BY 124L Kingdom Fungi
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are the 5 general characteristics of fungi?
Eukaryotic, Absorptive Heterotrophs, Haploid Stage Dominant, Cell Wall made of CHITIN, Mostly multicellular (exception- Yeast)
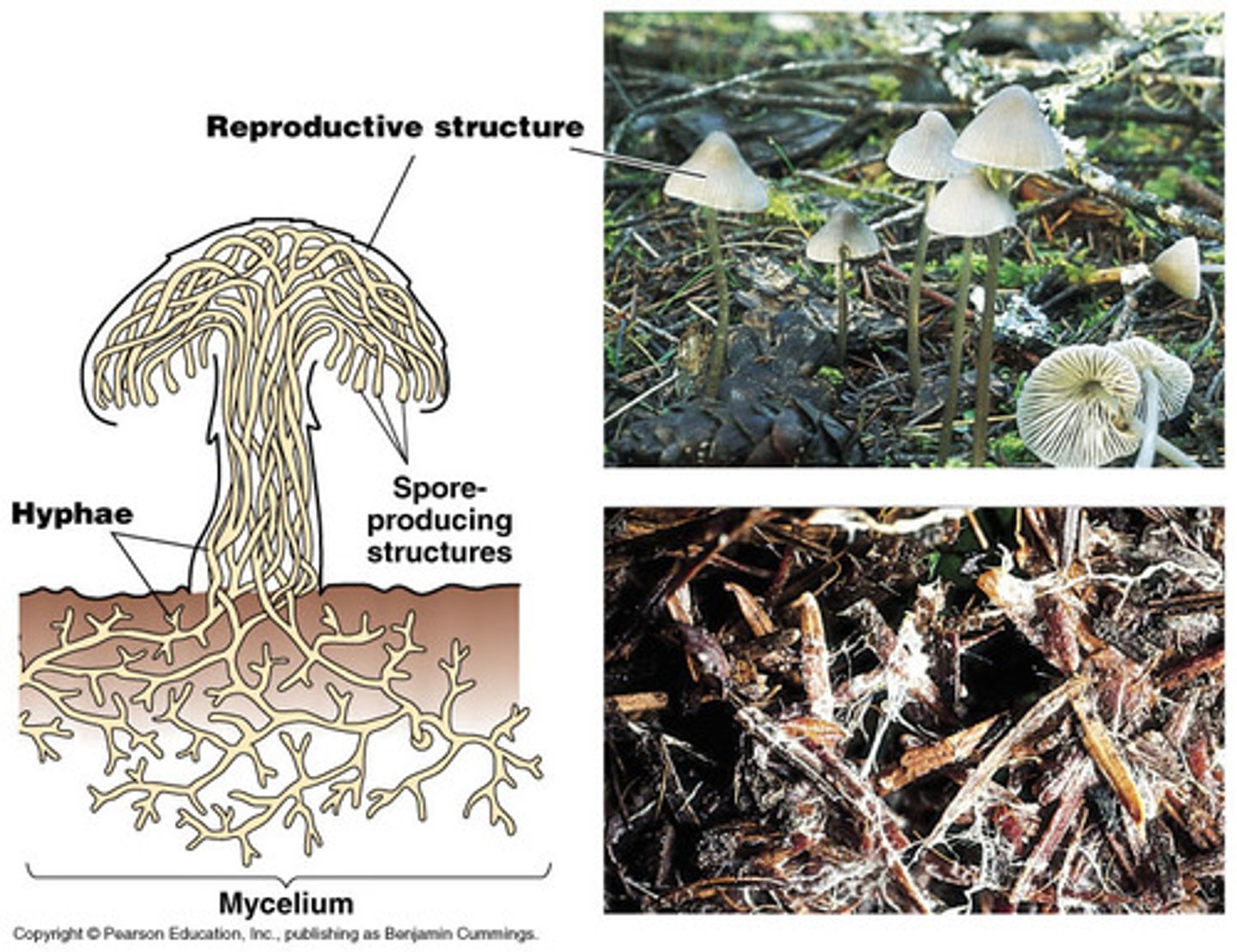
What are two main components of fungi anatomy?
hyphae and mycelium
What is hyphae?
