Understanding Speciation and Prokaryotic Diversity
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What is the basic definition of a species?
Groups of organisms that mate with one another.
What concept did Linnaeus use to describe species?
The morphological species concept, based on appearance.
What is the most frequently used definition of species?
The biological species concept: a group of populations whose members can interbreed and produce viable, fertile offspring.
What is reproductive isolation?
A condition where different species do not breed successfully with one another.
How can one species split into two reproductively isolated species?
A single population is divided into two, evolving independently and fixing new alleles at different loci.
What happens if two populations that have diverged come back together?
They may hybridize, but the hybrid offspring might be functionally inferior or lethal.
What are the two main models of speciation?
Allopatric speciation and sympatric speciation.
What is allopatric speciation?
Speciation that occurs when populations are separated by a physical barrier.
Why is allopatric speciation thought to be the dominant mode of speciation?
It is particularly prominent in island chains and other geographically isolated areas.
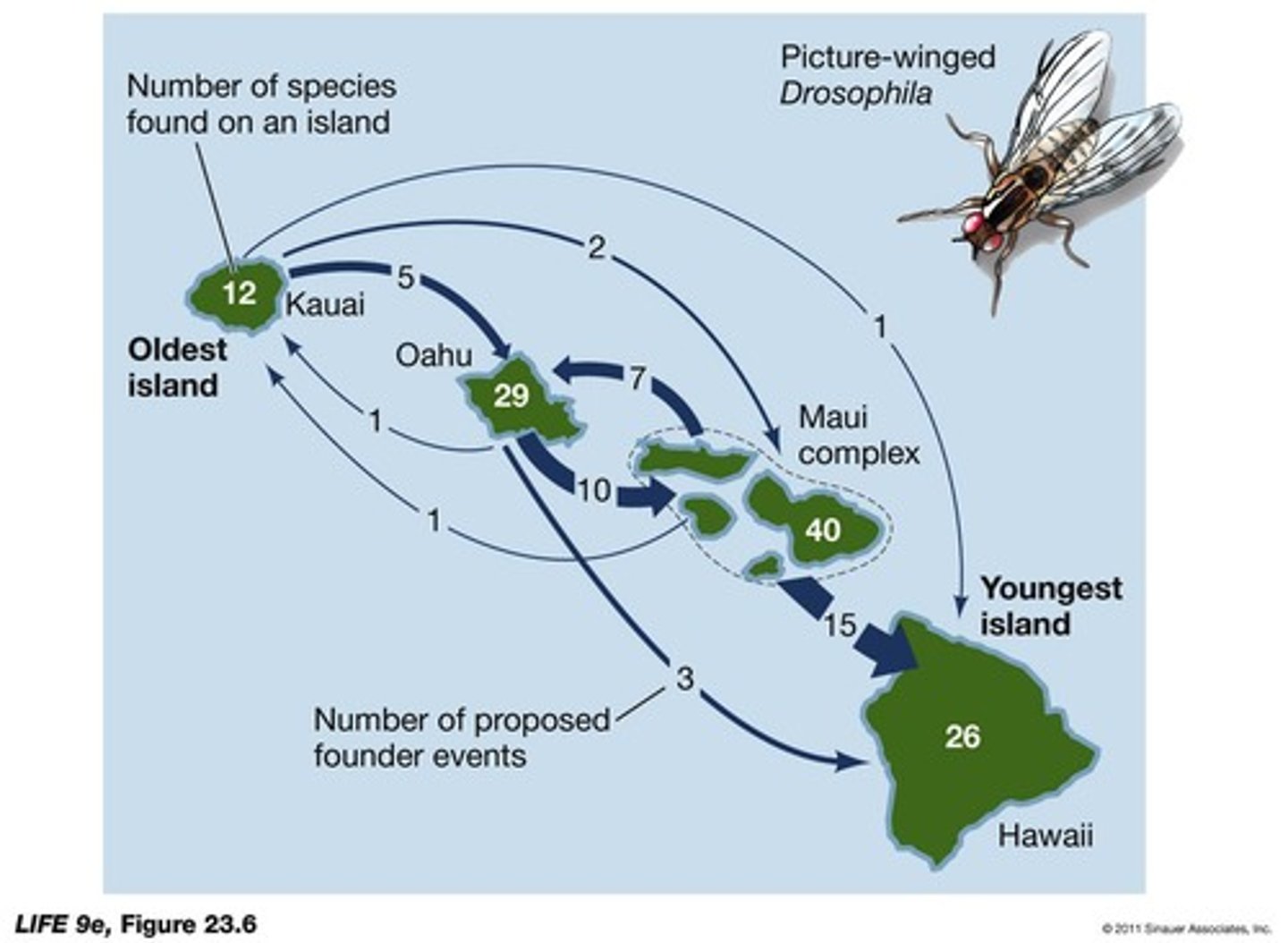
What is an example of allopatric speciation in the Hawaiian Islands?
