22 - Phylogenetics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is Systematics?
The study of diversity of organisms and evolutionary relationships
What are the two parts to systematics?
- Taxonomy
- Phylogeny
What is taxonomy?
- Describing, naming, and classifying
- Binomial nomenclature for naming species (unique 2-part name)
- Many names are still used today
Who developed the binomial nomenclature for naming species?
Carolus Linnaeus
How does the unique two-part name work?
Genus + Specific epithet
Homo + sapiens = Homo sapiens
How many species of plants and animals did Carolus Linnaeus name?
~11,000 spp of plants and animals
What are the rules for the naming system?
- Latin/latinized
- Genus name upper case, specific epithet is not
- Both italicized or underlined
- Genus can be abbreviated, specific epithet can NOT
- Genus is unique and can specify all species within a genus
- Specific epithet isn't necessarily unique
Examples of the rules
- Both italicized or underlined
Escherichia coli
- Genus can be abbreviated, specific epithet can NOT
E. Coli
- Genus is unique and can specify all species within a genus
Genus Escherichia
- Specific epithet isn't necessarily unique
Can NOT say "Species coli"
What is hierarchical classification?
Levels:
Domain -> Kingdom -> Phylum -> Class -> Order -> Family -> Genus -> Species
Species = smallest unit of classification
What is a taxon?
- It is the grouping of organisms at any one of the levels above
- Plural: Taxa
Moving from species to domain, what happens?
- Each level is more inclusive
What happens at each level?
All species on a certain level share characteristics of that group
Example of species sharing characteristics at each level
Class: Mammalia
- Hair and milk production
Order: Carnivora
- Above AND teeth modified for sharing meat
Family: Carnivora
- ALL above AND anatomy of a middle ear
Genus: Canis
- ALL above AND long limbs relative to head and body length, elongated snouts, well-developed canines
What is Phylogeny?
- The study of evolutionary history and relationship among organisms
- Based on shared ancestry, not phenotypic similarity
What is a Phylogenetic Tree?
- A branching diagram that shows patterns of descent from a common ancestor
- Hypothesis may change with more data
How to read an Unrooted Tree
Shows relationship, but does not show the ancestral root
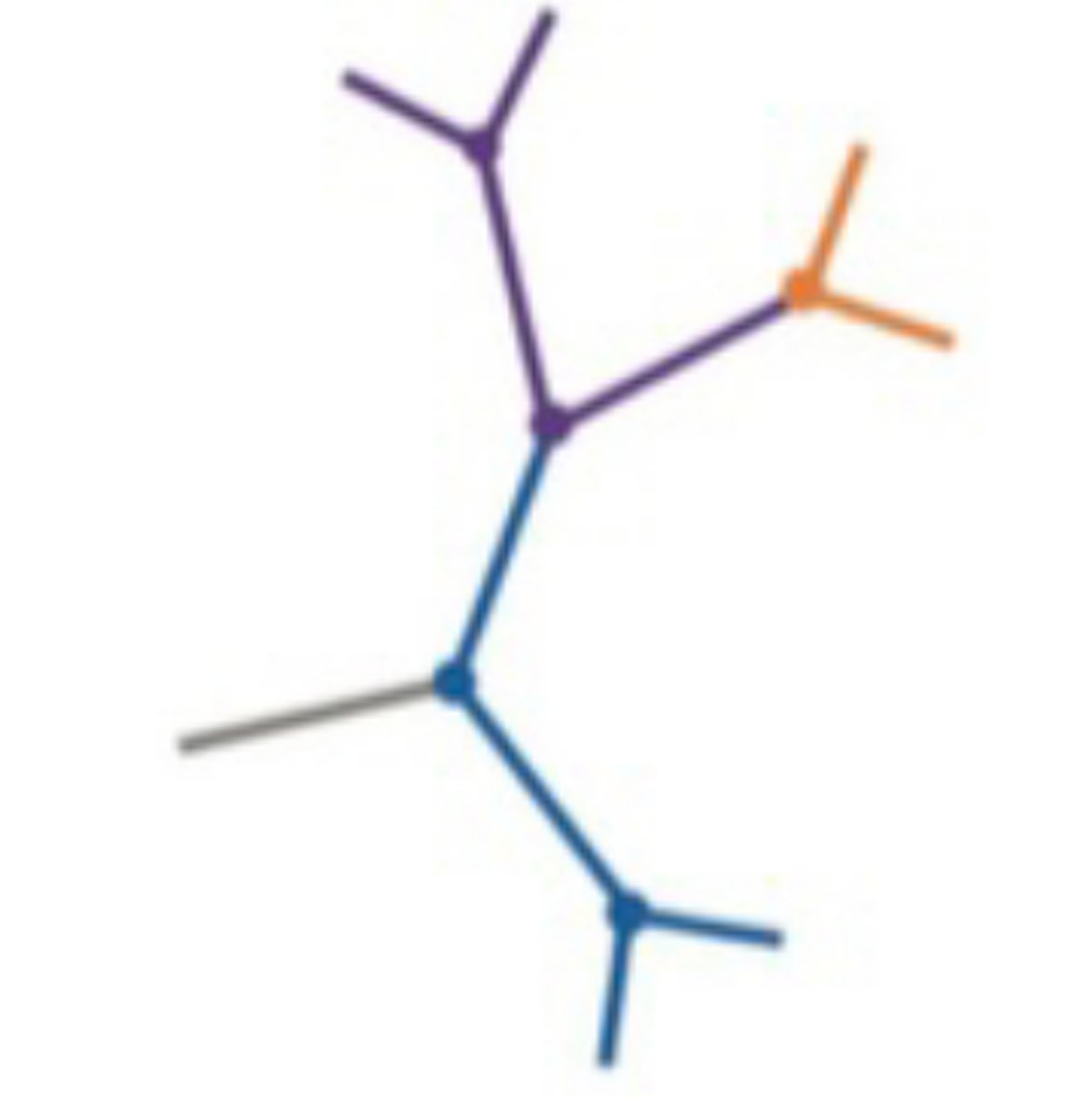
How to read a Rooted Tree
One branch point represents most recent common ancestor of all taxa on the tree
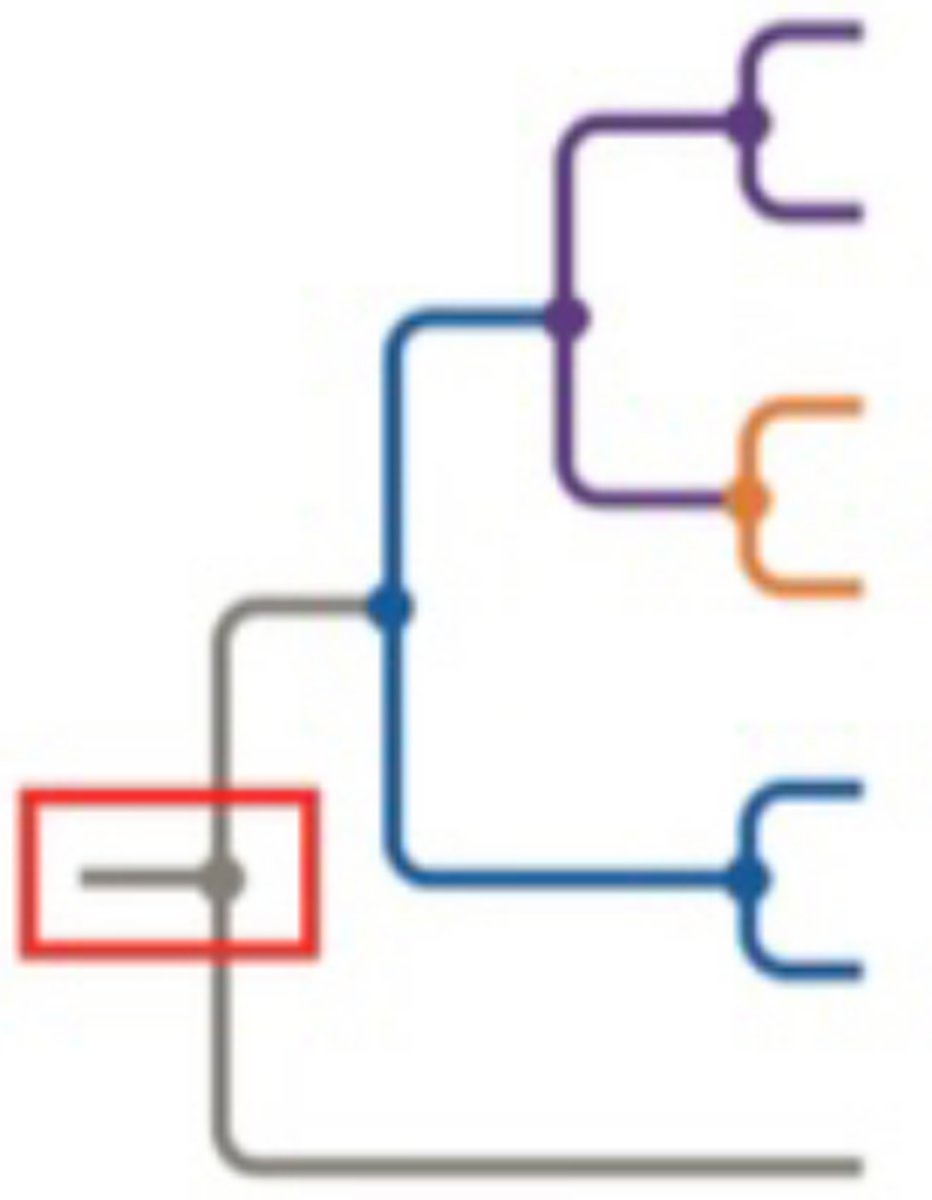
What do the branchpoints represent?
