AQA GCSE Geography - River Landscapes in the UK
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
what are the four types of river erosion?
hydraulic action
abrasion
attrition
solution
what is hydraulic action?
air becomes trapped in the cracks of the river bank and bed by the force of the water, and causes the rock to break apart
what is abrasion?
when pebbles grind along the river bank and bed
what is attrition?
when rocks that the river is carrying knock against each other, becoming smaller and more rounded
what is solution (erosion)?
when the water dissolves certain types of rocks
what are the four types of river transportation?
traction
saltation
suspension
solution
what is traction?
large, heavy pebbles are rolled along the river bed
what is saltation?
pebbles are bounced along the river bed
what is suspension?
lighter sediment is suspended within the water
what is solution (transportation)?
the transport of dissolved chemicals
what is deposition?
when a river loses energy and drops the sediments it has been carrying
what are the factors leading to deposition?
. shallow water
. reaching river's mouth
. when the volume of the water decreases
what is a drainage basin?
the area of land around a river that is drained by the river and its tributaries
what is the watershed?
area of high land forming the edge of a river basin
what is the source of a river?
where a river begins
what is the mouth of a river?
where the river meets the sea
what is a confluence?
a point at which two rivers meet
what is a tributary?
a small river or stream that joins a larger river
what is the river channel?
where the river flows
what is the long profile of a river and what does it show?
. a line representing the river from its source to its mouth
. it shows how the river changes over its course.
what is the river's load like in the upper course?
. often an upland area