The 800 species of Drosophila, many restricted to one island, resulting from at least 45 founder events.
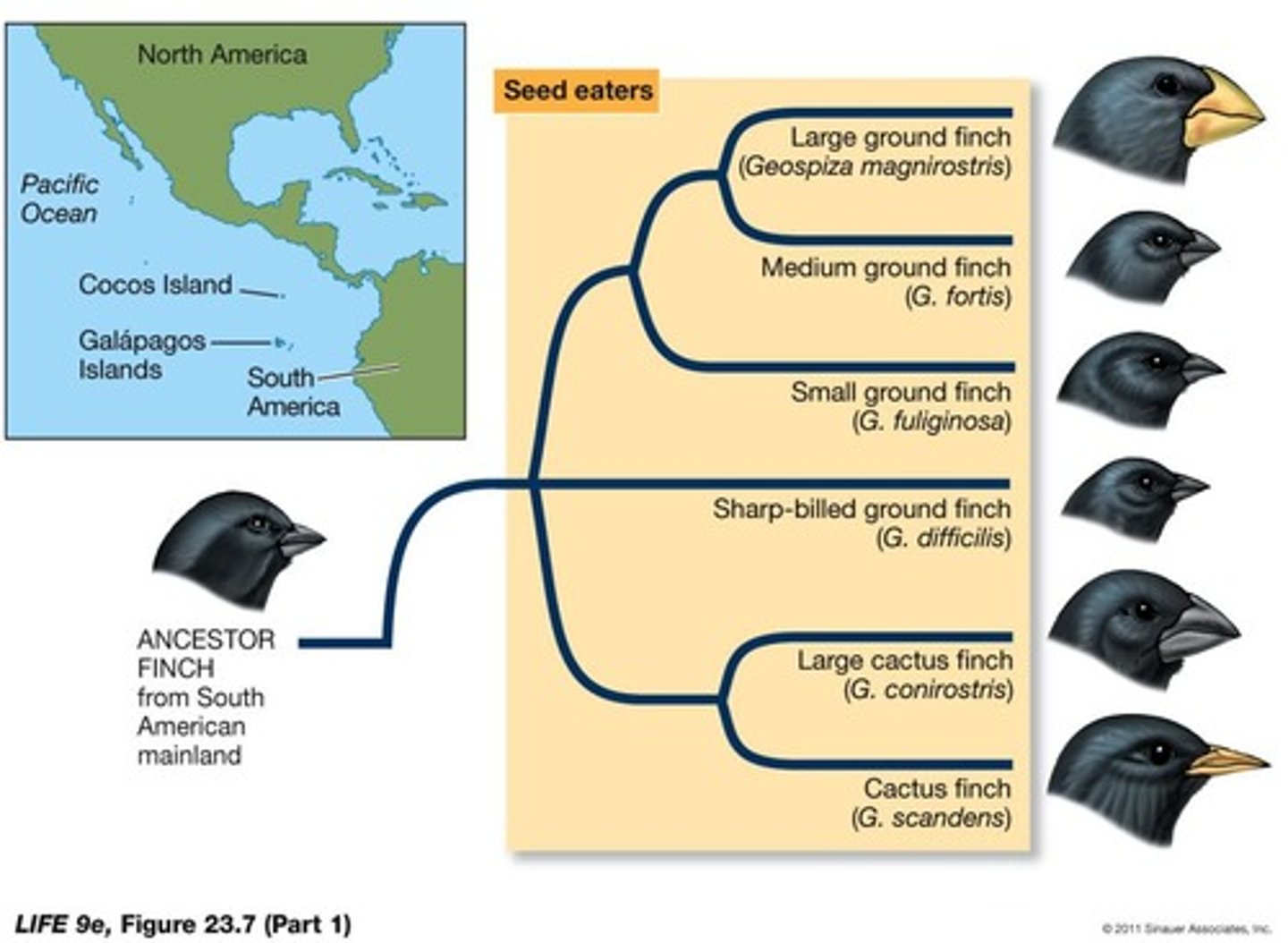
How did Darwin's finches exemplify allopatric speciation?