They are nodes
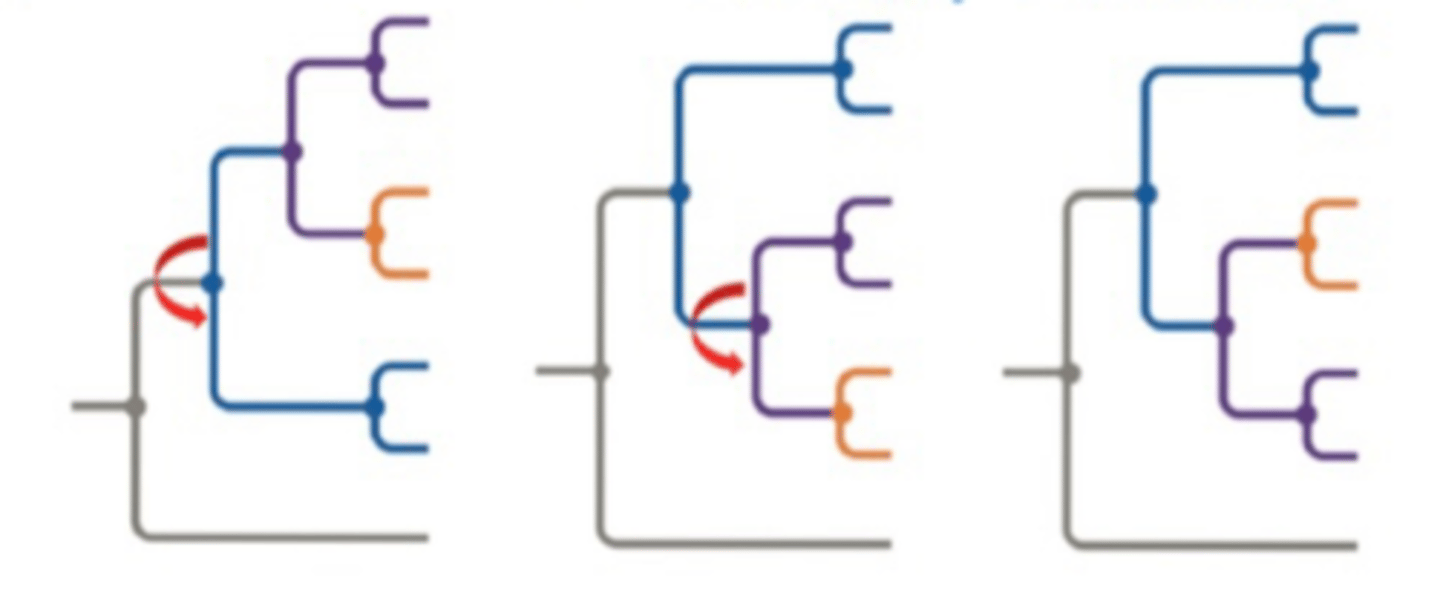
What are Dichotomies on a tree?
- The divergence of 2 lineages from a common ancestor
- Branches can rotate without changing relationships
What are Extant Species?
They are currently living and exist at the tip of the branches
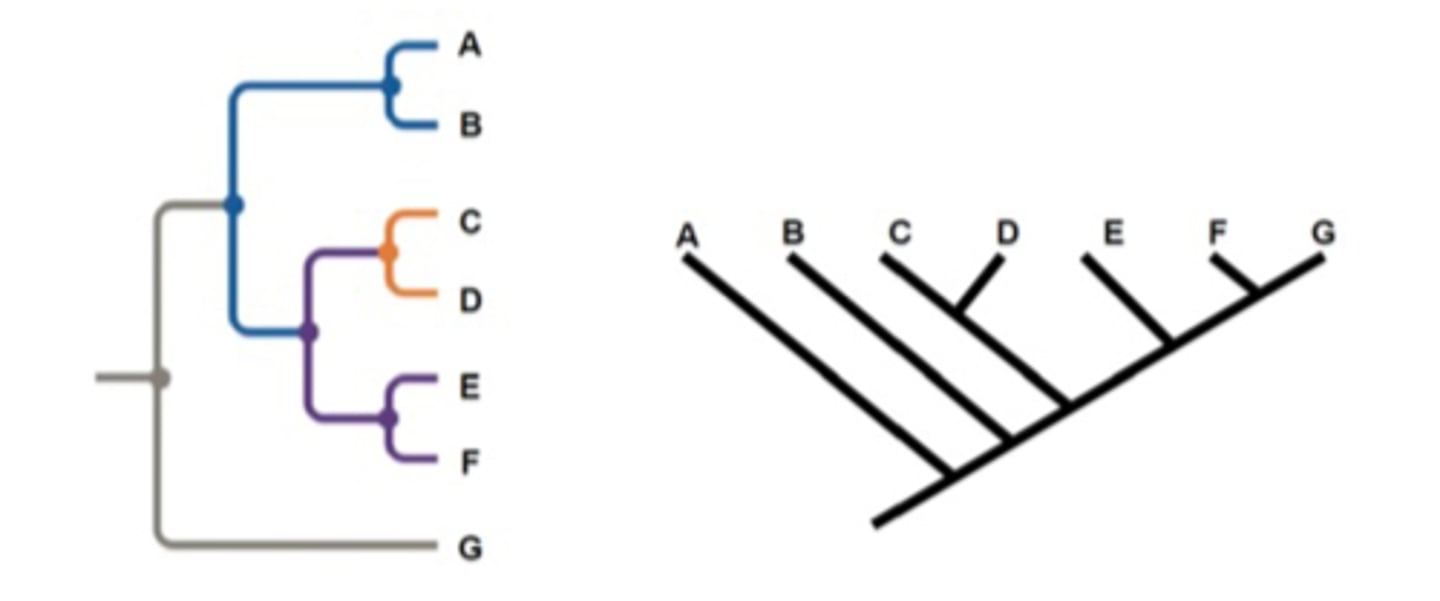
