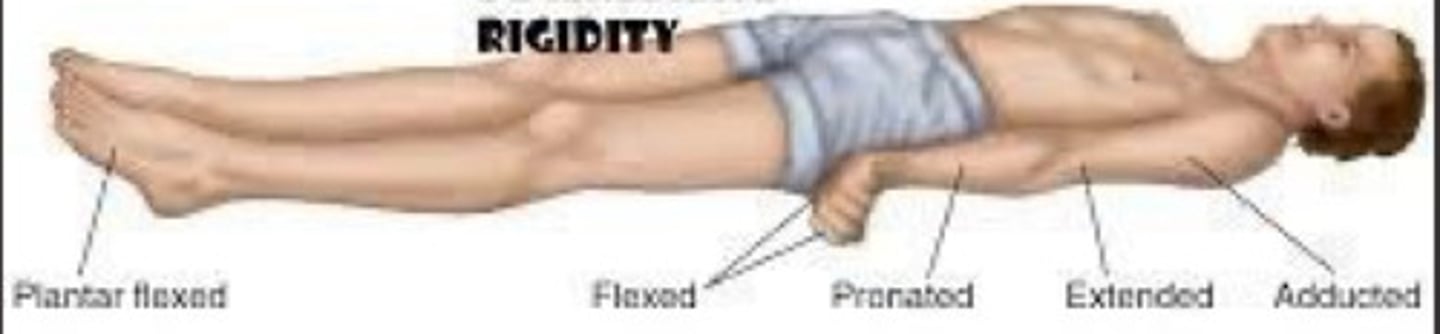
Decerebrate posturing
UE and LE in extension, adduction, int rot
Wrist/fingers in flexion
Lesion below superior colliculus, brainstem region
Poorer prognosis than clients with damage above superior colliculus
What are the different types of amnesia?
Retrograde
Anterograde
Post-traumatic
retrograde amnesia
Length of amnesia for events prior to injury, unable to remember events due to neurological damage
Anterograde amnesia
Length of amnesia following impact, injury, unable to consolidate info for storage and retrieval
Post-traumatic amnesia
Following injury where patient is confused and seems unable to store and recall new info
-can refer to anterograde or retrograde subtype
Length of post-traumatic amnesia
the time after injury when day to day recall returns and full orientation is present
Categories of post-traumatic amnesia
Mild: < 1 hour
Moderate: 1-24 hrs
Severe: 1-7 days
Very severe: 1- 4 weeks
Extremely severe: > 4 weeks
What are some secondary medical issues affecting those with TBI
Orthopedic-weight bearing status: ability to participate in rehab
Pulmonary- endurance/tolerance
Decubitus ulcers- pressure
Combo injuries- SCI/TBI
Combo injuries SCI/TBI account for ________% of brain injury cases
30-50%
prognosis of TBI depends on
Predictors
Age
Social support group
Premorbid drug/alcohol abuse
Length of time in coma/PTA
The length of stay in hospital is based on
Insurance authorization, functional goals, progress
Initial team evaluation consists of...
Interview and observation
Clinical evaluation (ROM, tone, sensation, balance, movement)
Cognition/perception/vision
Performance of mobility and functional activities
Endurance and pain
Behavior
Goal setting is based on...
Length of stay
FIM scale 1-7
Discharge destination/caregiver availability
Purpose of Evaluation
Identify problems that affect cognitive performance
Language
Perceptual, motor, visual deficits
Education/culture
Medications
Sensory deficits
Physical limitations
Previous level of expertise w/ task
Occupational therapy focus
Splinting/casting UE
Neuromuscular re-education
Cognitive retraining
Participation in ADLs (self care)
Bed positioning, transfers, mobility (w/c)
Transfers
Equipment needs
Caregiver training
Home evaluation
Glasgo Coma Scale (GCS)
A clinic tool designed to access the severity of coma and impaired consciousness and is one of the most commonly used scoring systems
-assess/monitor level of consciousness
Glasgo coma scale (GCS) categories
Severe TBI: 3-8
Moderate TBI: 9-12
Mild TBI: 13-15
What three aspects of coma are independently observed with the GCS?
Eye-opening (E)
Best motor response (M)
Verbal performance (V)
How are the overall GC scores obtained?
By adding up the total numbers (E+M+V)
A total of 3 is the least responsive
The highest score is 15
What are the other classification systems of TBI?
Abbreviated injury scale (AIS)
The trauma score
Abbreviated trauma score
What are the GCS scores for eye opening (E)?