part of the fruiting body, Vegetative bodies that are tubular in shape
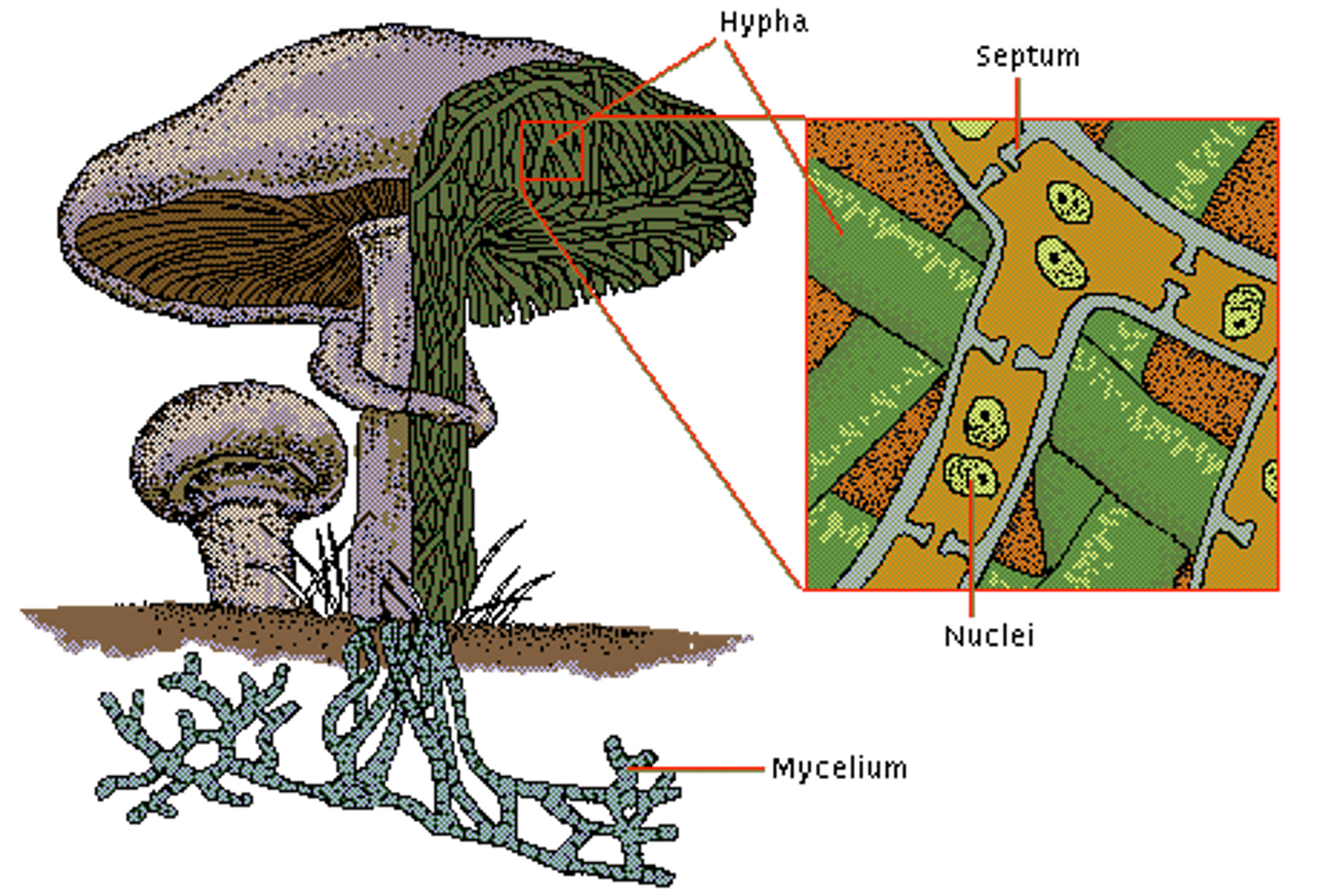
What is mycelium?
Filamentous mats of hyphae, SUBTERRANEAN
What does subterranean mean?
underground
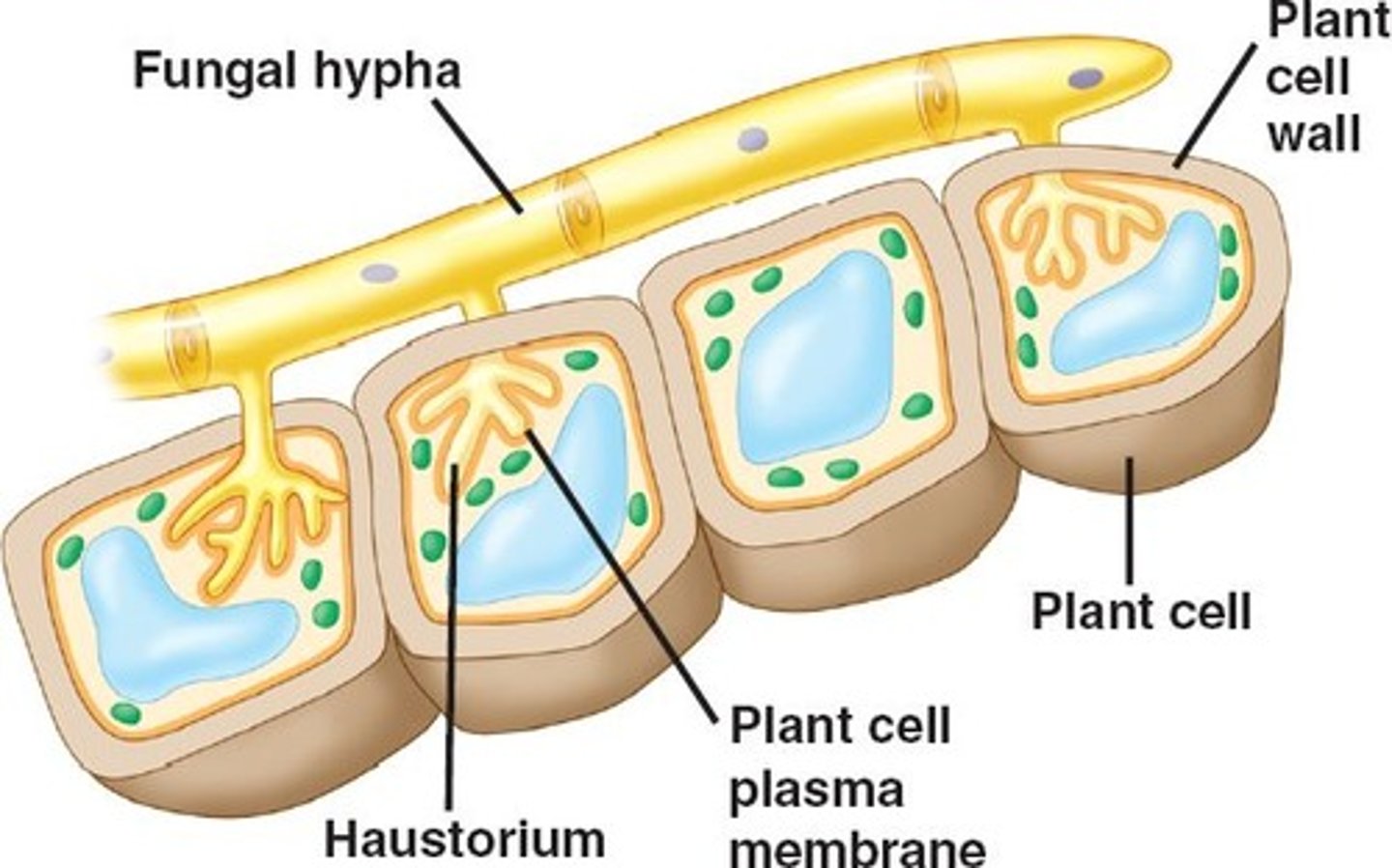
What are the three types of fungi cells?
haustoria, rhizoids, reproductive
What are haustoria cells?
Straw-like feeding tube which is inserted into a host cell (parasitic fungi)
What are rhizoids?
Root-like anchoring hyphae to its substrate