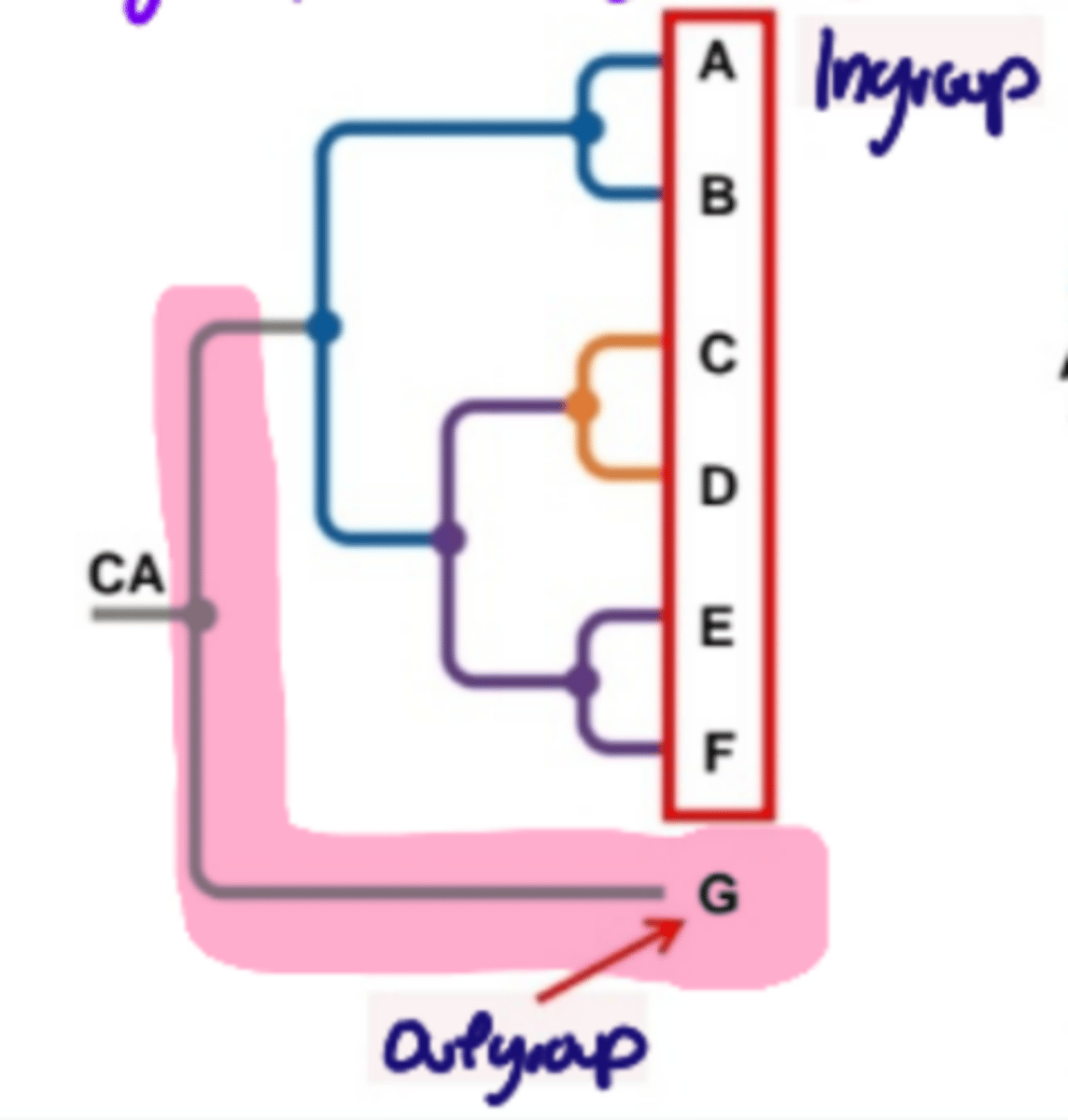
What is a Basal Taxon?
1st lineage to diverge from a common ancestor of a group
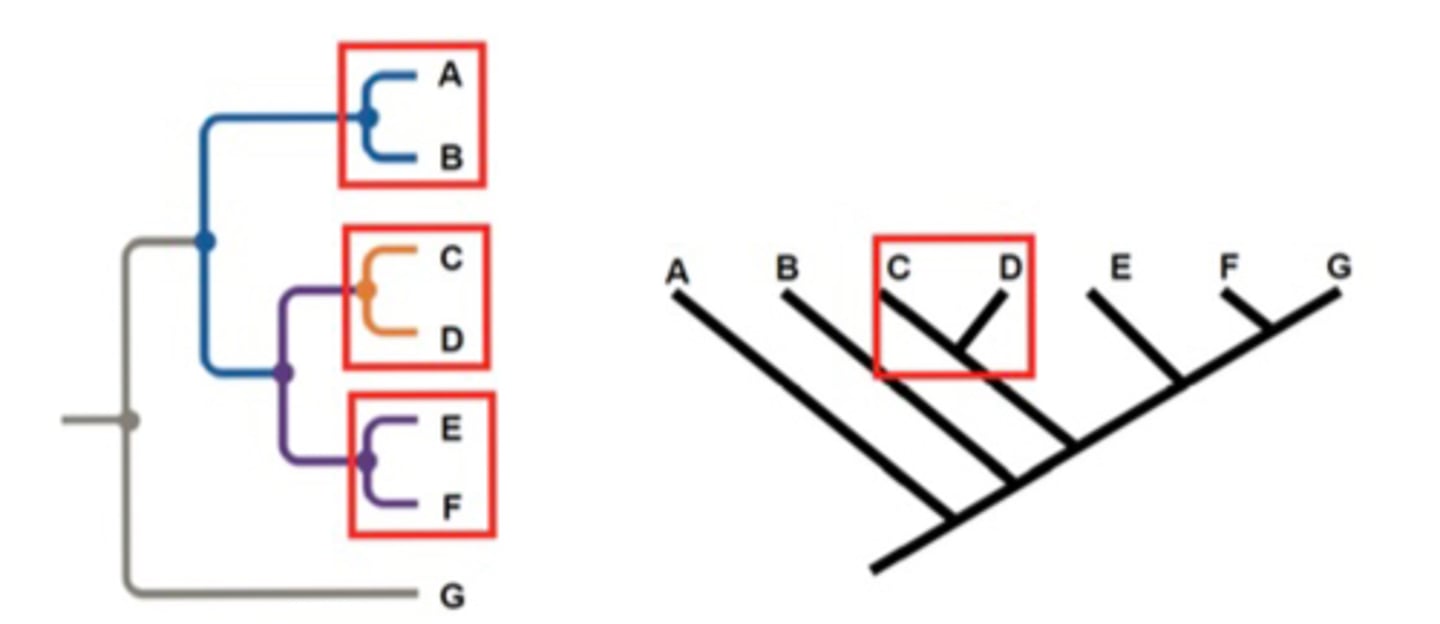
What is a Sister Taxa?
Organisms that share an immediate common ancestor, they are each others closest relatives
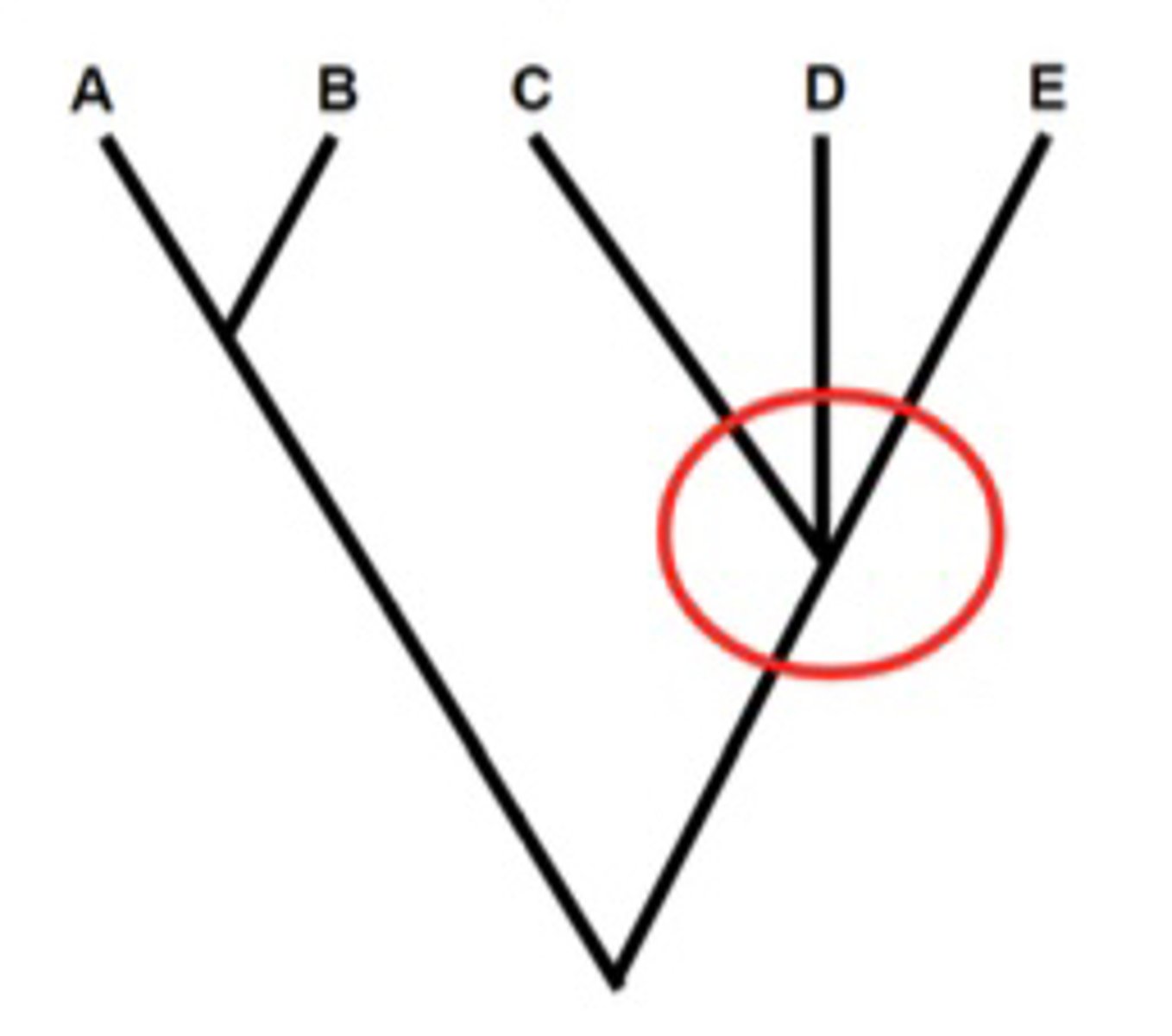
What is Polytomy?
