Fundamentals of Data Representation
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What are Natural numbers?
All positive whole integers including 0.
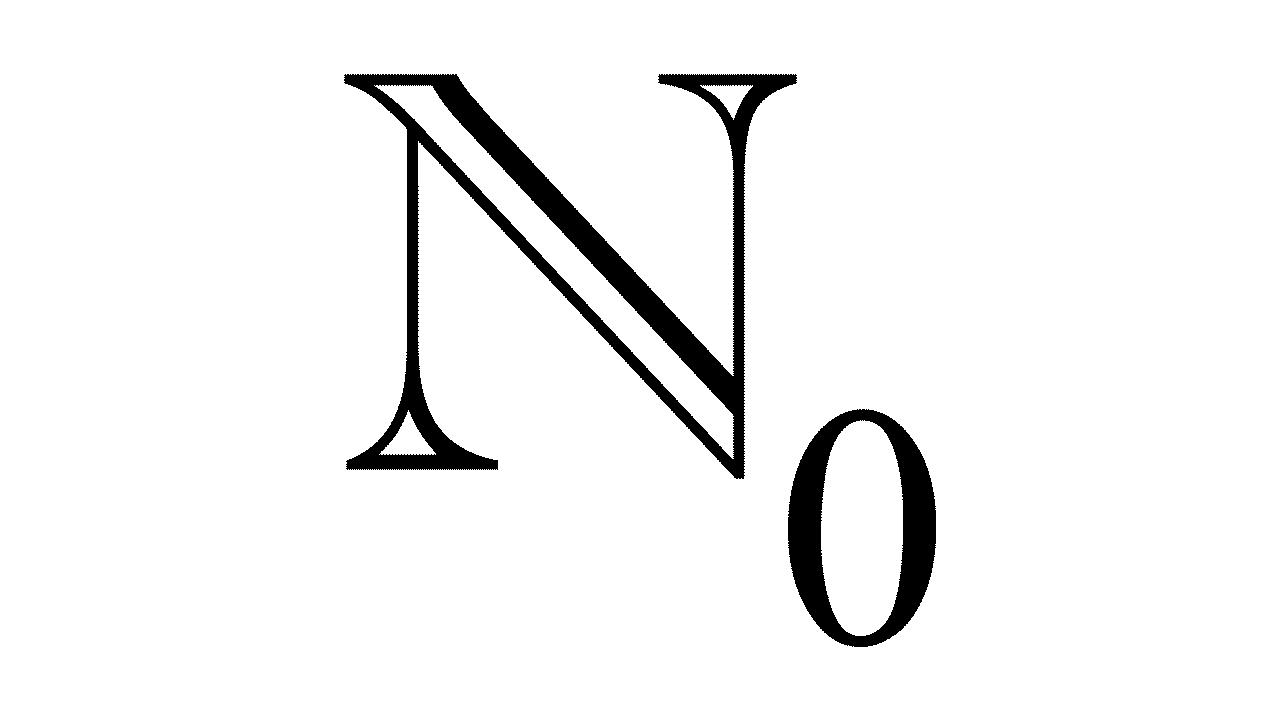
What are Integer numbers?
All whole numbers. Positive, 0, Negative

What are Rational numbers?
Or “Quotients“
Can but don’t need to be a fraction.
if the number can be written in a fraction format.
Its rational.

What are Irrational numbers?
Irrational numbers can’t be written in the fraction format.
What are Real numbers?
All possible numbers of this dimension.

