UA, BODY FLUIDS, IMMUNOLOGY
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
B Cell Maturation occurs in the
Thymus
Bone Marrow
Thyroid
Pituitary
Bone Marrow
Choose all of the correct statements regarding the spleen:
It filters antigens from the blood.
Contains primary and secondary nodules rich in neutrophiles.
It contains megakaryocyte precursors.
It functions to remove old and defective red blood cells from circulation.
It filters antigens from the blood.
It functions to remove old and defective red blood cells from circulation.
GALT Lymphoid tissues are associated with: (Choose all that apply)
IgA production
Brain
Peyer’s patches
Lymphoid Tissue of the intestines
IgA production
Peyer’s patches
Lymphoid Tissue of the intestines
The role the Tissue Mast Cell plays in regulating an immune response primarily involves receptors which bind to:
Ig M
Ig E
Ig A
B Lymphocytes
Ig E
MHC Class II antigens:
Have beta-2 macroglobulin in them
are found on every nucleated cell
are located on monocytes, B-cells and activated T-cells
bind to proteins inside the cell
are located on monocytes, B-cells and activated T-cells
The rapid rise of antibody on the secondary immune response is primarily due to:
Memory T cells
Memory B cells
IgA
NK cells
Memory B cells
Clonal expansion and differentiation of stimulated B cells will occur in:
Immunosuppression
Adaptive Immunity
Delayed Hypersensitivity
Innate Immunity
Adaptive Immunity
The Immunogenicity of a foreign agent is influenced by:
Chemical complexity
Molecular weight
Degradability
All of the available choices
All of the available choices
This is true when interpreting a Serum Protein Electrophoresis pattern:
a decreased or absent gamma peak is a hallmark for Waldenstrom's disease
Increased albumin is indicative of nephrotic syndrome
"immediate response" pattern shows a decrease in both albumin and alpha-2
an increased alpha-2 may be comprised of increased haptoglobin
an increased alpha-2 may be comprised of increased haptoglobin
The Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Anti Nuclear Antibody test (ANA) utilizes a fluorescent tagged antihuman antibody in conjunction with which of the following to demonstrate the presence of autoantibodies:
Fluorescent tagged nucleoli from trypanosomes
Hep-2 cell substrate
MLK cell line
Fluorescent dye to visualize cell nucleus
Hep-2 cell substrate
A patient with fibrous build-up in her skin has:
The autoantibodies are against microtubules.
The patient has rheumatoid arthritis
She has the fibrous build up due to anti-IgG depositing in her skin
The patient is suffering from scleroderma
The patient is suffering from scleroderma
CTL Cytoxic T Lymphocytes are recognized by which of the following cell markers?
CD19+
CD16 and CD56
CD4+
CD8+
CD8+
A 12 year old female presented to her physician with a sore throat, lymphadenopathy and fatigue. Her laboratory results were: 5000 lymphocytes/μL with 10% variant lymphocytes. CMV antibody screen and heterophile antibody screen were both negative. These results :
Confirm a diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis
Suggests a diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis but should be followed by a test for IgM anti-VCA to strengthen the diagnosis
Indicates that the diagnosis is not infectious mononucleosis because the heterophile screen is negative
Suggest a diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis but should be followed by FTA-ABS to confirm the diagnosis
Suggests a diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis but should be followed by a test for IgM anti-VCA to strengthen the diagnosis
Immunofluorescent antibody tests are best described as:
fluorescent test looking for viral antigen directly in the patient specimen
antibody mediated cell lysis enhanced with a fluorescent stain
a hemagglutination inhibition reaction
fluorescent test using serum and FITC tagged antihuman globulin
fluorescent test using serum and FITC tagged antihuman globulin
The acute phase reactant that responds the fastest, increases several hundred fold after injury and is the most sensitive indicator of acute inflammation is:
C-reactive protein
haptoglobin
fibrinogen
complement
C-reactive protein
A 50 year old male Is seen by his physician because of increasing fatigue and weakness. He also reports pain in his lower back and arms when he walks. The CBC reveals that he has anemia. His leukocyte count and differential are normal, except for rouleux appearance of the red blood cells. The physician orders the following tests: ESR, kidney screening profile, liver profile and radiographic skeletal survey. The tests reveal an elevated ESR, normal kidney function profile, normal liver profile except for increased globular protein, and bone lesions in various sites from the skeletal survey. Patients with this disease have defects in:
synthesis of normal immunoglobulins
cellular immunity
humoral immunity and synthesis of normal immunoglobulins
humoral immunity
humoral immunity and synthesis of normal immunoglobulins
The RPR test is:
can be falsely positive for patients who have SLE
a Treponemal antibody assay
needs to be interpreted with a microscope to see the agglutination
the confirmatory test for syphilis
can be falsely positive for patients who have SLE
A patient’s specimen is strongly positive in an ANA ELISA. Which of the following would not be an appropriate follow-up to this result?
