Vitreous
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Location of vitreous
Located adjacent to the lens, zonules, pars plana, retina, and optic disc. Occupies 4/5 of the globe
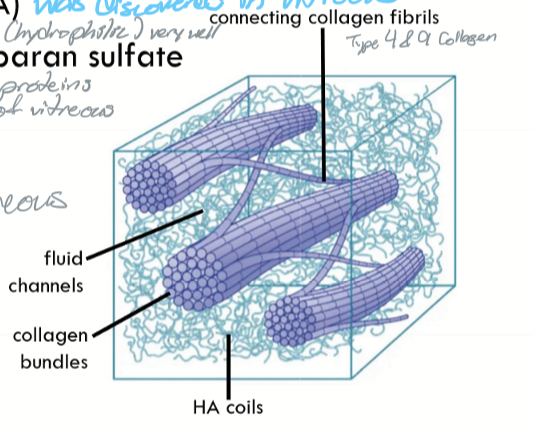
Composition of Vitreous
99-98% water
Collagen Type II
Hyaluronic acid
Chondrotin and heparan sulfate
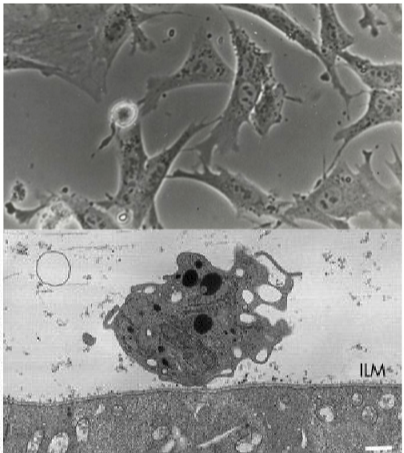
Cells in the vitreous
Hyalocytes = endogenous pluripotent cells
Secretory component
Phagocytic capability
anti-inflammatory
contractile capability
Outer surface of vitreous is composed of?
Condensation of fine collagen fibers
anterior hyaloid surface = more complete collagen to separate AH and vitreous
posterior hyaloid surface = less complete collagen bc ILM & stuff
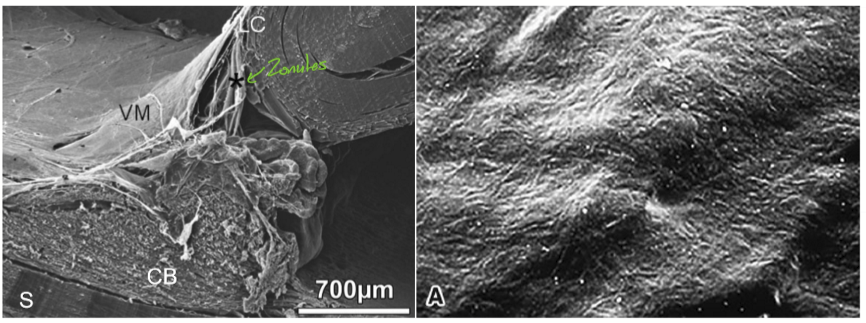
vitreal attachments
Three(ish) main points of attachments
Vitreous base (of von Slatzmenn);
hyaloideocapsular ligament (ligament of Wieger)
ring at optic disc
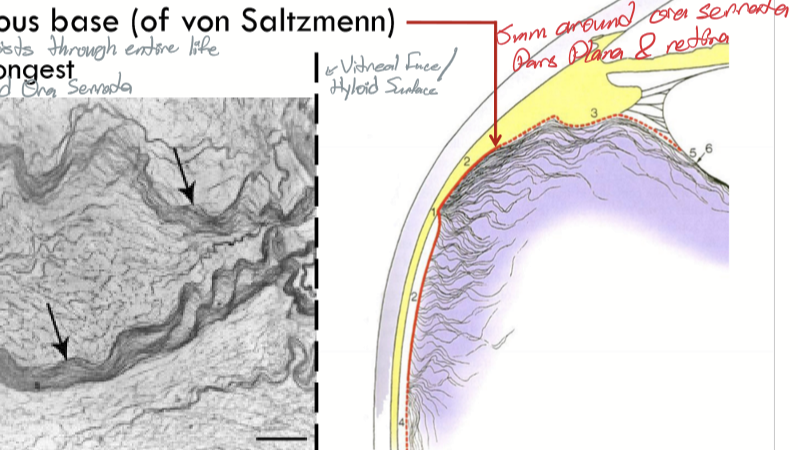
Location of Vitreous base (of von Saltzmenn)
around the ora serrata and is the strongest
Hyaloideocapsular ligament/ligament of Wieger
