RHS Green Book- Components of the X-Ray Machine
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What are the component parts of the X-Ray machine?
1: Control Panel
2:Extension Arm
3:Tubehead
What is included with the Control Panel:
Contains an on-off switch, indicator light, and exposure button.
Extension Arm:
Suspends the x-ray tubehead and houses the electrical wires
Tubehead:
A tightly sealed, heavy metal housing that contains the x-ray tube that produces the x-rays.
What are the components of the Tubehead?
Metal Housing, Insulating oil, Tubehead Seal (Aluminum Glass), X-Ray Tube, Transformer, Aluminum Disk, Lead Colimator, Position Indicating Device (PID).
Metal Housing:
It’s filled with oil that protects the x-ray tube and grounds the high voltage components.
Tubehead Seal (Aluminum Glass):
Permits the exit of x-rays and acts as a filter to the x-ray beam.
X-Ray Tube:
Heart of the X-Ray
Transformer:
A device that alters the voltage of the incoming electricity.
Aluminum Disks:
0.5 mm thick
It’s Aluminum placed in the path of the beam to filter out the non-penetrating long wavelength x-rays.
Lead Colimator:
A lead plate with a central hole that fits over the opening that restricts the size of the beam.
Position Indicating Device (PID):
Aims and shapes the x-ray beam
Components of the X-Ray Tube?
Leaded Glass Housing, Cathode, Tungsten Filament, Molybdenum Cup, Anode, Tungsten Target.
Leaded-Glass Housing:
A leaded Glass vacuum that prevents Scatter radiation. It has a “window” that permits the beam to exit and directs it to the lead collimator.
Cathode:
-Negative Electrode
-Supply’s the electrons needed to generate x-rays
What does the Cathode consist of?
Tungsten Filament & Molybdenum Cup
Tungsten Filament: (Coiled Wire)
Produces electrons when heated
Molybdenum Cup:
Focuses electrons into a narrow beam toward the tungsten target
Anode:
-(Positive Electrode)
-Converts electrons into x-ray photons
Components of the Anode?
Tungsten Target & Copper Stem
Tungsten Target:
It is the focal spot and converts electrons into x-ray photons
Copper Stem:
Dissipates heart from tungsten Target.
Step-down Transformer:
Decreases the voltage
Step-up Transformer:
Increases the voltage
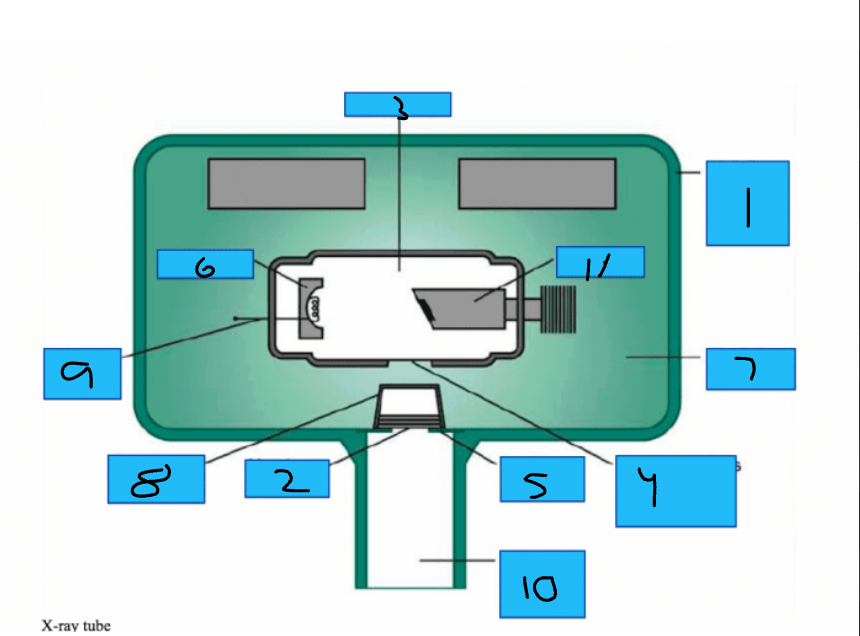
Whats number 1?