Specific ENA ELISA tests
IFA on human epithelial type 2 (HEp-2) cells
Specific anti-DNA ELISA
Rheumatoid factor (RF) assay
Rheumatoid factor (RF) assay
False negatives due to the over abundance of antibody is:
least often seen in agglutination reactions
prozone
postzone
polyzone
prozone
A 50 year old female complained of increased pain and stiffness in her fingers and wrists for over a year's duration. The laboratory results were as follows: ESR elevated, increased CRP, positive rheumatoid factor, negative ANA and normal complement levels. What is the most probable diagnosis?
CREST syndrome
SLE
Syphilis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Which disease might be indicated by antibodies to smooth muscle?
Sjögren syndrome
Atrophic gastritis
Autoimmune hepatitis
Myasthenia gravis
Autoimmune hepatitis
The rapid plasma reagin (RPR) for syphilis does not need to be read microscopically because the antigen is:
cardiolipin
inactivated bacterial cells
particulate (latex bead)
complexed to charcoal
complexed to charcoal
The role that the macrophage plays in regulating an immune response primarily involves its interaction with which of the following elements of the immune system:
Plasma cells
platelets
Immunoglobulin
CD4 cells
CD4 cells
Systemic lupus erythematosus and the presence of dsDNA are most likely associated with which of the following antinuclear antibody immunofluorescent patterns?
rim
homogeneous
nucleoli
speckled
homogeneous
The portion of the nephron which extends below the cortex and into the medulla of the kidney is:
Loop of Henle
Glomerulus
Afferent arteriole
Bowman's capsule
Loop of Henle
An emphysema patient is known to be in respiratory acidosis, a condition in which CO2, carbon dioxide, is retained. In compensation, large amounts of (NH4) ammonia are released. You would expect the urine pH to be:
acidic
basic
>9.0
normal
acidic
A runner suffering from heat prostration is brought to the Emergency Room for observation. A urine sediment revealed no bacteria, (1+) 10-15 WBC, rare RBC, and (3-4+) hyaline cast. From this information you can assume:
the patient is essentially normal
the patient has toxic nephrosis
the patient suffers from acute pyelonephritis
the patient is in an acute phase of cystitis
the patient is essentially normal
A 68-year-old male is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of Chronic End-Stage Renal disease. You would expect his urine sediment to predominate with:
waxy casts
fatty casts
red blood cell casts
d. epithelial cell casts
waxy casts
Which of the following will be least affected in an unpreserved specimen left at room temperature overnight?
Urobilinogen
Bilirubin
Red blood cells
Protein
Protein
Which statement regarding normal salt and H2O handling by the nephron is correct?
