Networking
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
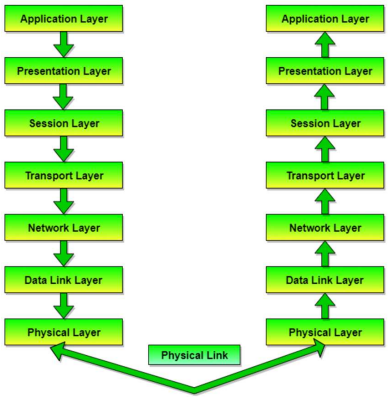
Network Models
ISO/OSI Model (Theoretical)
TCP/IP Model (Practical)
ISO/OSI Model (Theoretical)
international standards organisation (ISO) - open systems interconnection model (OSI)
conceptual framework that describes how communication happens over a network
7 layers
used for understanding and teaching how different network functions interact
universal reference model
OSI Layers
Application - your program
Presentation - encoding, encryption, compression
Session - connections are established and managed
Transport - reliable transmission, segmentation of large data
Network - routing between multiple devices to a destination
Data Link - between two connected devices
Physical - electrical transmissions
Why is OSI Theoretical?
designed as a universal reference to explain how computers should communicate over a network
doesn’t specify real protocols or software
like a textbook model or ideal standard, useful for teaching, documentation, and conceptualising how networks should work
TCP/IP Model (Practical)
used on the internet
real-world implementation of how data is transferred over networks
typically 4 layers:
Application - your program
Transport - end to end links and persistent connections
Internet - between different networks/routers
Network Access (link) - physical, local network
Why is TCP/IP Practical?
used in real world communication systems, especially the internet
includes real protocols
actually implemented in OS, routers, and web servers, what makes the internet work everyday
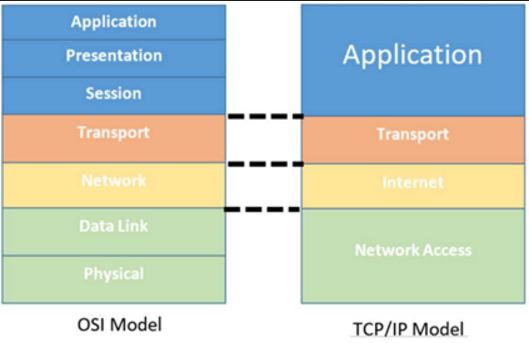
OSI vs TCP/IP
Feature | ISO/OSI Model | TCP/IP Model (Protocol) |
Purpose | Theoretical/Reference | Practical/Implementation |
Layers | 7 | 4 |
Developed by | ISO | US department of Defence |
Protocols Included | None (only structure) | Yes (TCP, IP, HTTP, etc) |
Usage | Teaching, documentation | Real-world internet and LANs |
Flexibility | More detailed and layered | Simplified for performance |
Network Delay - Latency
the time it takes for data (a packet) to travel from the source (sender) to the destination (receiver) over a network
can be very small (milliseconds), but even small delays matter a lot in real-world applications
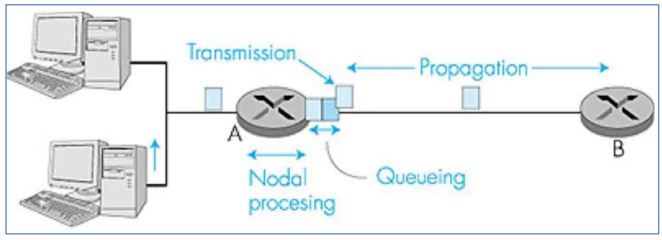
Types of Network Delays and How to Reduce Them
Delay Type | Description | Affected by | How to Reduce |
Processing Delay | Time to examine the packet header and determine where to send it next, happens at routers or end devices | Router performance | Faster processors |
Queueing Delay | Time the packet waits in queue before being transmitted, happens when many packets are waiting to be sent | Traffic congestion | Better scheduling |
Transmission Delay | Time to push all the packets bits onto the link | Packet size, bandwidth | Faster links |
Propagation Delay | Time for a signal to travel from sender to receiver across the medium | Distance, medium | Shorter paths |
Total Nodal Delay
to find the total delay at a single router (or node), we sum all 4 delays:
total delay = processing delay + queueing delay + transmission delay + propagation delay
Real-World Examples of Delay
Application | Delay Sensitivity | Example |
Online Gaming | High | Even 50ms delay can cause lag |
Video Calls | Medium to high | Causes echo, talking over |
Email or File download | Low | Delay is less noticeable |
Reducing Delay
use faster links - higher bandwidth
optimise routing paths
avoid congestion e.g. through load balancing
use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to reduce distance