Metal Housing
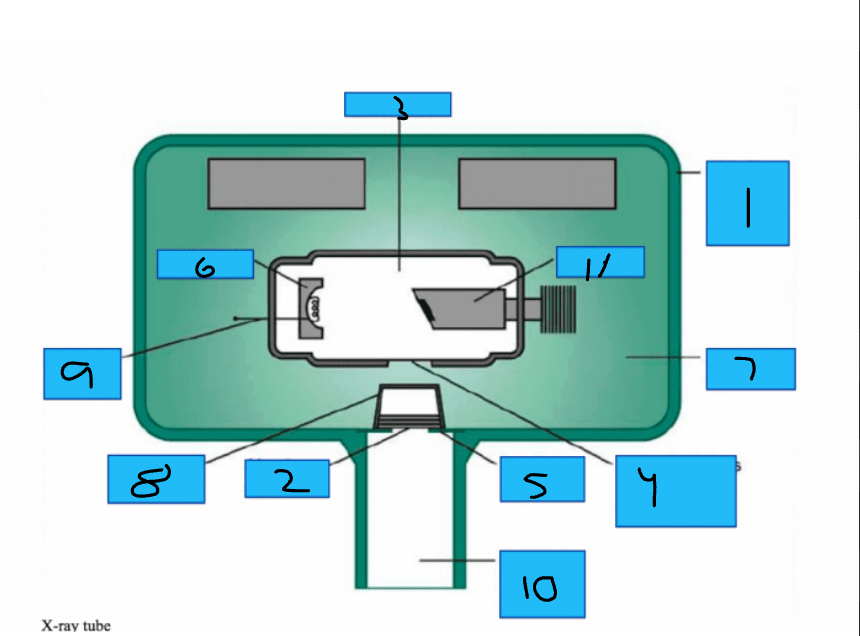
Whats number 2
Aluminum Disks
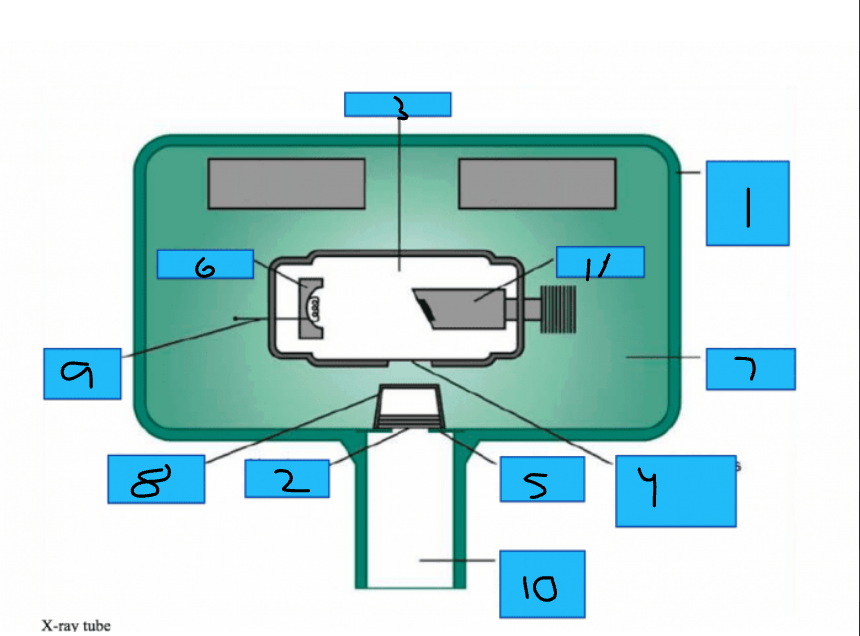
Whats number 3?
x-Ray Tube
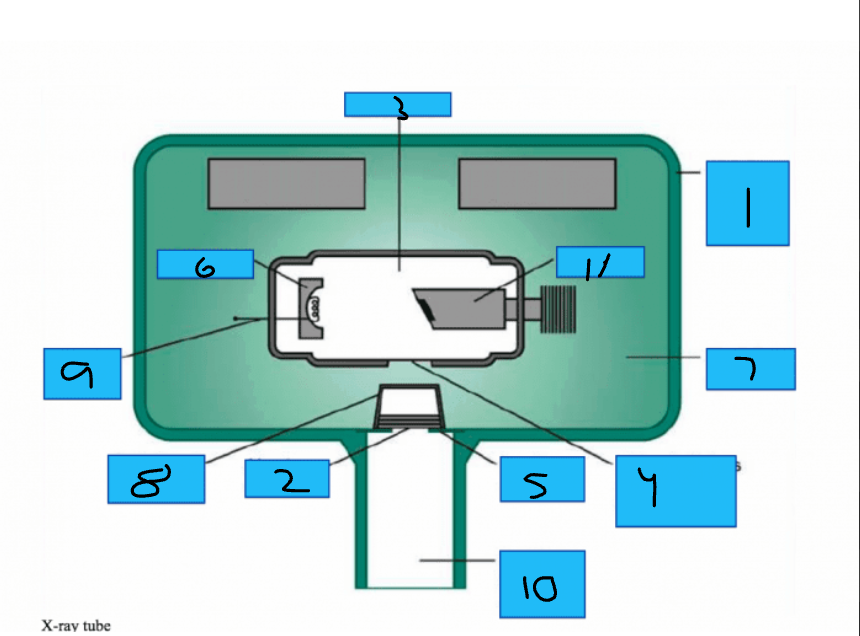
Whats number 4?