The descending limb of the tubule is impermeable to urea but highly permeable to salt
The stimulus for ADH release is low arterial pressure in the afferent arteriole
Renin is released in response to high plasma osmolality
The thick ascending limb of the tubule is highly permeable to salt but not H2O
The thick ascending limb of the tubule is highly permeable to salt but not H2O
Concentration of the tubular filtrate by the countercurrent mechanism is dependent on all of the following except:
Collecting duct
Proximal convoluted tubule
Descending loop of Henle
Ascending loop of Henle
Ascending loop of Henle
Calculate the creatinine clearance for a patient of average size from the following data:
Urine volume: 720 mL for 12 hours
Urine creatinine: 120 mg/dL
Serum creatinine: 1.5 mg/dL
80 mL/min
60 mL/min
100 mL/min
120 mL/min
80 mL/min
For accurate evaluation of renal tubular concentrating ability, patient preparation should include:
Increased hydration
Fasting
Fluid deprivation
Abstaining from all medications
Fluid deprivation
Following injection of ADH, a patient has a serum osmolality of 290 mOsm and a urine osmolality of 450 mOsm. The patient:
Continued to observe water deprivation
May have ingested excess alcohol
Should be evaluated with a creatinine clearance
Lacks tubular response to ADH
Lacks tubular response to ADH
SITUATION: A 6-mL pediatric urine sample is processed for routine urinalysis in the usual manner. The sediment is prepared by centrifuging all of the urine remaining after performing the biochemical tests. The following results are obtained:
SG = 1.015 | Blood = Large | Leukocytes = Moderate |
Protein = 2+ | RBCs: 5–10/HPF | WBCs: 5–10/HPF |
Select the most appropriate course of action.
Report biochemical results only; request a new sample for the microscopic examination
Recentrifuge the supernatant and repeat the microscopic examination
Report these results; blood and protein correlate with microscopic results
Request a new sample and report as quantity not sufficient (QNS)
Report biochemical results only; request a new sample for the microscopic examination
SITUATION: A urine specimen is dark orange and turns brown after storage in the refrigerator overnight. The MLS requests a new specimen. The second specimen is bright orange and is tested immediately. Which test result would differ between the two specimens?
Ketone
Leukocyte esterase
Nitrate
Urobilinogen
Urobilinogen
The pigment responsible for a pink precipitate in refrigerated urine is:
Urochrome
Biliverdin
Bilirubin
Uroerythrin
Uroerythrin
Which of the following conditions is associated with a negative blood test result and an increase in urine urobilinogen?
Extravascular hemolytic anemia
Calculi of the kidney or bladder
Crush injury
Malignancy of the kidney or urinary system
Extravascular hemolytic anemia
Failure to blot the edge of the reagent strip may result in errors in color interpretation caused by:
Reagent leaching
Runover
Chemical concentration
Excess dilution
Runover
A moderately positive result on the blood test and trace protein test are seen on the dry reagent strip, and 11 to 20 RBCs/HPF are seen in the microscopic examination. These results are most likely caused by which of the following?
Transfusion reaction
Intravascular hemolytic anemia
Myoglobinuria
Recent urinary tract catheterization
Recent urinary tract catheterization
The ketones that are produced in normal adult metabolism include all of the following except:
Beta-hydroxybutyric acid
Acetoacetic acid
Acetone
Phenylketones
Phenylketones
Detection of hemosiderin in the urine can be associated with:
Hematuria
Myoglobinuria
Hemoglobinuria
Albuminuria
Hemoglobinuria
When bilirubin is detected in the urine, it can be assumed that:
It has passed through the small intestine
The patient is diabetic
It is attached to protein
It has been conjugated in the liver
It has been conjugated in the liver
Which of the following tests is affected least by standing or improperly stored urine?
Bilirubin
Protein
pH
Glucose
Protein
Urine production of less than 400 mL/day is:
Consistent with normal renal function and H2O balance
Termed isosthenuria
Defined as oliguria
Associated with diabetes mellitus
Defined as oliguria
What do the following results suggest?
