liver abdomen ultrasound
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
224 Terms
coronary
anterior superior surface of the liver runs of superiorly, then posteriorly on the right to the anterior leaf of the coronary ligament.
retroparetnial tumors may move the liver slightly
anteriorly
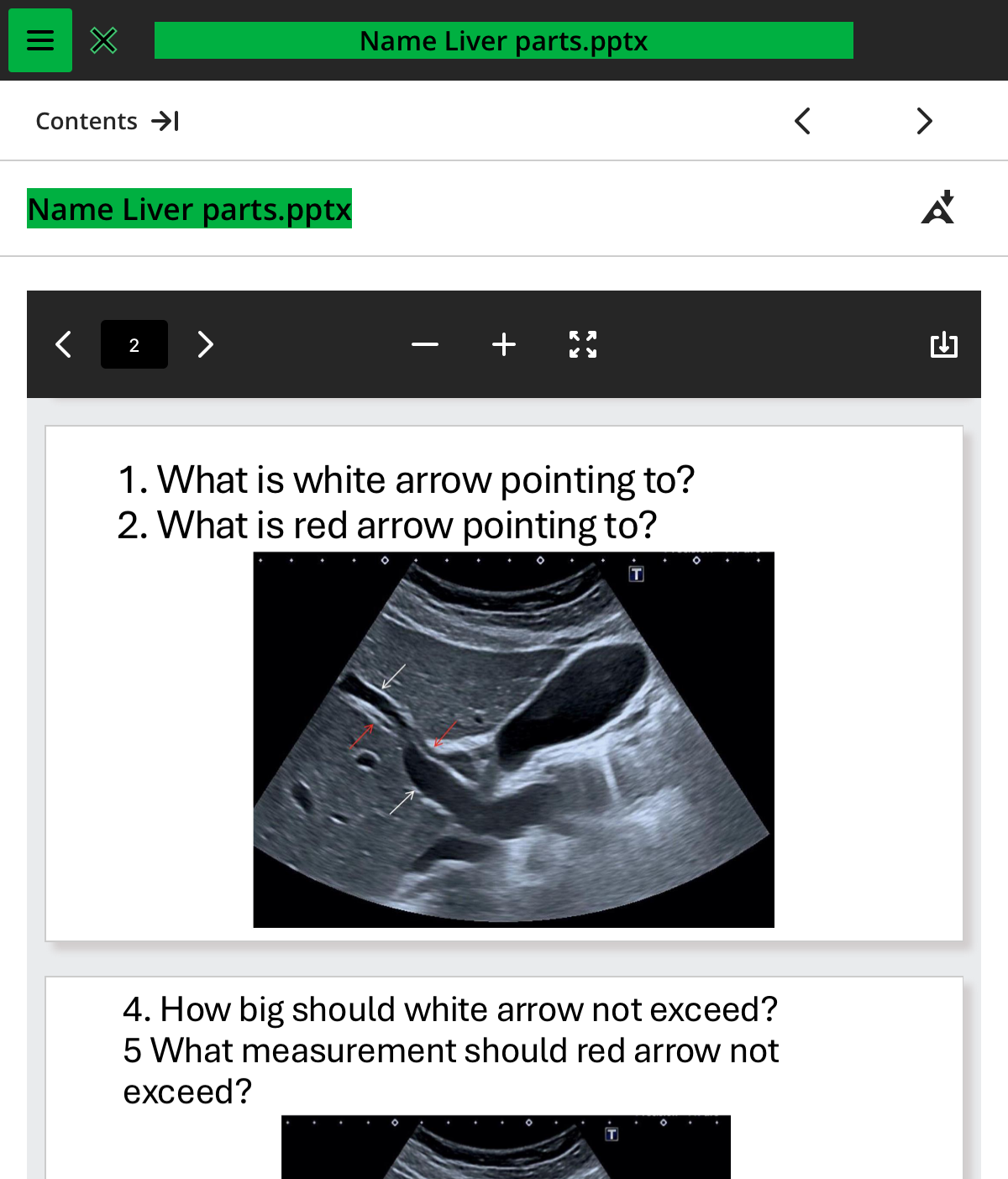
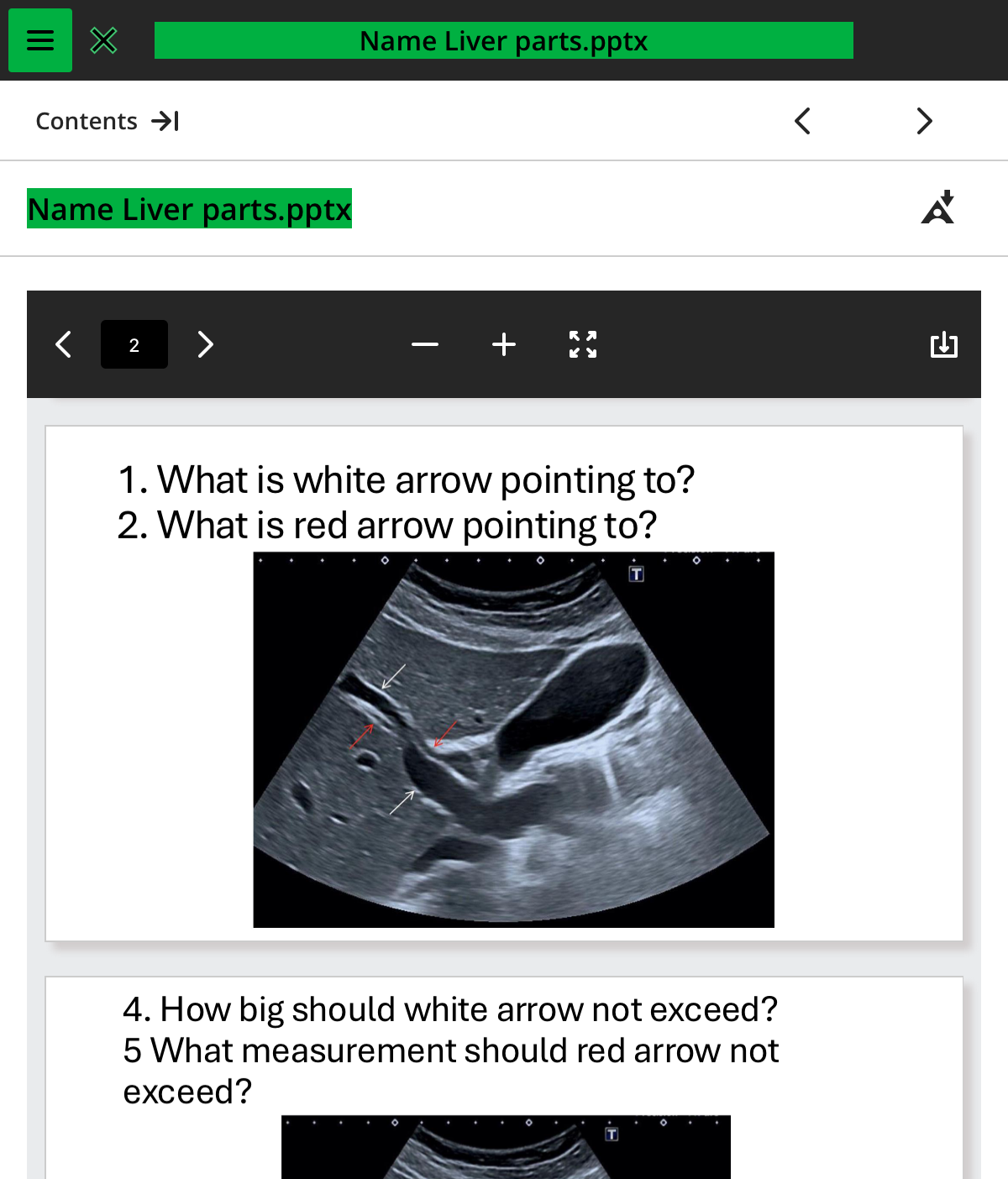
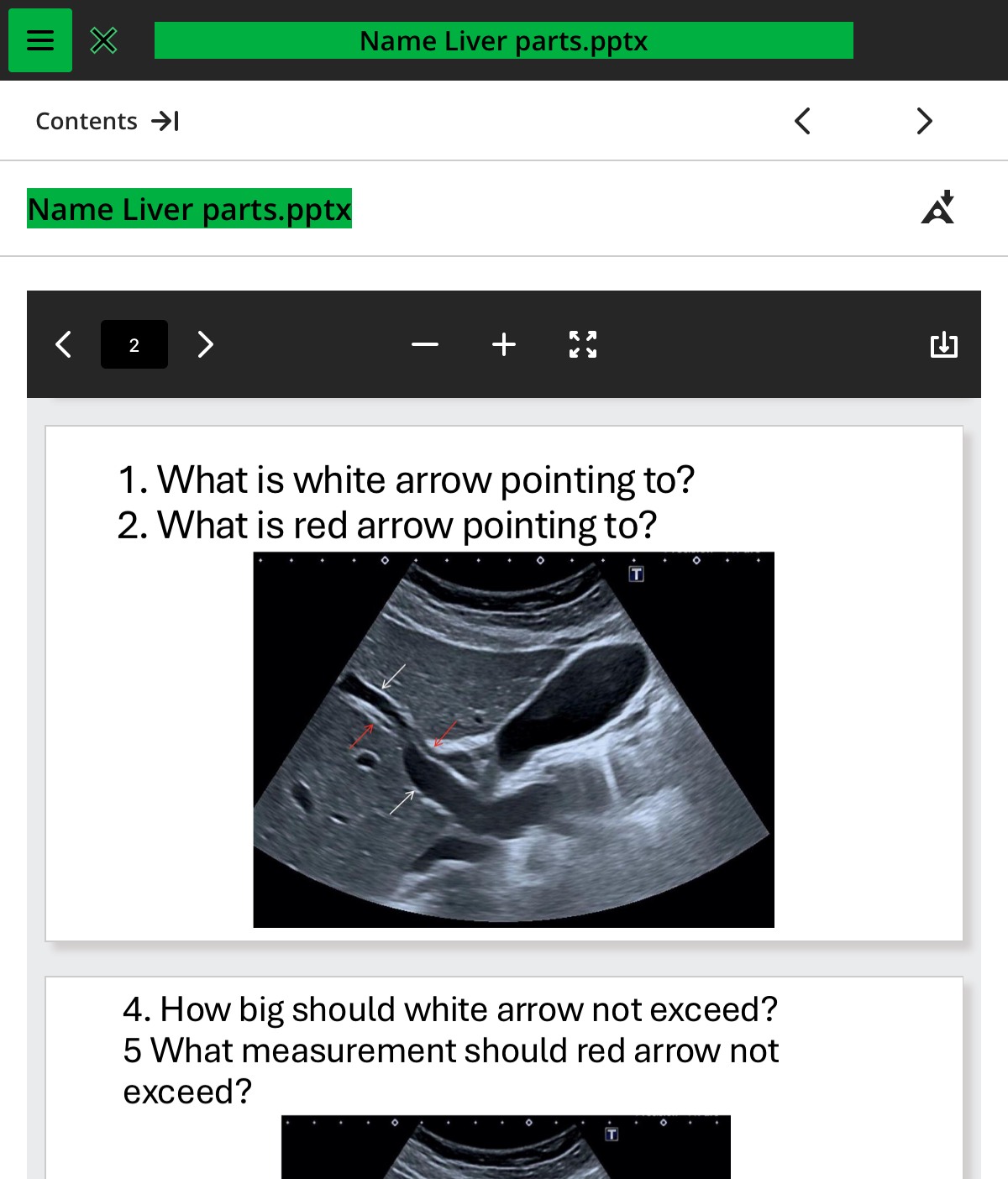
1.what is the white arrow pointing to
PV
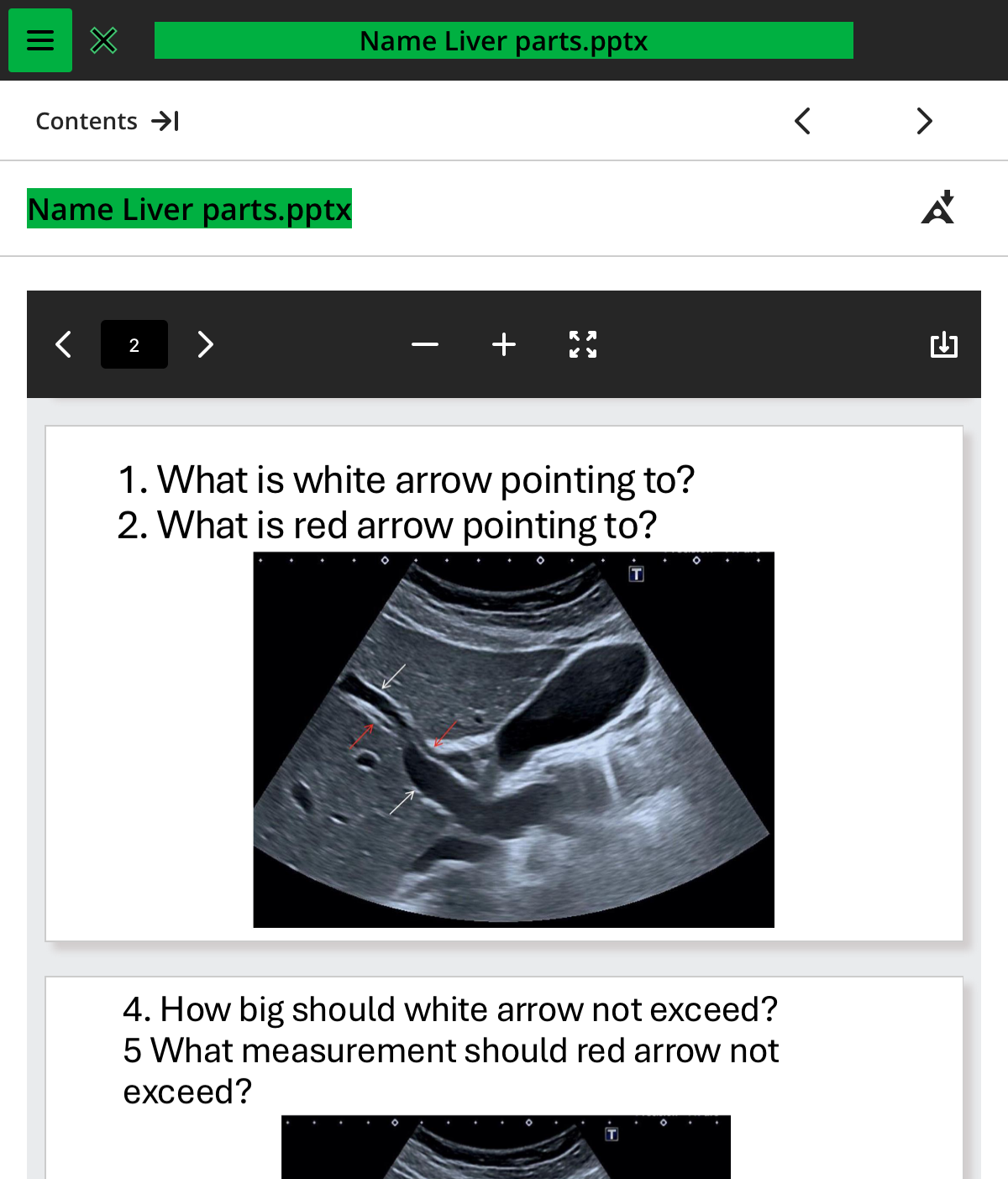
2.what is the red arrow pointing to
CBD
how big should the white arrow not exceed
1.3cm
what measuremt should red arrow not exceed
1cm
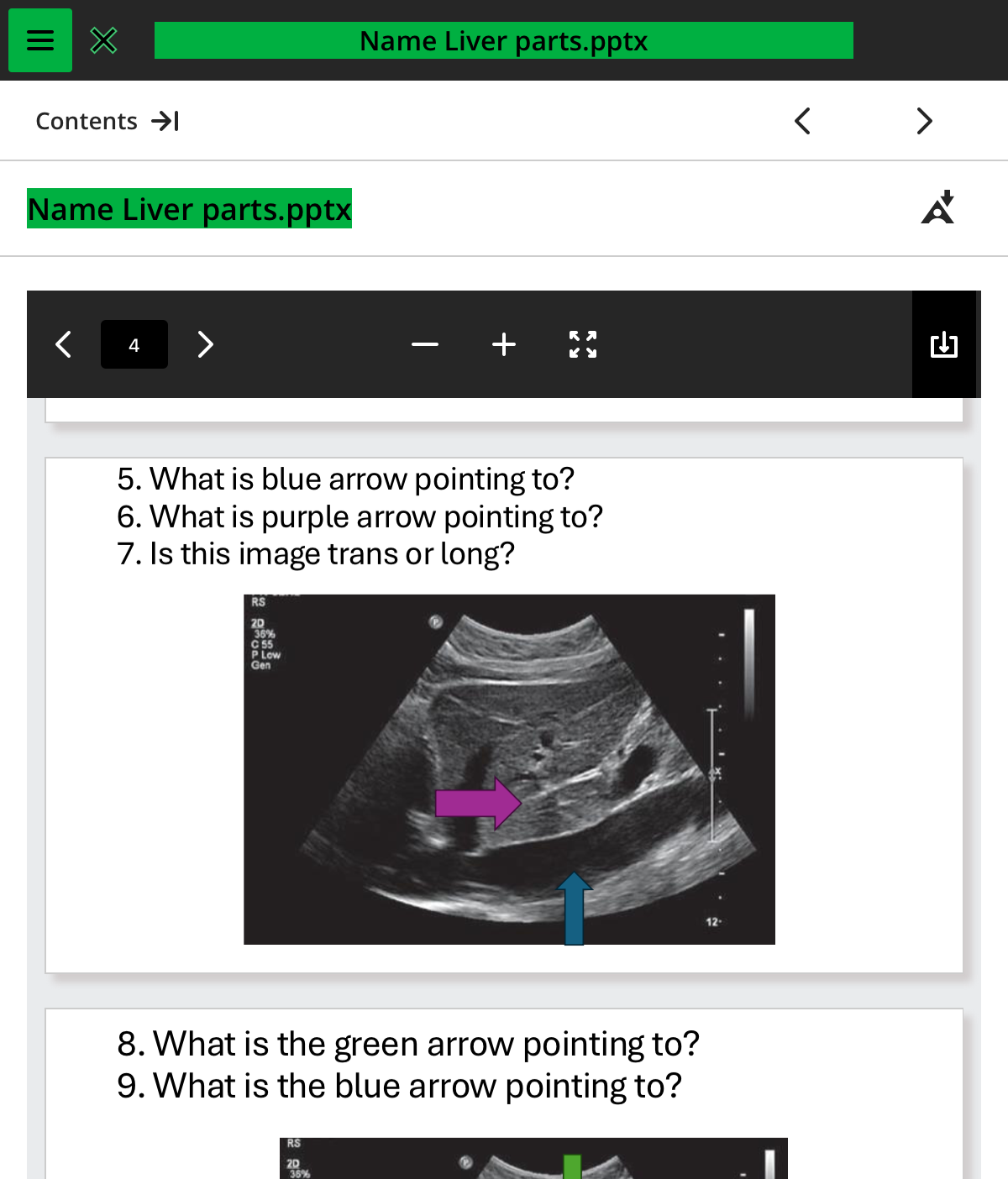
what is the blue arrow pointing to
ivc
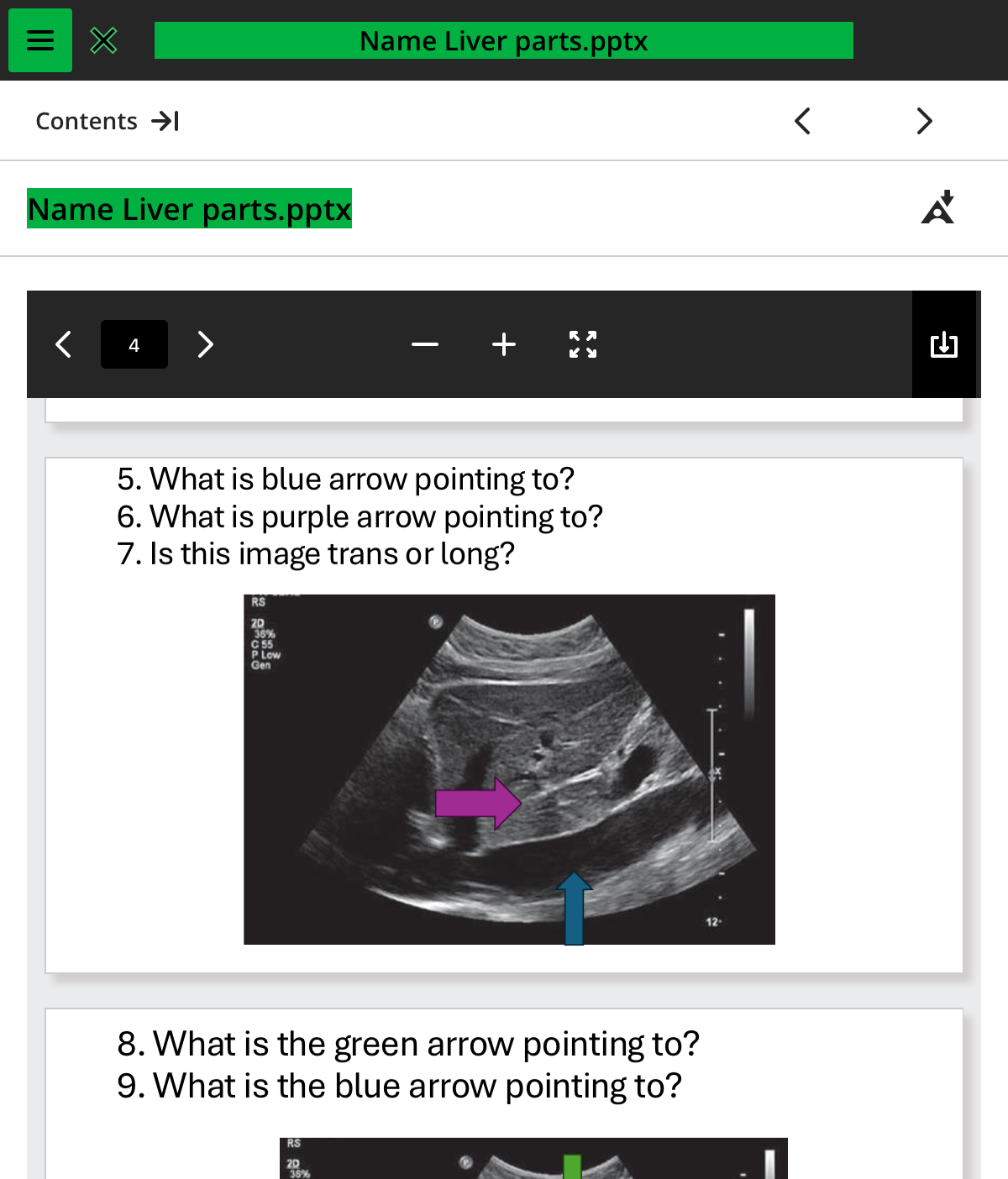
what is the purple arrow pointing to
ligamentum venosum
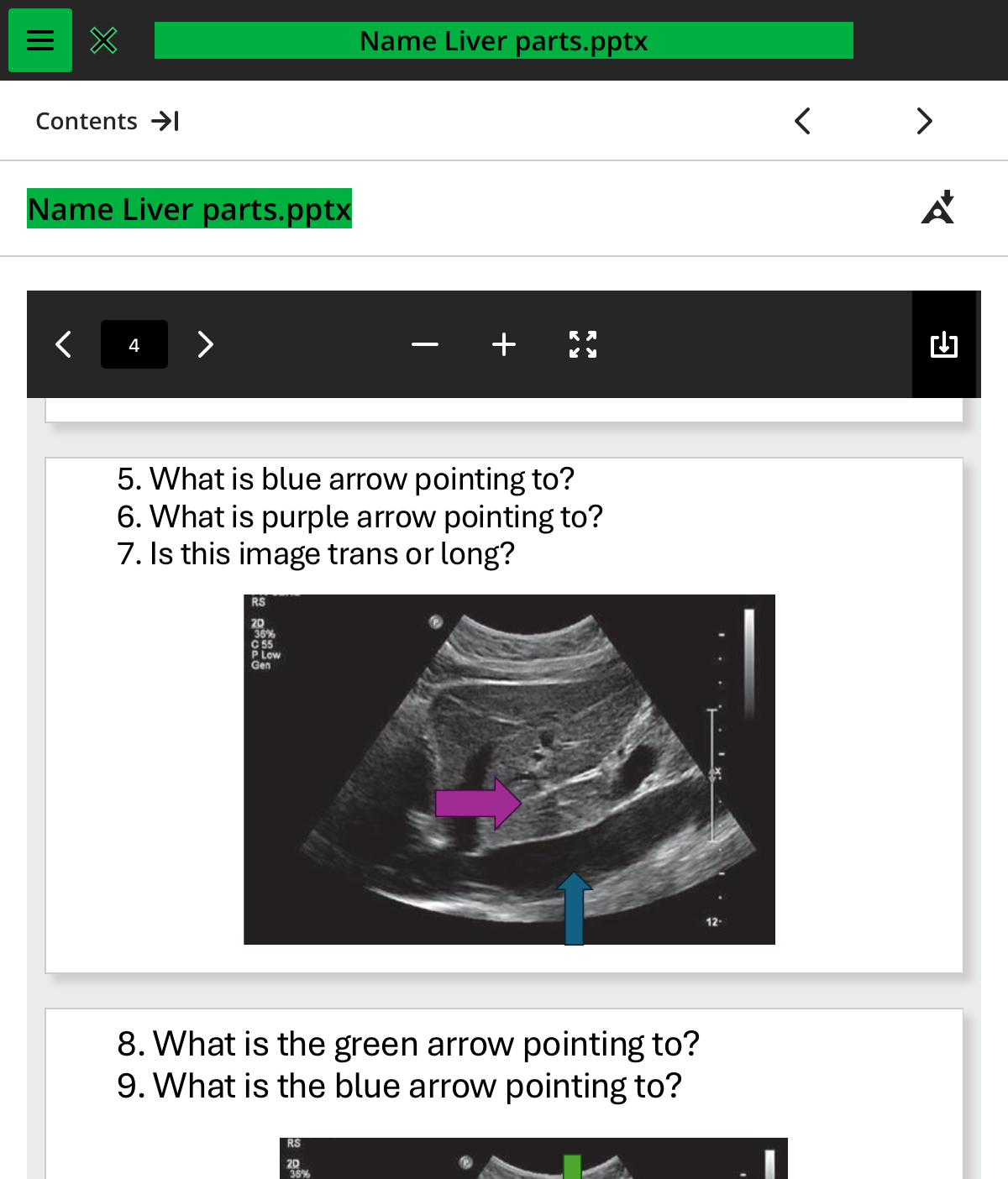
is this image trans or long
long
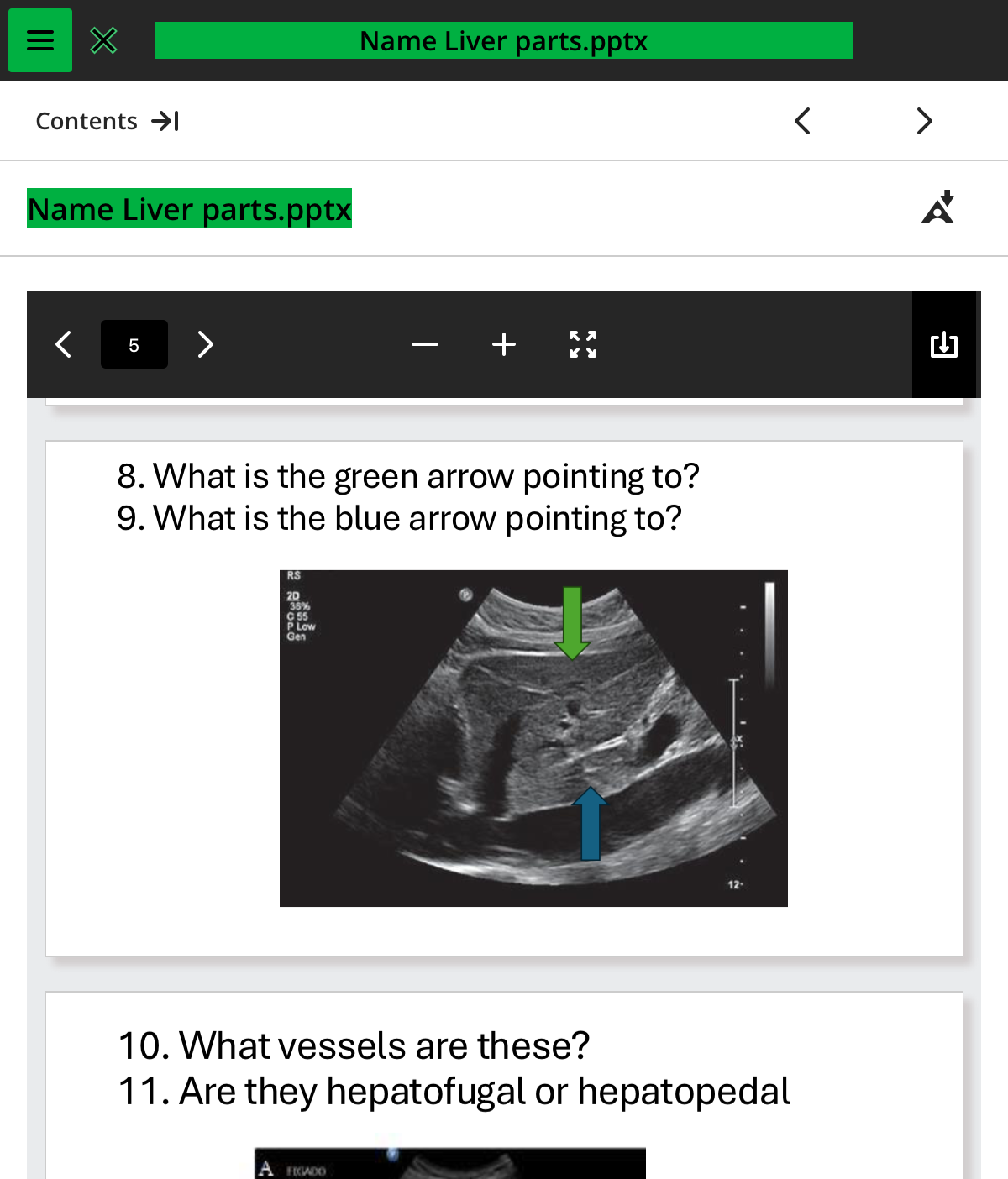
what is the green arrow pointing to
left lobe of the liver
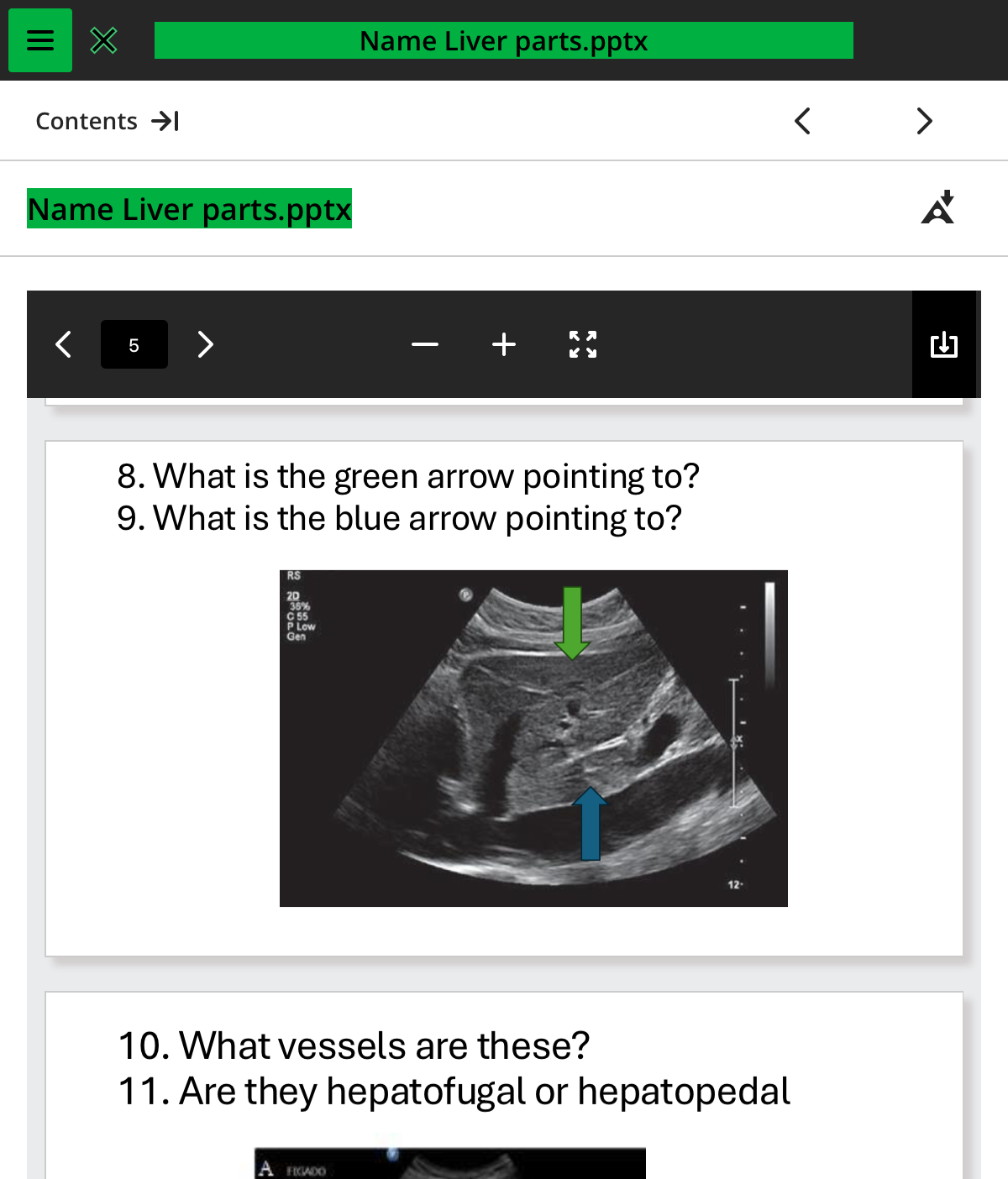
what is the blue arrow pointing to
caudate lobe
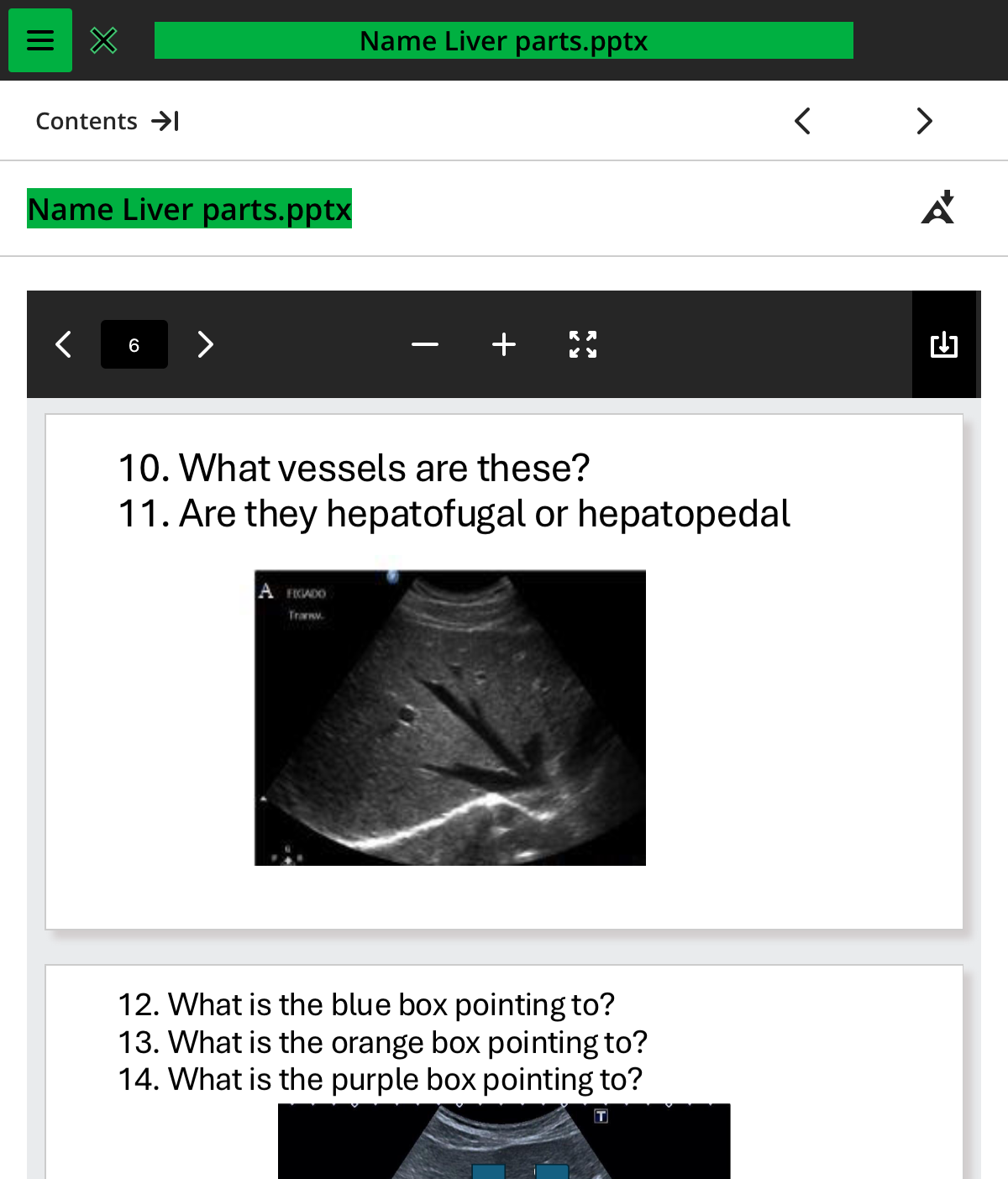
what vessels are these
.hepatic
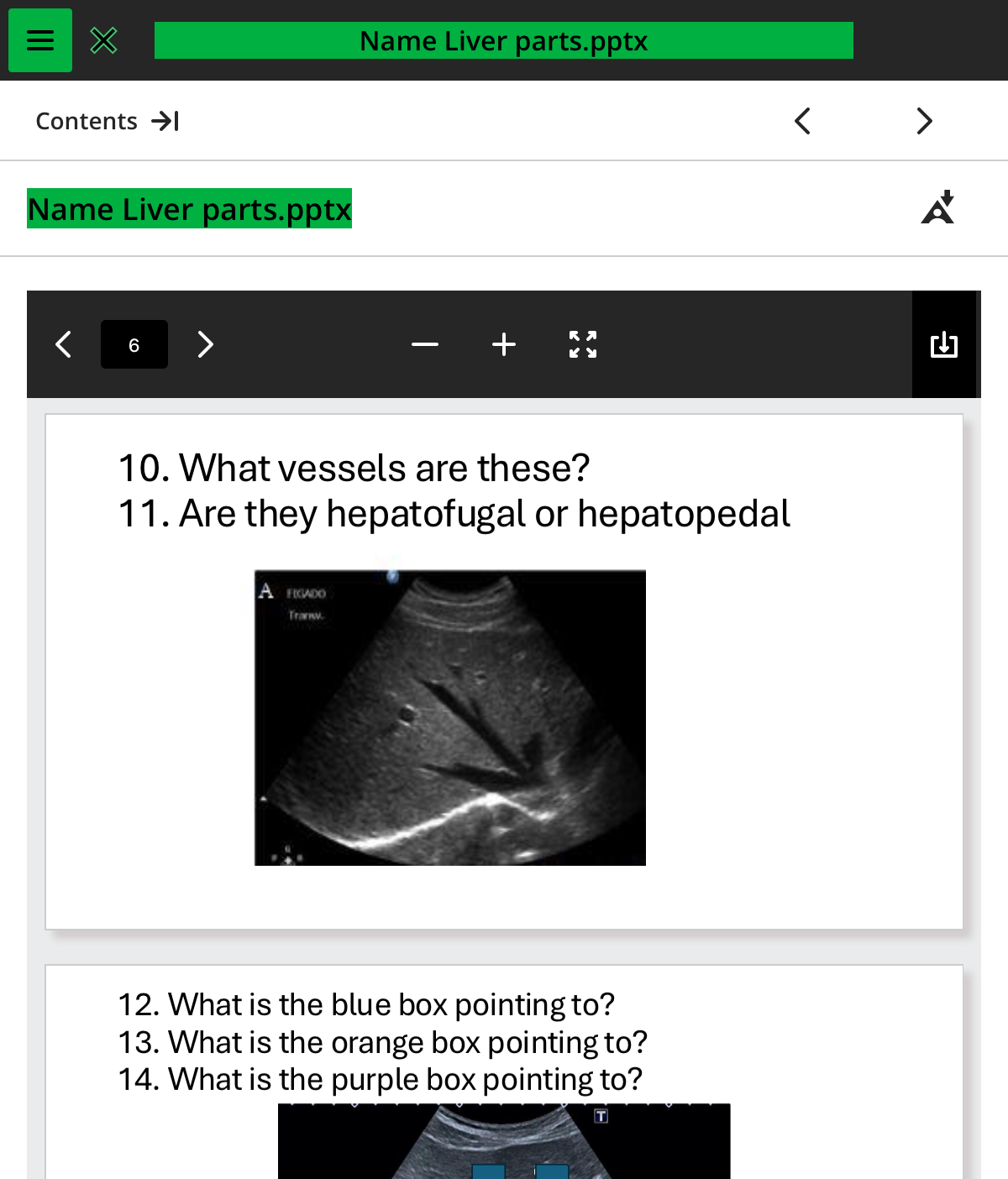
are they hepatofugal or hepatopedal
hepatofugal
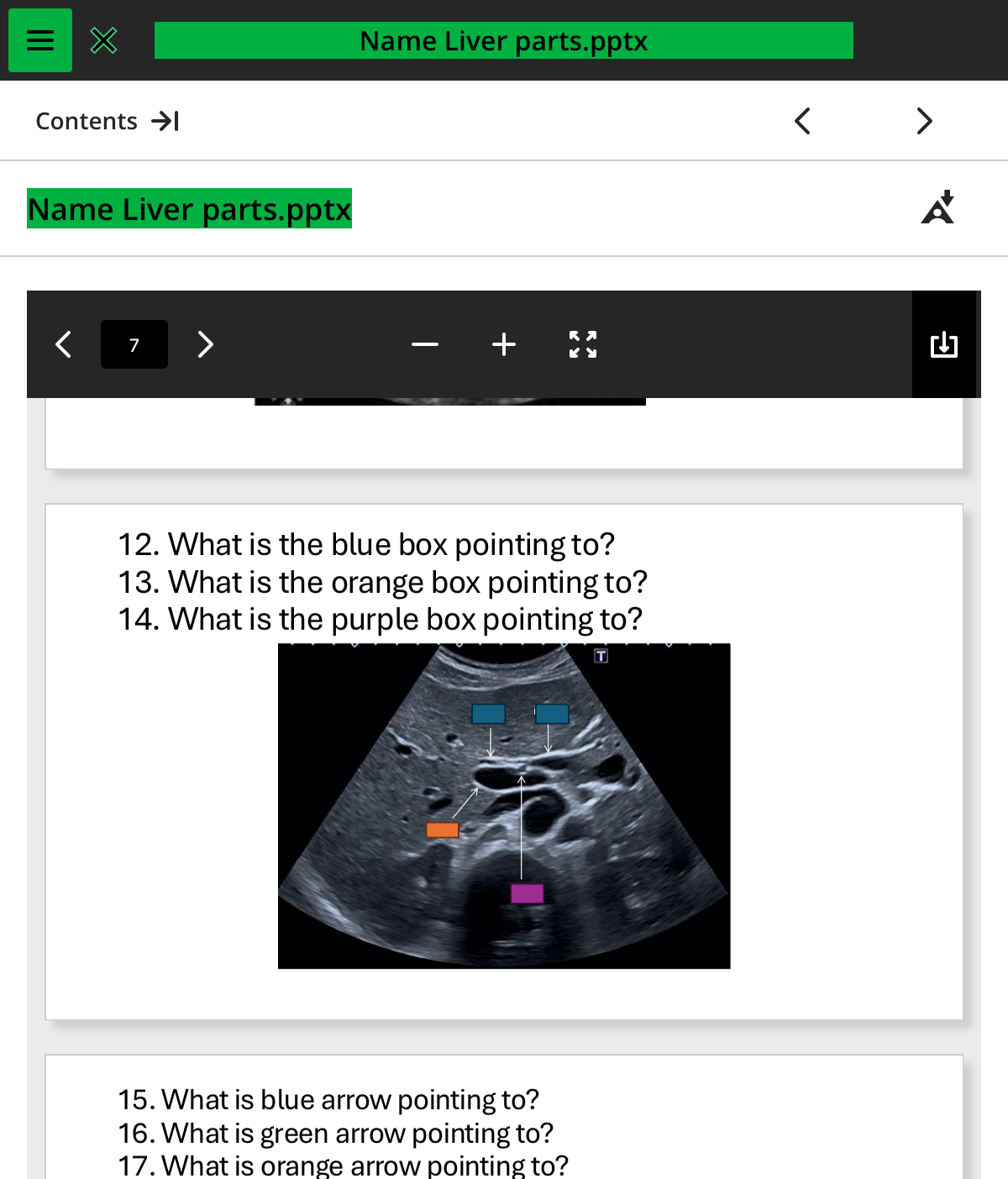
