Intro Animal Evolution and Development
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
All Animals have what characteristics?
multicellular, lack cell walls, heterotrophs
External Fertilization vs Internal Fertilization
External fertilization occurs outside of the female body while internal fertilization occurs inside of the female body.
Hox Genes
control the body plan along the anterior-posterior axis of an embryo.
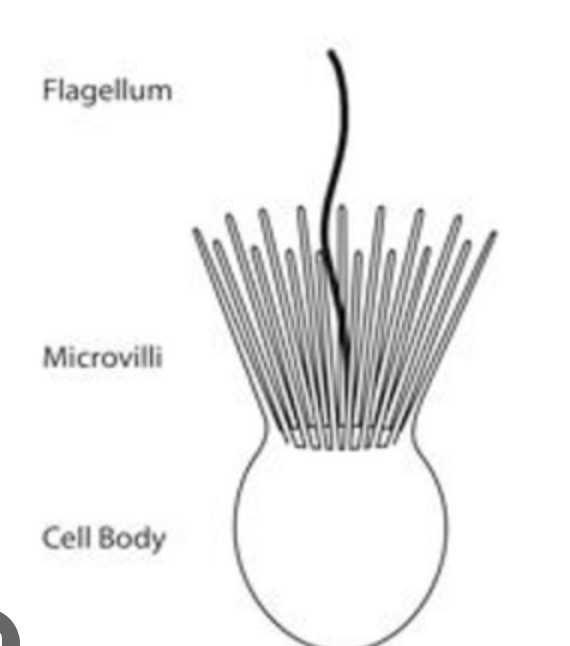
Properties of Choanoflagellates
Closest living ancestor to humans
Under eukaryotic supergroup Opisthokonta
Many are sessile, some can swim
A single flagellum and a collar of microvilli attached to the cell body.
The Protists (Kingdom Protista)
Eukaryotic, aerobic, unicellular microorganisms
Characteristics of the Protozoans
without a cell wall
heterotrophy
motillity
When did animal life begin on Earth?
600 mya
Cambrian Explosion
Many phyla appeared (533-525 mya)
Amniotic Egg
Adaptation that prevented egg from drying out. Allowed animals to be terrestrial for entire life. (300 mya)
How do we classify animals?
tissue types
morphological data (symmetry)
Embryological data (development processes)
Genetic Data (DNA, mRNA, Proteins)
Development
Describes the progressive changes in an individual from it’s beginning to maturity.
Stages of embryonic development
Gamete formation
fertilization
cleavage
gastrulation
organogenesis
growth
Gametogenesis
the process for which gametes are produced.
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which sperm cells are produced in the testes. Sperm are haploid.
Oogenesis
Oogenesis is the process by which a female's ovaries produce ova, or eggs, that are capable of developing into an embryo after fertilization. Oocytes are haploid.
Haploid
Single set of unpaired chromosomes.
Fertilization
contact and recognition between egg and sperm . Sperm and egg fuse diploid zygote.
Cleavage
Repeated divisions of zygote, converting a single large cell into many smaller cells called blastomeres. Zygote cells perform cleavage according to symmetry.
Morula
Mass of blastomeres
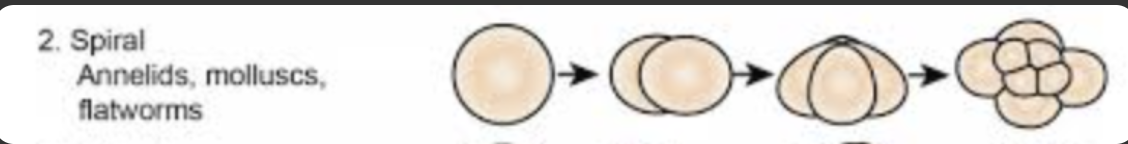
Spiral Cleavage
occurs in most protostomes
Cleavage planes are not parallel or perpendicular to the animal-vegetal axis of the egg, but instead in a spiral arrangement.