Color: Yellow | Protein: Trace | Blood: Negative |
Clarity: Cloudy | Glucose: Negative | Urobilinogen: 0.1EU |
Specific Gravity: 1.019 | Ketones: Negative | Nitrite: Positive |
pH: 8.0 | Bilirubin: Negative | Leukocyte esterase: Positive |
Unsatisfactory specimen
Normal female specimen
Urinary tract infection
Diabetes mellitus
Urinary tract infection
In ascending order, the location of epithelial cells in the urinary tract is:
Squamous, renal tubular, urothelial
Renal tubular, transitional, squamous
Transitional, renal tubular, squamous
Squamous, transitional, renal tubular
Squamous, transitional, renal tubular
Urinary casts are formed in the:
Proximal and distal tubules
Distal and collecting tubules
Distal tubules and loops of Henle
Proximal tubules and loops of Henle
Distal and collecting tubules
To differentiate a bacterial cast from a granular cast, a clinical laboratory scientist could:
use polarizing microscopy
perform a Hansel stain
perform a gram stain
add acetic acid to the sediment
perform a gram stain
Abnormal crystals are most frequently seen in a urine that is:
acid
neutral
alkaline
collected for 24 hours
acid
The following results are obtained on a urinalysis from a student athlete. Based on the information provided, why is only a trace of blood detected by reagent strip?
Color: Dark Yellow | Protein: 2+ | Blood: Trace |
Clarity: Cloudy | Glucose: Negative | Urobilinogen: 1 EU |
Specific gravity: 1.032 | Ketones: Negative | Nitrite: Negative |
pH: 6.0 | Bilirubin: Negative | Leukocyte esterase: Negative |
Microscopic:
15-20 crenated RBC's hpf 2-3 hyaline casts/lpf
Rare squamous epithelial cell 1-2 granular casts/lpf
Protein inhibition
Acid pH
Dilute specimen
Crenated RBCs
Crenated RBCs
Urinalysis results are being monitored on a patient following an adverse reaction occurring during surgery. Based on the information provided, what is the significance of the elevated urobilinogen reading?
Color: Red Brown | Protein: 1+ | Blood: Large |
Clarity: Cloudy | Glucose: Negative | Urobilinogen: 8.0 EU |
Specific gravity: 1.012 | Ketones: Negative | Nitrite: Negative |
pH: 7.0 | Bilirubin: Negative | Leukocyte esterase: Negative |
Microscopic:
6-10 RTE cells/hpf (intracellular yellow/brown granules)
3-4 homogenous RBC casts/lpf
1-2 dirty, brown casts/lpf
1-2 RTE cell casts/lpf
Many yellow-brown granules
Urine Color
Liver damage
Intravascular hemolysis
Constipation
Intravascular hemolysis
Which of the following contributes to SG, but not to osmolality?
Salt
Urea
Protein
Glucose
Protein
In which part of the kidney is uromodulin produced?
Nephrons and collecting ducts
Proximal and distal tubules
Bowlman's capsule and nephrons
Descending and ascending loop of Henle
Proximal and distal tubules
In which of the following disorders would waxy and broad casts be most likely to be seen?
chronic renal failure
acute inerstitial nephritis
acute renal failure
chronic pyelonephritis
chronic renal failure
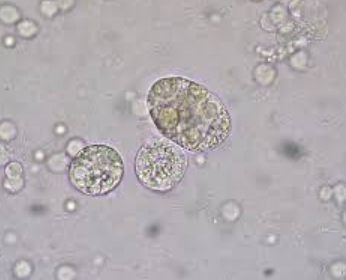
Identify the following cell:
Clue Cell
Glitter Cell
Oval Fat Body
Ghost Cell
Glitter Cell
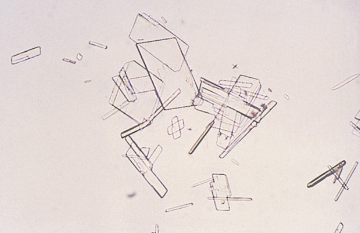
Identify the following:
Ammonium biurate
Cholesterol
Triple phosphate
Cystine
Calcium carbonate
Cholesterol
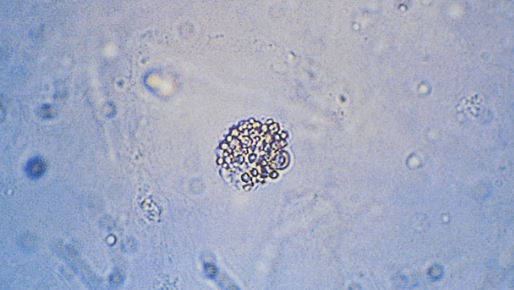
Identify the following cell:
Oval Fat Body
Spherical cell
No answer text provided.