What are Ordinal numbers?
Integers used in order to define a numerical position.
1st, 2nd, 3rd
What are the 3 Number bases in Computer Science?
Denary or Decimal being 0 - 10
Binary being 2
Hexadecimal being 16
What are the rounded quantities for data? ASC
Petabyte — 1000
Terabyte — 1000
Megabyte — 1000
Kilobyte — 1000
Byte — 8
Nibble — 4
Bit — 1
What are the accurate quantities for data? ASC
PeBiByte — 1024
TeBiByte — 1024
MeBiByte — 1024
KiBiByte — 1024
Byte — 8
Nibble — 4
Bit — 1
What is the difference between Analogue & Digital Data?
Analogue is continuous with no limits while digital is only able to take particular captures and do particular things.
What does ADC stand for?
Analogue to Digital Converter.
What does DAC stand for?
Digital to Analogue Converter.
How do you calculate the storage required for a bitmap image?
Resolution (x * y) * Bit Depth
What typical data is stored in Metadata for a bitmap image?
Width
Height
Date Created
Colour Depth
How do vector images work?
They make use of geometrics and shapes as well as special commands in order to specially generate images.
The name for the number of samples taken per second is?
The Sampling Rate and its expressed in Hertz.
Who found that digital audio files must be at least double the frequency of sound being recorded?
Nyquist — with this discovery being named after them:
The Nyquist Theorem.
What does MIDI stand for?
Musical Instrument Digital Interface.
What are the two types of data compression?
Lossy
Lossless
What is the difference between Lossy and Lossless compression?
One loses data after compressing (Lossy) while the other one doesn’t.
What is some information that might be stored within a MIDI event message?
Duration
Type of Instrument
Volume
Sustained or not.
What does RLE stand for?
Run Length Encoding (RLE)
How does RLE compress a bitmap images file size?
RLE (Run-Length Encoding) compresses bitmap images by encoding consecutive pixels of the same color into a single value and count pair, reducing redundancy and file size.
How does using a Dictionary-Based method compress a bitmap image file size?
By instead of using a full 8 bits per every single letter through this method it will look for commonly used words and letters assigning them their own value.
Considering encryption what is the text called once its been processed?
Ciphertext
What are the Hexadecimal values?
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | A B C D E F
A = 10
B = 11
C = 12
D = 13
E = 14
F = 15
What are the Binary values?
0|1
What are the Denary values?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0
What is the difference between ASCII and Unicode?
The overall amount of characters that can be represented with:
ASCII making use of 7bits to represent their characters.
Unicode on the other hand looks at using 8 to 48 Bits allowing for a MUCH wider and larger varietal range of characters.
What does ASCII stand for?
American Standard Code Information Interchange
What is a parity bit?
A singular bit sent along with a transmission in order to check whether its all there or not.
What are the two different types of parity?
Even
Odd
How do you distinguish between Even and Odd parity?
It refers to the total count of 1’s within a binary string. if the total count of 1’s is even. Its even and if its odd. its odd.
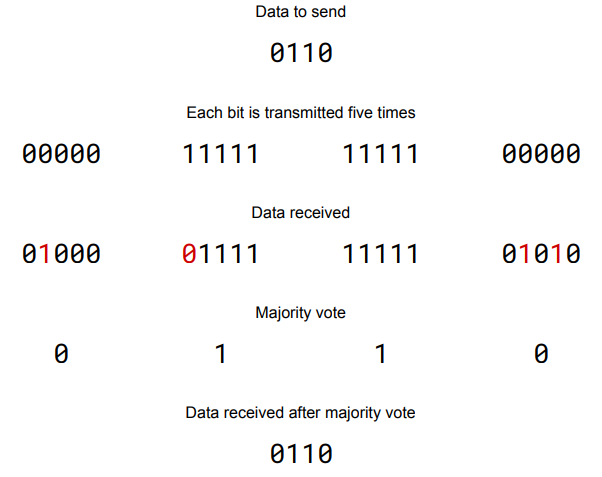
How does majority voting work?
Majority Voting like in Among Us will take the thing with the majority of votes and respond accordingly being exactly like how it works here.
Firstly it will separate every bit and then multiply it 5 times with more simply meaning more secure.
Next it will send these seperated large packages
Then it will recieve them and these brand new packages being larger and if they do happen to be possibly manipulated they won’t be able to be changed that much meaning that most of the original will still be there and to triple check this the majority part finally plays its part.
It will look at the MAJORITY seeing if there are more 1’s or 0’s and which ever has more it will take in as the final answer.
Simpler explanation featured in the image.
What is another added benefit of Majority Voting?
Because of how it functions even if the data is manipulated instead of having to resend it you can simply keep it as the actual data is still there.
How does a checksum work?
Similar to parity bits it actually adds to the value but with Checksums it takes it to another level with firstly it making use of numbers featured within the data itself in order to make it more secure.
(The calculation used in order to generate the checksum is not agreed upon a single algorithm instead being bespoke to each use.)
How does a check digit work?
Similar to that of a checksum as it only considers a single digit.
This makes it harder to crack and variety of possible errors.
What are 4 ways of safely transmitting data.
Parity Bit
Majority Vote
Checksum
Check Digit
What does DAC stand for?
Digital to Analogue Converter
What does ADC stand for?
Analogue to Digital Converter
What are the 2 different ways a Computer can view an image?
Bitmap
Vector
How does a bitmap image work?
A bitmap image is simply made up of pixels with a greater resolution of pixels meaning a higher quality image.
What is a resolution?
Resolution refers to the X and Y of a screen or image which in the end states the total size or rather the amount of pixels within.
What is a caeser cipher?
A Caesar Cipher is a type of encryption.
They are the worst level of cipher
How does Caesar Ciphers work?
There are 2 main ways being:
Shift
Substitution
overall they work by replacing one letter with another being mainly how they work however the process of how its done is what changes.
A shift considers two sets of data with one being where one of the sets are SHIFTED so its not a one to one relation with these brand new values (even though it still is if even one is found) while a substitution will completely remove the order of a shift and entirely assign each to their own from this second set.