what is the blue box pointing to
cbd
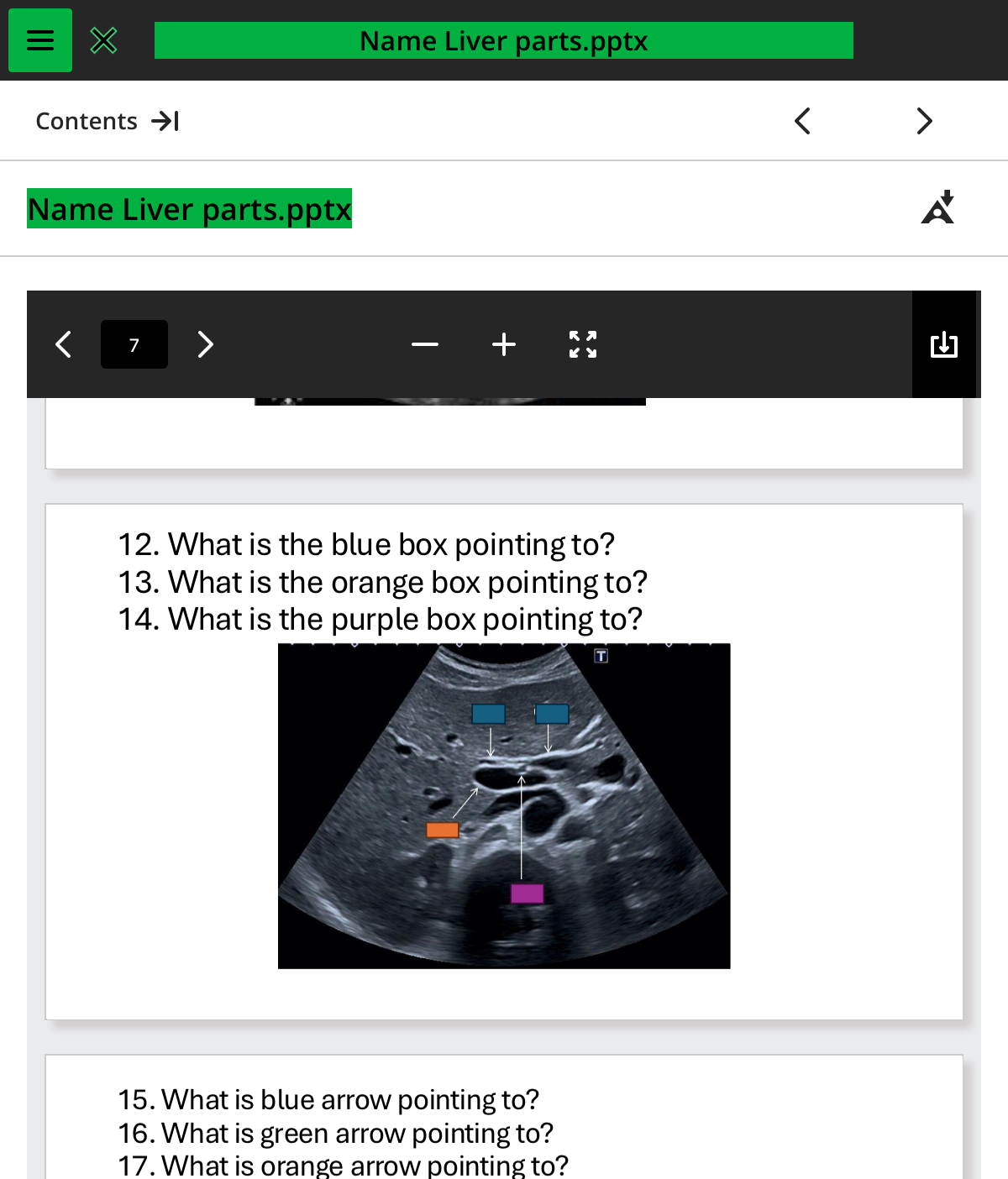
what is the orange box pointing to
pv
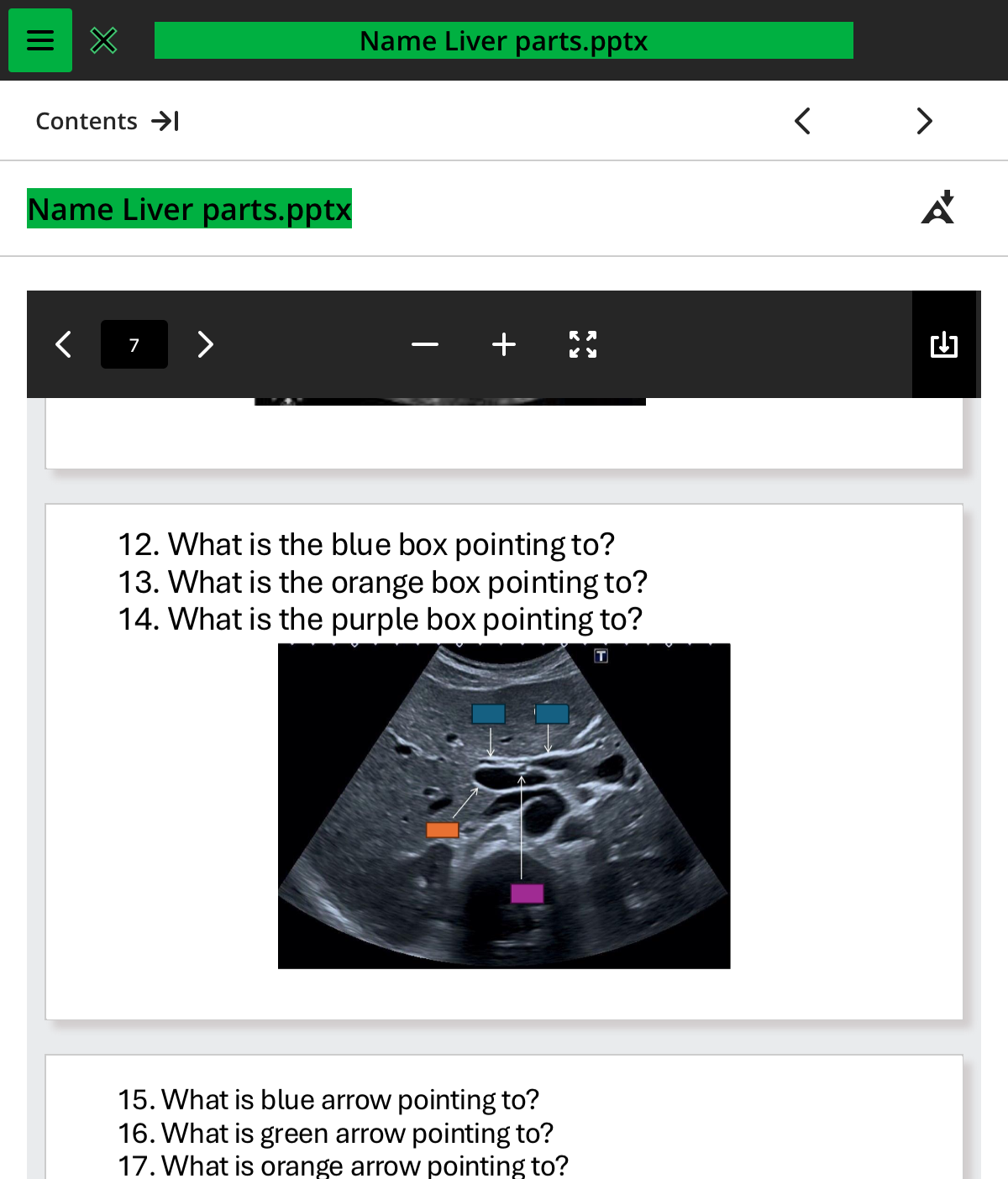
what is the purple box pointing to
ha
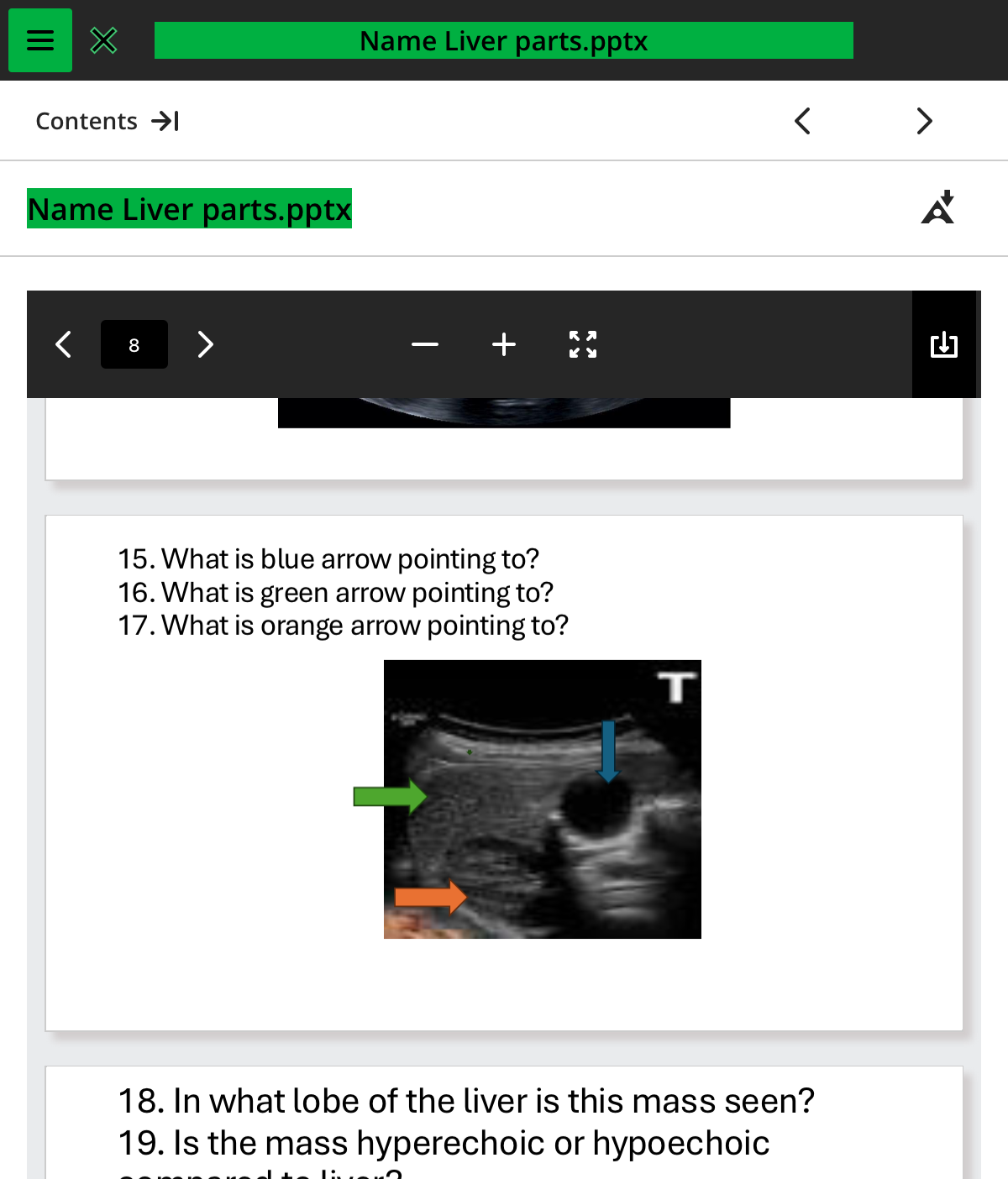
what is the blue arrow pointing to
gb
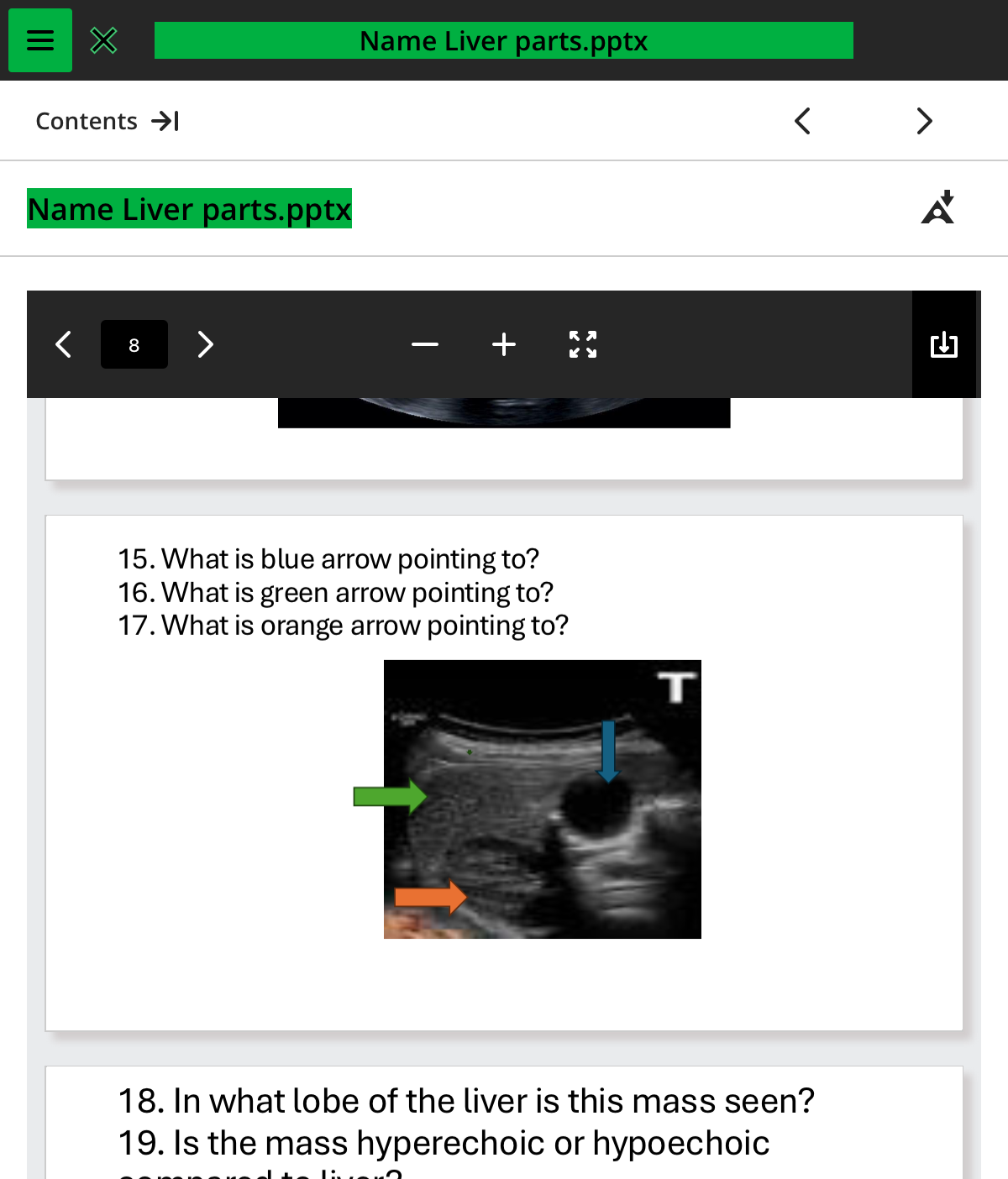
what is the green arrow pointing to
right lobe
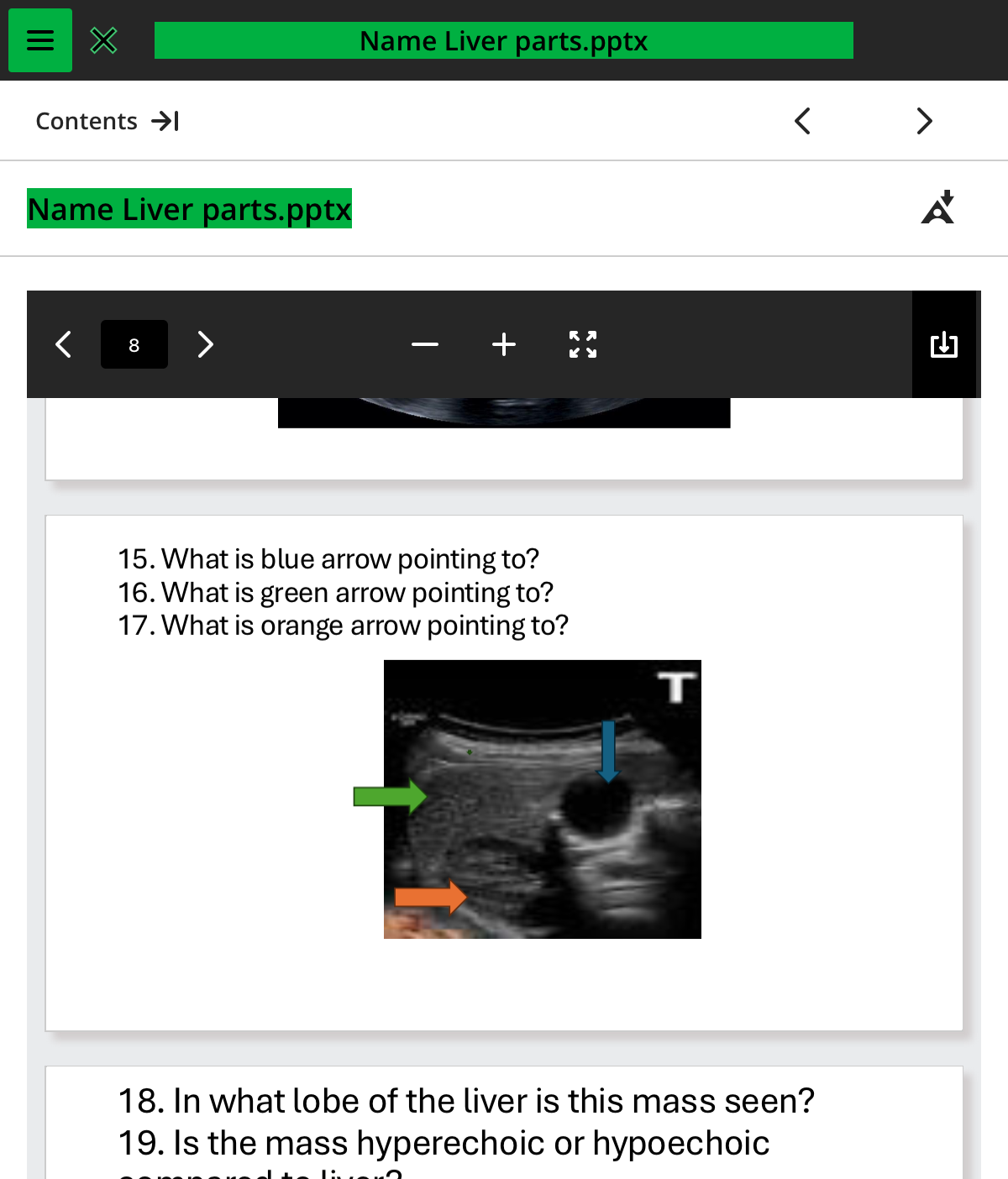
what is the orange arrow pointing to
kidney
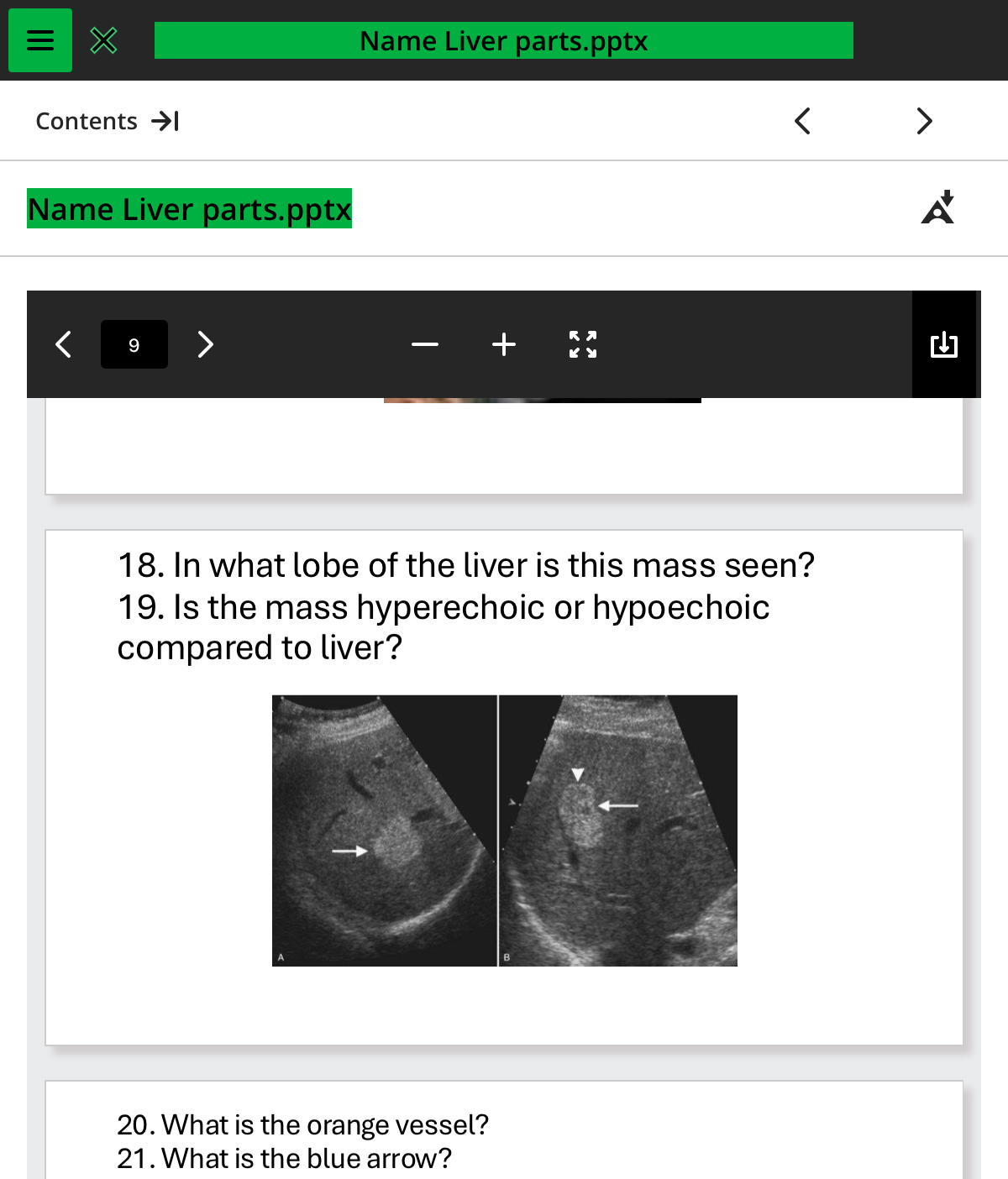
in what lobe of the liver is this mass seen
rightl
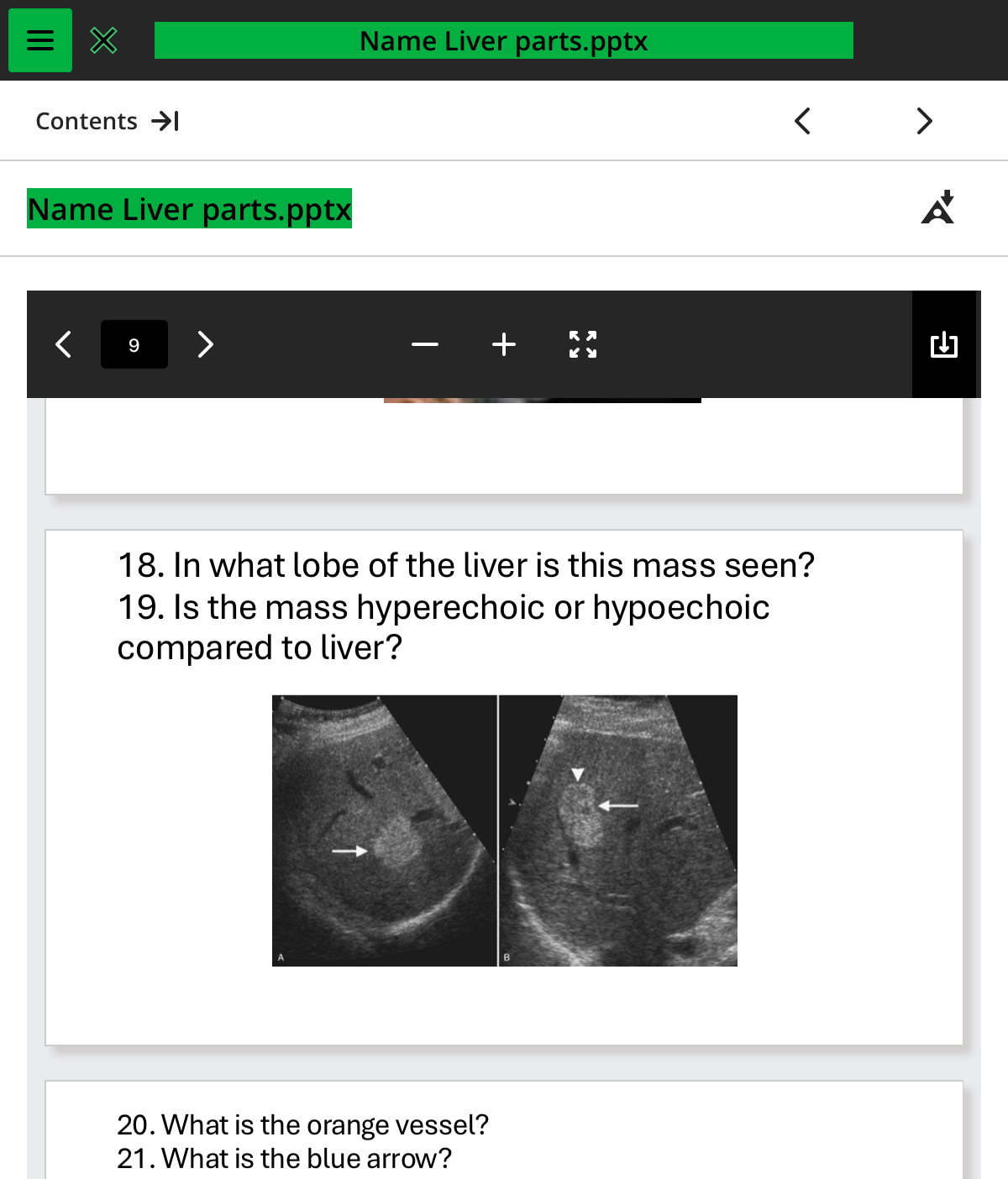
is the mass hyperechoic or hypoechoic compared to the liver
hyperechoic
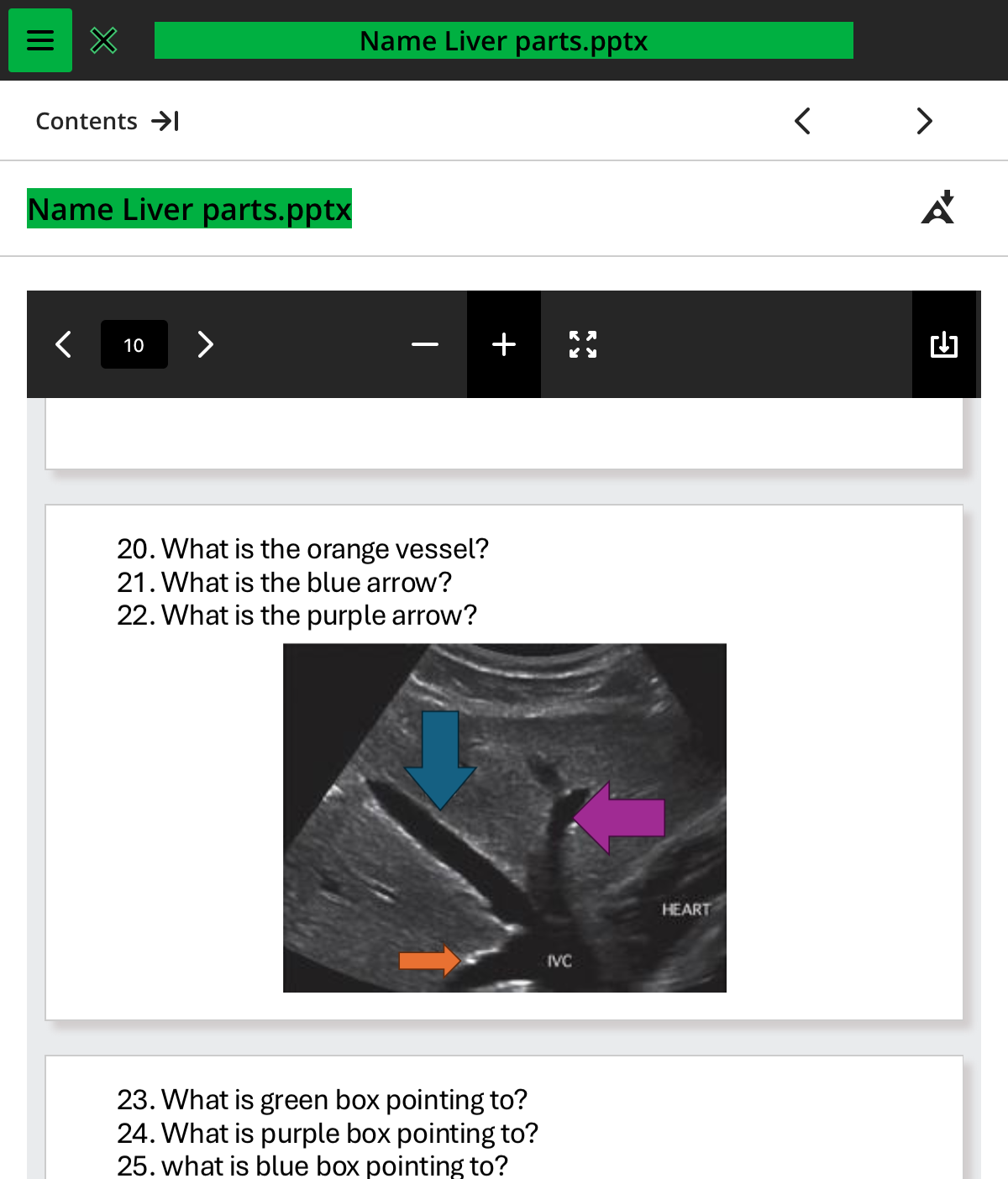
what is the orange vessel
rhv
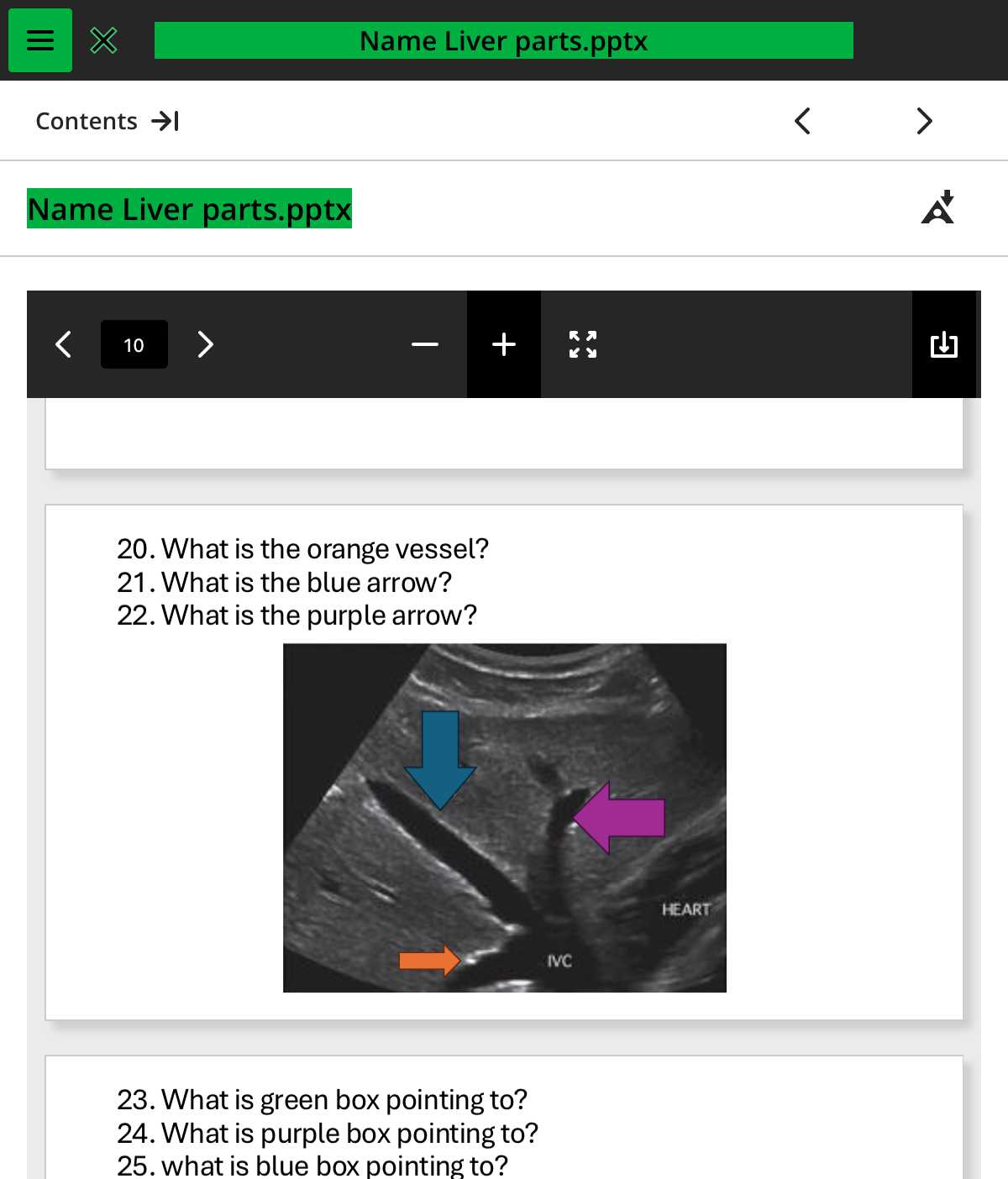
whats the blue arrow
mhv
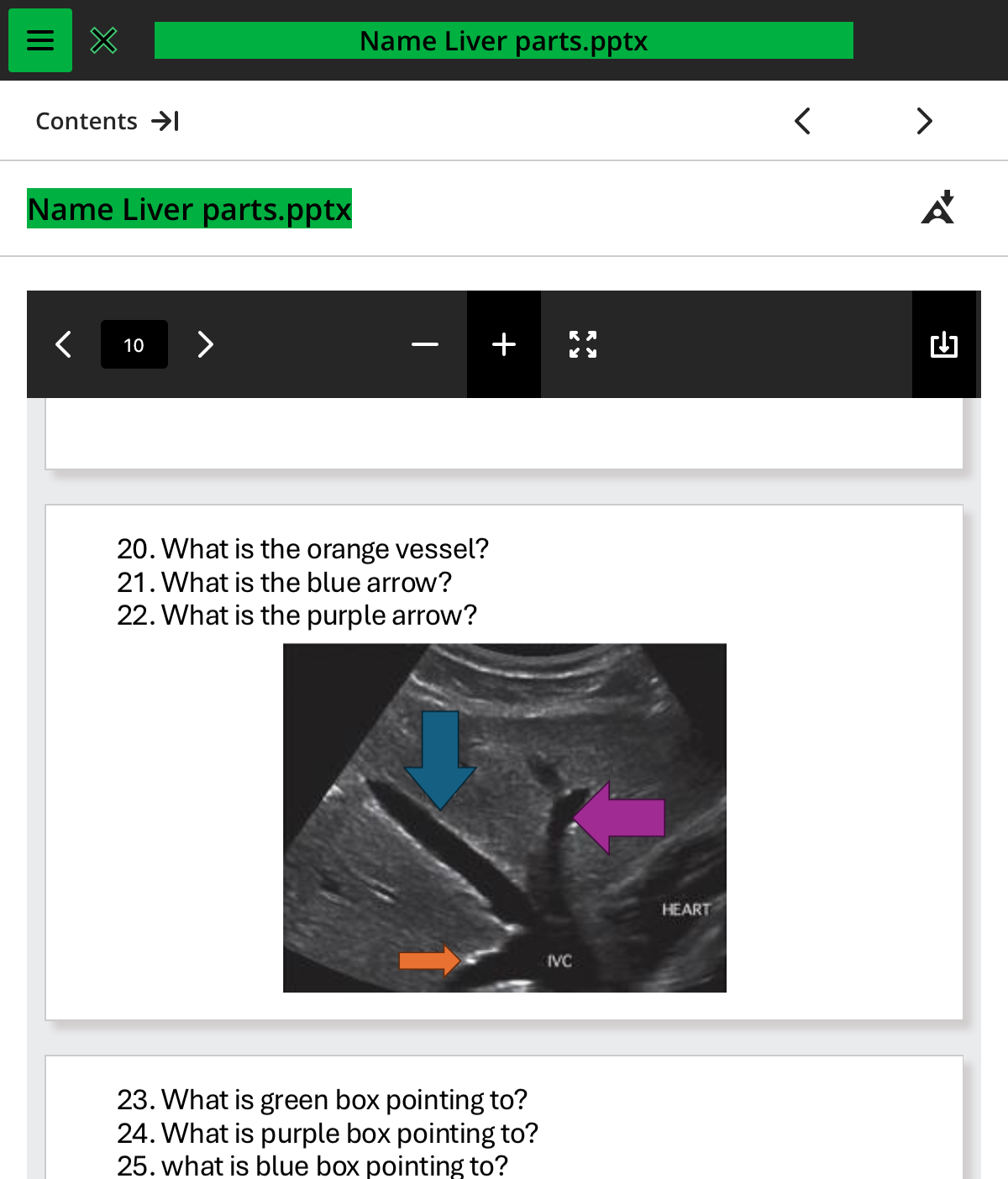
what the purple arrow
lhv
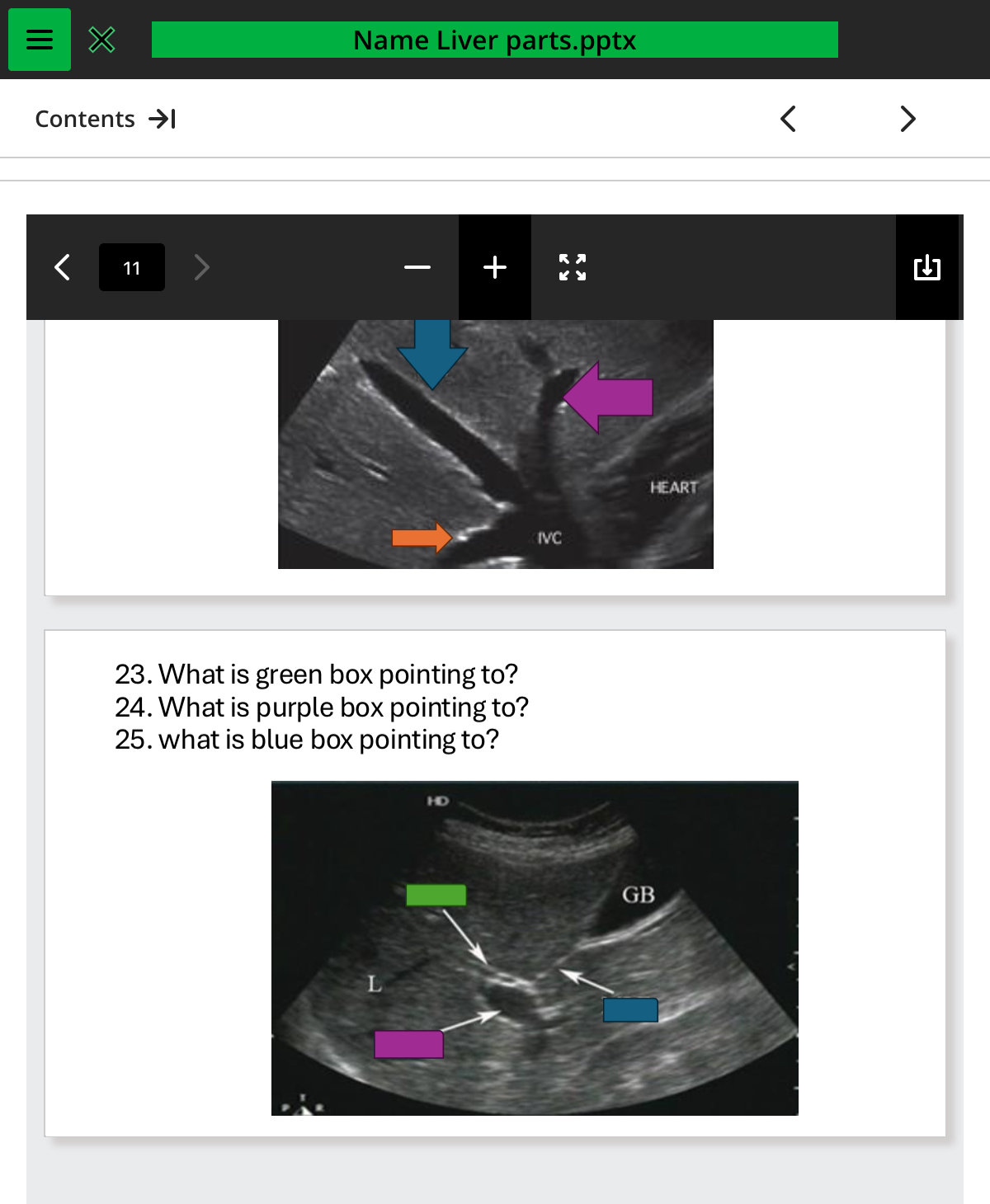
what is green box pointing to
.cbd
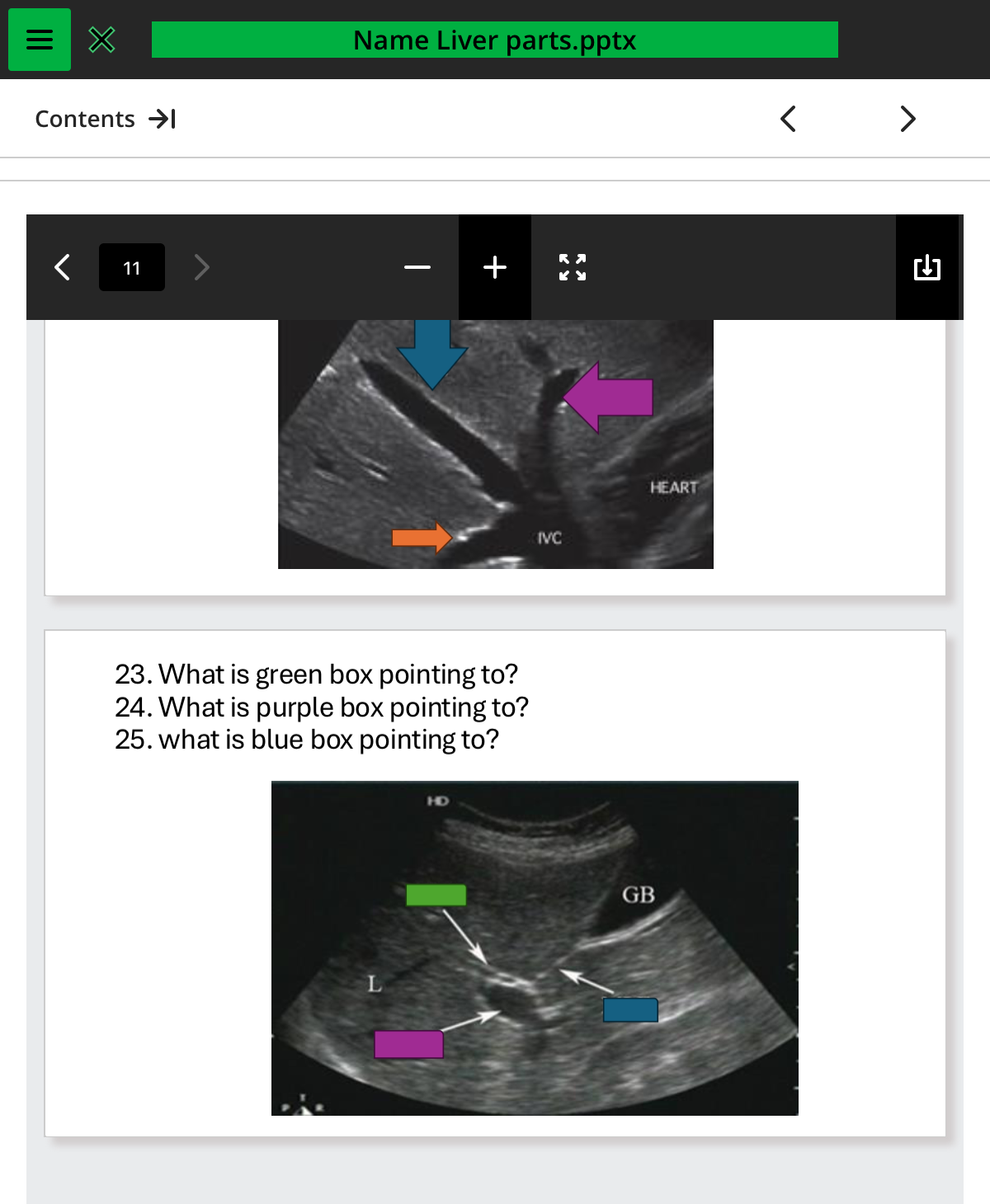
what is purple box pointing to
pv
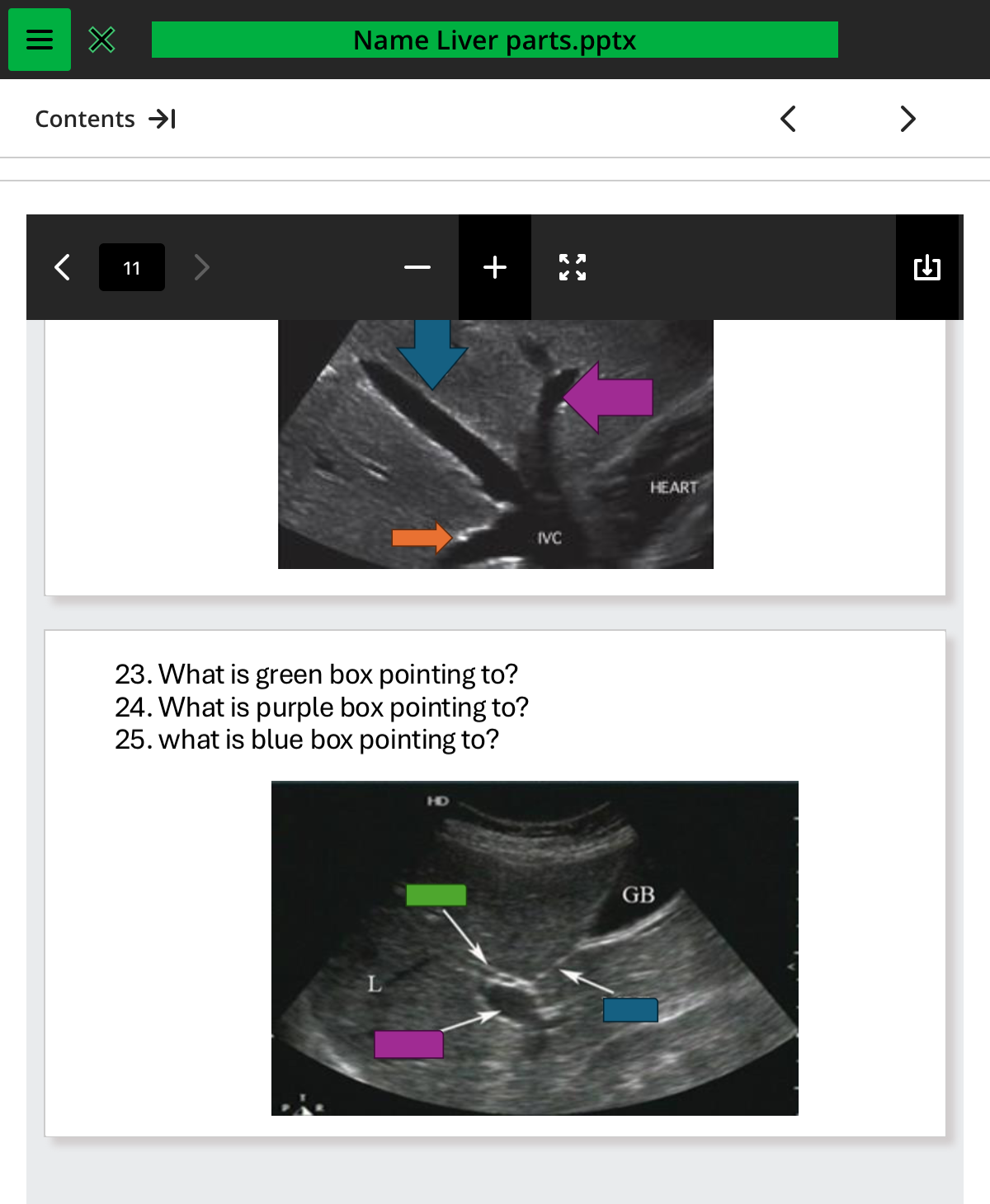
what is the blue box pointing to
mlf
the landmarks of the liver include all the except:
d. right hypogastrium
which characteristic of the right lobe of the liver is untrue
a. the right lobe exceeds the left by a ratio of 2:1