. the river's load is large in the upper course, as it hasn't been broken down by erosion yet
what is the river's load like in the lower course?
. land is a lot flatter
. the river's load is fine sediment, as erosion has broken down the rocks
what is the cross profile of a river?
it is a cross-section of a river's channel and valley at a certain point along the river's course
what is happening in the upper course in a cross profile?
. as the river flows downhill there is an increase in vertical erosion
. the channel is shallow and narrow because there is not a lot of water in it
what is happening in the middle course in a cross profile?
. as the river flows into the middle course, there is some vertical erosion but more lateral erosion
. the channel is wider and deeper as a result
what is happening in the lower course in a cross profile?
. in the lower course there is a lot less erosion, with only some lateral erosion
. the channel is at its widest and deepest
what is a waterfall?
a sudden drop along the river course
what does the rock have to be like for a waterfall to form?
horizontal bands of resistant rock over exposed, less resistant rock
what is the process of the formation of a waterfall?
. the soft rock is eroded faster than the hard rock, creating a step
. erosion continues, hard rock is undercut forming an overhang
. abrasion and hydraulic action create a plunge pool
. over time this gets bigger, increasing size of overhang until hard rock is no longer supported and collapses
. process continues, waterfall retreats upstream
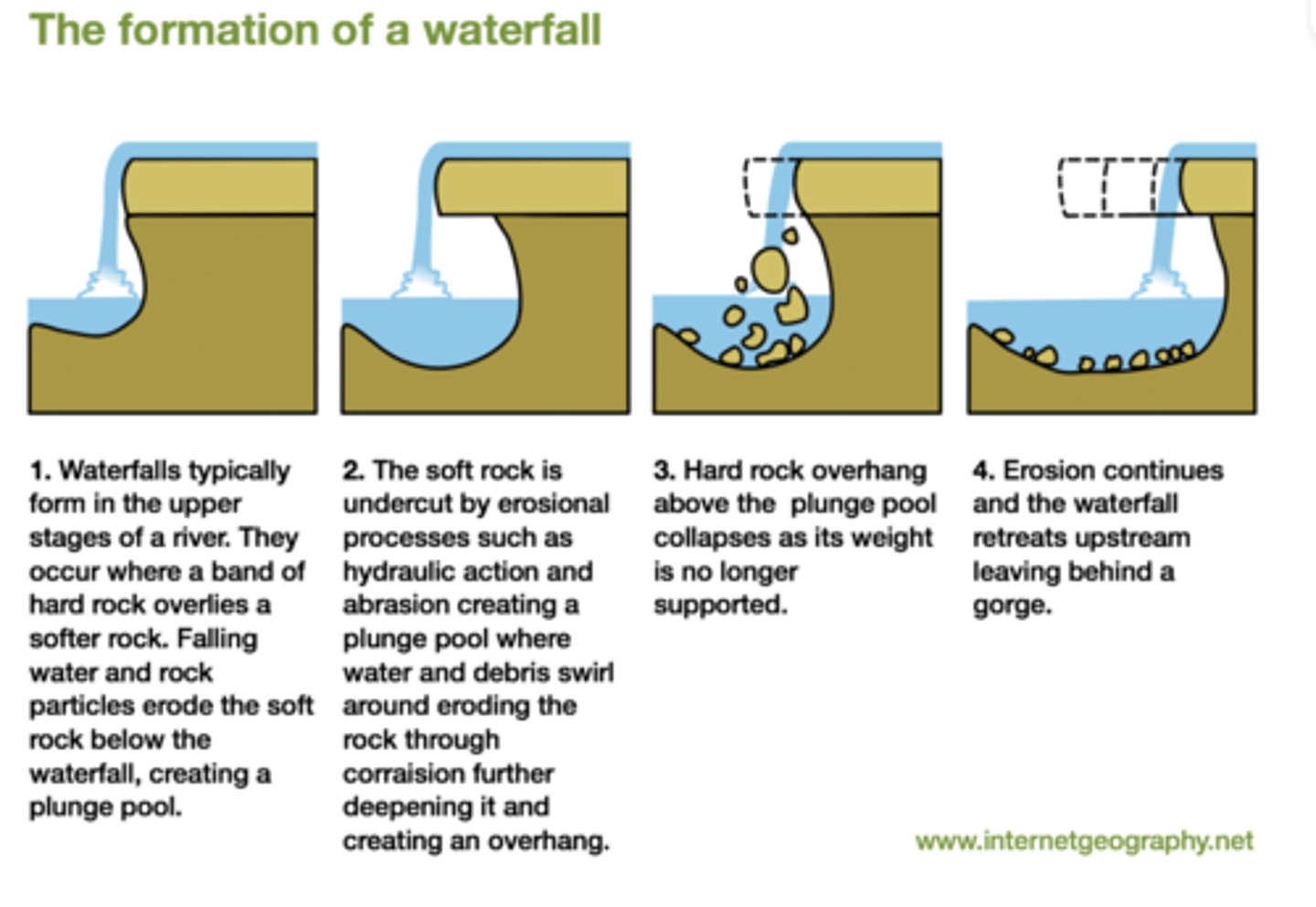
what is created by waterfall retreat?
a steep sided valley, called a gorge
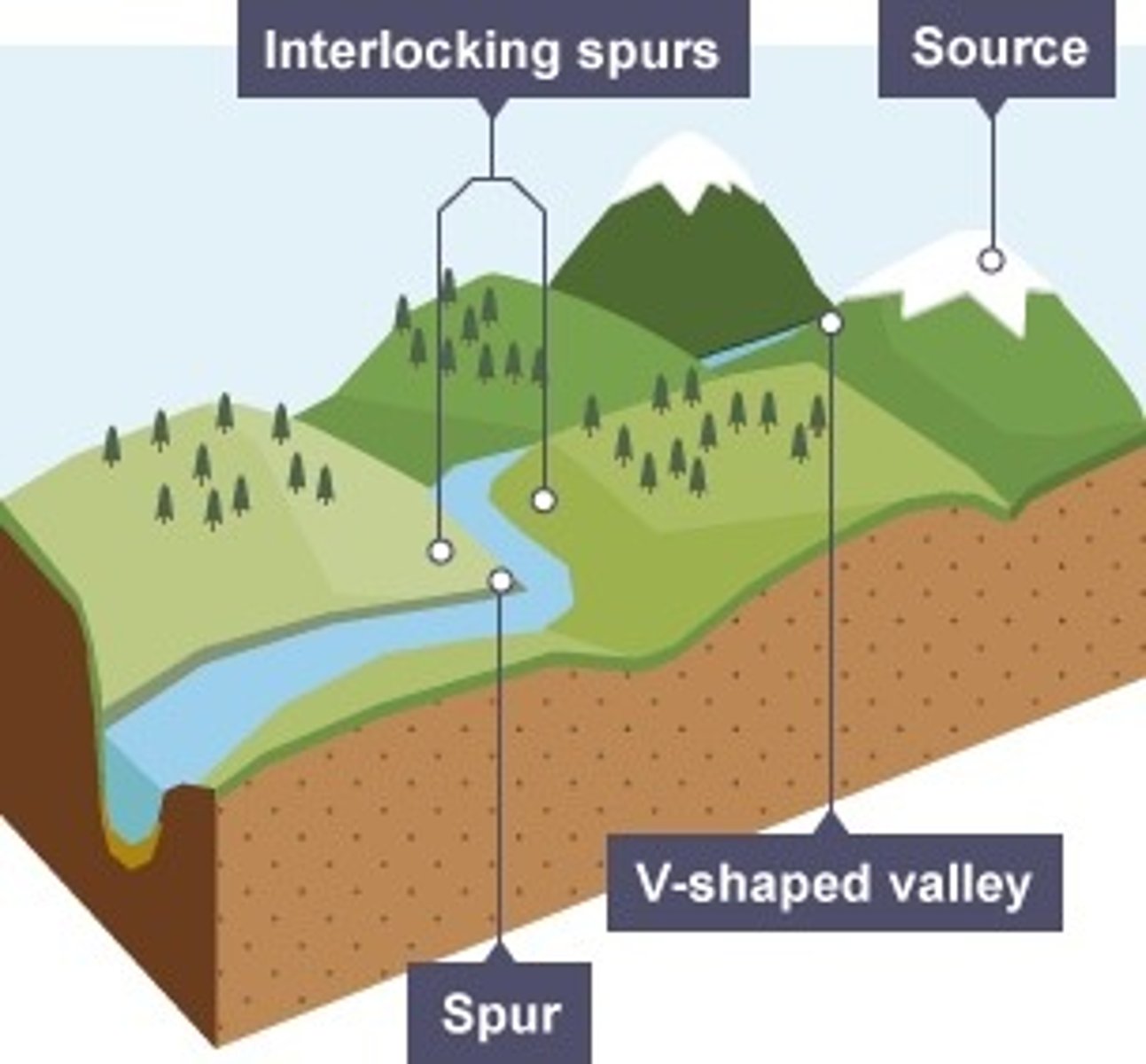
what are interlocking spurs?
a series of ridges projecting out on alternate sides of a valley around which a river winds its course
how are interlocking spurs formed?