What are septae?
wall-like structures that can separate cells
Some fungi lack septae and are called what?
coenocytic (fancy for multinucleated)
Coenocytic cells can have one unique stage in which 2 distinct nuclei types ("+" and "-") are in the same cell, what is this called?
dikaryon
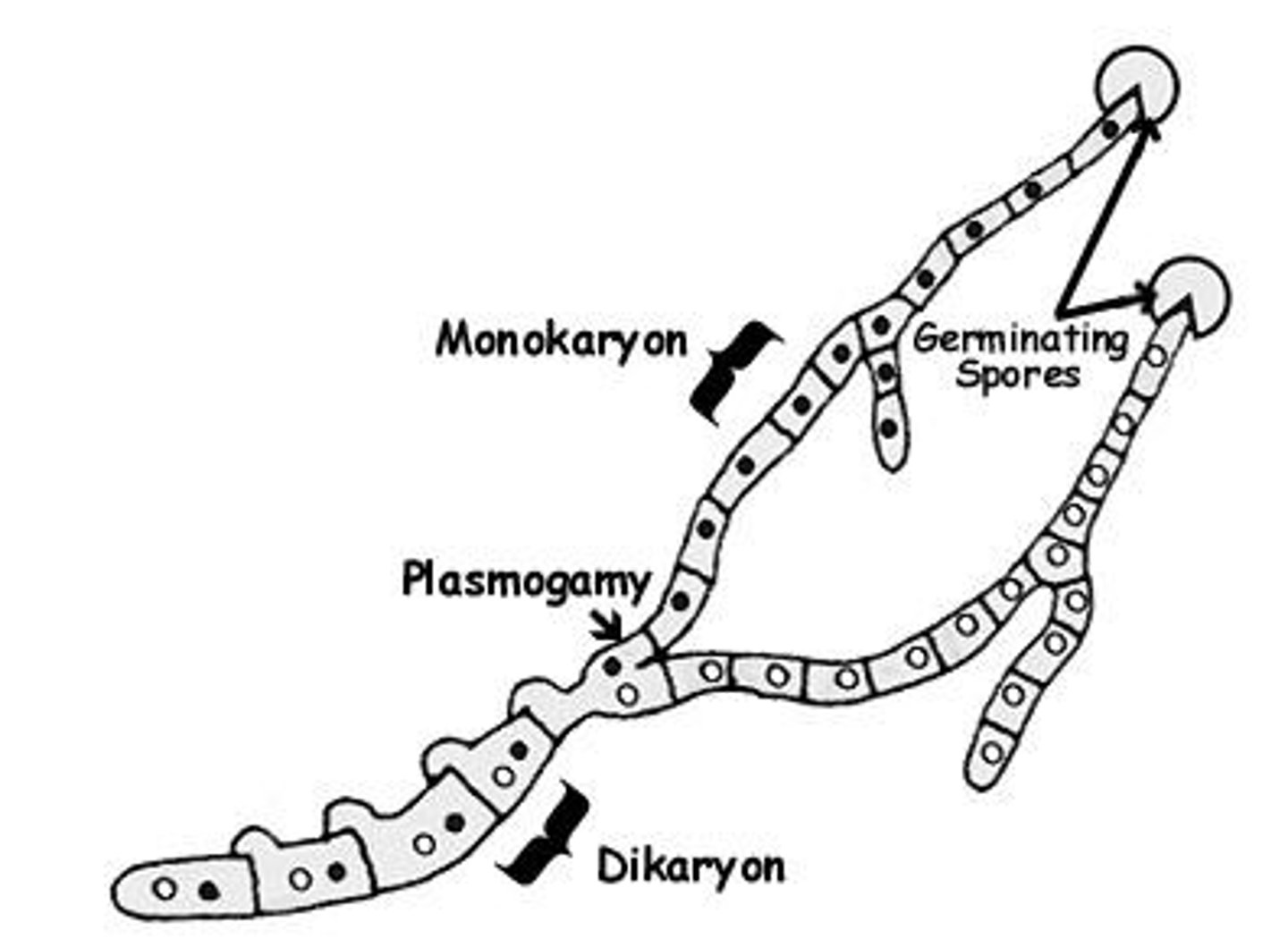
Coenocytic cells can have another unique stage where different nuclei remain separate within the same mycelium, what is this called?