Unleaded Glass Window
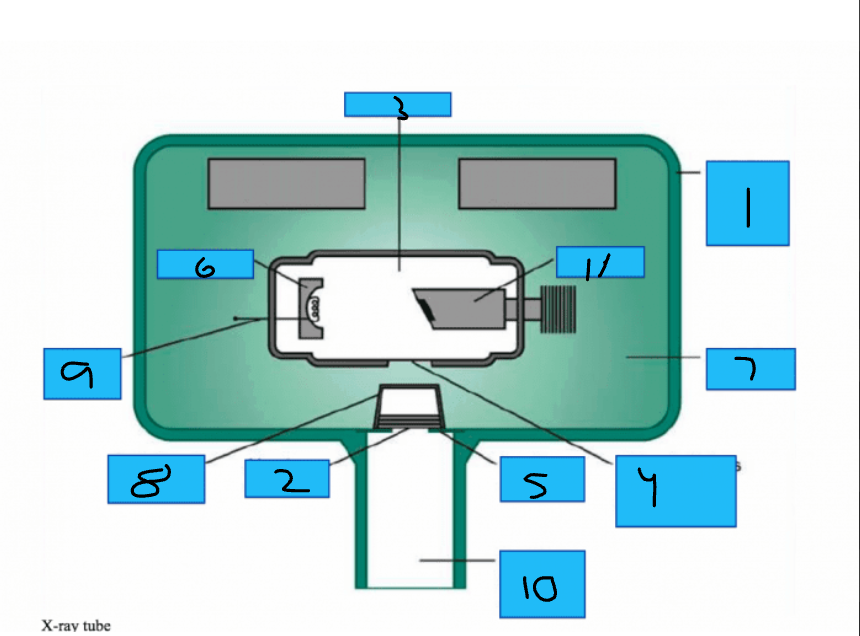
Whats number 5?
Lead Collimator
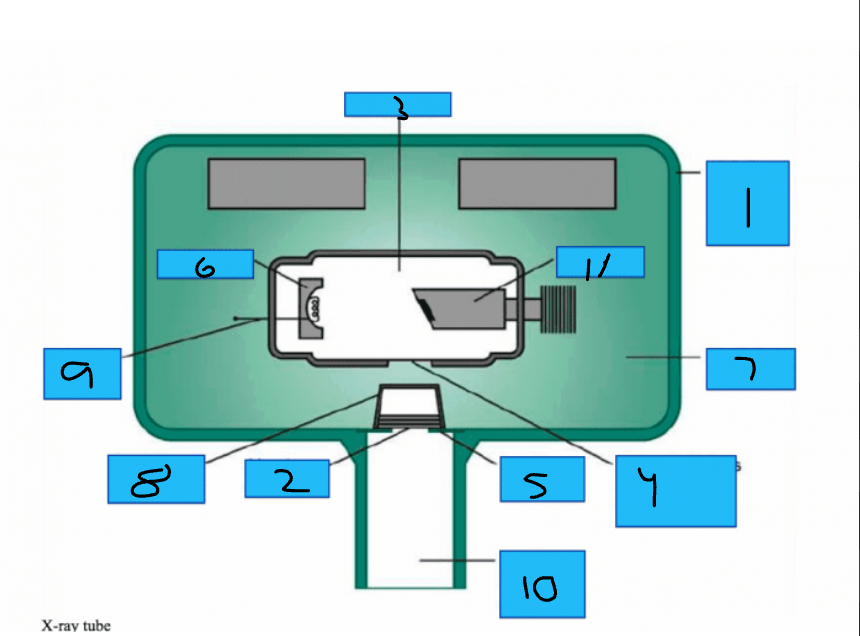
Whats number 6?