. in the upper course there is more vertical erosion
. the river cuts down into the valley
. if there are areas of hard rock which are harder to erode, the river will bend around them
. this creates interlocking spurs of land which link together
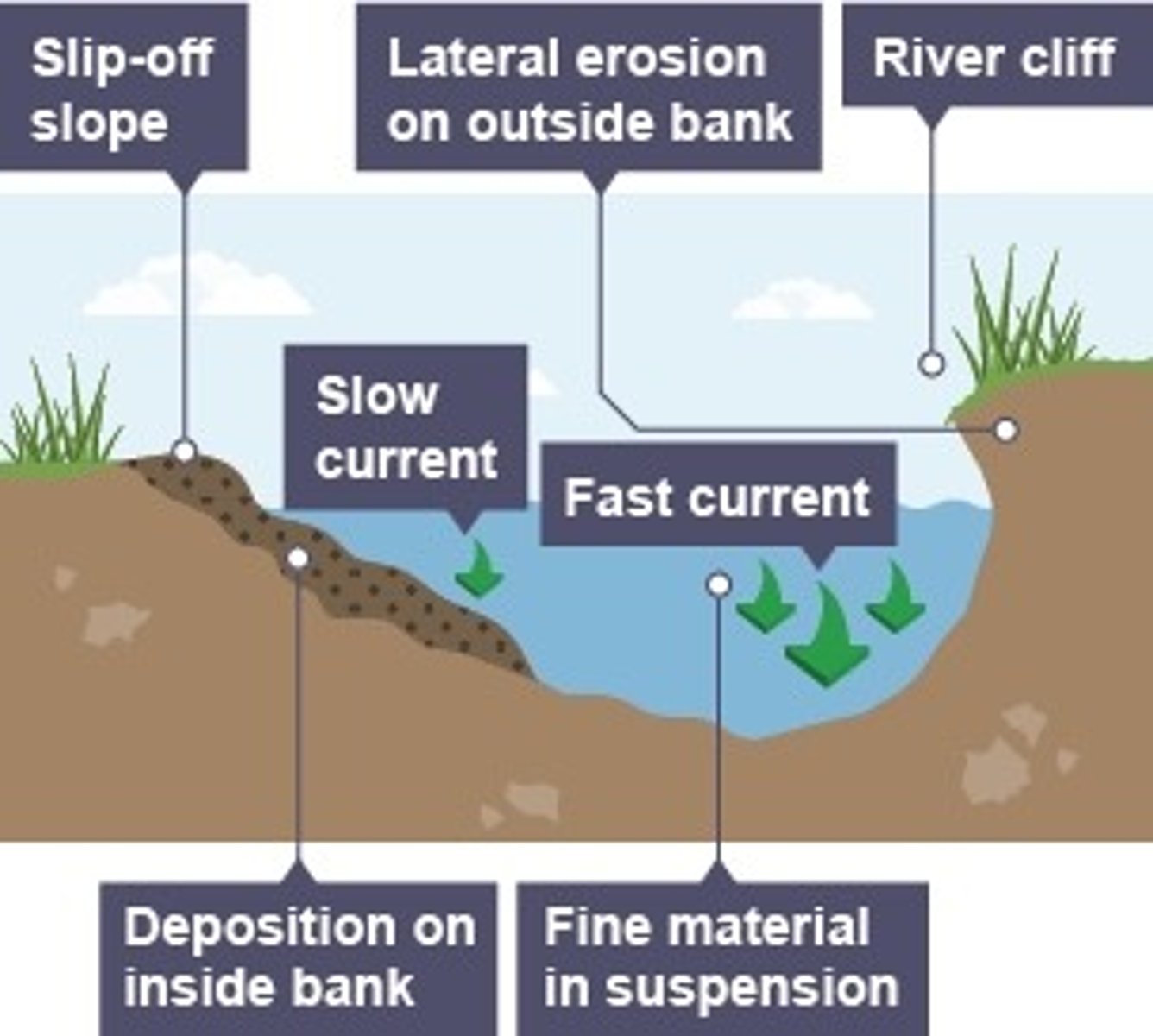
what are meanders?
large bends in a river
how are meanders formed?