What is a Vernam cipher?
A one-time pad cipher. Also being theoretically uncrackable.
What is a one-time pad cipher?
It means that for the cipher to properly work each key used along with the cipher should only ever be used once.
How does a Vernam cipher work?
Aligning plaintext and corresponding key
conversion of each part of plaintext to binary with use of ASCII or Unicode.
Application of XOR to both sets
then turning the represented binary back into the human legible ASCII, Unicode equivalent

What is meant by Computational Security?
It means that although a cipher might take a long time to crack it doesn’t say that it is not crackable unlike the vernam cipher. Meaning that the only requirement would be greater computing meaning that’s the only issue in the way of cracking such a cipher therefore.
Computationally Secure.
What is the difference between Signed and Unsigned binary?
Unsigned means that it cannot try to display a negative number.
Signed means that it HAS to display the type of number (positive or negative) at all times
Examples:
Unsigned — 5 + 4
Signed — +5 + + 4
How do you find maximum permutations with duplicates?
a^b
a — Total number of elements
b — Number of slots of which need to be filled
0 - 9 = 10 = a
4 digit lock = 4 = b
What is an absolute error?
The actual amount a value is inaccurate by which can be used to find the actual value.
What is a relative error?
A percentage proportionally describing the difference compared to the absolute error simply just providing the numbers.

How to calculate relative erorr?
Relative Error = (Measured Value - True Value) / (True Value) × 100
Multiplying by 100 isn’t a requirement but overall its more useful this way.
How to calculate absolute error?
Absolute Error = (Measured Value) - (True Value)
What is the difference between Fixed and Floating point?
Use of floating point binary allows for a greater and large range of bits compared to fixed point.
Considering floating point what are the 2 possible configurations?
Large Exponent, Small Mantissa — Large range but less precision.
Small Exponent, Large Mantissa — lighter range but more precision.
What is underflow?
Refers to that if the number trying to be represented in binary is just too small to be shown then this results in an underflow.
What is overflow?
Overflow triggers whenever the binary version of a number trying to be represented is too large. Overflow especially plays its part when it comes to signed binary.
What is the minimum number possible considering unsigned binary?
0
What is the maximum number possible considering unsigned binary?
2^n-1 (255 if dedicating 8 bits)
What makes 2’s Complement different?
The First number is always signed and is considered to be negative.
How do you subtract in 2’s complement?
Convert the number being subtracted to negative
then simply add both numbers together
What is the mantissa?
The actual binary number
What is the exponent?
Simply just the location of the decimal in the binary number
What if the exponent is positive?
It means that the decimal point should move right
What if the exponent is negative?
it means that the decimal point should move left