A branch point with more than 2 descendent groups, meaning evolutionary relationships are not clear (Not Good!)
What is a Character?
An attribute of a species
What are States?
Alternate forms of a character
What is an example of a state?
Four legs: Present vs. Absent
Body Covering: Hair vs. Feathers vs. Scales
Compare characters and states
- They more closely 2 species are related, the more characters they share
- Must result from common ancestry
Where do homologous traits come from?
They are inherited from a common ancestor
What is an example of a homologous trait?
- Look at function of wings in birds and bats
- Underlying structure is the same because it was inherited from a common ancestor
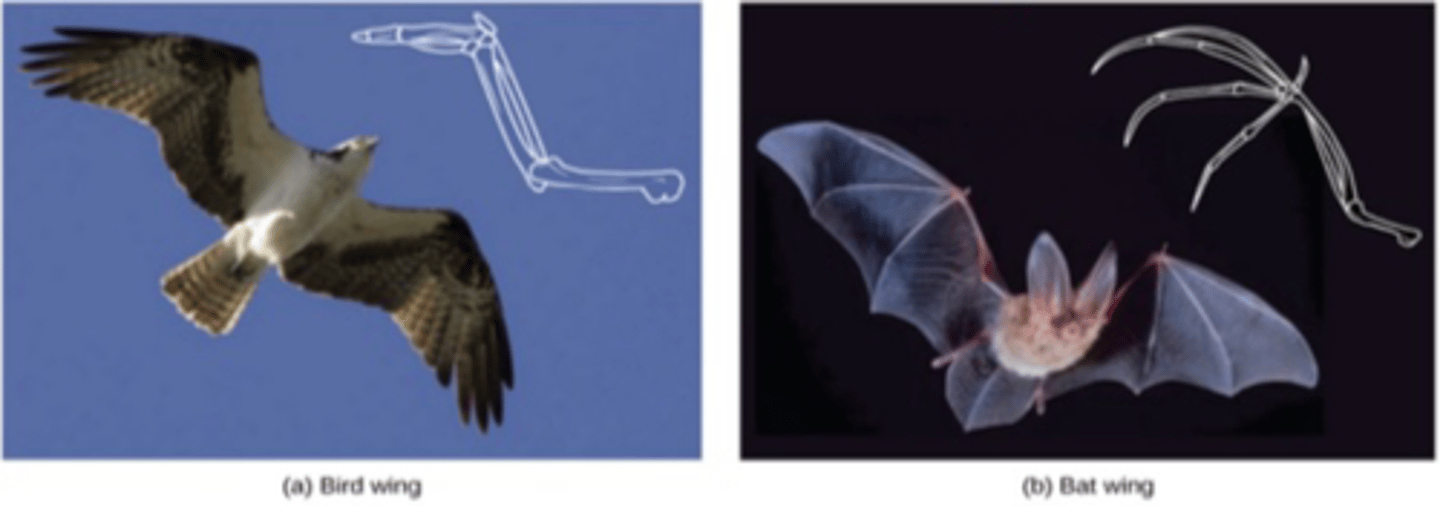
What can be connected to homologous traits?
Darwinian evolution
What traits are a result of Convergent Evolution?
Analogous
What are Analogous traits?
- Independently acquired
- Similar adaptations in organisms from different evolutionary lineages
- Similar environment can cause this (similar selection pressure, similar character although they do not share a CA)
What is an example of an analogous trait?
- Birds and Honeybees do not share a common ancestor with the same wing structure
- Bird wings are different from insect wings
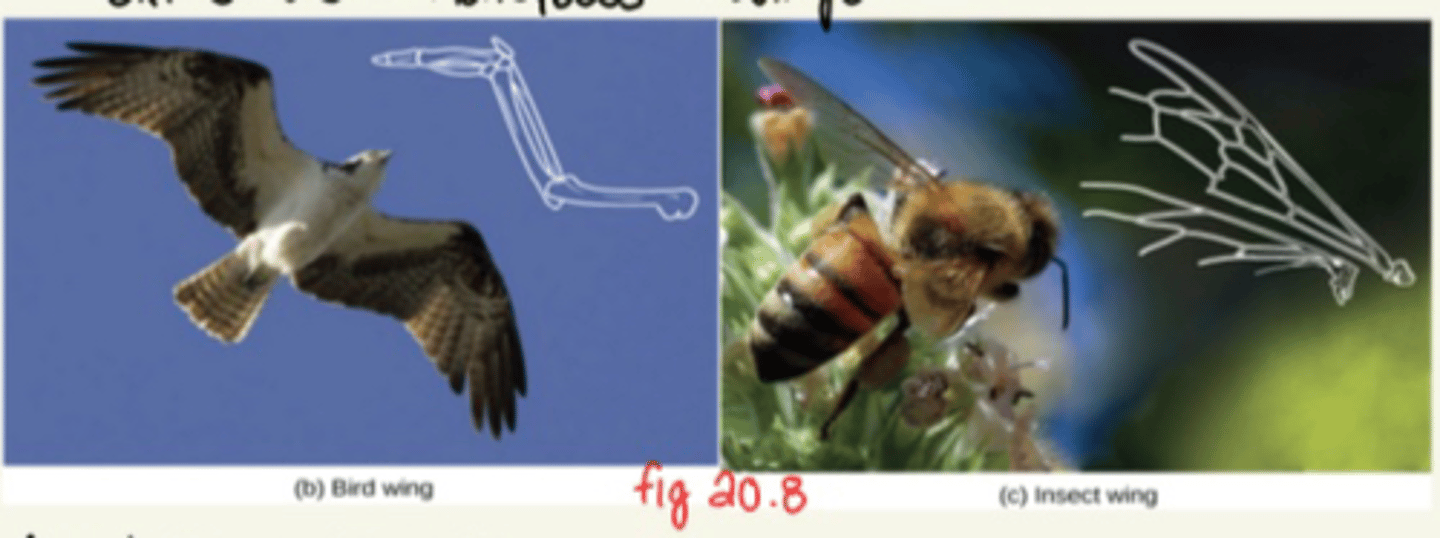

Why do birds and honeybees both have wings even though they don't have a common ancestor?
Aerodynamic pressure, they converged on structures for flight
What is an example of choosing a character?
Anatomical/Morphological features (developmental and life history traits)
How do we get Molecular Data?
- Compare DNA sequences
- Genes are sequences of 100's of nucleotides
- Compare RNA seqs
- Compare aa seqs of proteins
- If a gene in 2 organisms shares many nucleotides, then possibly homologous
An example of molecular data
12 nucleotides --> 12 characteristics
- A, C, G, or T at each site -> States
What are Cladistics?
- It is a widely used method of systematics
- Uses homologous to classify organisms based on common ancestry
What is a Clade?
A group which includes ancestral species and all of its descendants
What are the three possible groups of clades?
