U7 APES Atmospheric pollution
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
N/A
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Primary pollutant
A pollutant that is put directly into the atmosphere by human or natural activity
(Ex. combustion)
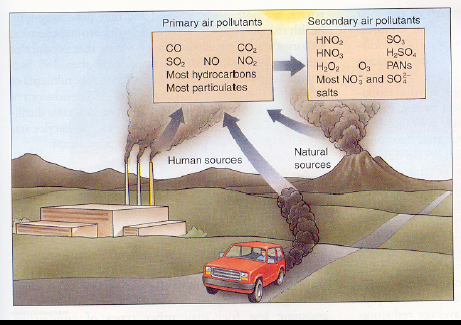
Secondary pollutant
A primary pollutant that has undergone transformation in the presence of sunlight, water, oxygen, or other compounds to form new pollutants
CO
carbon monoxide
- source: incomplete combustion of fossil fuels
- health impact: headaches, dizziness, unconsciousness, death - Desc: is a colorless, odorless gas
CO2
carbon dioxide
- source: volcanoes, decomposition, respiration, combustion of hydrocarbons
- health impact: increased death from rates due to heat waves, severe storms, loss of agricultural productivity
Desc: colorless, odorless gas that is essential for photosynthesis and is produced by respiration.
VOC’s
Volatile Organic Compounds
group of primary pollutants that comes from gas, solvents, and evaporating chemicals; component of photochemical smog
Clean Air act of 1970
The law aimed at combating air pollution, by charging the EPA with protecting and improving the quality of the nation's air
- CO2, O3, lead, N2, PM, SO2
Ozon
O₃ is a harmful air pollutant, created by chemical reactions between sunlight and pollutants like nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). It can cause respiratory issues and harm plants.
Tropospheric Ozone
Ground-level ozone is considered bad because it is closer to the ground level, making it more likely for someone to breathe it in. It is also more dangerous because it is made up of particulate matter.
Asbestos
a heat-resistant fibrous silicate mineral that is used in fire-resistant and insulating materials
- PM pollution
- naturally composed mineral
- cancers/diseases
Radon-222
A gas that arises from the earth where radioactive materials are present
- produced with decay of uranium
- moves into home though cracks/holes
- dissolves into ground water (wells)
- second leading cause of lung cancer
Noise Pollution
Any unwanted, disturbing, or harmful sound that impairs or interferes with hearing, causes stress, hampers concentration and work efficiency, or causes accidents
- higher in urban areas
- masks sounds for animal communication/hunting
- damages ecolocation
- changes migratory routes
SOx
Sulphur Oxides
a primary pollutant that comes from the combustion of Coal
NOx
Nitrogen Oxides
A primary pollutant that comes from Vehicles (Gasoline)
Photochemical Smog
air pollution that forms from the interaction between chemicals in the air and sunlight
NOx, VOCs, sunlight are photochemical smog reactants
Stratospheric Ozone
good ozone, produces oxygen molecules to interact with UV radiation and prevent 95% of it from reaching the surface
Particulate Matter (PM)
a small discrete mass of solid that remains individually dispersed in gas or liquid emissions (usually considered to be an atmospheric pollutant)
Thermal Inversion
This is when the usual temperature gradient is reversed so warm air is trapped closer to the surface where majority of pollutant are.