Glitter Cell
Oval Fat Body
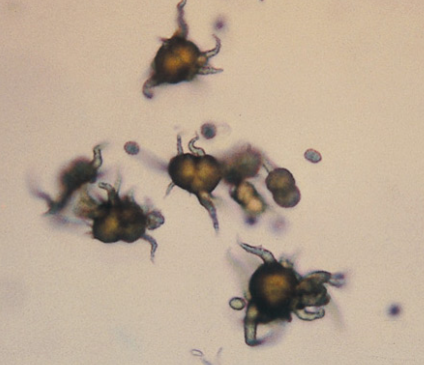
Identify the following:
Ammonium biurate
Calcium carbonate
Triple phosphate
Cholesterol
Cystine
Ammonium biurate
Where does most cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) originate?
Ventricles
Cerebral arachnoid space
Choroid plexus
Lumbar region
Choroid plexus
How many white blood cells should be considered normal for adult cerebrospinal fluid?
0-5 WBCs/uL
6-10 WBCs/uL
Any number of WBC's is considered abnormal
up to 30 WBCs/uL
0-5 WBCs/uL
Which of the following would be considered normal for a glucose level in cerebrospinal fluid?
120 mg/dL
30 mg/dL
150 mg/dL
60 mg/dL
60 mg/dL
A sperm concentration of 25 x 106 spermatozoa/mL would be considered an abnormally low concentration, according to the lower normal reference limit stated in WHO 5th edition.
True
False
False
A semen specimen was collected three hours before it was brought to the laboratory for examination. What course of action should be taken?
Perform the wet mount only
Report the specimen as compromised on the final report
Complete macroscopic and microscopic examination as quickly as possible
Perform the macroscopic and morphology procedures only
Report the specimen as compromised on the final report
On a cytospin preparation from a pleural fluid, 50% of the cells have the following characteristics:
uniform, regular arrangement
some cells resemble a "fried egg"
multiple nuclei
smooth nuclear outline and homogeneous chromatin
when present in clumps, there are clear spaces between the cells ("windows")
How should these cells be classified?
atypical cancer cells
ependymal cells
tumor cells
mesothelial cells
mesothelial cells
Which is the best method for examination of synovial crystals:
Phase contrast
Polarized light
Darkfield microscopy
Brightfield microscopy
Polarized light
Which of the following parameters is generally NOT considered to be a part of a seminal fluid analysis?
Motility
Glucose concentration
Viscosity assessment
Sperm count
Morphology examination
Glucose concentration
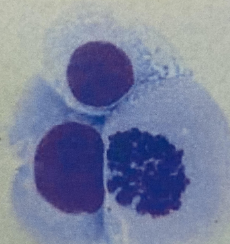
The image is a Wright-Giemsa stained smear (1000x) of a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). What is the identification of the cells in the smear?
Presumptive malignant cells
Immature white blood cells
Atypical lymphocytes
Ependymal cells
Presumptive malignant cells
A 3 year old girl was brought to the ER with a temperature of 103F, lethargy, and cervical rigidity. Three tubes of cloudy CSF were delivered to the Lab, and preliminary test results showed:
WBC: 4,500/uL Differential: 88% neutrophils
Glucose: 15 mg/dL 12% lymphocytes
Protein: 140 mg/dL
Gram stain: No organisms observed
Brain tumor
subdural hematoma
viral meningitis
Bacterial meningitis
Bacterial meningitis
Which of the following is characteristic of an exudates effusion?
Protein concentration less than 3.0g/dL
Clear appearance
Absence of fibrinogen
Leukocyte count greater than 1000 WBC/uL
Leukocyte count greater than 1000 WBC/uL
Which of the following characteristics is higher for synovial fluid than for the serous fluids?
Total protein
Viscosity
Glucose
Specific gravity
Viscosity
A 1:10 dilution is made on a CSF sample. Five squares on each side of the hemacytometer are counted for a total of 10 squares and a total of 150 cells are recorded. What is the count per microliter?
