Organic Chemistry Melting Point Lab
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Melting point
temperature at which the solid phase and liquid phase are at equilibrium at a given pressure
factors affecting melting point
bonding and attractive forces, intermolecular forces, size, shape, pressure, and impurity
bonding and attractive force affect on melting point
ionic bonds have higher melting points due to stronger attractions between particles than covalent bonds
intermolecular attractive force affects on melting point
stronger forces like hydrogen bonding have a higher melting point
size affects on melting point
larger molecules have higher melting points due to increased van der Waals forces.
shape affects on melting point
molecules with more symmetry typically have higher melting points due to more efficient packing.
pressure affects on melting point
Increased pressure can increase the melting point by forcing molecules closer together.
what molecule is exempt from the increase pressure equals increased mp
ice
impurity affects on melting point
The presence of impurities typically lowers the melting point of a substance as they disrupt the orderly packing of molecules.
ranges of mp for pure substances
narrow
ranges of mp for impure substances
wide
energy needed to convert solid to liquid
heat of fusion; endothermic
energy needed to convert a solid to a gas
heat of sublimation; endothermic
condensation
reverse of sublimation; -Hsub, exothermic
energy needed to convert a liquid to a gas
heat of vaporization; endothermic
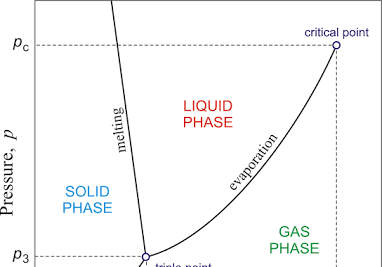
triple point
when both the temperature and pressure of the three phases of the substance coexist in equilibrium
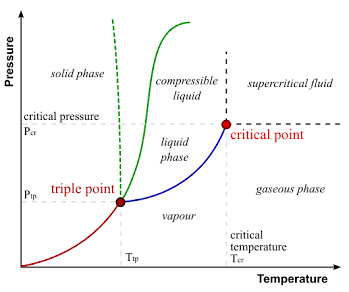
critical point
temperature and pressure at which a substance's liquid and gas phases become indistinguishable