OIA1011 PHASE EQUILIBRIUM
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Definition of Gibbs Free Energy.
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS, where ΔG determines reaction spontaneity, but does not indicate rate of reaction.
Explain Gibbs Free Energy, ΔG.
ΔG = 0, equilibrium
ΔG <0, spontaneous
ΔG = -ve, exergonic
ΔG = +ve, endergonic
Phase Transition
Change in phase without altering chemical composition (e.g., ice melting).
Transition Temperature
The temperature at which two phases are in equilibrium & ΔG =0, e.g., H2O(s)↔H2O(l) at 0°C.
Phase Diagram
A map showing conditions at which various phases of substance are thermodynamically stable.
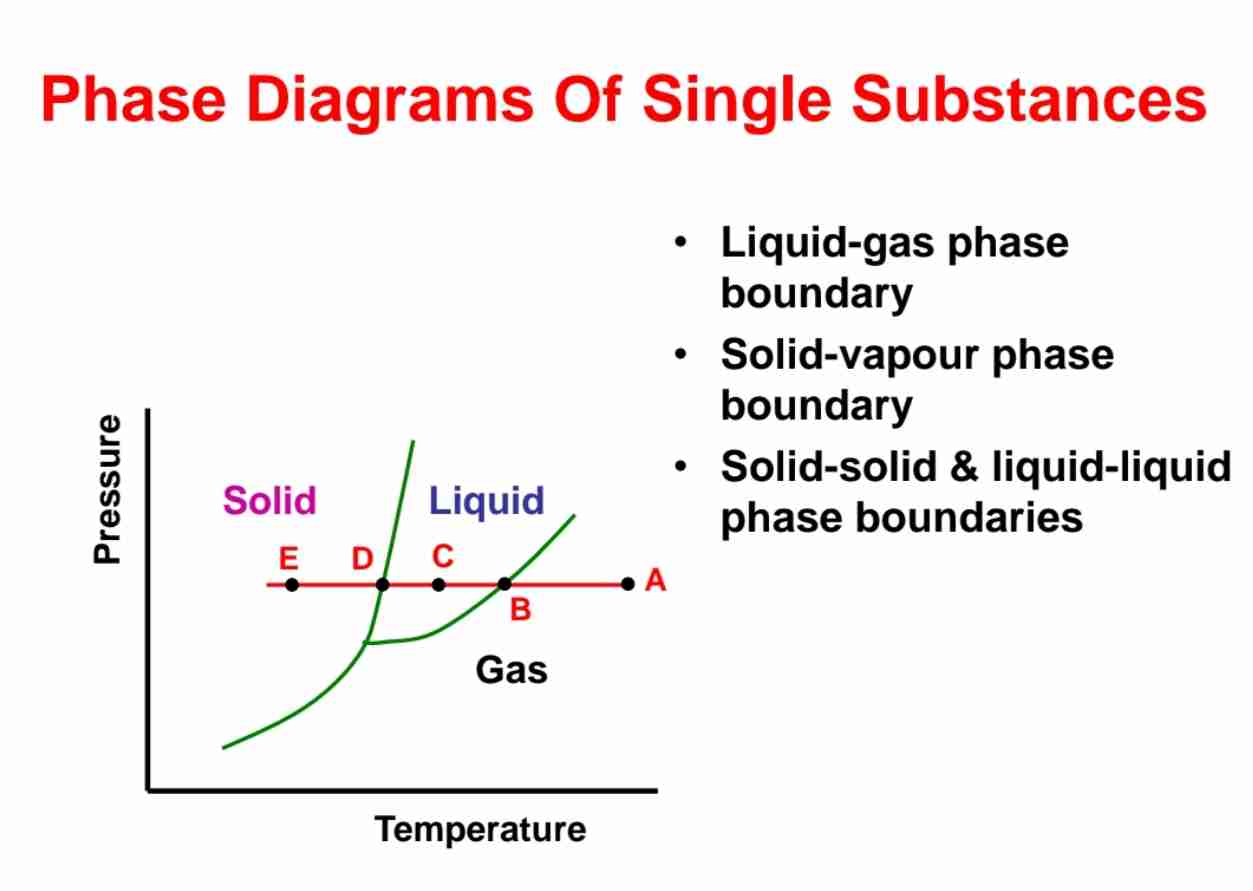
Define a phase.
A homogenous, physically distinct portion of system which is separated from each other portions of system by bounding surfaces.
Critical Point
End point of pressure-temperature curve that designate conditions where liquid & it’s vapour can coexist.
At higher temperatures, gas cannot liquefied by pressure alone.
At Critical Point, phase boundaries vanish as it is defined by Critical Temperature & Critical Pressure.