Mosaic Development
Examples of protostomes with spiral cleavage
Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
Annelids (earthworms)
Molluscs (snails, squid)
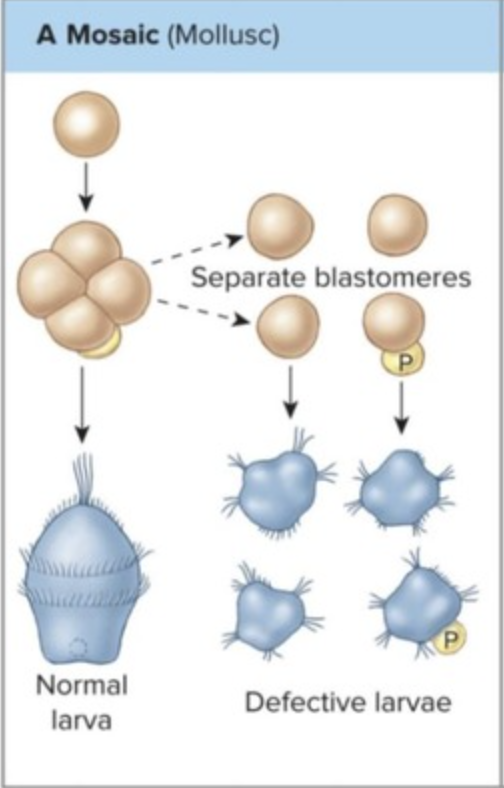
Mosaic Development
need all cells for growth
goes with spiral cleavage
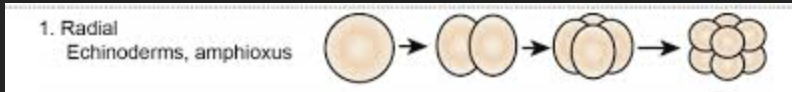
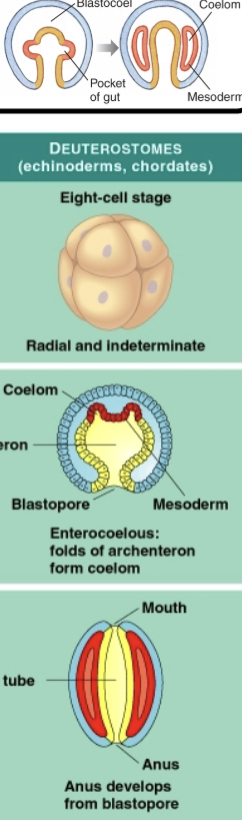
Radial Cleavage
The cleavage planes are either parallel or perpendicular to the vertical axis of the embryo.
Examples of Deuterostomes with Radial Cleavage
Echinoderms
Hemichordates (acorn worms)
Chordates
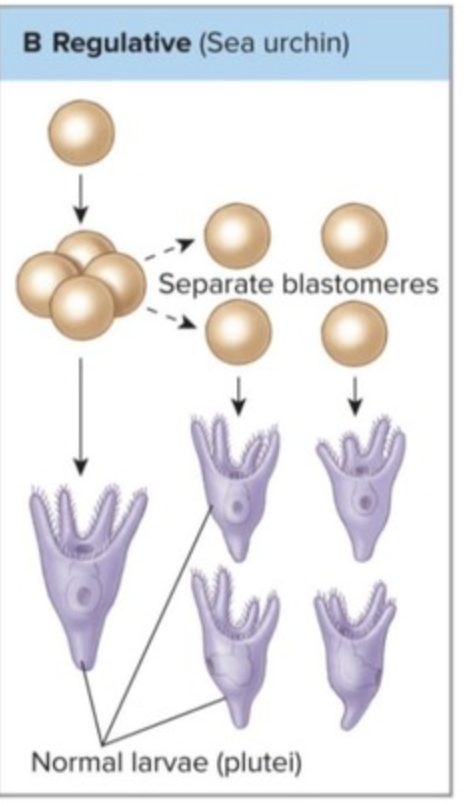
Regulative Development
can divide and form normal larva
goes with radial cleavage
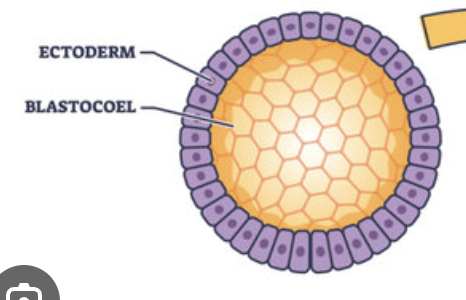
Blastula
A sphere of cells
a hollow ball of cells
Germ Layers
layers of cells
Gastrulation
an area of the blastula folds inward, or invaginates, creating in the process a structure called the gastrula.