The 14 species arose from a single species that colonized the Galápagos Islands and adapted to different environments.
What is an evolutionary radiation?
The proliferation of a large number of species from a single ancestor.
What is adaptive radiation?
An evolutionary radiation where the resulting species live in a wide array of environments.
Why do rates of speciation vary?
Rates of speciation can vary due to environmental factors, genetic changes, and reproductive isolation mechanisms.
What is a hybrid?
An offspring resulting from the interbreeding of two different species.
Give an example of a hybrid. What are its parent species?
A mule, which is a hybrid of a horse and a donkey.
What is the significance of reproductive isolation in speciation?
It reinforces the divergence of species when they come into contact.
What role do new alleles play in speciation?
New alleles at different loci can lead to reproductive isolation between diverging species.
What is the relationship between speciation and population subdivision?
Speciation is a natural consequence of population subdivision.
How can speciation occur in sympatry?
Speciation can occur in the same geographic area without physical barriers, often through mechanisms like polyploidy or behavioral changes.
What is the importance of understanding species concepts in biology?
Different species concepts provide various approaches to understanding biodiversity and evolutionary processes.
What is sympatric speciation?
Partition of a gene pool without physical isolation, often occurring with disruptive selection.
What is an example of sympatric speciation?
The apple maggot fly in eastern North America, which began laying eggs on apples instead of hawthorn fruits.
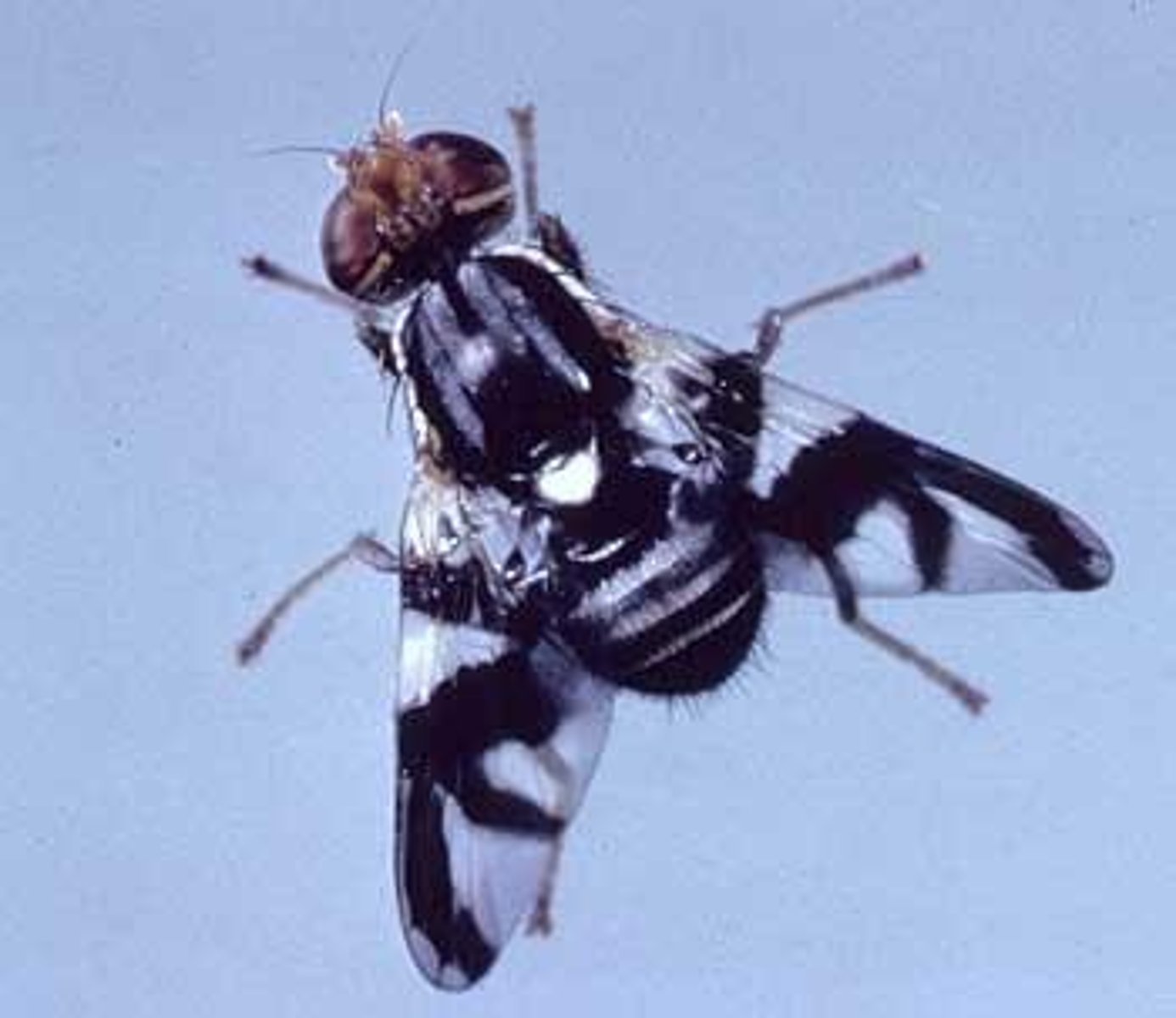

How do apple maggot flies exhibit reproductive isolation?