. as a river goes around a bend, most of the water is pushed towards the outside, causes increased speed and increased erosion
. lateral erosion on outside bend causes undercutting of the bank to form a river cliff
. water on inner bend is slower, causing water to slow down and deposit eroded material, creating a gentle slope of sand and shingle - a slip-off slope
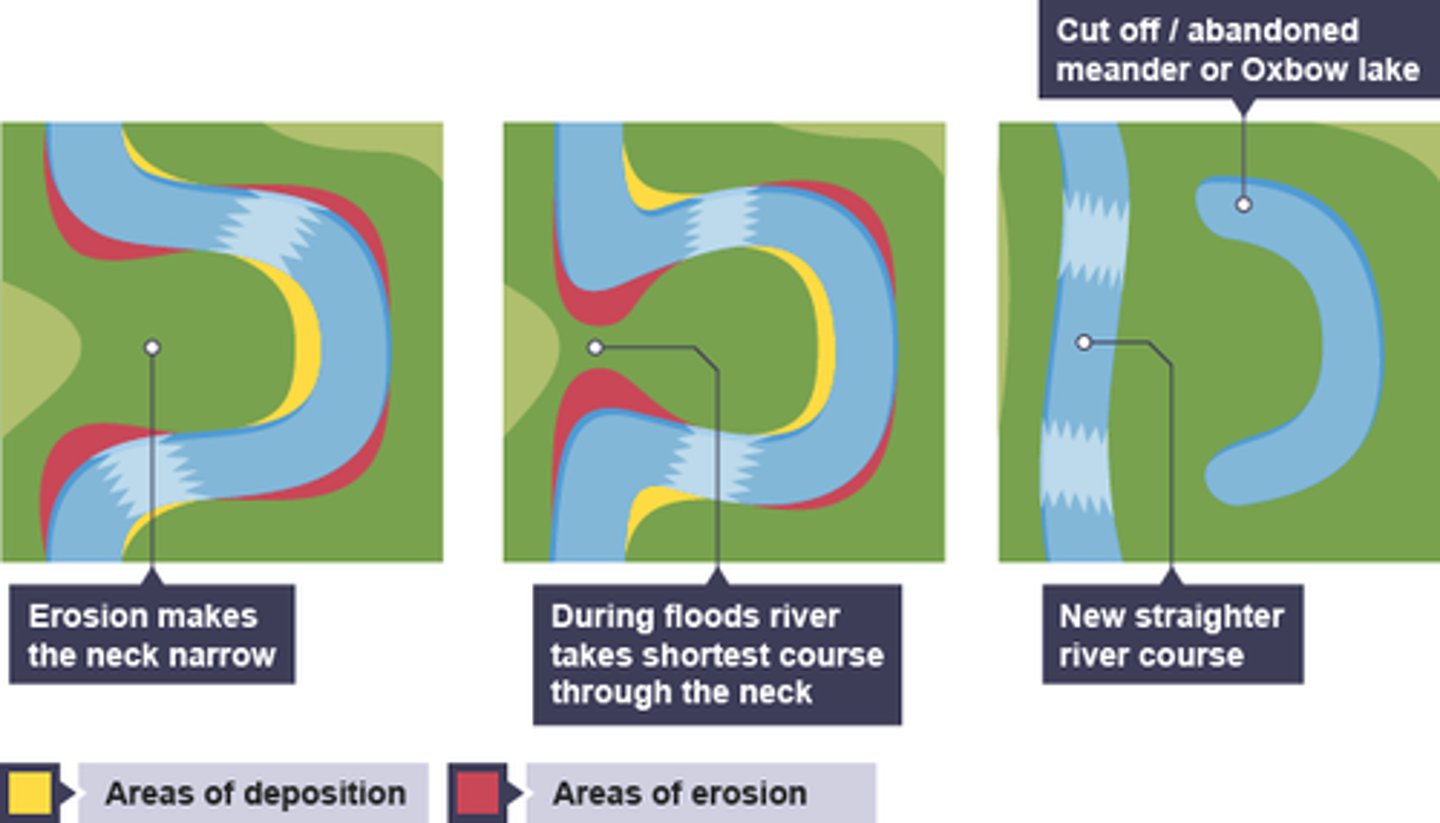
what are oxbow lakes?
curved lake formed from a meander cutoff
how are oxbow lakes formed?
. erosion narrows neck of land within meander, as the process continues meanders move closer together
. when there is a very high discharge the river cuts across the neck, taking a new, straighter and shorter route
. deposition will occur to cut off the original meander, leaving a horseshoe-shaped oxbow lake
what is a floodplain?
an area of land which is covered in water when a river bursts its banks
how do floodplains form?