heterokaryotic
What is septate hyphae?
hyphae with cross walls
What is coenocytic hyphae?
hyphae that lack septa (single cell)
What is monokaryon?
one type of nuclei present in a cell
What are the two ways fungi reproduce?
asexual and sexual
How do fungi reproduce asexually?
spores
How and why do fungi reproduce sexually?
when environmental conditions change (very stressful, lots of energy)
Fungi are what type of heterotrophs?
absorptive heterotrophs
What does it mean that fungi are absorptive heterotrophs?
extra-cellular digestion, has exoenzymes
What does the fact that fungi are absorptive heterotrophs make them useful/important for?
chemical recycling, very important in environments and ecosystems
What are exoenzymes?
Breaks down organic molecules, and absorbed across the cell wall
What are the three modes of feeding?
Saprobic, Parasitic, Mutualistic
What does saprobic mean?
Feeds on dead organic material (decomposer)
What does parasitic mean?
Feeds on living organisms (80% of plant disease)
What is an example of mutualistic?
mycorrhizae
What are mycorrhizae?
Symbiotic relationship where hyphae wrap around the root of a plant
How does mycorrhizae benefit both the plant and the fungi?
Increased surface area from the hyphae help with water intake for the plant, the fungus receives carbohydrates from the plant
What are the phylums under the kingdom Fungi?
Chytridomycota, mucoromycota, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, Dueteromycota
What are some (7) characteristics of the phylum Chytridomycota?
chytrid (common name), Found in lakes and soil; Saprobes or Parasites (plants, animals, protists); Diverged early in fungal evolution; Cell walls of CHITIN; Zoospores- Flagellated spores; killer of small animals
What are some (5) characteristics of mucoromycota?
Black bread molds, no longer zygomcota, coenocytic, major ground of mycorrhizal fungi, Will form a zygosporangium during sexual reproduction (Freeze and desiccation resistant)
What are two genuses under the phylum mucoromycota?
Rhizopus, Pilobolus (the shut-gun fungus) aims it spores to an area of light
What are some chracteristics of the phylum Ascomycota?
"Sac/Cup Fungi"; Largest and most diverse fungi group; Marine, terrestrial, freshwater; yeasts, truffles, morels, ergot (LSD); main fungus in lichens, 3 types of reproduction
What was a probably factor of the Salem Witch Trials?
Ergot (LSD) bread wasn't stored correctly and ergot arose making some women hallucinate
What are Lichens?
Symbiotic with green algae or cyanobacteria
What are the 3 reproductive differences in phylum ascomycota?
yeasts (Unicellular organisms reproduce by budding), asexual (imperfect; results in conidia), sexual (perfect; formation of an ascocarp)
What are ascocarps?
Fruiting body containing tube-like ascus; Ascus contain the spores
What are ascospores?