Spontaneous (4)
To speech (3)
To pain (2)
Nil (1)
Eye Opening Response (GCS) - 4
Eyes open spontaneously
Eye Opening Response (GCS) - 3
Eyes open to speech
Eye Opening Response (GCS)- 2
Eyes open to pain
Eye Opening Response (GCS) - 1
no response
What are the GCS scores for Best Motor Response (M)?
obeys (6)
localizes (5)
Withdraws (4)
Abnormal flexion (3); decorticate posturing
Extensor response (2); decerebrate posturing
Nil (1)
Best Motor Response (GCS) - 6
Obeys
Best Motor Response (GCS) - 5
Localizes
Best Motor Response (GCS) - 4
Withdrawal (flexion)
Best Motor Response (GCS) - 3
Abnormal flexion (decorticate)
Best Motor Response (GCS) - 2
Extensor response (decerebrate)
Best Motor Response (GCS) - 1
None
What are the GCS scores for Verbal response (V)?
Orientated (5)
Confused conversation (4)
Inappropriate words (3)
Incomprehensible sounds (2)
Nil (1)
Verbal response (GCS) - 5
Oriented
Verbal response (GCS) - 4
confused conversation
Verbal response (GCS) - 3
inappropriate words
Verbal response (GCS) -2
incomprehensible sounds
Verbal response (GCS) - 1
none
Galveston orientation and amnesia (GOAT)
Measures cognitive level of patients post-injury so that a more realistic recovery plan can be communicated
(LOS, rehab plan, prediction of recovery info for family)
Low score=longer duration of PTA amnesia period
Increased duration of PTA found w/ diffuse/bilateral brain injuries
Longer confused state=more difficult to return to pre-injury cognition
Rancho Los Amigos (RLA) Scale
Scale of cognitive functioning; rehab evaluation tool that focuses on clients abilities and behaviors
I-VIII
-Clients move through the stages during recovery process
Rancho level I
no response (coma); Total A
-not arousable, not responsive
-absence of awareness
-no periods of wakefulness
-coma rarely lasts > 3-4 wks unless medication induced
Rancho level II
Generalized response, persistent vegetative state (PVS); awake but unaware; Total A
-no awareness of self/environment (no attend, verbal, motor, incontinence)
-positive signs (sleep cycles, autonomic functions, random vocalizations/movements)
What are the types of vegetative states?
Persistent vegetative state (PVS)
Permanent (irreversible) vegetative state
Persistent Vegetative State (PVS)
condition in which a person is alive but unable to communicate or to function independently at even the most basic level; Past and current state
-after 1 mo in this state
Permanent (irreversible) vegetative state
12 months after TBI
3 months after non traumatic brain insult.
Determine level of medical support, nutrition
Advanced Directives helpful, but rarely present!
Rancho Level III
Localized response, minimally conscious state; Total A
Definite reproducible behavioral evidence of some awareness of self or environment
-follows commands
-gestures/verbal response to Qs
-intelligible sounds
-crying/laughing/smiling to stimuli
-reach/hold objects
-visual tracking
Locked-in syndrome
Loss of voluntary motor control in a setting of preserved consciousness; damage to corticospinal/corticobulbar pathways
Tetraplegia/bulbar weakness, vertical eye movement/blinking intact
-May be difficult to demonstrate conscious behavior because of motor limitations
Rancho Level IV
Confused/agitated; Max A
-alert/heightened activity
-purposeful attempts to remove tubes, crawl out bed
-absent short term mem
-cry/scream out of proportion to stimulus
-aggressive/flight behaviors
-mood swings w/ no relationship to environment
Rancho Level V
Confused, inappropriate, non-agitated; Max A
-alert but not agitated
-not oriented person, place, time,
-frequent periods of non-purposeful sustained attention
-unable to learn new material
-respond to simple commands matching external cues
-verbalizations often inappropriate and confused
Rancho Level VI
Confused, appropriate; Mod A
-inconsistently oriented to person, place, time
-remote mem more accessible than recent mem
-use assistive mem devices w/ Max A
-carry over for relearned familiar tasks (self care)
-unaware of impairments, disabilities, safety risks
Rancho Level VII
automatic, appropriate; Min A for ADLs
-Consistently oriented person, place, time
-incr attention/able to work for 30 mins on familiar tasks
-Min supervision for new learning
-initiates/carries out familiar self care/household tasks (may have limited mem of events)
-unrealistic planning for future/ overestimates
-unable to think about consequences
-unaware of others needs/feelings
Rancho Level VIII
Purposeful, appropriate; SBA/supervision
-consistently orientated to P, P, T
-attention incr to 60 min for familiar tasks
-recall past events/ integrate w/ recent events
-initiates/carry out steps for familiar tasks (personal, house, community, work, leisure) can slight mod plan w/ min A
-no A one new task is learned
-needs A to make corrective measures to plans
-thinks about consequences
-irritable/depressed
-acknowledges others needs/feelings
Neurological Examination process
Clients history
Present condition
Prior history
Familial history
Neurological examination basics
Mental status (Orientation, Memory, Cognition)
Orientation status
Person, place, time, situation- 0 x 4 etc
-Take into consideration if client has been unconscious, etc. when deciding orientation status
Memory status
Objects- show 4-5 objects, then cover and have client name the objects
Events- what did they eat for breakfast
Cognition status
Serial 7s
Interpret proverbs- developmentally/culturally appropriate
The cranial nerves
12 paired nerves coming off of the ventral side (underneath) the brain and bringing info to and from the brain, face, tongue, ears, eyes, throat, and visceral organs
CN I
Olfactory nerve (sense of smell); sensory
-test with coffee, lemon
CN II
Optic nerve: vision; sensory
-visual acuity and visual fields, assess w/ eye chart
central scotoma
a partial loss of vision or a blind spot in an otherwise normal visual field.