converts the spherical blastula into a two-or three- layered embryo
Endoderm
Inner layer of cells in a blastula. Lines the primitive digestive tract.
Ectoderm
outer layer of the blastula. Covers surface of embryo and differentiates into the epidermis and nervous system.

Archenteron
internal cavity formed by invagination

Blastopore
Opening formed during gastrulation in an embryo.
Blastocoel
the internal cavity within a blastula
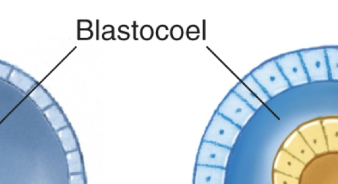
Coeloblastula
a type of blastula with a blastocoel cavity
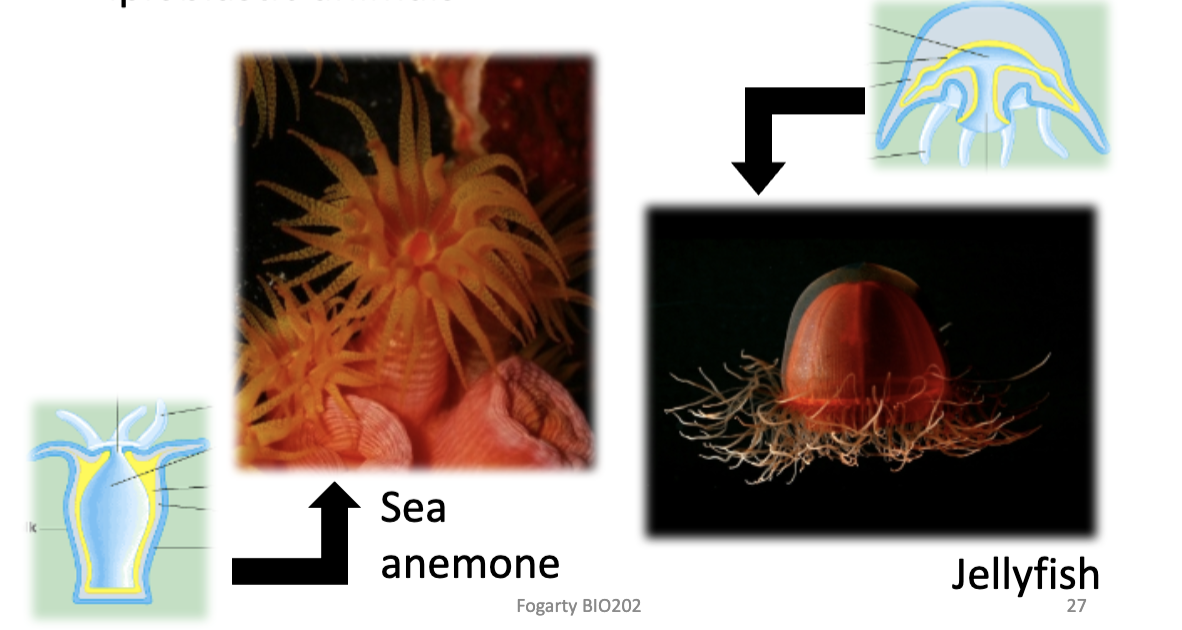
Diploblastic
Organisms with two germ layers: the ectoderm and endoderm.