sexual spores
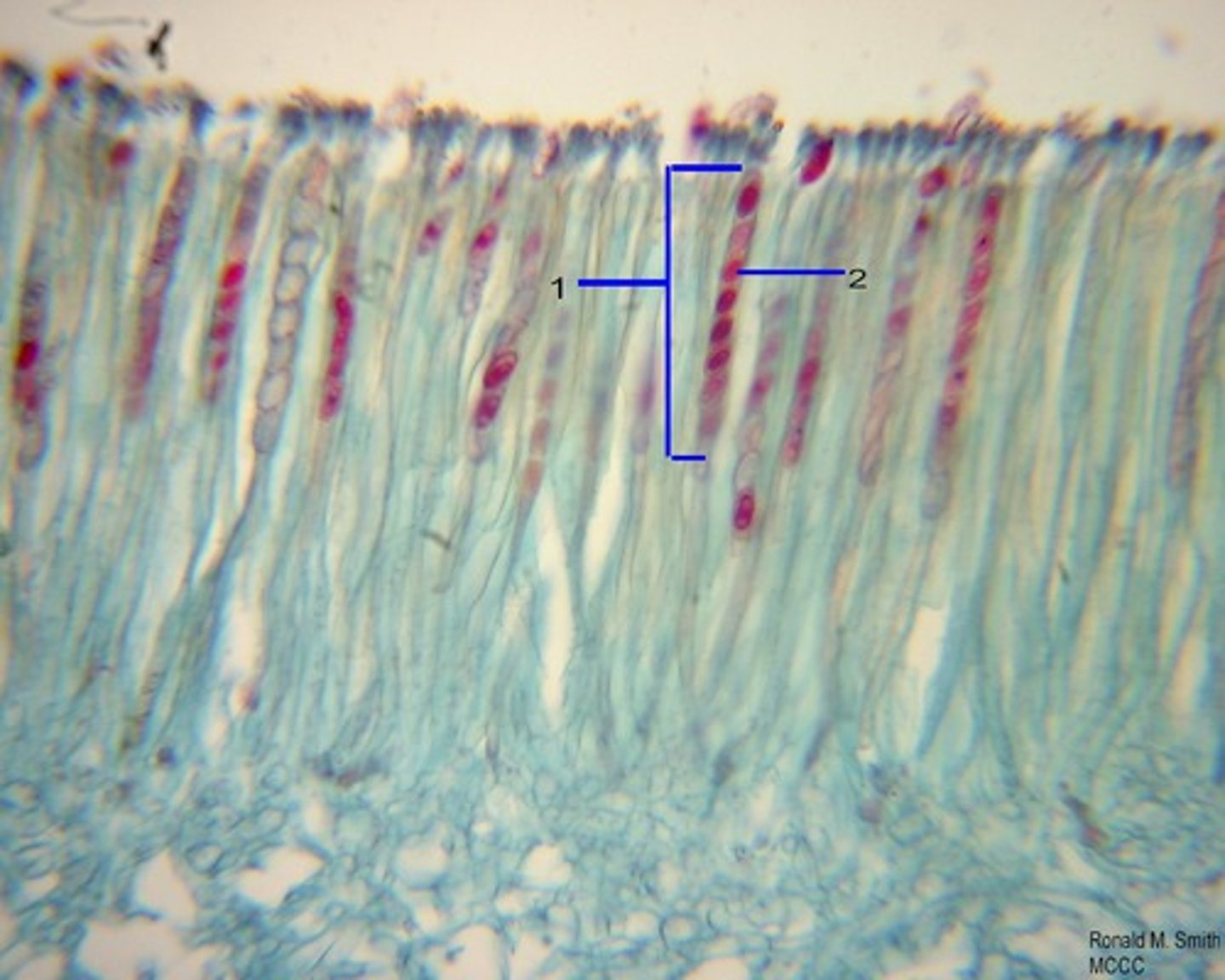
What are the three types of ascocarps?
Cleistothecium, Perithecium, Apothecium
What is Cleistothecium?
Completely surrounded by fungal tissue, no opening (spread through digestive tracks)
What is Perithecium?
"Closed" ascocarp with a narrow opening near the top
What is Apothecium?
"Open" form of an ascocarp
What are some genuses under the phylum Ascomyota?
peziza, sordaria, scizosaccharomycetes, penicillium, aspergillus
What are conidia?
asexual spores
What is a conidiophore?
the stalk that carries conidia
What are Lichens? (Ascomyota)
Fungal layer can secrete acids which help mineral uptake (some are toxic); Algal layer is usually internal, sheltered by fungal layer (provides carbon compounds to fungus); If combined with cyanobacteria, can fix atmospheric nitrogen, providing nitrogen to the fungus
What are the three types of lichens?