Cathode
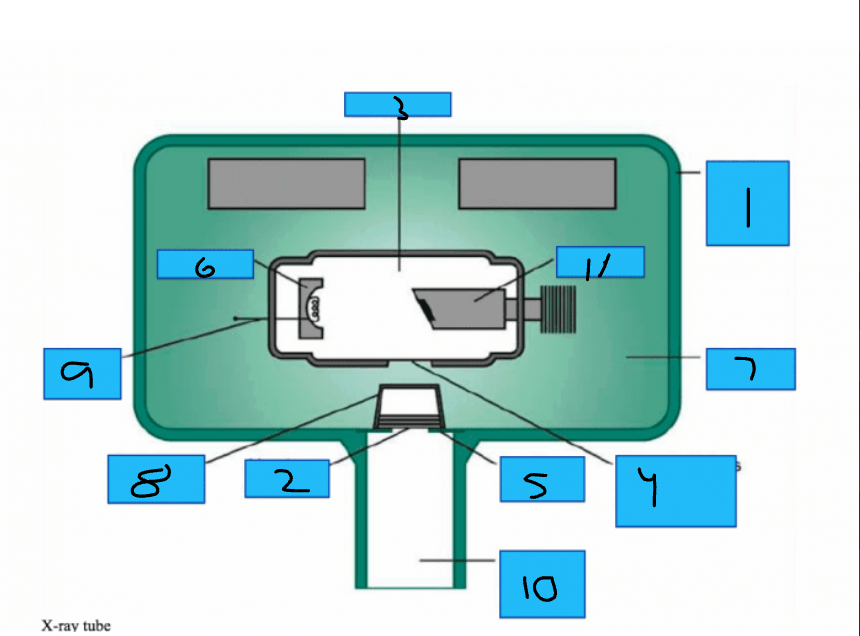
Whats number 7?
Insulating oil
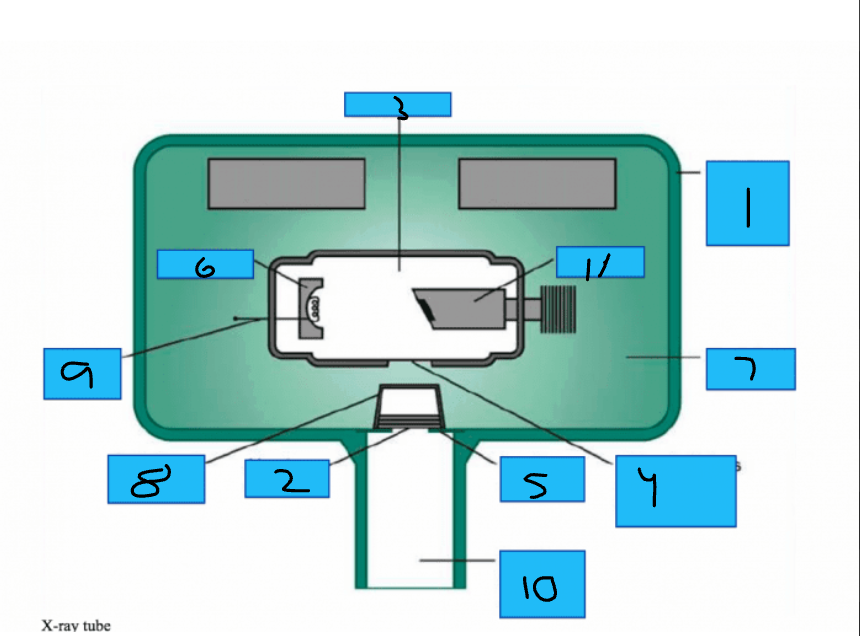
Whats number 8?
Tubehead Seal
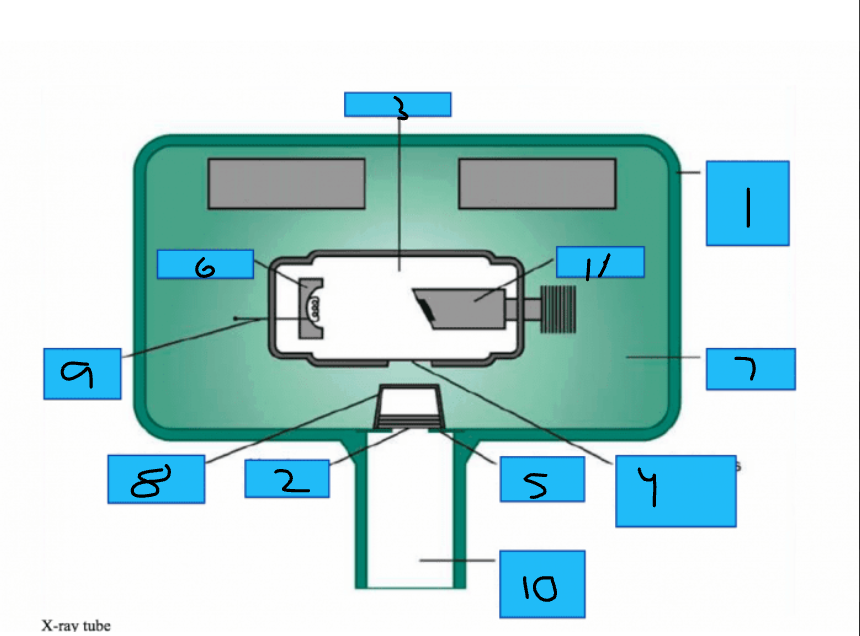
Whats number 9?