- Monophyletic clade
- Paraphyletic clade
- Polyphyletic clade
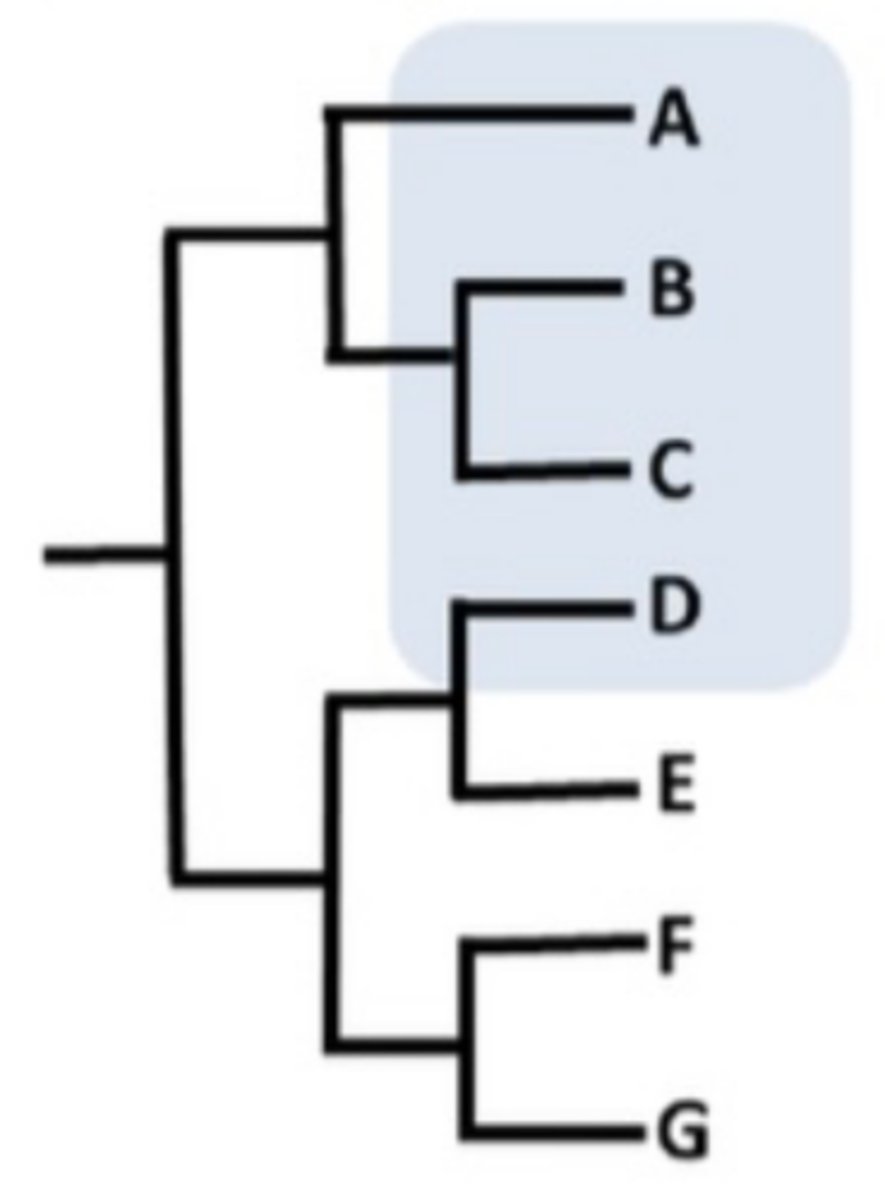
What is a monophyletic clade?
Common ancestry and ALL descendants
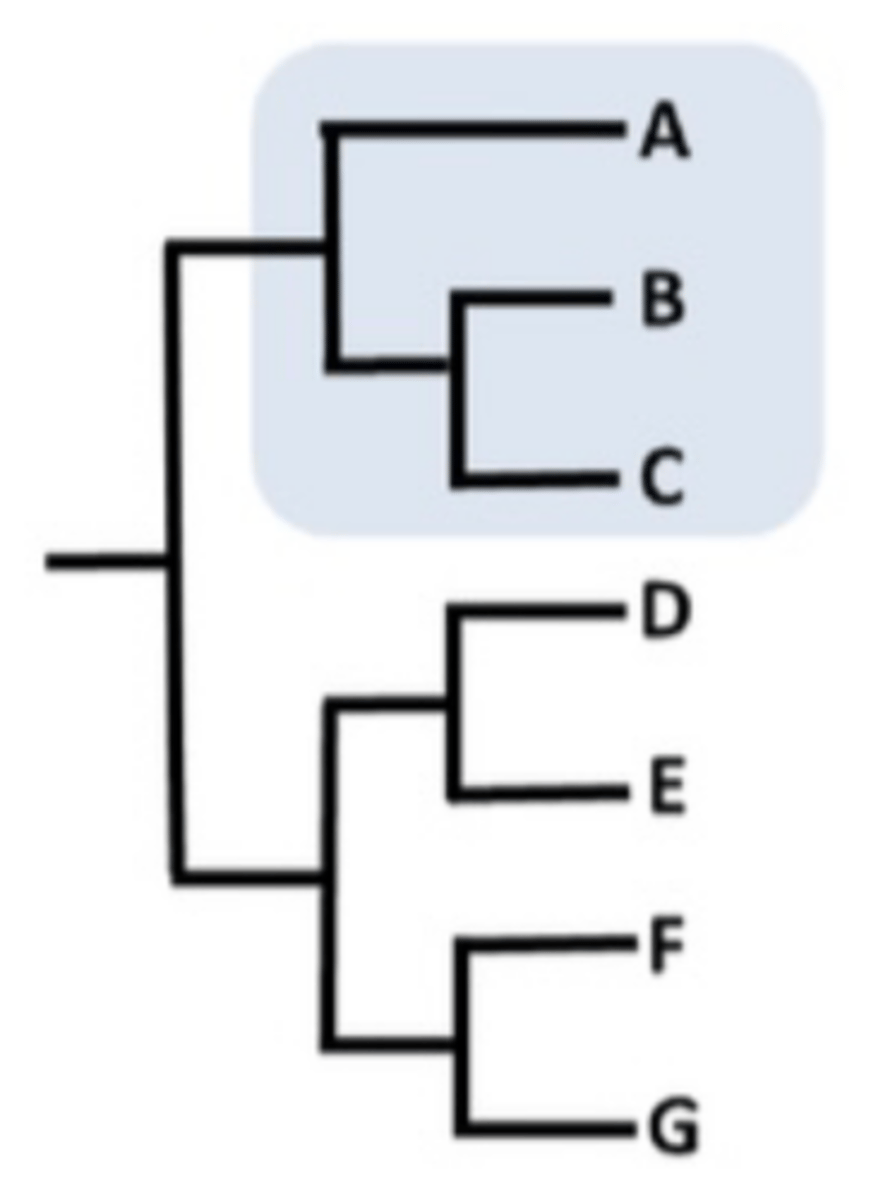
What is paraphyletic clade?