which charasteric of the left lobe of the liver if incorrect
c. the portal hepatis is the anterior border
which ligament and fissure is not found within the hepatic parenchyma
b. Transverse fissure
which statement is incorrect to sigtinguish hepatic veins from portal veins
b. splenic veins flow into the ivc
the portal flow is shown to be _ whereas the hepatic venous flow is _
toward, away
falciform ligament
divides left and right lobes, ends at the ligaments teres, or round ligament inferiorly.
gastrohepatic portion of the lesser omemtum
extends across the transverse fissure for the ligamentum venosum at the porta hepatis of the lesser curvature of the stomach
hepatoduodenal
this is a portion of the lesser omentum that extends as the right free boarder of the gastrohepatic ligament to the proximal duodenum and the right flexure of the colon
left triangular
anterosuperior surfacer of the liver runs superiorly then postereiorly on the right to the left triangular ligament
ligamentum venosum
marks the left anterolateral boarder of the caudate lobe. this travels in the transverse fissures
right triangular ligament
helps forms the boundary of the bare area
ligamentum teres
the terminal end of the falciform ligament
common hepatic artery
branch of the celiac axis that supplies the liver and divides into the GDA and PHA
Left hepatic vein
one of the three main veins draining the liver via the IVC; drains the left lobe
left portal vein
branch of the main portal vein; marks the anterior border of the caudate lobe: carries blood from the GI tract to the left lobe
main portal vein
formed by splenic and superior and inferior mesenteric veins: drains blood from the GI tract to the liver to be processed
middle hepatic vein
one of three main veins draining the liver via the IVC; drains a portion of the right and medial left lobes of the liver
portal confluence
union of the splenic and superior and inferior mesenteric veins near the head of the pancreas that forms the portal vein before entering the liver
proper hepatic artery
division of the common hepatic artery that supplies the liver
right hepatic vein
one of three main veins draining the liver via the IVC: drains the right lobe of the liver
right portal vein only
branch of the main portal vein: carries blood from the GI tract to the right lobe of the liver
bare area
only area of the liver not covered by peritoneum
caudate lobe
smallest lobe in the liver bordered by the fossa for the IC falciform ligament, lesser omentum
couinaud’s liver segmentation
divine of liver segments based on hepatic or portal venous anatomy used for dividing the liver into 8 segments