Triple Point
The temperature & Pressure at which three phases (gas, liquid & solid) of substance coexist in thermodynamics equilibrium.
Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
Express relationship between vapour pressure & absolute temperature of liquid to calculate mean heat of vapourisation of liquid
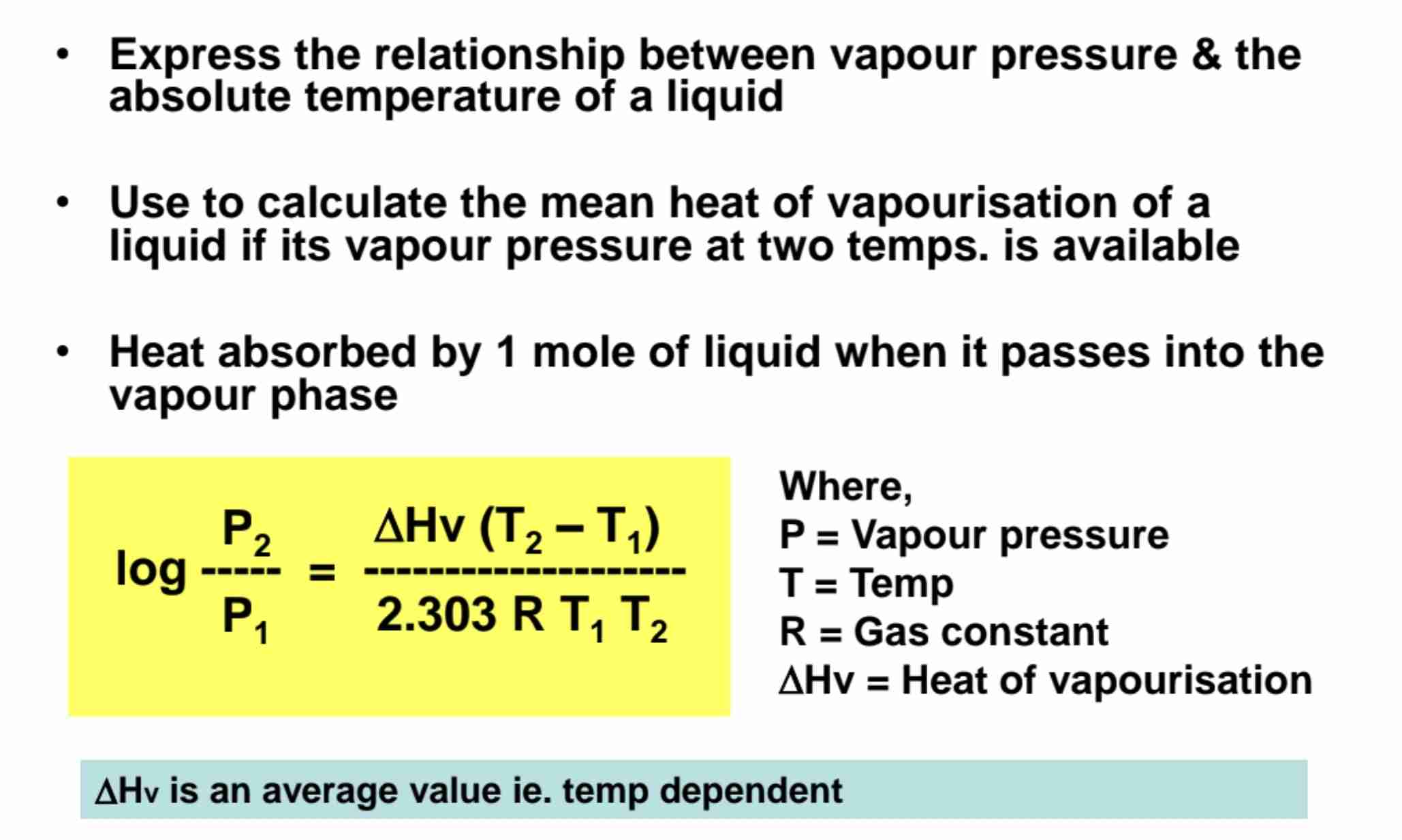
Define mean heat of vapourisation.
Heat absorbed by 1 mole of liquid when it passes into vapour phase.
Phase Rule
F = C - P + 2, where F is degrees of freedom.
Define no. of degree of freedom.
Least number of intensive variables (Temperature, pressure, concentration & etc.), which must be fixed to describe system completely.
Eutectic Point
The lowest temperature at which a mixture of components will melt.
Applications of Phase Equilibrium
Lyophilization (freeze-drying) for preserving drugs sensitive to heat/moisture.