They mate primarily with individuals raised on the same fruit and emerge at different times.
What is polyploidy and how does it relate to sympatric speciation?
Polyploidy is the duplication of whole sets of chromosomes, commonly occurring in plants, leading to reproductive isolation.
How can polyploidy result in reproductive isolation?
Tetraploid individuals can self-fertilize or mate with other tetraploids, while their hybrid offspring with diploids are often sterile.
What are the two classes of reproductive barriers?
Prezygotic barriers (prevent mating) and postzygotic barriers (prevent viable offspring development).
What is mechanical isolation?
A prezygotic barrier where physical differences prevent mating between species.
What is habitat isolation?
A prezygotic barrier where species live in different habitats and do not meet.
What is temporal isolation?
A prezygotic barrier where species breed at different times.
What is behavioral isolation?
A prezygotic barrier where species have different courtship rituals.
What is gametic isolation?
A prezygotic barrier where sperm from one species cannot fertilize eggs from another species.
What are reduced hybrid viability and reduced hybrid fertility?
Postzygotic barriers where hybrid offspring are less viable or fertile.
What is hybrid breakdown?
A postzygotic barrier where hybrid offspring are viable but their descendants are inviable or sterile.
What happens if populations are reunited before complete reproductive isolation?
Interbreeding can occur, mixing gene pools and preventing speciation.
What is reinforcement in the context of speciation?
If hybrid offspring are less fit, it may lead to the development of more prezygotic barriers.
What is a hybrid zone?
An area where recombinant individuals from hybridization occur, often with reduced fitness.
Why do rates of speciation vary among groups?
Speciation occurs faster in populations with specialized diets, high sexual selection, or poor dispersal abilities.
What is an example of a species with poor dispersal abilities?
Land snails in the Hawaiian Islands, many of which are restricted to a single valley.
What is the significance of hybrid zones in speciation?
They persist due to continued mating between species, despite strong selection against hybrids.
What is the role of gene flow in speciation?
If hybrid offspring are fit and interbreed, gene pools mix and speciation may not occur.
What is the impact of strong selection against hybrids in a hybrid zone?
It results in a narrow hybrid zone due to reduced fitness of hybrids.
What is the relationship between sexual selection and speciation rates?
Species with a high degree of sexual selection tend to speciate faster.
What are the three domains of life?
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
What type of organisms are Bacteria and Archaea?
Prokaryotes.
What is a key characteristic of Archaea?
They are usually extremophiles.
What common metabolic process do members of all three domains conduct?
Glycolysis.