what is porta hepatis? what vessels enter and exit here?
Portal Vein, Hepatic Artery, Common Bile Duct
what is apart of the portal triad
portal vein, hepatic artery, common bile duct
glisson’s capsule
this is a tight fibrous capsule covering the liver
hemiliver
part of the liver defined as right or left half, as used in co\ouinauds liver segmentation system
main lobar fissure
echogenic line connecting neck of the gallbladder to the right portal vein: also referred to as the plane associated with the rex-cantle RC line for the couinauds ; liver segmentation system. the rc line runs from the gallbadder fossa to the IVS alone the plane of the main lobar fissure
morrisons pouch
space between the posterior subphernic and posterior sub hepatic space. it should be free of fluid
papillary process
normal variatnts of the caudate lobe. process can extend distally from the lobe and mimic a lesion
porta hepatis
area of the hilus where portal vein and hepatic artery enter and cbd enter and exit
portal triad
portion of the portal veins, biliary ducts and hepatic artery which are all throughout the liver
quadrate lobe
“4” lobe of the liver
reidels lobe
normal variants of the right lobe where the right love extends caudal into the abdomen towards the iliac crest
right lobe
largest lobe of the liver occupying most of the right hypochondrium
subhepatic space
located posteriorly and interiorly forms morrisons pouch
subhrenic space
located posteriorly and inferiorly forms morisons pouch
transverse fissure
fissure that conveys the ligaments venosums
epiploic foramen of Winslow
is the communication between greater and lesser sacs of the peritoneum
greater omentum
fold of momentum that extends from lesser curvature of the stomach and covers the intestines
greater sac
is the protective thin layer that encloses most of the abdominal organs
lesser omemuntum
is the double layer of the omentum that extends from the liver to part of the duodenum
lesser sac
it is also known as omentum bursa small sac posterior to the stomach and anterior to the pancreas and part of the transverse colon
caudate lobe
smallest lobe of the liver situated on the posteruperior surface of the left lobe: the ligament venosume is anterior border
ligamentum venosum
separates left lobe from caudate lobe: shown as echogenic line on the transverse and sagittal images
bare area
area super to the liver that is not covered ny peritoneum so that IVC may enter the chest
left lobe of the liver
lies in the epigastrium and left hypochondrium