758
833
527
1500
1500
Two CSF specimens were sent to the Lab with the following results:
Tube #1 = 11,200 rbc/µL
Tube #2 = 300 rbc/µL
The results on these CSF specimens are indicative of:
an old intracranial bleeding episode
faulty lab equipment
an infection
a recent subarachnoid hemorrhage
a traumatic tap
a traumatic tap
What is generally accepted as the lower threshold value for semen pH from fertile males?
7.2
6.5
8.0
5.5
7.2
Normal adult CSF may have 0-5 white blood cells (WBCs)/µL. Which of the following cell types account for 60-100% of these WBCs?
Neutrophils
Monocytes
Eosinophils
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes
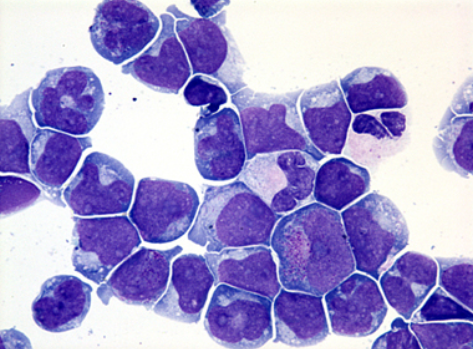
The image is a stained smear of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The cells indicate which of the following conditions?
Leukemia with CNS involvement
Bacterial meningitis
Viral meningitis
Allergic reactions
Leukemia with CNS involvement
A semen sample for semen analysis should generally be received at the testing site within what period of time?
One hour
Two hours
Four hours
Three hours
One hour
For BEST results, a semen sample should remain at which of the following temperatures following collection?
37C
56C
-40C
Room temperature
4C
37C
Which of the following would be the most characteristic finding in synovial fluid in a case of pseudogout:
Monosodium urate crystals
Macrophage infilitration
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals
Mixed RBC/WBC infiltration
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals
The lining covering the abdominal organs is called the
Arachnoid membrane
Pseudo-membrane
Parietal membrane
Visceral membrane
Visceral membrane
The layer of superficial squamous cells which covers the serous cavities are
impervious to sodium
made up of columnar cells
impervious to water
made up of mesothelial cells
made up of mesothelial cells
Serous fluid is formed when there is: (Choose all that apply)
a decrease of plasma colloid osmotic pressure
an increase of hydrostatic pressure
a decrease in blood pressure
an increase of plasma colloid osmotic pressure
a decrease of plasma colloid osmotic pressure
an increase of hydrostatic pressure
Which statement about CSF protein is true?
Antibodies to Treponema pallidum disappear after successful antibiotic therapy
An abnormal serum protein electrophoretic pattern does not affect the CSF pattern
CSF IgG is increased in panencephalitis, malignancy, and neurosyphilis
The upper reference limit (URL) for CSF total protein in newborns is one half the adult level
CSF IgG is increased in panencephalitis, malignancy, and neurosyphilis
A urine sample taken after a suspected transfusion reaction has a positive test result for blood, but intact RBCs are not seen on microscopic examination. Which test result would rule out an intravascular hemolytic transfusion reaction?
Serum unconjugated bilirubin below 1.0 mg/dL
Negative urine urobilinogen
Serum potassium below 6.0 mmol/L
Normal plasma haptoglobin
Normal plasma haptoglobin
A WBC count and differential performed on ascites fluid gave a WBC count of 20,000/µL with 90% macrophages. The gross appearance of the fluid was described by the MLS as “thick and bloody.” It was noted on the report that several clusters of these cells were observed and that the majority of the cells contained many vacuoles resembling paper-punch holes. What do the observations above suggest?