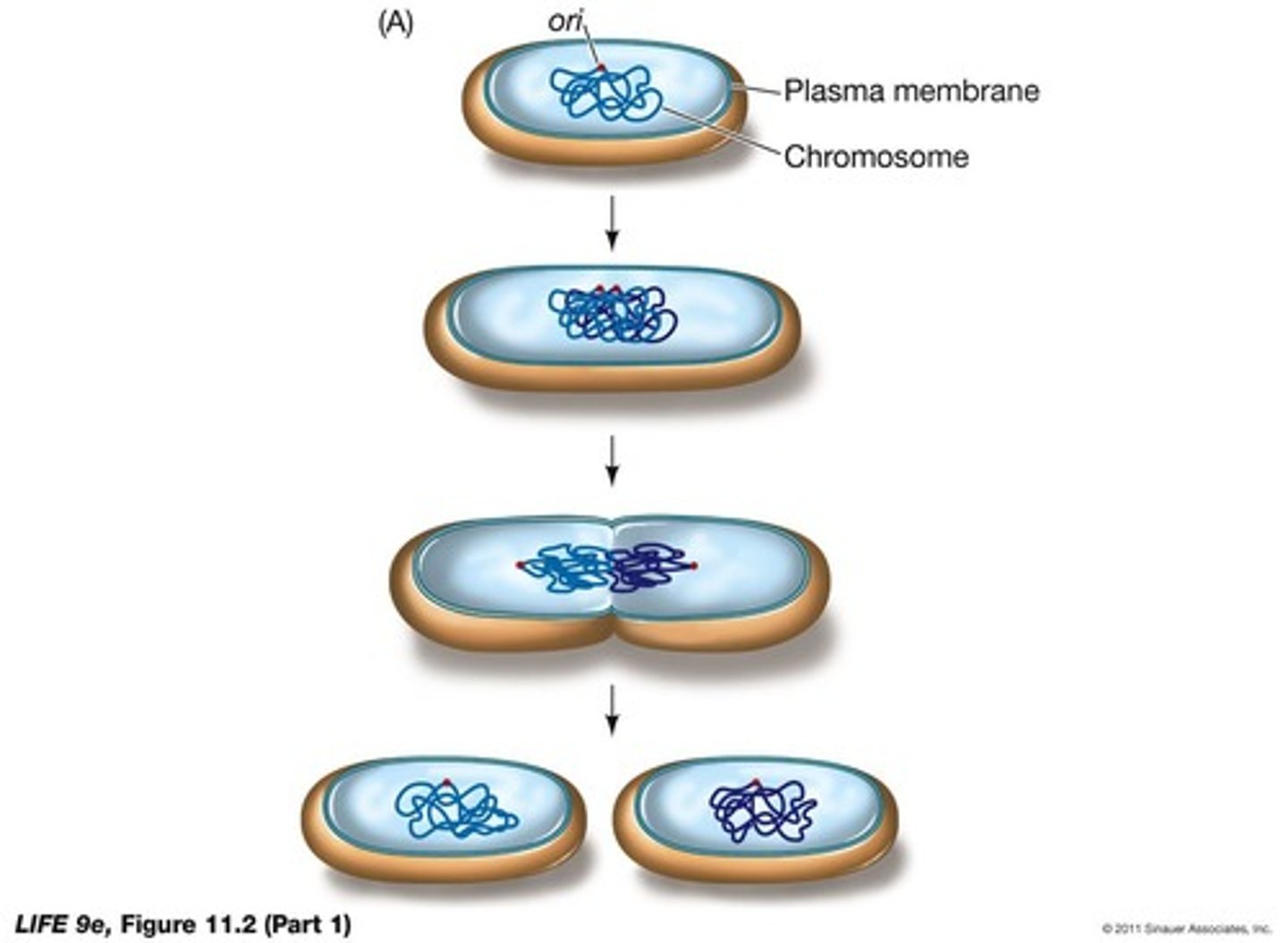
How do prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells in terms of DNA?
Prokaryotes have a single circular molecule of DNA, not enclosed in a membrane.
What is the method of reproduction for prokaryotes?
Binary fission.
What are the three common shapes of bacteria?
Sphere (coccus), rod (bacillus), and spiral (helix).
What is the composition of bacterial cell walls?
Bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan.
How do Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria differ in their cell wall structure?
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan, while Gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan and an outer membrane.
What does the Gram stain method reveal?
The complexity of bacterial cell walls, with Gram-positive bacteria staining violet and Gram-negative bacteria staining red.
What is the primary target of antibiotics like penicillin?
The synthesis of bacterial cell walls.
What is the most common type of locomotion in prokaryotes?
By flagella.
How do spirochetes move?
They have a corkscrew-like motion using modified flagella.
What processes allow for the exchange of genetic information in prokaryotes?
Transformation, conjugation, and transduction.
What is the significance of stromatolites?
They are early prokaryotic fossils.
What is the estimated age of the earliest prokaryote fossils?
At least 3.5 billion years.
What is the role of gas vesicles in cyanobacteria?
They allow cyanobacteria to move up and down in water by adjusting the amount of gas.
How does the genetic relationship between eukaryotes and Archaea compare to that with Bacteria?
Eukaryotes share a more recent common ancestor with Archaea than with Bacteria.
What is the significance of prokaryotes in terms of their numbers?
Prokaryotes are the most successful organisms on Earth, with more individuals in a handful of dirt than the total number of humans who have ever lived.
What is the function of the basal body in prokaryotic flagella?