Common ancestor and SOME of its descendants
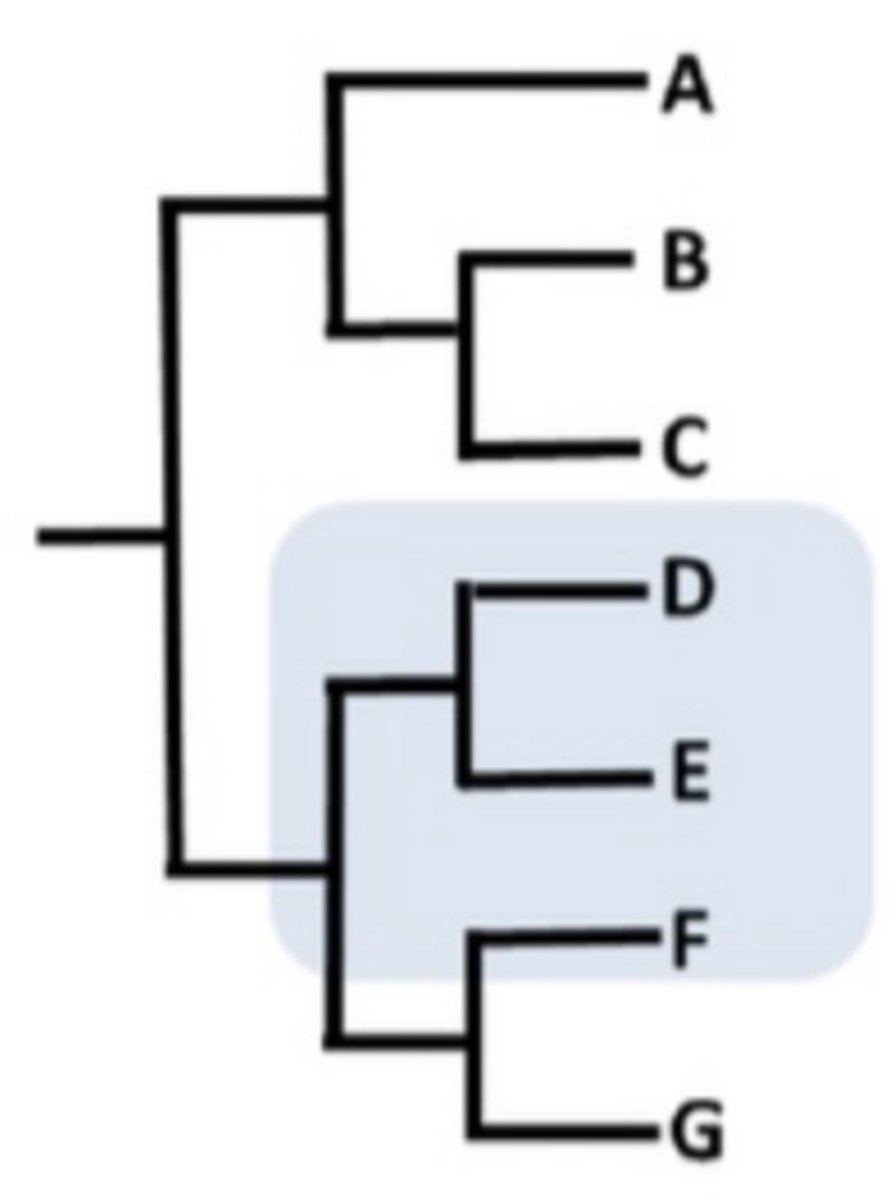
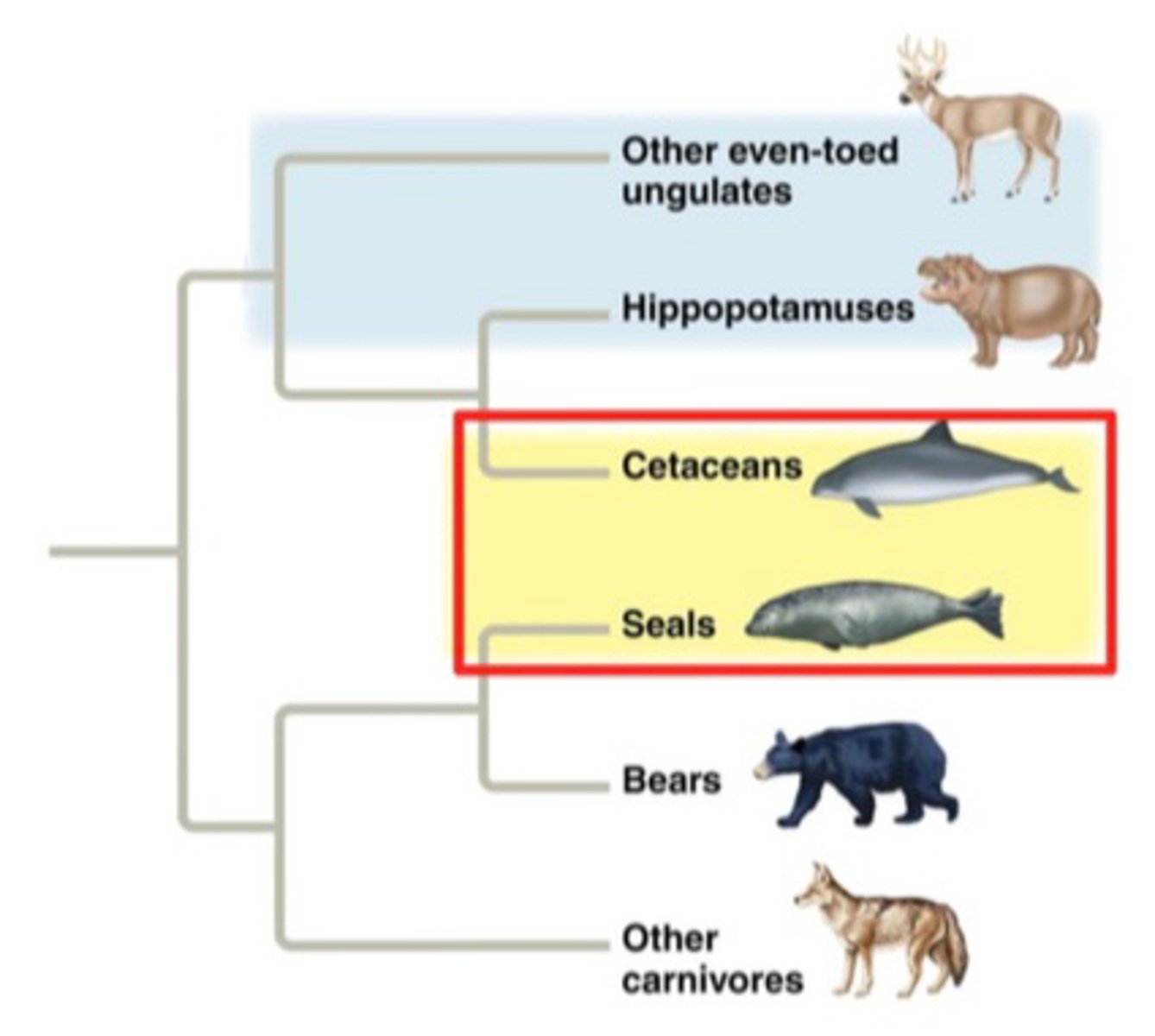
What is a polyphyletic clade?
Distantly related species and it does NOT include the most recent common ancestor
What is an example of a monophyletic group?
Vertebrates
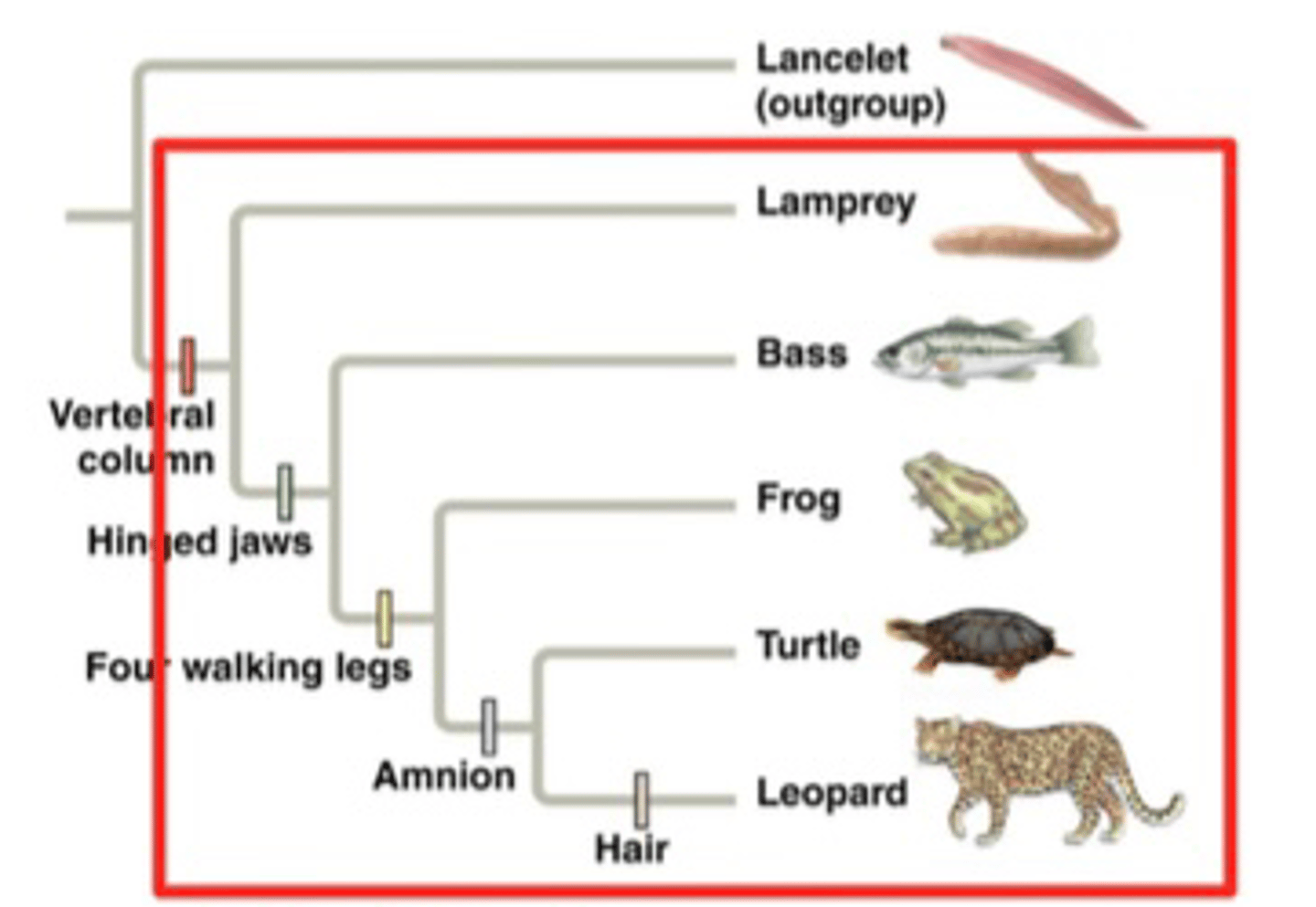
What is an example of a paraphyletic group?