Hemianopsia
blindness in half the visual field
Monocular vision loss
A lesion to the optic nerve of one eye will lead to loss of the complete visual field of that eye.
-The other eye can still perceive the entire visual field.
Bitemporal hemianopsia
loss of both temporal half of the vision in each eye due to damage to optic chiasm
homonymous hemianopsia
a visual field defect involving either two right or the two left halves of the visual fields of both eyes
CN III
Oculomotor nerve: motor to eye/eyelid (movement) and pupil constriction; Motor
CN IV
Trochlear nerve: eye movement (superior oblique moving eye down/lateral); Motor
CN V
Trigeminal nerve: chewing muscles, sensory (touch/pain) to face/head (somatosensory); Both
-light touch on face
-have client close eyes and use a a tip to touch face randomly (client identifies location of touch)
CN VI
Abducens nerve: eye movement (lateral movement); Motor
CN VII
Facial nerve: taste (taste for ant 2/3 of tongue), facial expression muscles, somatosensory from ear; Both
-taste on tip of tongue (sugary/salty)
-ask client to smile, close eyes, wrinkle forehead (watch for spontaneous movement, droop, symmetry)
Bell's Palsy
Unilateral facial paralysis resulting from damage or trauma to CN 7
-usually temporary due ti inflammation of nerve
CN VIII
Vestibulocochlear nerve: hearing and balance/equilibrium; Sensory
-rub fingers by ear w/ eyes closed
static labyrinth
utricle and saccule
linear motion, position of head when static
dynamic labyrinth
Semi-circular canals
Movement of head, initial speed of movement
nystagmus
Involuntary, rapid, repetitive eye movements (vert, horizontal, rotary)
Slower phase/movement
Rapid phase w/ refixation back to midline
-induced to check CN VIII function
CN IX
Glossopharyngeal nerve: taste (post 1/3 of tongue), somatosensory from tongue, tonsils, pharynx, motor to swallowing muscles; Both
CN X
Vagus nerve: sensory, motor and autonomic functions of the viscera (digestive organs, heart, glands), some taste; Both
-somatic/visceral components
CN XI
Accessory nerve: motor control of head movement/swallowing; Motor
-(spinal accessory) turn head side to side and elevate shoulders
CN XII
Hypoglossal nerve: motor control to tongue; Motor
-tongue mobility for protrusion, push tongue side to side inside mouth to collect bolus after chewing
How do you check the integrity of CN VIII?
Cold calorics
COWS: cold opposite, warm same
physician does this test NOT OT
cold calorics
irrigating one ear canal w/ cold water, normally induces nystagmus to opposite side
-if system intact there will be fast phase and then opposite slow phase for few beats
-if only slow phase w/ eyes deviating towards cold water, indicates lack of activity
Deep tendon reflex
involuntary muscle contraction in response to striking muscle tendon with reflex hammer; test used to determine whether muscles respond properly
-use quick stretch to elicit response from muscle spindle
-two scales to rate
What are the two scales to rate a deep tendon reflex?
+/-
Normal= +
Absent= -
Or
0= no response; always abnormal
1+= slight but present response; may/may not normal
2+= brisk response; normal
3+= very brisk response; may/may not normal
4+= repeating reflex; always abnormal
Muscle tone
resting tension of the muscles
Hypotonia
Too little muscle tone, compromises posture/core stability
-damage to cerebellum
Low tone that impacts movement (voluntary movement disorder)
Hypertonia
Too much muscle tone, compromises efficiency of movement strategies
-cortical damage
High tone
Spasticity
Resistance to movement in only one direction for each degree of freedom, velocity dependent, classically termed clasp knife spasticity
-more tone during the initial part of movement
Rigidity
Resistance to movement in both directions for each degree of freedom, velocity independent
-does not vary w/ speed of movement of muscle groups involved
Types: cogwheel rigidity and lead pipe rigidity