It is responsible for motion.
What is the difference between peptidoglycan and pseudopeptidoglycan?
Peptidoglycan is found in bacterial cell walls, while pseudopeptidoglycan is found in some archaea.
How do prokaryotes contribute to ecological communities?
They play essential roles in nutrient cycling and ecosystem functioning.
What is the shortest known generation time for prokaryotes under favorable conditions?
Ten minutes.
How long can some bacteria living deep in Earth's crust suspend growth?
For more than a century without dividing.
What do many prokaryotes form in unfavorable conditions?
Metabolically inactive endospores that can remain viable indefinitely.
What is quorum sensing in prokaryotes?
The ability of bacteria to monitor the size of their population by sensing the amount of chemical signals present.
What is an example of bioluminescence in prokaryotes?
Vibrio colonies emit light to attract fish, thriving best in their guts.
What types of metabolic pathways do prokaryotes utilize?
Aerobic and anaerobic pathways for making ATP.
How do prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes in terms of metabolic mechanisms?
Prokaryotes use a wider diversity of metabolic pathways; eukaryotes use fewer mechanisms primarily in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
What are photoautotrophs?
Organisms that perform photosynthesis, such as cyanobacteria, which use chlorophyll a and produce O2 as a by-product.
What do photoheterotrophs use for energy and carbon?
They use light as an energy source and obtain carbon from compounds made by other organisms.
What are chemoautotrophs?
Organisms that obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic compounds and use that energy to fix CO2.
What is the role of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in ecosystems?
They convert N2 gas into ammonia, which is important for plant growth.
What is the significance of prokaryotes in the cycling of elements?
They are crucial in the global cycling of elements such as nitrogen and sulfur.
What impact did cyanobacteria have on ancient life?
They started generating O2 as a by-product of photosynthesis, leading to the loss of anaerobic species and the development of cellular respiration and eukaryotic life.
How do prokaryotes contribute to human health?
They form microbiomes that aid in digestion, produce vitamins B12 and K, and maintain skin health.
What is the role of bacteria in the digestive tracts of animals?
They help digest cellulose, as seen in cattle rumens where cellulase is produced.
What factors can affect the microbiome communities in our bodies?
Diet, medicines, toxins, and lifestyle.
What is the function of the biofilm that lines human intestines?
It facilitates the uptake of nutrients and induces immunity to gut contents.
In what applications do prokaryotes play positive roles?
Cheese making, sewage treatment, and production of antibiotics, vitamins, and chemicals.
What is the significance of prokaryotes as decomposers?
They metabolize organic compounds in dead organisms, returning products like carbon dioxide to the environment.
What is the relationship between prokaryotes and ecosystems?
Prokaryotes are a part of all ecosystems, with only a small minority being human pathogens.
How do prokaryotes alter the availability of elements in the environment?
By processes such as nitrogen fixation, which is essential for plant growth.
What health problems are linked to microbiome disruption?
Many complex health problems, including autoimmune diseases.
What are the two main factors that determine the consequences of bacterial infection?
Invasiveness of the pathogen and toxigenicity of the pathogen.
What are endotoxins and how are they released?
Endotoxins are released when certain Gram-negative bacteria are lysed and are rarely fatal.
Which bacteria are known to produce endotoxins?
Salmonella and Escherichia.
What are exotoxins?
Soluble proteins released by living bacteria that are highly toxic and often fatal.
Name some diseases caused by exotoxins.
Tetanus (Clostridium tetani), botulism (Clostridium botulinum), cholera (Vibrio cholerae), plague (Yersinia pestis), and anthrax (Bacillus anthracis).
Why are viruses not considered cellular organisms?
Viruses are not cellular and can only reproduce in the cells of other living organisms.
What types of genomes do viruses possess?
Viruses have either DNA or RNA genomes.
How do viruses interact with cellular life?
Viruses infect all cellular forms of life and can replicate, mutate, evolve, and interact with other organisms.
What challenges exist in resolving virus phylogeny?
Viral genomes are tiny, have a rapid mutational rate, and there are no known viral fossils.
What are the two types of viral nucleic acids?
Double- or single-stranded DNA, or double- or single-stranded RNA.
What is a capsid?
A capsid is the protein shell that encloses the viral genome.
What are capsomeres?
Capsomeres are the protein subunits that make up a capsid.
How do viruses cause symptoms in infected cells?
Viruses may damage or kill cells by causing the release of hydrolytic enzymes, producing toxins, or having toxic envelope proteins.