Exchange Rates, Balance of Payments, and Foreign Investment
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards based on lecture notes about exchange rates, balance of payments, foreign investment and related concepts in the Australian economy.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Exchange Rate
The price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency.
Appreciation
A rise in the exchange rate.
Depreciation
A fall in the exchange rate.
Foreign Exchange Market
The market in which the currencies of different countries are bought and sold.
Trade Weighted Index
A basket of currencies weighted according to their importance in trade flows with Australia.
Commodity Prices
Prices for key exports like iron ore and coal that can affect the demand for AUD.
Relative Inflation Rate
Inflation rate compared to other countries, influencing the competitiveness of Australian goods.
Clean Float
When currency is allowed to float free from interference of the central bank.
Dirty Float
When the central bank intervenes to prevent the exchange rate from falling too low.
Managed Exchange Rate
Where there is official intervention in the foreign exchange market by the reserve bank.
Equilibrium Exchange Rate
The point where the quantity demanded of AUD equals the quantity supplied.
Interest Rate Differential
The difference between the Australian interest rate and foreign interest rates.
Foreign Investment Income
Income earned by Australians from investments in foreign countries, affecting the demand for AUD.
Foreign Investment into Australia (FIA)
Investment made by foreign entities in Australian assets, increasing the demand for AUD.
Australian Investment Abroad (AIA)
Australian investors investing in foreign opportunities, increasing the supply of AUD.
Trade Balance
The difference between a country's exports and imports.
Net Exports
The difference between a country's total value of exports and total value of imports.
Foreign Investment
Flows of financial capital into and out of the Australian economy.
Foreign Liabilities
Something that you owe from Inflow of money into Australia.
Foreign Assets
Something that you own or represent outflows of money out of australia.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Investment with a minimum of 10% equity, giving the investor influence over the firm's operations.
Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI)
Investment with less than 10% ownership, primarily for financial return and diversification.
Net International Investment Position (IIP)
Calculated by subtracting Australia’s foreign assets from Australia’s foreign liabilities.
Foreign Debt
The amount of money that Australian residents owe to the rest of the world.
Foreign Equity
Represents the extent to which foreign residents own Australian assets.
Net Foreign Liabilities
Net foreign debt (borrowing) and net foreign equity (foreign ownership).
Financial Flows
Associated with the buying and selling of financial assets (outflows and inv
Current Account
Trade in goods and services, income flows, and current transfers.
Capital and Financial Account
Investment flows, loans, and financial asset transactions.
Commodities
Raw materials or primary agricultural products that can be bought and sold.
Inflation
A general increase in prices and fall in the purchasing value of money.
Trade deficit
The amount by which the cost of a country's imports exceeds the value of its exports.
Capital outflow
The movement of assets out of a country.
Capital inflow
The movement of assets into a country.
Terms of trade
The ratio of an index of a country's export prices to an index of its import prices.
J-Curve Effect
The trade balance may worsen, as higher import values outweigh export gains.
Financial Account Surplus
A net inflow of foreign investment.
Financial Account Deficit
A net outflow of foreign investment.
I-S gap
Investment - Saving
Budget Deficit
Amount by which government spending exceeds taxation revenue.
Public Debt
Debt owned by the Government
Private Debt
Debt owned by private citizens.
Multiplier Effect
An increase in spending produces an increase in national income and consumption greater than the initial amount spent.
Real Exchange rate
Nominal exchange rate adjusted for relative price between countries.
Australian assets
Property, plant and equipment and shares in companies
Investment Needs
Level of financial capital needed to expand industry and productivity.