- creates poor air quality
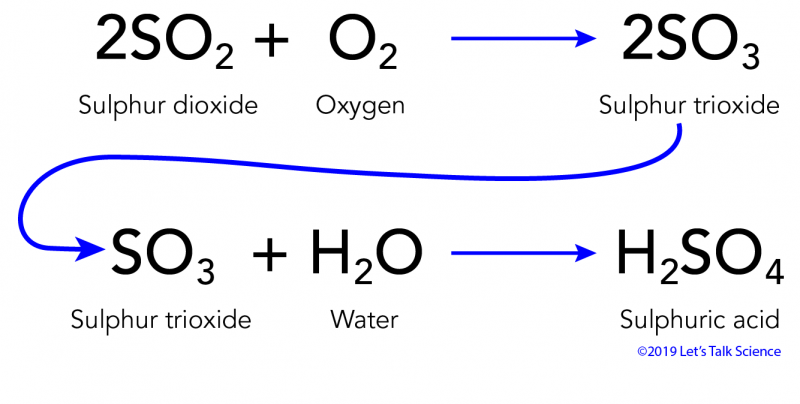
Acid Rain
rain containing nitric and sulfuric acids
- can occur naturally or by secondary air pollutants
Motor vehicles & Coal burning power Plants
anthropogenic source of SOx
Methods for Air pollution reduction
scrubbers, electrostatic precipitator, catalytic converter, vapor recovery system
Wet & Dry scrubbers
A mechanism used to reduce industrial exhaust steams (Removes Particulates and Sulfur Oxides)
Vapor Recovery Nozzle
Device on gasoline pump
Addresses VOCs
Catalytic Converter
Converts pollutants into less
harmful molecules
Converts CO, NOX, Hydrocarbons
to CO2, N2, O2, & H20
Electrostatic Precipitator
air filter with charged plates
Attract Particulate matter
Indoor air pollutants
Substances that contribute to poor indoor air quality and may lead to health problems or other undesirable effects
MOLD
common in poor ventilated areas, damp/humid areas in homes
- allergic reactions/asthma/respiratory issues
- use ventilation to control
Lead
found in old paint, chipped/deteriorating paint can create dust particles