Diploblastic animals have radial symmetry
Triploblastic
Animals with a 3rd germ layer, the mesoderm. The mesoderm is often derived from the endoderm.
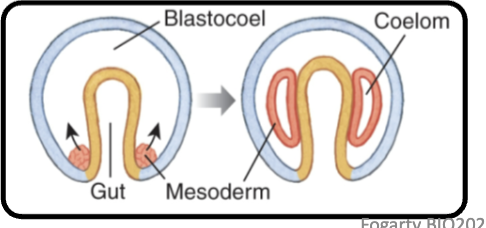
Protostomes (coelomates)
Cells arise from ventral area and proliferate into blastocoel
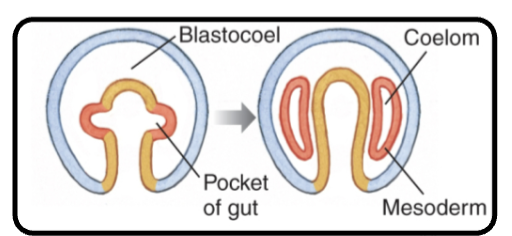
Deuterostomes
Central region of archenteron wall pushes outward
Coelom
a cavity surrounded by mesoderm formed by schizocoely or enterocoely
Schizocoely
Mesoderm surrounds gut and splits open to form coelom
found in schizocoelous coelomates in protostomes
spiral cleavage
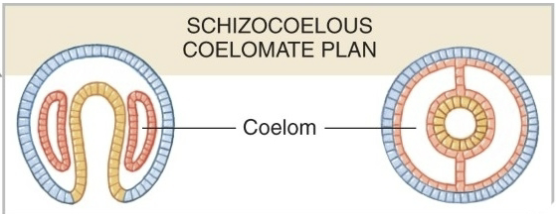
Protostomes
the blastopore becomes the mouth. Originate from spiral cleavage, mosaic (determinate) development.
Acoelomates
Pseudocoelomates
Schizocoelous coelomates

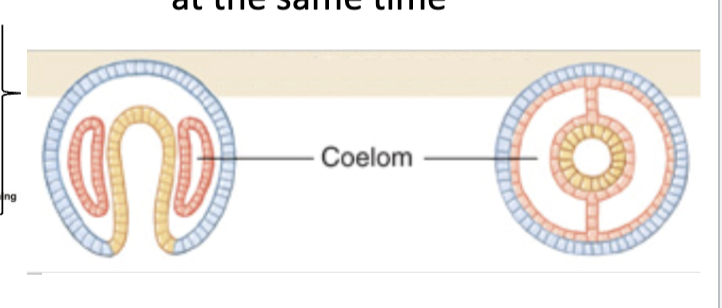
Enterocoely
mesoderm and coelom are made at the same time
in deuterostomes
radial cleavage
Deuterostomes
mouth is newly formed. Anus often is derived (but not always) from the blastopore. Originate from radial cleavage.
anus is formed from blastopore (or not!)
Diploblastic
animals do not have organs
Two tissues: epidermis and gastrodermis
gastrodermis: endoderm in the context of cnidarians
Organogenesis
the differentiation of the three embryogenic layers into tissues and organs.
Organogenesis: Ectoderm
Nervous system and outer epithelium (skin)
Organogenesis: Endoderm
Digestive tube (gut) and gill arches
Gill arches
In fish:
gills and supportive structures
In humans:
involved in the formation of jaws, inner ear, tonsils, parathyroid glands and thymus
Organogenesis: mesoderm
support, movement, circulatory system, urinary and reproductive organs.
Factors determined by growth
genes, nutrients, environment