crustose, foliose, fruticose
What is a thallus? (Lichen)
a vegetative body of a fungus (fungal, lichen, then cyanobacteria in fungal layers)
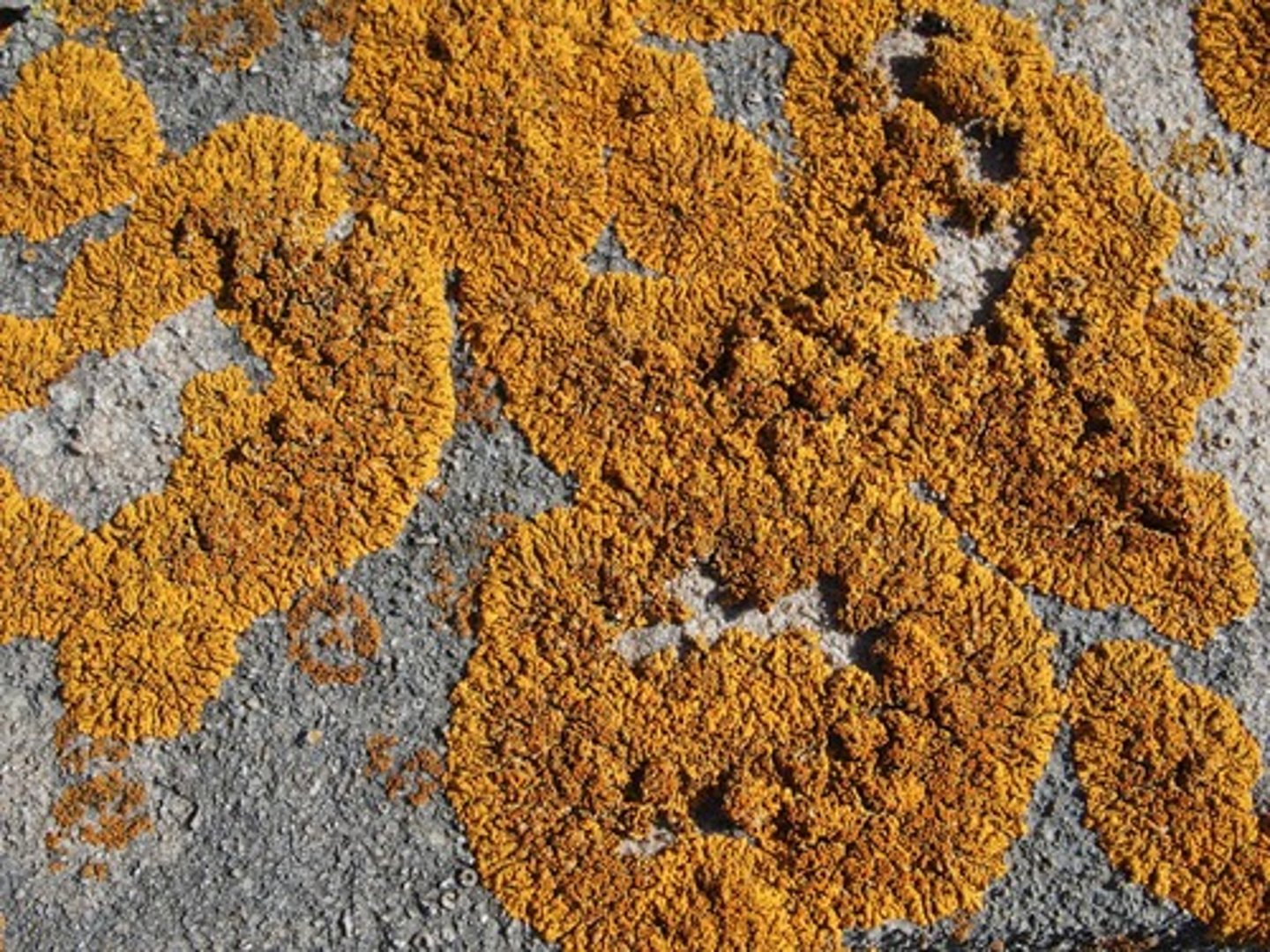