Circular adhesion ring between anterior face of vitreous and posterior face of lens. Most posterior zonules involved in this attachment. (orange lines)
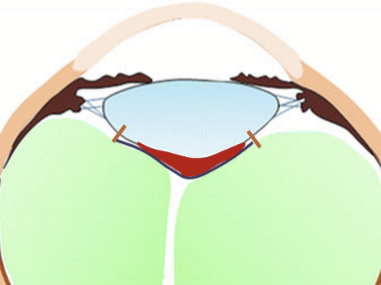
Patellar fossa
divit behind lens, also called hyaloid fossa (purple line)
Space of Berger
potential space behind the lens and in front of the vitreous (red space)
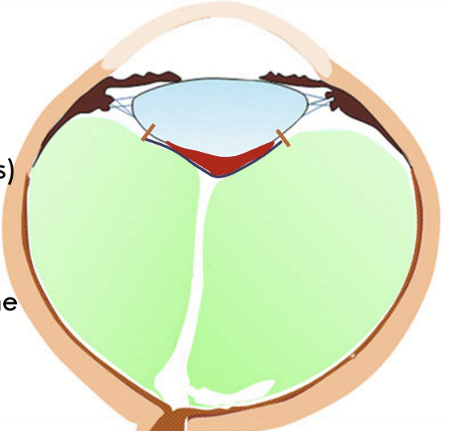
What area is associated with the ring at the optic disk
Area of Martregiani
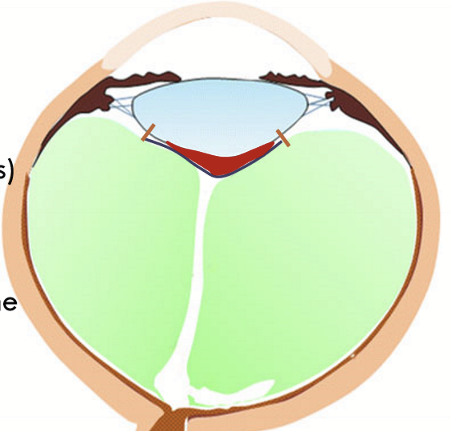
What is the loose attachments at the macular region and around the large retinal blood vessels?
Perimacular attachment (red lines)
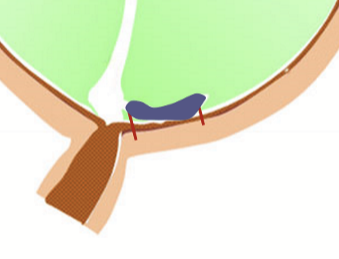
Space of vitreous around the macula
Bursa premacularis (purple area)
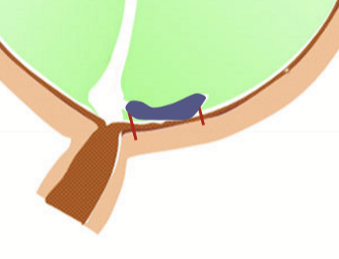
if the vitreous is detached in the back of the eye, it is called:
Posterior vitreal detachment (PVD)
What is the cortex of the vitreous?
A thin layer of the outermost zone of the vitreous, composed of the highest concentration of collagen fibers and hyaluronic acid
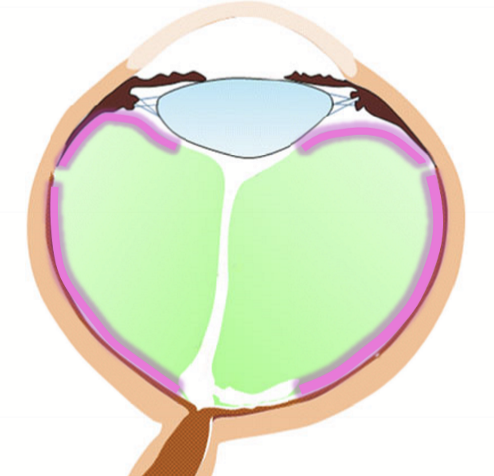
What zones can the cortex be broken up into?