. erosion removes any interlocking spurs, creating a wide, flat area on either side of the river
. during a flood, material being carried by the river is deposited
. over time, the height of the floodplain increases as material is deposited on either side of the river
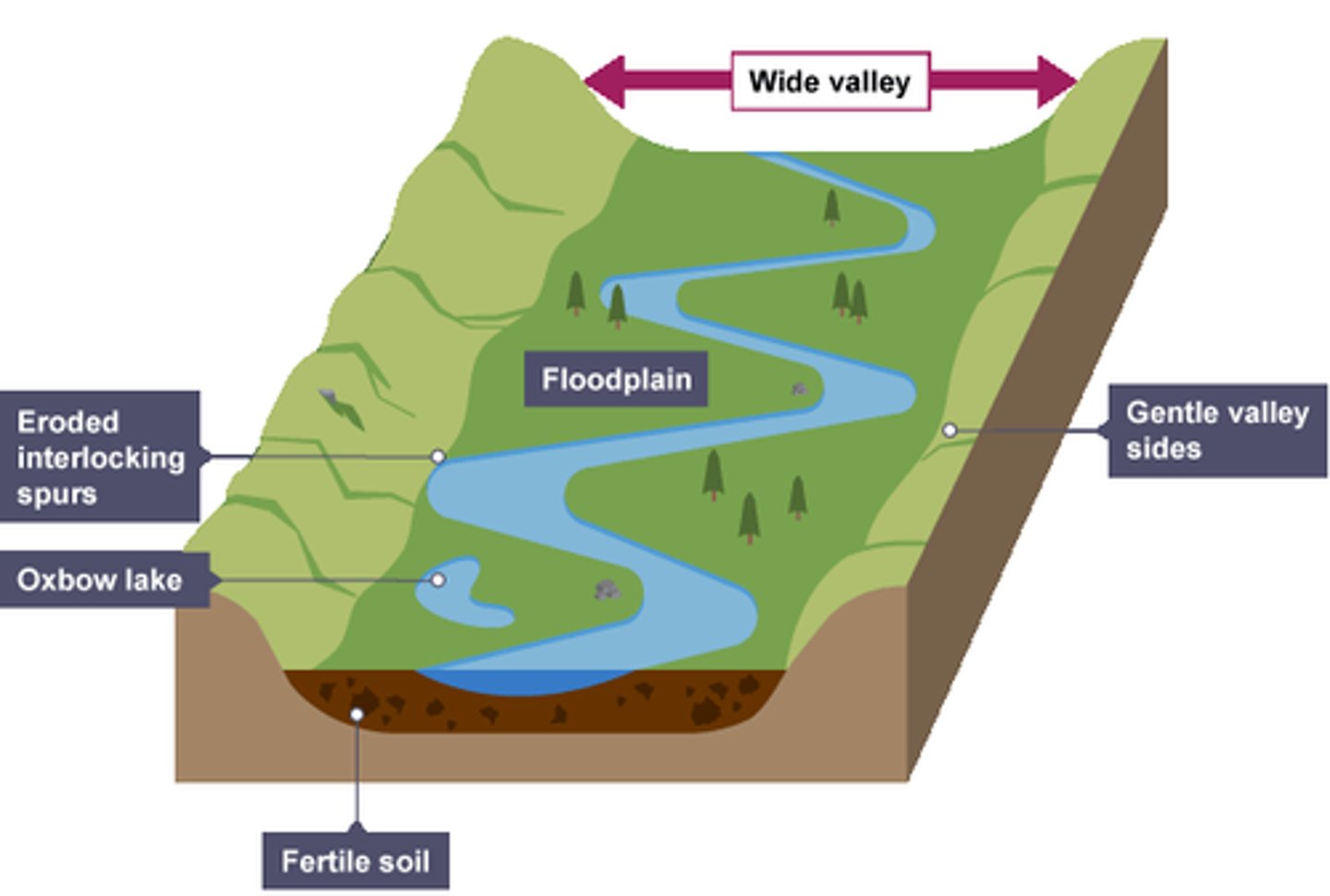
what are floodplains used for?
agriculture due to high fertility
what are levees?
natural embankments along the edges of a river channel
how are levees formed?
. sediment is transported downstream.
. when the river floods, the sediment spreads out across the floodplain
. as the river loses energy, the largest material is deposited first on the sides of the river banks and smaller material further away
. after many floods, sediment builds up to increase the height of the river banks
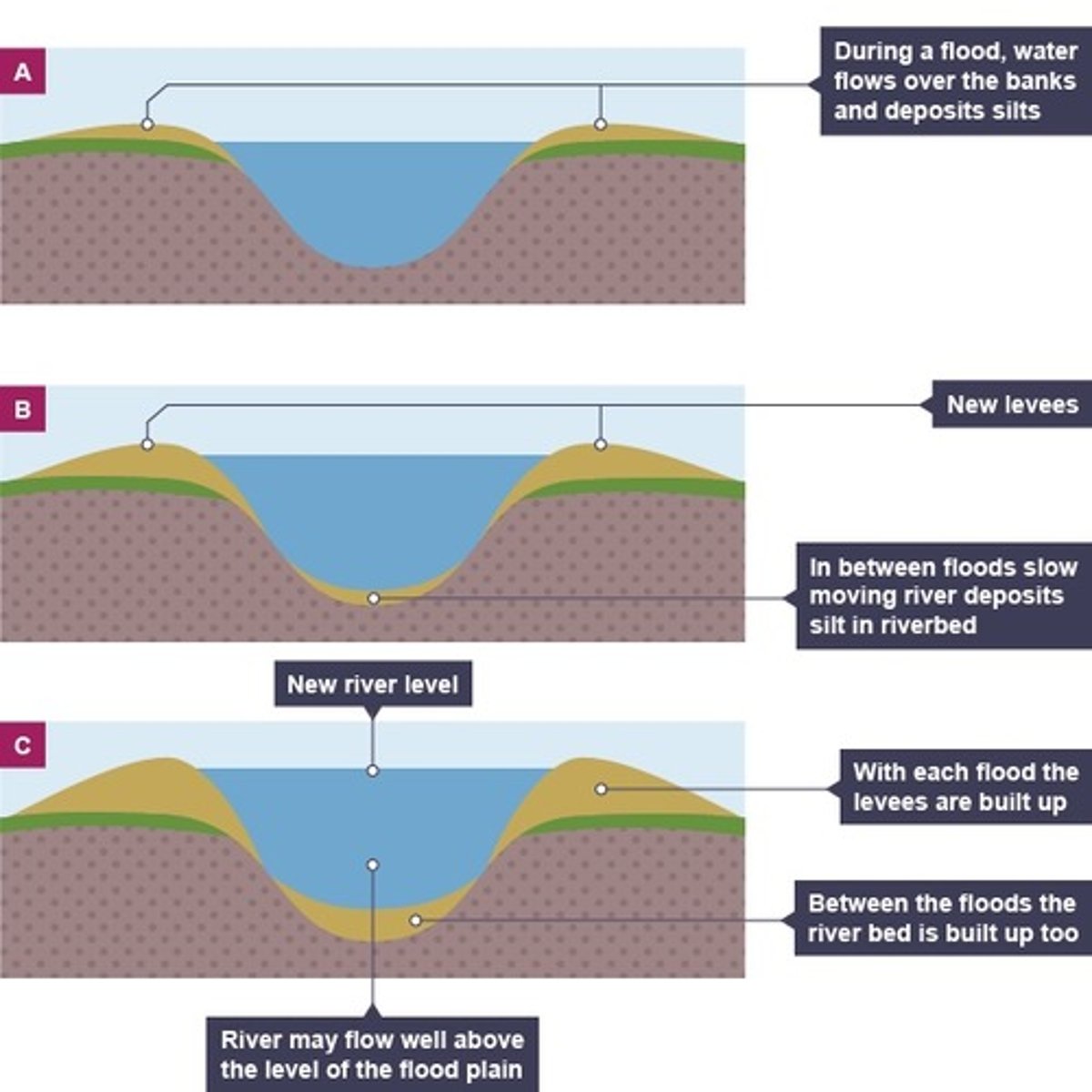
how are levees helpful?
they mean that the channel can carry more water and flooding is less likely to occur in the future