What is crustose lichen?
looks like paint, white/gray color.

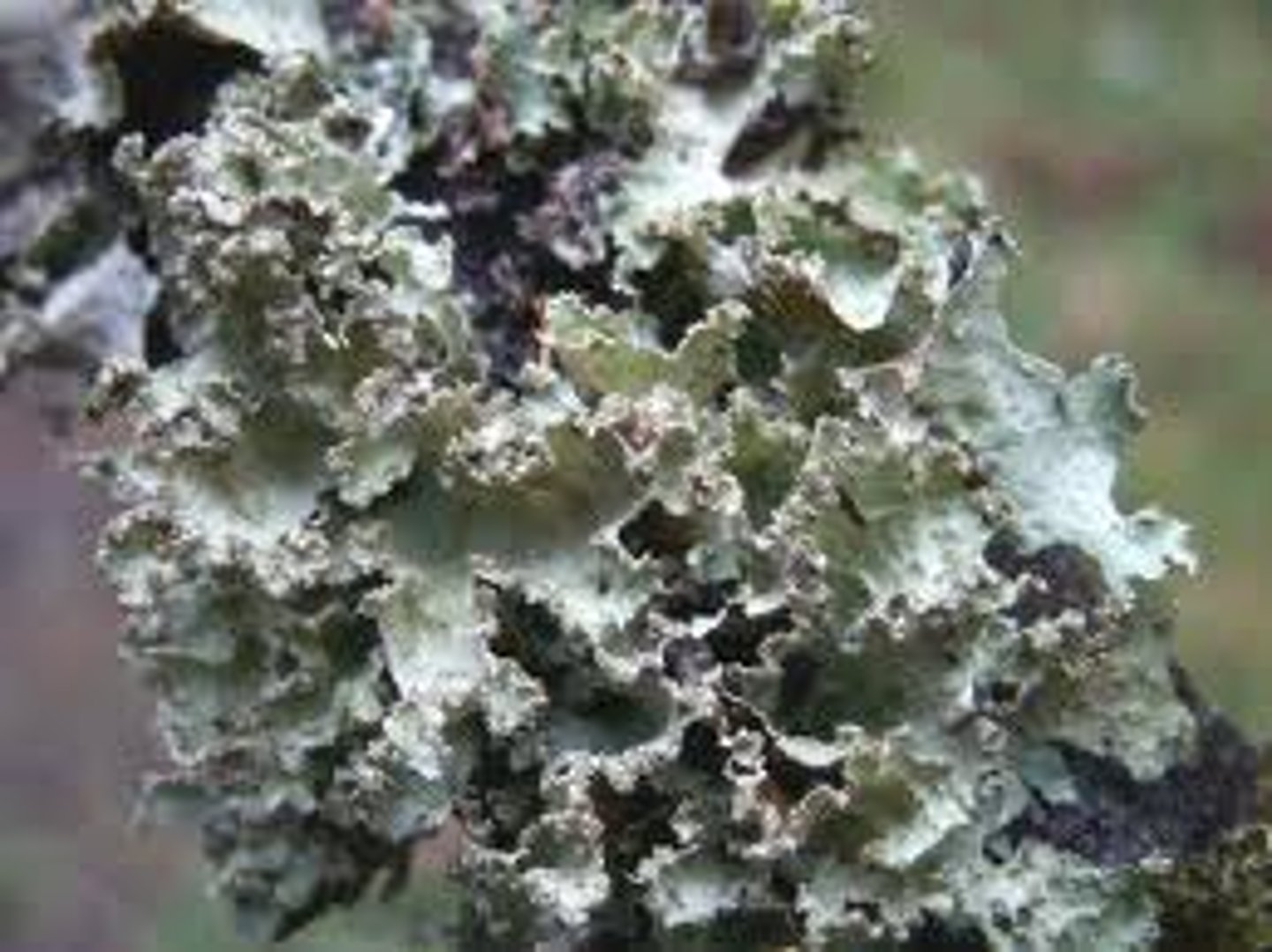
What is foliose lichen?
leaf-like

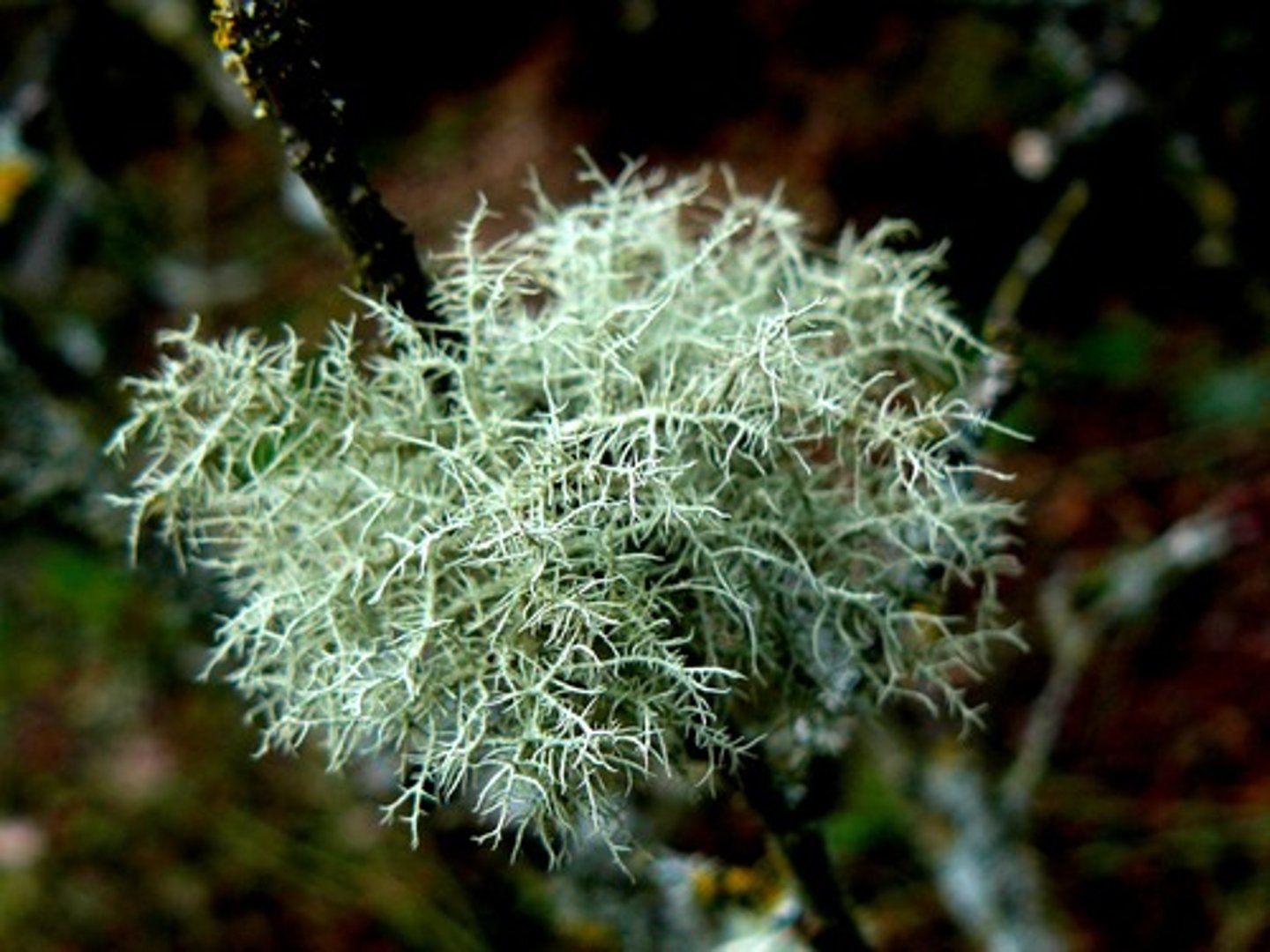
What is fruticose lichen?