Anterior cortex and posterior cortex
Where is the anterior cortex:
Anterior to the vitreal base, adjacent to the ciliary body, posterior chamber, and lens
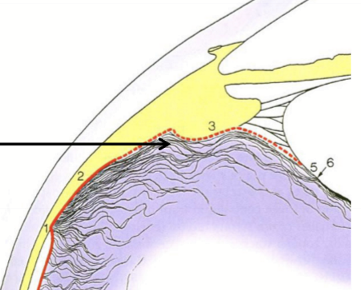
Where is the posterior cortex:
extends posterior to the vitreal base
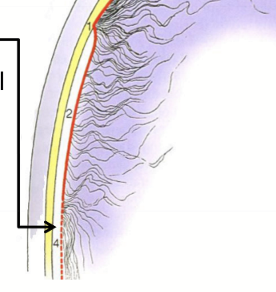
What is the intermediate zone?
the vitreal core, fibers are continuous and arise in the vitreal base (VB)
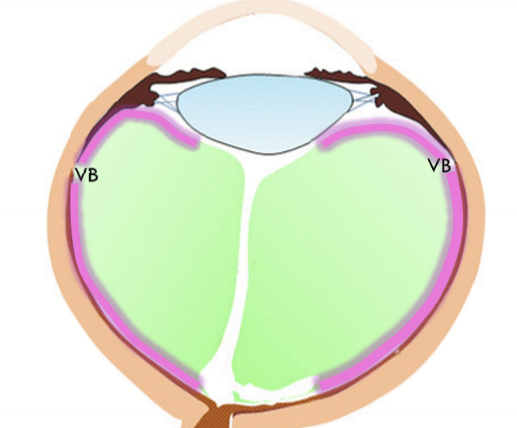
What is cloquet’s canal
Primary vitreous first formed during embryology
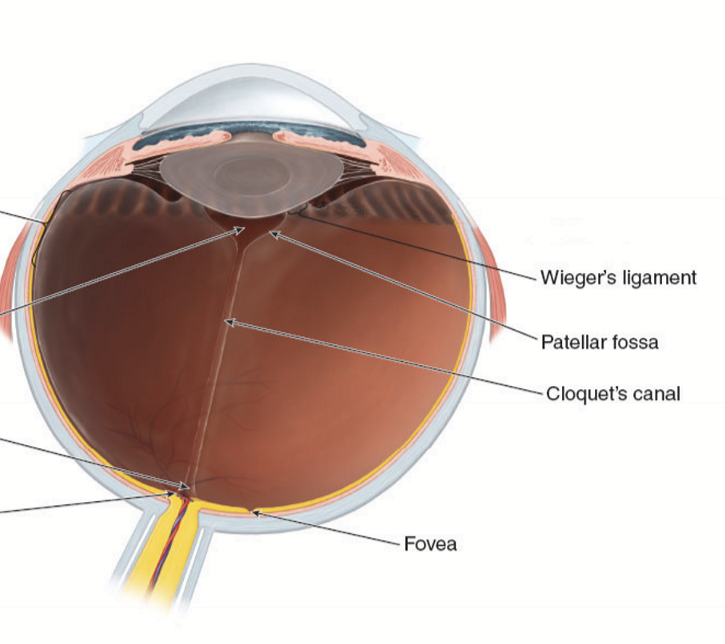
Central zone contains what structures?
patellar fossa and the peripapillary attachment
Vitreous functions
avenues for exchange of metabolites
support of the retina
optical transmission
eye growth
barrier function (keeps O2 against the retina and away from lens)
Vitreal changes
with age the liquid:gel ration changes (liquification is largely in the center of the vitreal core)
vitreous shrinks (vitreous syneresis) and may pull away
fibers aggregate into sheets and collapse into bands
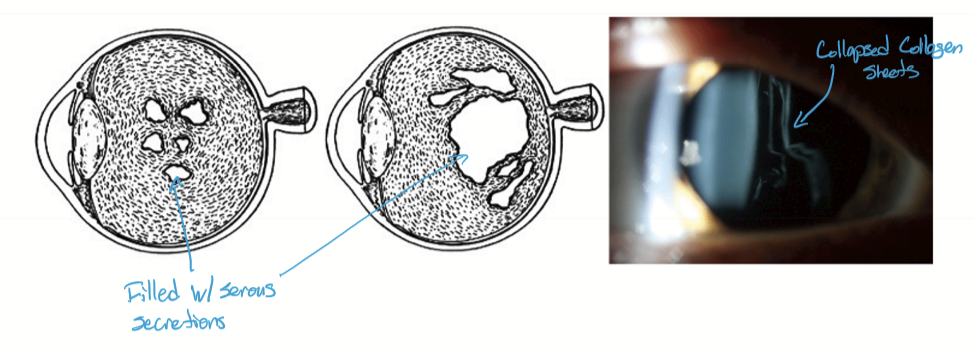
Persistent remnants
muscae volitantes (floaters) are likely debris, noticed because of their motion and shadows