what is an estuary?
the tidal mouth of a large river, where the sea meets the river
what do rivers form at estuaries?
. when the sea retreats the volume of the water in the estuary is reduced
. the river deposits silt to form mudflats which are an important habitat for wildlife
where is the river tees located?
. north of England
. source is located in the Pennines
. flows east to its mouth where the river joins the North Sea
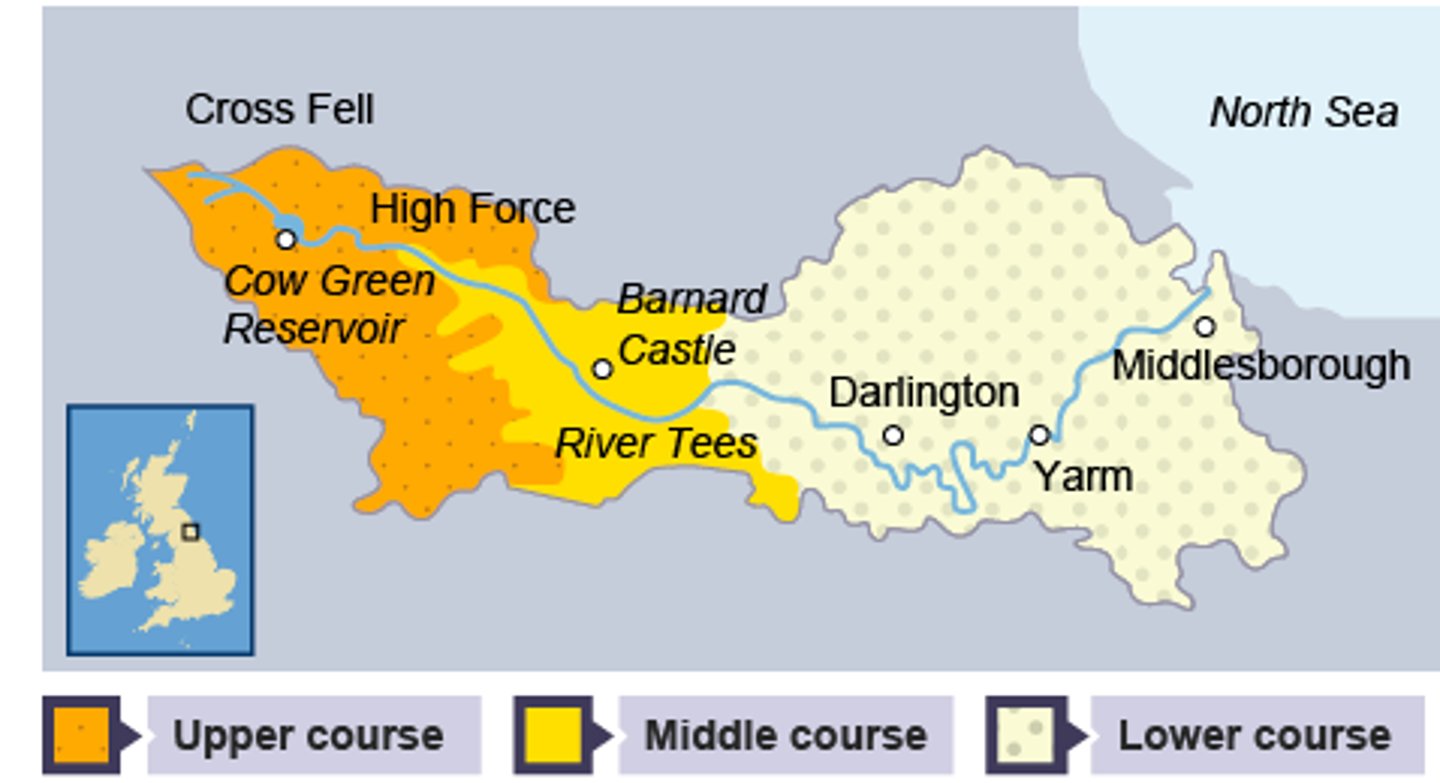
what is the upper course of the river tees like?
. it has hard impermeable rocks.
. vertical erosion has formed a V-shaped valley
. High Force, the UK's largest waterfall by volume when in full flow is located in the upper course
what is the middle course of the river tees like?
. as the river starts to erode sideways it forms meanders
. these can be identified in the middle course near Barnard Castle
what is the lower course of the river tees like?