shrub-like

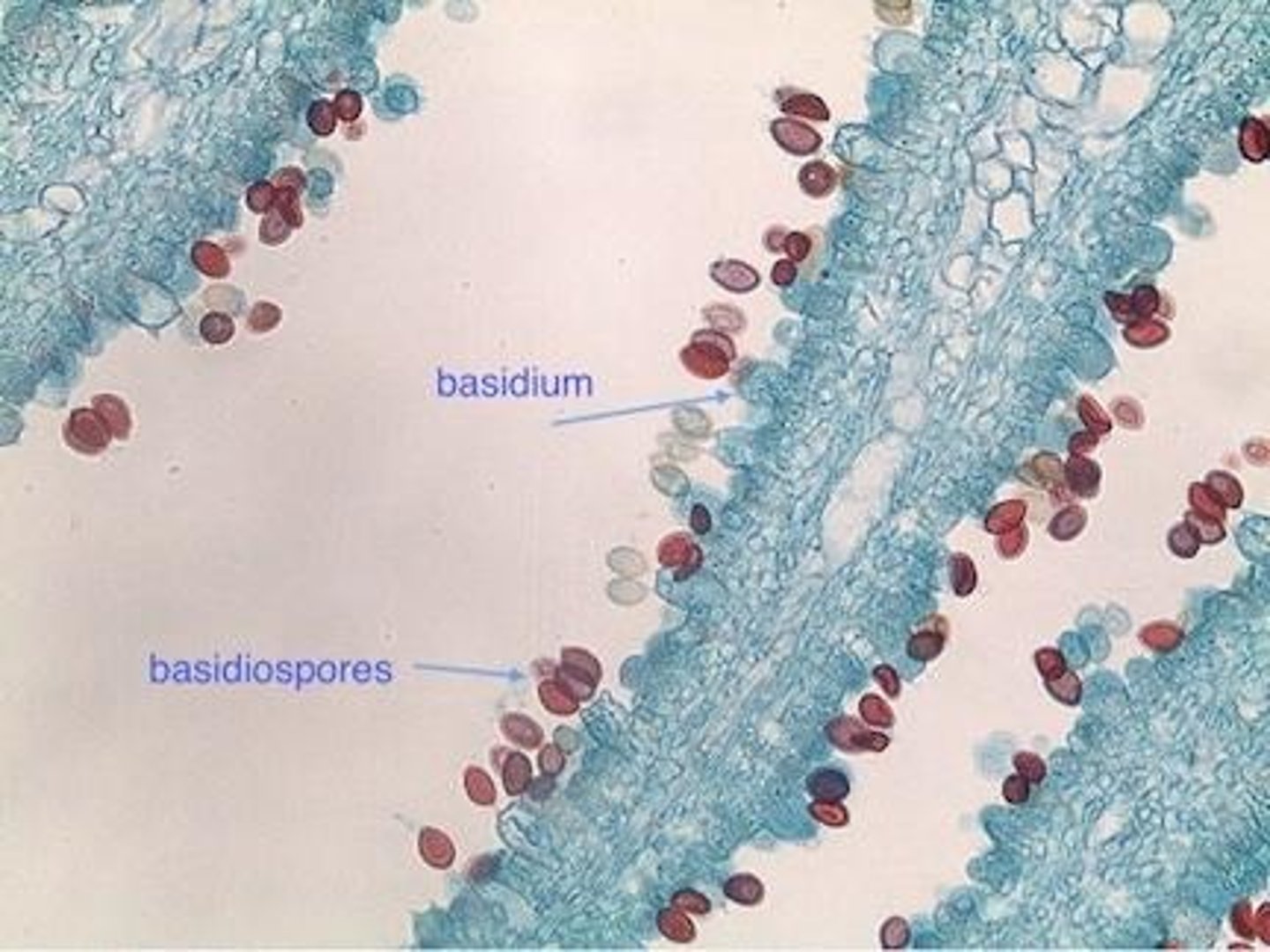
What are some characteristics of the phylum Basidiomycota?
club fungi (Shelf Fungi, Toadstools, Mushrooms, smuts, puff balls), reproductive differences
What are the two reproductive differences of basidiomcyota?
asexual (less common compared to other phyla), sexual (formation of basidiospores from the basidia)
What is a genus under basidiomycota?
coprinus
What are some characteristics of the phylum Deuteromycota?
imperfect fungi, no sexual stage found (nothing shown off, so we don't know what phase it is)