Anatomy & Physiology Midterm 2025
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
Pathway that goes from stimulus to brain
afferent
pathway that goes from brain to muscle
efferent
mechanism that returns the level of a chemical or condition back to set point level
negative feedback
examples of negative feedback
sweating, goosebumps
process in which changes cause additional similar changes that produce unstable conditions
positive feedback
examples of positive feedback
blood clotting, giving birth
deals with the structure of the body parts of the body you can see
ex: brain, bone, heart, eye
anatomy
studies the function of body parts
physiology
Levels of organization of the body (small to big)
atom, molecule, macromolecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
above
superior
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
below
inferior
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
front
anterior
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
back
posterior
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
towards midpoint
medial
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
far from midpoint
lateral
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
close to midpoint (limbs)
proximal
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
far from midpoint (limbs)
distal
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
outside of body
superficial
ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY:
under the skin
deep
plane of the body that cuts it left and right
sagittal
plane of the body that cuts it top and bottom
transverse
plane of body that cuts it front and back
frontal
head neck and trunk
axial
arms and legs
appendicular
4 types of tissue
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
4 main functions of epithelial tissues
protection, absorption, filtration, secretion
one layered tissue
simple
more than one layer tissue
stratified

what kind of tissue is this?
simple squamous

What kind of tissue is this?
simple cuboidal

What type of tissue is this?
simple columnar
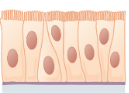
What type of tissue is this?
pseudostratified columnar
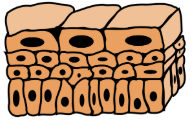
What type of tissue is this?
transitional epithelia
the most abundant & widely distributed tissue type in the body
connective tissue
Functions of connective tissue
protection, support, binding together body parts
Types of connective tissue
bone, cartilage, dense connective, loose connective, blood
3 types of cartilage
hyaline, fibro, elastic
What is the most abundant type of cartilage in the body?
hyaline
What type of connective tissue is avascular?
cartilage
What are the type of fibers in the ECM in conenctive tissue?
collagen, elastic, reticular
attach muscles to bone
tendons
connect bones to bones
ligaments
Types of dense connective tissue
tendons and ligaments
Types of loose connective tissue
areolar, adipose, reticular
What is the most widely distributed conenctive tissue in the whole body?
areolar

What type of tissue is this?
muscle

What type of tissue is this?
areolar

What type of tissue is this?
adipose
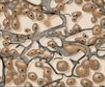
What type of tissue is this?
reticular
Function of muscle tissue
contracts and shortens to produce movement
3 types of muscle tissue
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
What type of muscle tissues are voluntarily controlled?
skeletal
What type of muscle tissues are involuntarily controlled?
cardiac, smooth
What types of muscle tissues are striated?
skeletal & cardiac
What type of muscle tissues are not striated?
smooth
Function of nervous tissue
irritability and conductivity
Two types of nervous tissue
neurons and glia
replacement of destroyed tissue by the same kind of cells
regeneration
replacement of destroyed tissue with scar tissue
fibrosis
4 steps of tissue repair
injury occurs
capillaries allow clotting proteins to go to wound
clot forms
granulation tissue forms under scab
surface epithelium regenerates below scab
What type of tissue the easiest to heal?
epithelial
What type of tissues are replaced by scar tissue?
connective and nervous
ductless glands that produce hormones
endocrine
have ducts and empty secretions through the ducts onto the epithelial surface
(eg sweat & oil glands)
exocrine
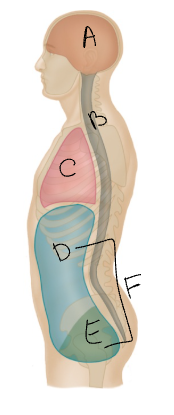
What body cavity is A?
cranial
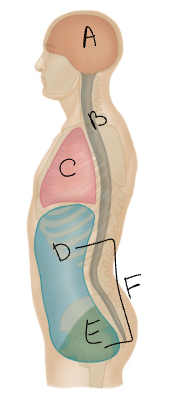
What body cavity is B?
vertebral
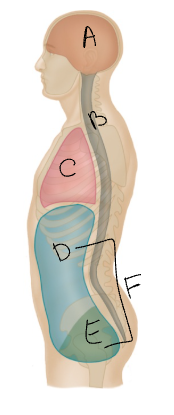
What body cavity is C?
thoracic
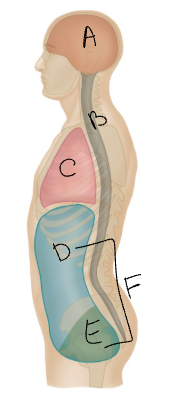
What body cavity is D?
abdominal
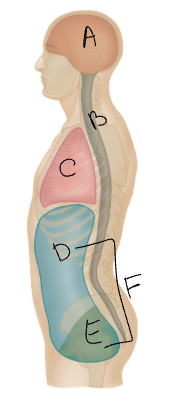
What body cavity is E?
pelvic
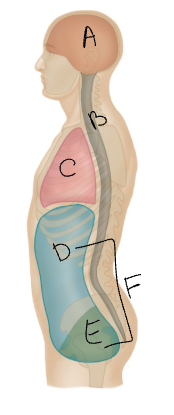
What body cavity is F?
abdominopelvic
Function of the Integumentary system
protection for deeper tissues
temperature regulation
aids in excretion of acids
synthesizes Vitamin D
What are the 3 layers of skiin
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
5 layers of the epidermis in order
corneum
lucidum
granulosum
spinosum
basale
Which layer of the epidermis can you only find on your palms of your hands and feet?
lucidum
Two regions of the dermis
papillary and reticular
What is the hypodermis made of?
adipose tissue
pigment in the skin that provides skin’s color
melanin
protein that fills your skin making it waterproof
keratin
are nails living or nonliving
nonliving
oil glands
sebaceous
sebaceous glands produce oil through what
hair follicles
Two kinds of sweat glands
eccrine and aprocrine
What is the most numerous sweat gland and is located all over the body
eccrine
What type of sweat gland has ducts that empty into hair follicles
apocrine
What are the three types of skin cancer?
basal cell carcinoma
squamous cell carcinoma
malignant melanoma
Squamous cell carcinoma affects what layer of the epidermis
spinosum
least malignant and most common skin cancer
basal cell carcinoma
Most serious form of skin cancer
malignant melanoma
ABCDE rule- what does each letter stand for
assymmetry
border
color
diameter
evolving
First degree burns damage what layer of skin
epidermis
2nd degree burns damage what layers of skin
epidermis and upper dermis
3rd degree burns damage what layers of skin
all except hypodermis
Is regeneration of skin possible with 3rd degree burns?
no
blue appearance of the skin or nail beds common in heart failure and severe breathing disorders)
cyanosis
the white crescent area located over the nail matrix is called the
lunula
red skin, can indicate embarrassment, fever, hypertension, inflammation, or allergy
erythema
yellow discoloration caused by bile in the blood as a result of liver or gallbladder disease
jaundice
pale skin, can indicate fear or anger as well as anemia, low blood pressure, or impaired blood flow
pallor
excessive sweating without activity
hyperhydrosis
itchy red peeling of skin between toes from a fungal infection
athletes foot