. near Yarm, the meanders are much larger, and oxbow lakes have formed.
. there are also levees which have formed when the river has flooded
. very large estuary with mudflats and sandbanks which supports wildlife in the area
. sites such as Seal Sands are protected areas
what are some causes of flooding?
. prolonged rainfall - if it rains for a long time, the land around a river can become saturated
. heavy rainfall - if there is heavy rainfall there is less chance of it being soaked up by the soil
. relief - steep valley is more likely to flood than flatter valley
. geology - permeable rocks allow water to pass through pores and cracks, impermeable rocks do not
. vegetation - trees and plants absorb water, interception
. urban land use - area surrounding a river built on, an increase in impermeable surfaces
what does a hydrograph show?
how a river responds to a period of rainfall
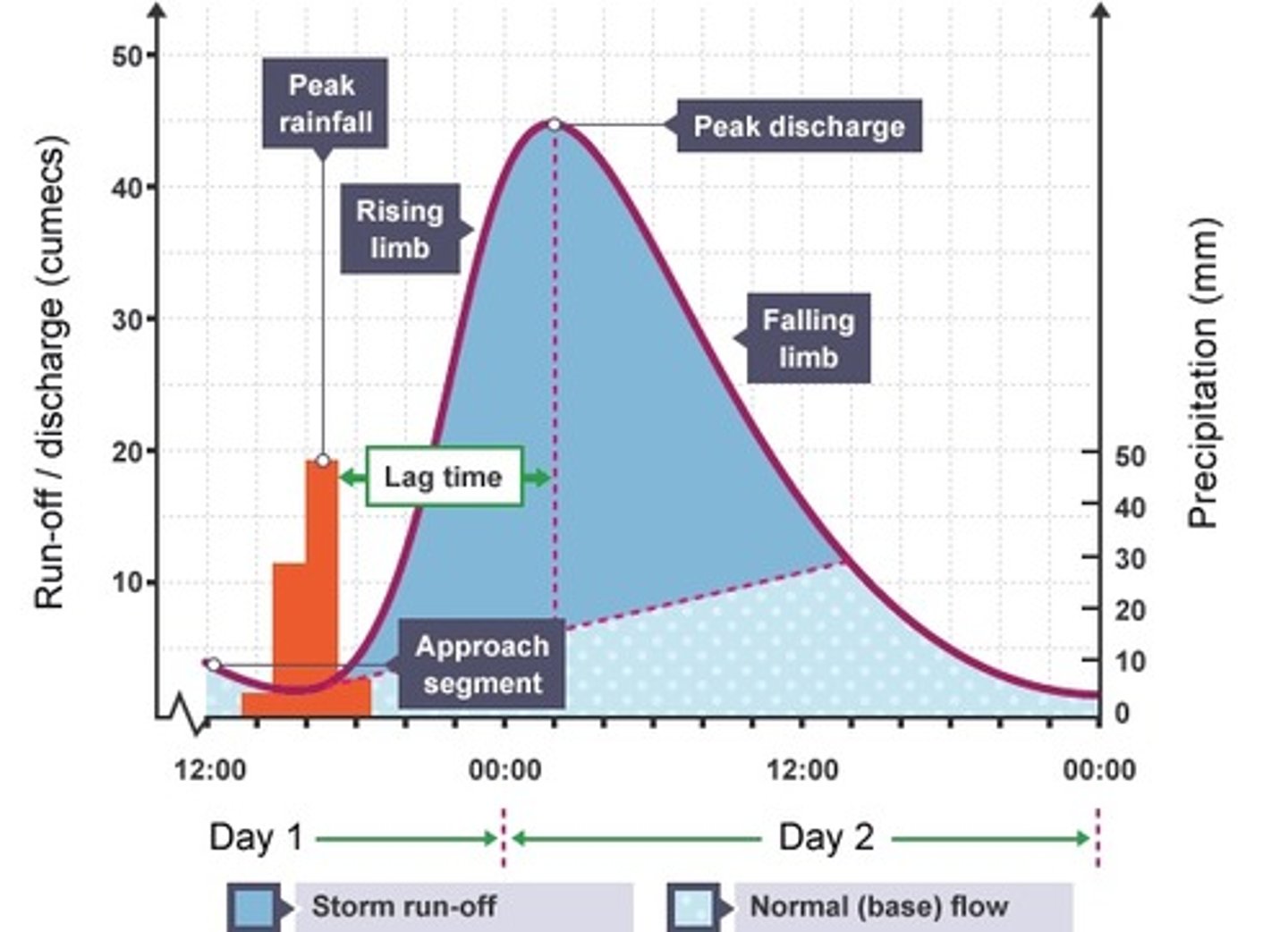
what is the peak discharge on a hydrograph?