Tungsten Fillament
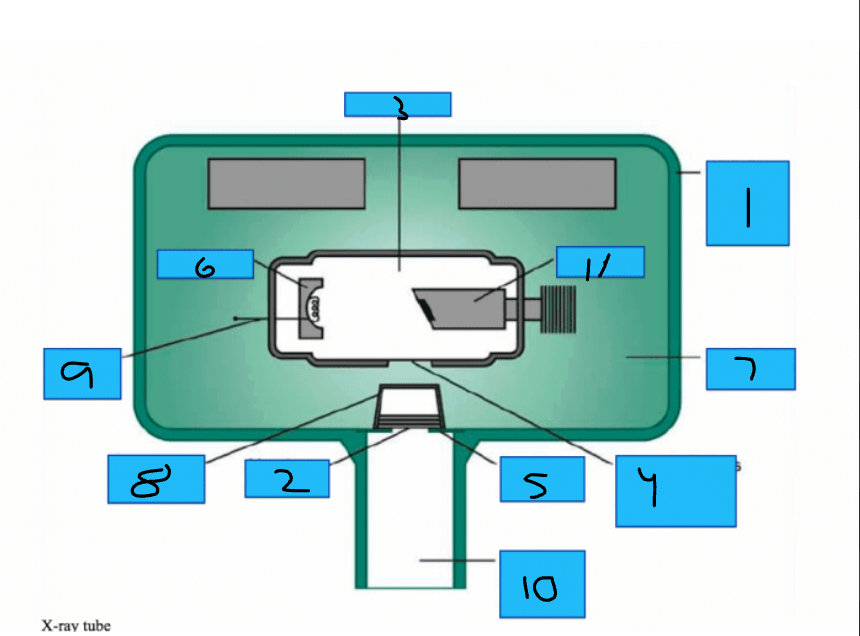
Whats number 10?
PID
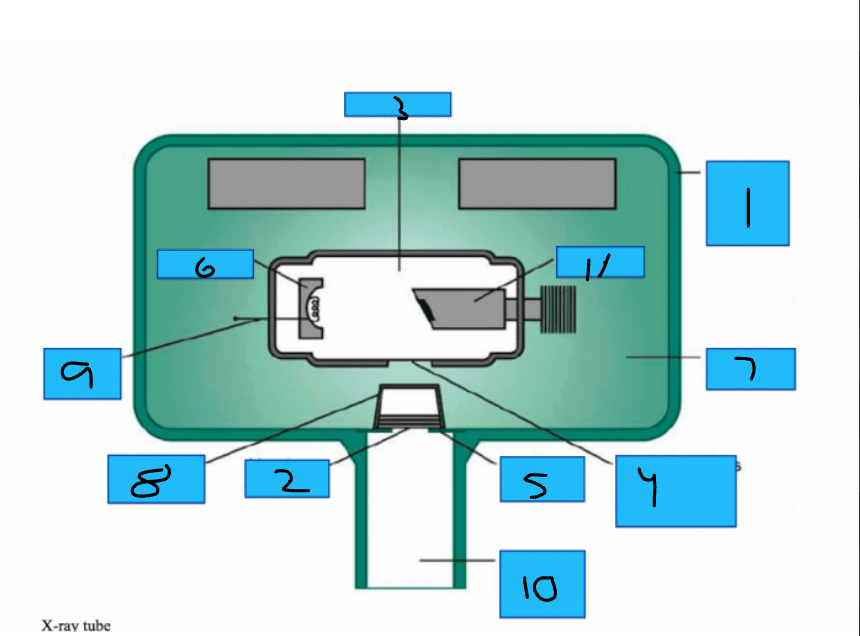
Whats number 11?
Anode