Costs of Foreign Investment
foreign investment into areas of critical infrastructure may create a national security risk e.g. 99 year lease of Darwin port to a Chinese Company
inward foreign investment is in the form of borrowing which adds to the stock of Australia’s foreign debt which could impose a burden on the economy - borrowing is irrelevant as long as it leads to a higher national income
interest payments on foreign debt have become the largest debit item in the income category of the current account
foreign investment in Aus real estate market can ‘crowd out’ domestic residents by increasing property prices - foreign investors cannot legally by existing residential property in Australia - foreign buyers only make up 1% of Aus real estate purchases
Australia’s credit rating can be affected if the level of borrowing increases - future borrowing could be subject to higher interest rates - the higher rates would reduce the amount of foreign borrowing which is a normal market reaction
a depreciation in the Australian dollar will increase the value of Australia’s foreign liabilities (incorrect) - denominated in Australian dollars so a change in exchange rate has a minimal effect on the outstanding debt
IIP Formula
IIP = FIA - AIA
Factors that affect demand for AUD
relative price levels
commodity prices
expectations and speculation
relative interest rates
World real GDP
Factors that affect supply of AUD
relative price levels
relative interest rates
aus preferences for foreign goods and services
aus real gdp
effect on CAD
depreciation = boosts CAB
appreciation = worsens CAB
effect on CAF
depreciation = deter FIA but can make aus assets cheaper and more attractive
appreciation = improves CAF - can attract capital inflows due to expectations of currency strength and higher returns in AUD terms
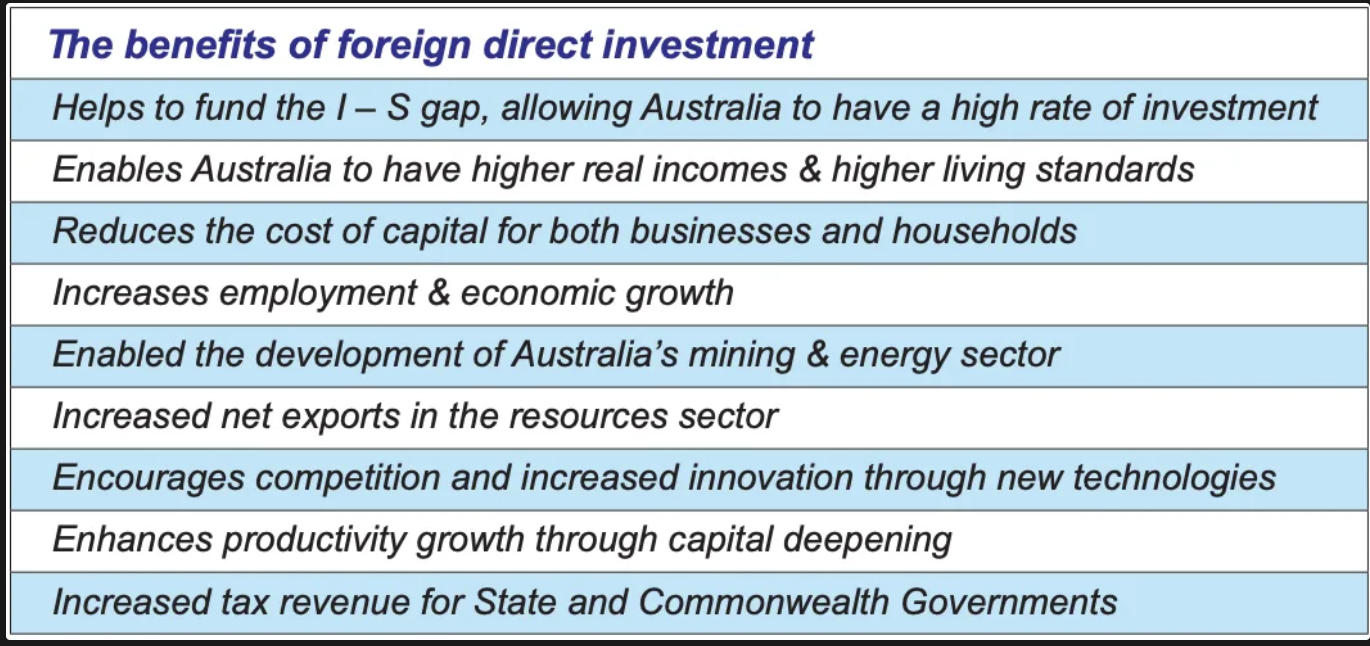
benefits of foreign investment