- remodeling, dry scraping
CFC’s (Chlorofluorocarbons)
a group of man-made chemical compounds made up of carbon, fluorine, and chlorine. They were widely used in the 20th century, especially in:
Refrigerants
Aerosol propellants
The Montreal Protocol (1987)
An international agreement to phase out CFCs and other ozone-depleting substances. It's considered one of the most successful environmental treaties.
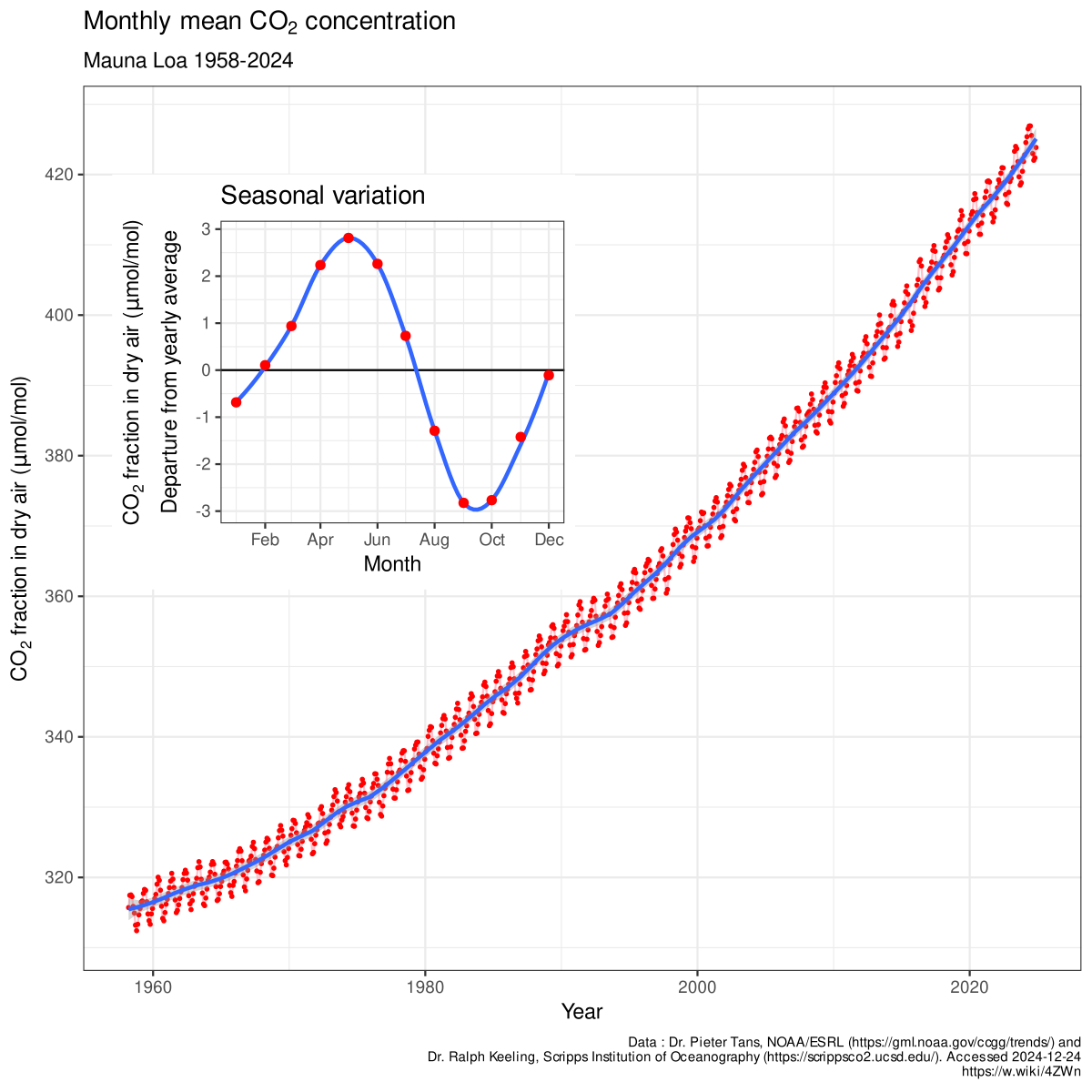
Keeling curve
a graph that shows the ongoing change
in the concentration of carbon dioxide in
Earth’s atmosphere.
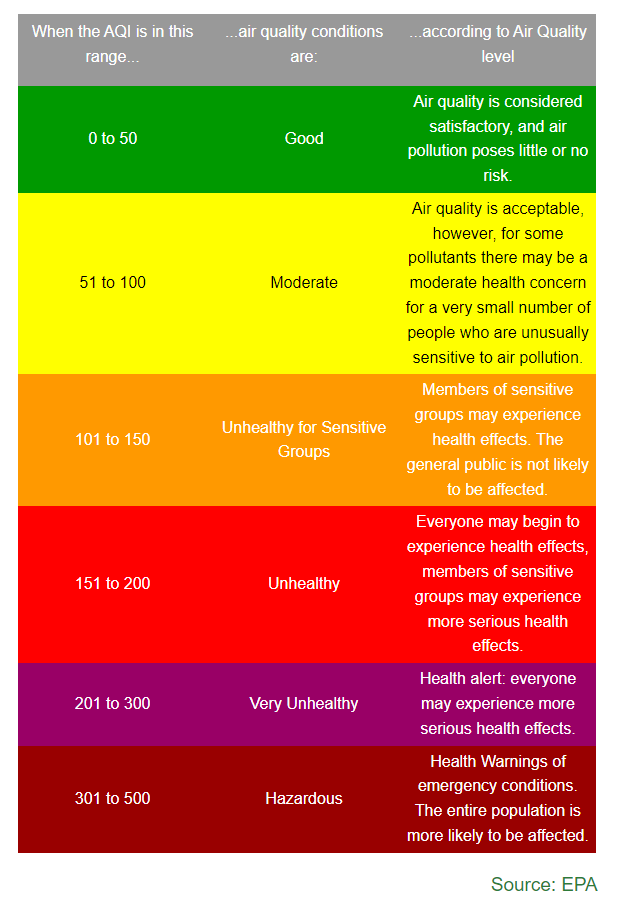
Air quality Index (AQI)
A unitless number that represents the standardized scale of air pollution levels
The AQI is based on the levels of major pollutants:
particulate matter (PM2.5 or pm10)
ozone (O3)
carbon monoxide (CO)
sulfur dioxide (SO2)
nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are chemical compounds made only of hydrogen and carbon atoms.
They’re the main part of fuels like:
Petrol (gasoline)
Diesel
Natural gas
Propane
Acid rain formula