right lobe of the liver
largest lobe of the liver
main lobar fissure
boundary between the left and right lobes of the liver; seen and as glow line on the image from the portal vein of the gallbladder
falciform ligament
extends from the umbilicus to the diaphragm in a sagitall plane and contains the ligaments teres
left portal vein
supplies the left lobe of the liver
ligamentum teres
appears glowing on transverse; falciform ligament, divides, medial and lateral segments of left lobe of the liver
main portal vein
enter the liver at the portal hepatis
right hypochondrium
ruq of the abd that contains the liv and gb
right portal vein
supplies the right lobe of the liver ; branches into anterior and posterior segments
left hypochondrium
luq of the abd contains the left lobe of the liver, spleen and stomach
epigastrium
area between the left and right hypochondrium
a congenital variant __ lobe, can sometimes be seen as anterior projection of the liver and may extend inferiorly as far as the iliac crest
riedls
the liver is covered by a thin connective tissue layer called __ capsule
glissons
the __ fissure is the boundary between the right and left lobes of the liver
main lobar
the __ ligament extends from the umbilicus to the diaphragm in a parasagittal plane and contains the ligaments teres
falciform
the ligamentum __ appears as a bright echogenic focus on the sonogram and is seen as the rounded termination of the falciform ligament
teres
the fissure fpr the ligaments __ separates the left lobe from the caudate lobe
venosum
the hepatic veins are divided intro 3 components , and _
right middle left veins
the liver is a major center of __which may be defined as the physical and chemical processed whereby foodstuff are synthesized into complex elements
metabolism
a ligament released when the red blood cells are broken down is -__
billirubin
the liver is also a center for __ of the waste products of metabolism accumulated from other sources in the body and from chemicals that enter the body
storage
sugars may be absorbed from the blood in several fors but only __ can be used by cells through tt he body as a source of energy
detoxification
the accompanying loss of oncotic pressure in the vascular system allows fluid to migrate into the interstitial space resulting in __ in dependent areas
edema
hemoglobin released from the red cells in converted to __ within the reticuloendothelial system and is the relased into the bloodstream
bilirubin
elevation of serum bilirubin result in __ which is a yellow coloration of the skin sclera and body secretions
jaundice