Lymphoma infiltrating the peritoneal cavity
Malignant mesothelial cells were counted as macrophages
Adenocarcinoma from a metastatic site
Nodular sclerosing type Hodgkin disease
Malignant mesothelial cells were counted as macrophages
The Serum-Ascites Albumin Gradient is a reflection of
Excessive IV Therapy (Hyper hydration)
Inadequate Reticuloendothelial System (RES) function
Hydrostatic pressure of the portal system
none of the above is correct
Hydrostatic pressure of the portal system
Most transudates have a leukocyte count of
>10,000 uL
<5 uL
>1000 uL
<1000 uL
<1000 uL
Synovial Fluid is composed of
all of the above are correct
plasma dialysate
hyaluronidate
protein
all of the above are correct
A 12 year old boy sustained an injury to his knee while skating. The knee appeared slightly swollen, red, and warm to the touch. The synovial fluid revealed the following:
Joint Fluid | Blood |
Color: Dark pink | WBC 5.1 x 103/mm3 |
Viscosity: Decreased | RBC 3.96 x 103/mm3 |
RBC count: 5,800 cells/ uL | ESR 22 mm/hr |
WBC count: 160 cells/uL | Uric Acid: 4.5 mg/dL |
% Neutrophils 20% |
|
Glucose 90 mg/dL | Glucose: 110 mg/dL |
They synovial fluid would be categorized as:
Type II - Inflammatory
Type I - Non Inflammatory
Type V - Hemorrhagic
Type III - Septic
Type V - Hemorrhagic
Neoplastic cells found in a pleural fluid may exhibit which of the following morphologic characteristics:
cohesive three-dimensional clusters
decreased nuclear cytoplasmic ratio
none of the available choices are correct
evenly distributed chromatin pattern
cohesive three-dimensional clusters
Complement levels in synovial fluid may be decreased in which of the following diseases?
Multiple Myeloma
Gout
Rheumatoid arthritis
none of the available choices
Rheumatoid arthritis
Xanthochromia would most likely be associated with:
Fungal infections
Auto-immune disease
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Cerebral tumor
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
A 35 year old male developed sudden onset of severe headache. Three hours later he fell to the floor, striking his head. At the hospital he was in coma with bruises over his right eye. Spinal fluid examination showed the following:
CSF Tube #1 |
|
Pressure: | 420 mm (Normal 70-200 mm) |
Color: | Reddish, cloudy |
Supernatant: | Yellow (after centrifugation) |
Glucose: | 75 mg/dL |
RBC Count: | 39,000 cells/uL |
WBC Count: | 28 cells /uL (96% lymphocytes) |
Other: | Few erythrophages present |
The most likely diagnosis is:
Multiple sclerosis
Traumatic lumbar puncture
Tuberculosis
Ruptured cerebral aneurysm
Ruptured cerebral aneurysm
The concentration of Lamellar bodies in amniotic fluid is used to determine:
Alpha-fetoprotein
Trisomy 21
Fetal lung maturity
Hemolytic disease of the newborn
Fetal lung maturity
The absence of fructose in semen is indicative of
nercozoospermia
aspermia
azoospermia
all of the available choices
azoospermia
Which of the following serial dilutions contains an incorrect factor?
1:5, 1:15, 1:45
1:4, 1:8, 1:16
1:2, 1:6, 1:12
1:1, 1:2, 1:4
1:2, 1:6, 1:12
SITUATION: A 54-year-old man was admitted to the hospital after having a seizure. Many laboratory tests were performed, including an RPR, but none of the results was positive. The physician suspects a case of late (tertiary) syphilis. Which test should be performed next?
Treponemal test, such as TP-PA on serum
VDRL on CSF
Repeat RPR, followed by VDRL
No laboratory test is positive for late (tertiary) syphilis
Treponemal test, such as TP-PA on serum
A specimen appears to have a perinuclear staining pattern in an antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) immunofluorescent assay using ethanol-fixed neutrophils, suggesting the possibility of a perinuclear ANCA (pANCA). On which of the following substrates would this specimen display cytoplasmic speckling?
HEp-2 cells
Unfixed neutrophils
Formalin-fixed neutrophils
Rabbit kidney tissue
Formalin-fixed neutrophils
Which statement about synovial fluid in RA is true?
Total hemolytic complement is elevated
Ninety percent of RA cases test positive for rheumatoid factor in synovial fluid
Synovial:serum IgG is usually 1:2 or higher
Demonstration of rheumatoid factor in joint fluid is diagnostic for RA
Synovial:serum IgG is usually 1:2 or higher