Fish
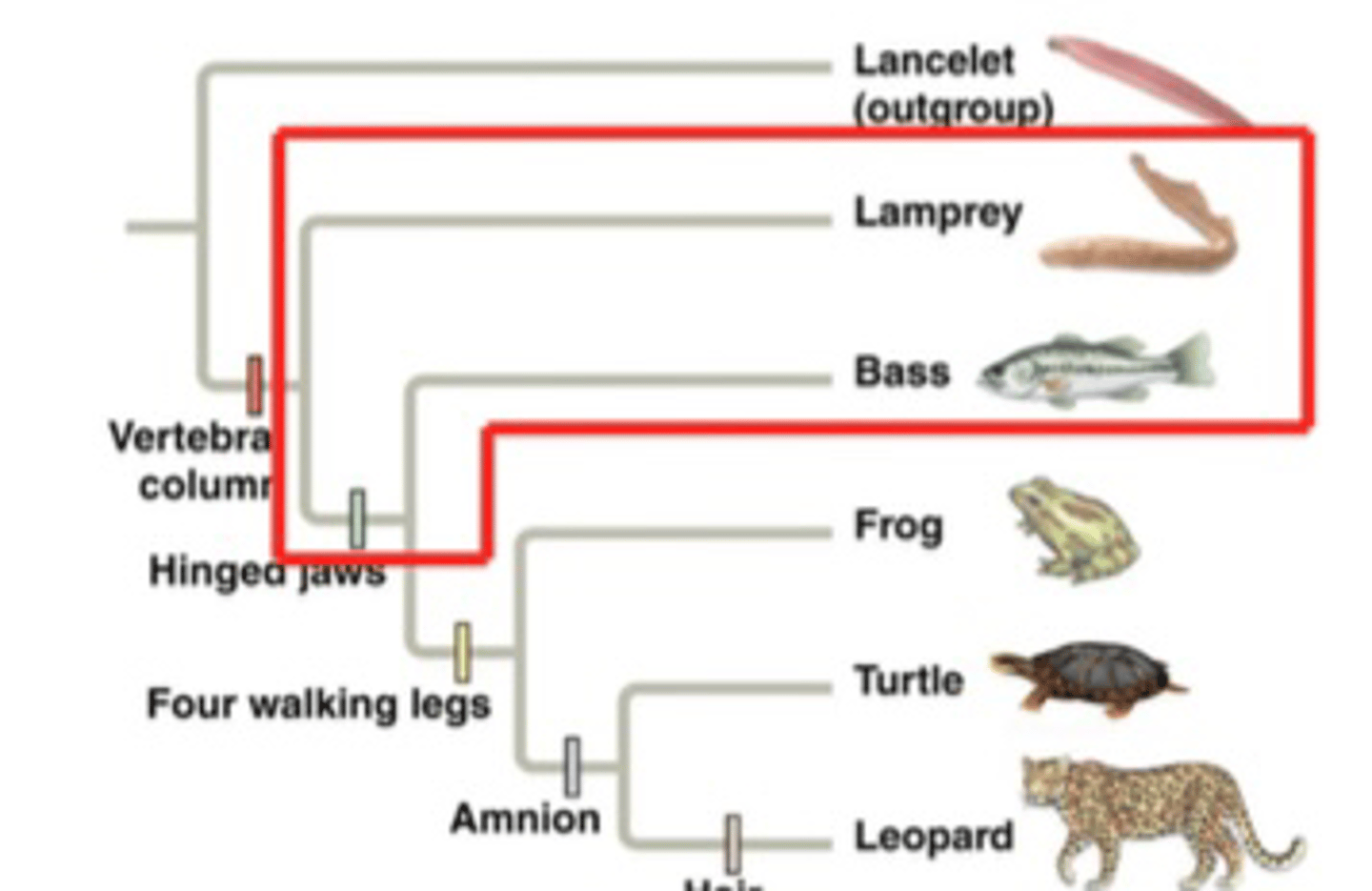
What is an example of a polyphyletic group?
Mammalian fins
What are shared ancestral characters?
- Not unique to clade
- Originated in ancestor
- Point 1
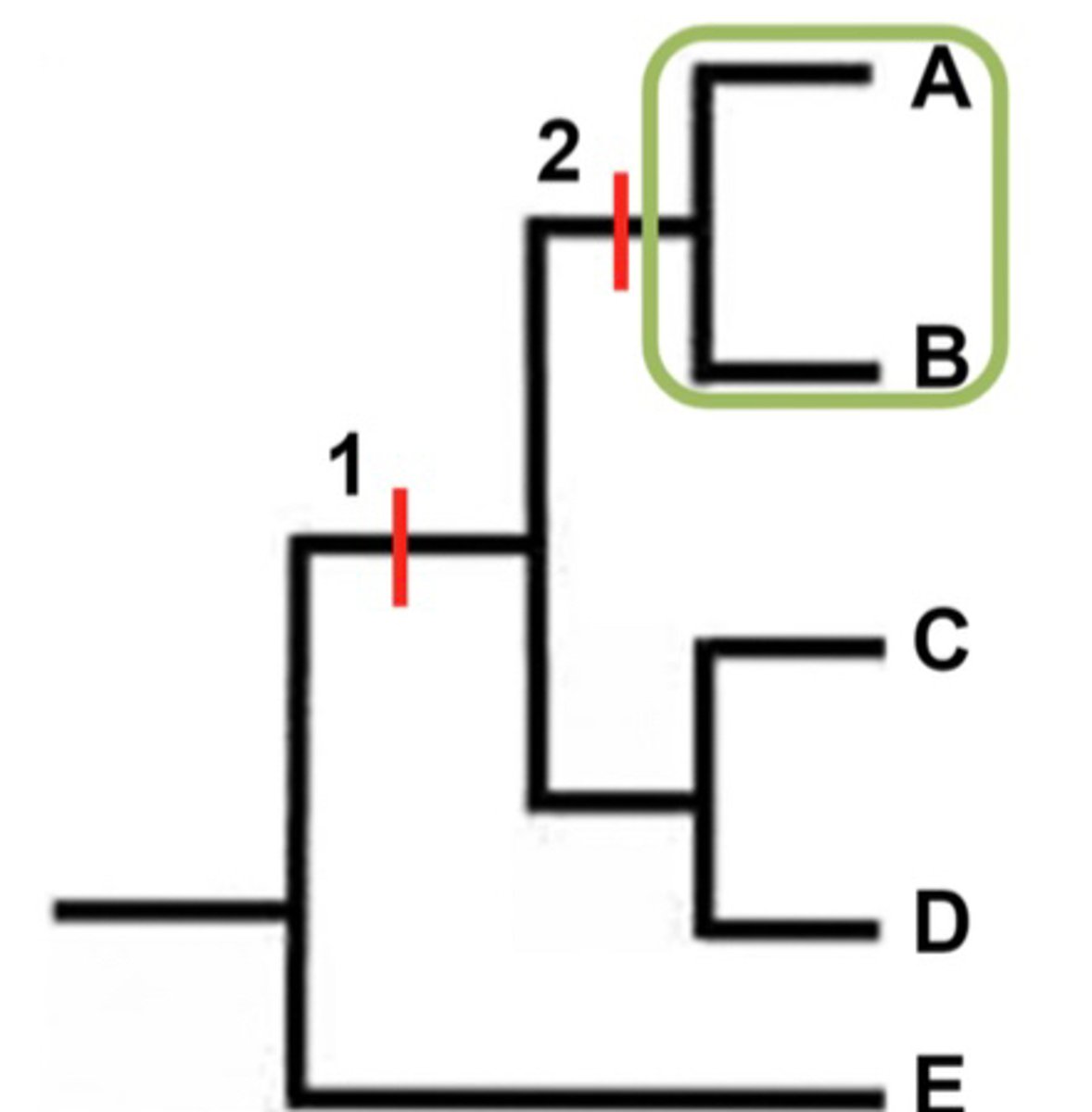
What are shared derived characters?