maximum amount of water held in the channel
what is the peak rainfall on a hydrograph?
maximum amount of rainfall (millimetres)
what is the lag time on a hydrograph?
the time taken between peak rainfall and peak discharge
what is the rising limb on a hydrograph?
shows the increase in discharge on a hydrograph
what is the falling limb on a hydrograph?
shows the return of discharge to normal
what is the base flow on a hydrograph?
the normal discharge of the river
what are some factors influencing lag time?
size of drainage basin
vegetation
valley side steepness
soil type
what strategies are used to reduce flooding?
hard and soft engineering
what are dams and reservoirs?
hard engineering strategy
the dam traps water, which builds up behind it, forming a reservoir
water can be released in a controlled way
what are some advantages of dams and reservoirs?
can be used to produce electricity by passing the water through a turbine within the dam
reservoirs can attract tourists
what are some disadvantages of dams and reservoirs?
very expensive
dams trap sediment which means the reservoir can hold less water
habitats are flooded often leading to rotting vegetation which releases methane
settlements are lost leading to the displacement of people
what is river straightening and dredging?
hard engineering strategy
straightening the river speeds up the water so high volumes of water can pass through an area quickly
dredging makes the river deeper so it can hold more water
what are some advantages of river straightening and dredging?
more water can be held in the channel
can be used to reduce flood risk in built-up areas
what are some disadvantages of river straightening and dredging?
dredging needs to be done frequently
speeding up the river increases flood risk downstream
what are embankments?
hard engineering strategy
raising the banks of a river so that it can hold more water
what are some advantages of embankments?
cheap with a one-off cost
allows for flood water to be contained within the river
what are some disadvantages of embankments?
looks unnatural
water speeds up and can increase flood risk downstream
what are flood relief channels?
hard engineering strategy
the floodwater flows into the relief channel and is taken either to an area where it can be absorbed, or re-enters the river further down its course
what are some advantages of flood relief channels?
removes excess water from the river channel to reduce flooding
what are some disadvantages of flood relief channels?
expensive to build
if water levels continue to rise, the relief channel may also flood
what are flood warnings and preparation?
soft engineering strategy
the environmental agency monitors rivers and issues warnings when areas are likely to flood so people can prepare
what are some advantages of flood warnings and preparation?
people have time to protect their properties, eg with sandbags
many possessions can be saved, resulting in fewer insurance claims
what are some disadvantages of flood warnings and preparation?
some people may not be able to access the warnings
flash floods may happen too quickly for a warning to be effective
they do not stop land from flooding
what is floodplain zoning?
soft engineering strategy
allowing only certain land uses on the floodplain reduces the risk of flooding to houses and important buildings
what are some advantages of floodplain zoning?
more expensive buildings and land uses are further away from the river, so have a reduced flood risk
less damage is caused, leading to fewer insurance claims
what are some disadvantages of floodplain zoning?
not always possible to change existing land uses
planners have to decide what type of flood to plan for
what happened to cause the 2004 flood in boscastle, Cornwall?
a month's worth of rain fell in two hours
what factors contributed to the flash flood in boscastle?
the drainage basin of Boscastle is steep and impermeable rock
Boscastle is also located on a confluence of three rivers
how much did the environment agency invest in boscastle to present future floods?
£10 million
what were the flood management strategies implemented in boscastle?
widening and deepening the river channel - so the river can carry more water
removing low bridges and replacing them with wider bridges - so larger amounts of water can flow freely
raising car park and using permeable surface - less surface runoff
tree management - dead trees removed to prevent them being swept away, causing blockages under bridges