- Unique to clade
- Point 2
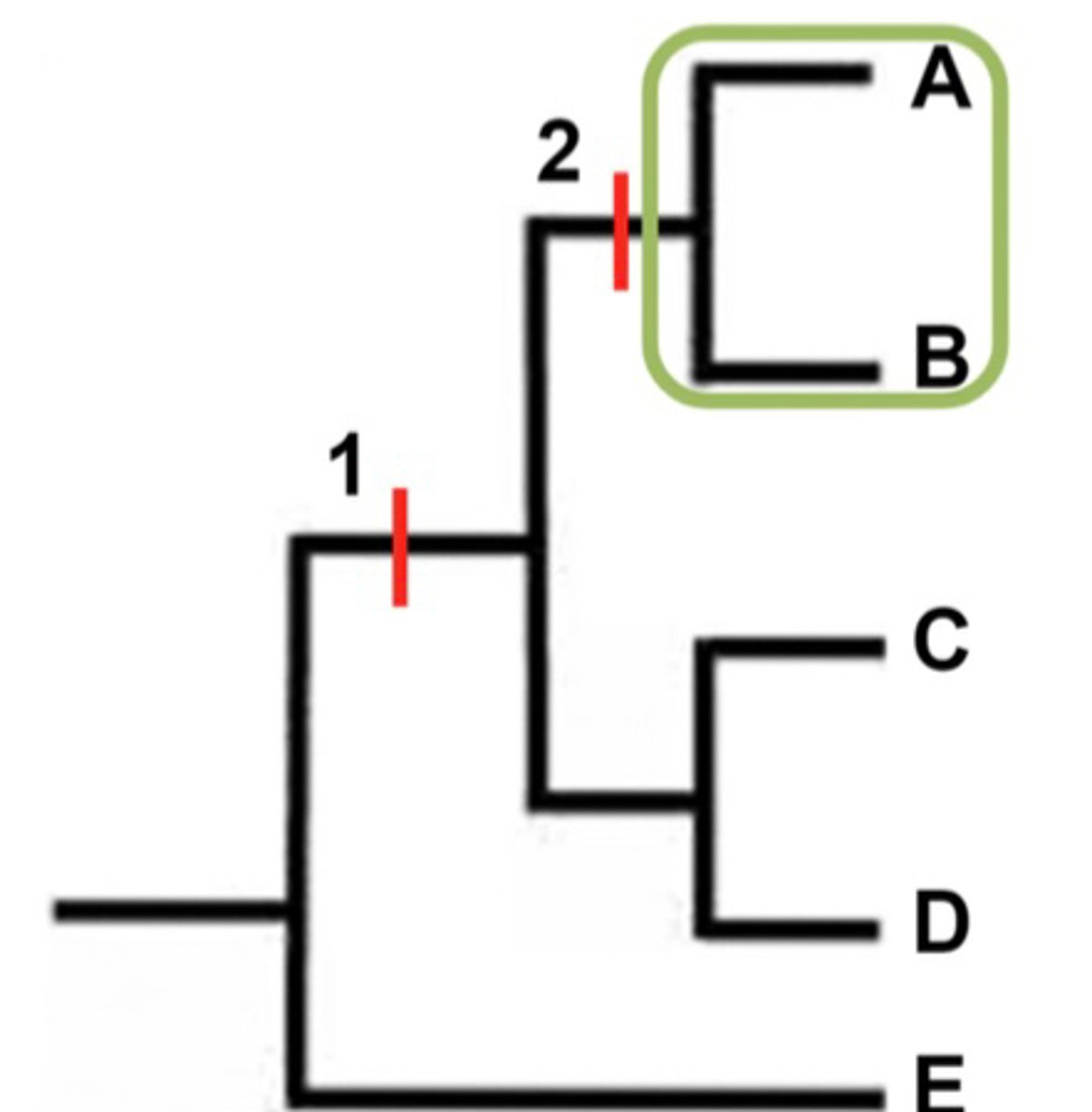
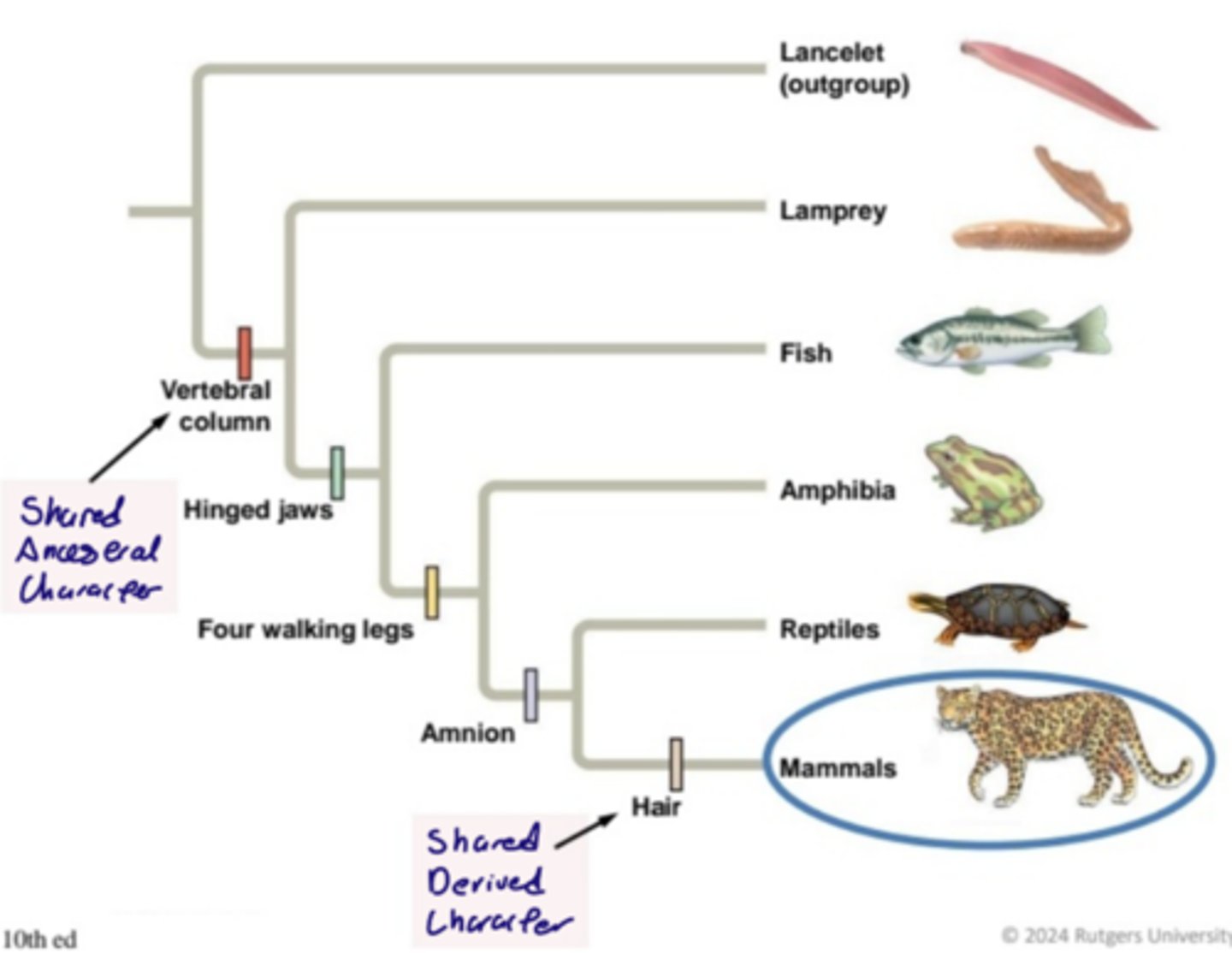
An example of Shared Characteristics
Shared Ancestral Character = Vertebral Column
Shared Derived Character = Hair