Discovering Biodiversity- topic test 2: evolution
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is the definition of evolution?
the process that changes the proportion of heritable traits in a population from one generation to the next
What are the evolutionary forces/ mechanisms that drive evolution?
natural selection
genetic drift
gene flow
mutation
What is an adaptation?
A heritable trait that better allows an organism to survive and reproduce
What causes adaptation?
Natural selection alone
Where are darwin’s finches found?
Daphne island in the galapagos
What were the effects of the drought on the medium galapagos finches on daphne island?
the average beak depth increased and the population size shrunk rapidly
What are darwin’s 3 postulates?
phenotypic variation exists within a population
variation is genetically heritable
different reproduction/ survival occurs based on that phenotypic variation
when these postulates are true, natural selection is acting on that trait
Is adaptation “need based”?
NO. finches dont suddenly grow bigger beaks because they need to, they change in population over time because the ones who dont have the necessary traits are eliminated from the gene pool.
changes caused by natural selection often lag behind environmental change
What happened to the finches mean beak depth when rain returned to the islands?
It lowered again
What is directional selection?
Selection where one of the phenotypes on one of the ends of the spectrum results in better adaptation, so the mean shifts in that direction
ex. the average beak depth increasing following the drought
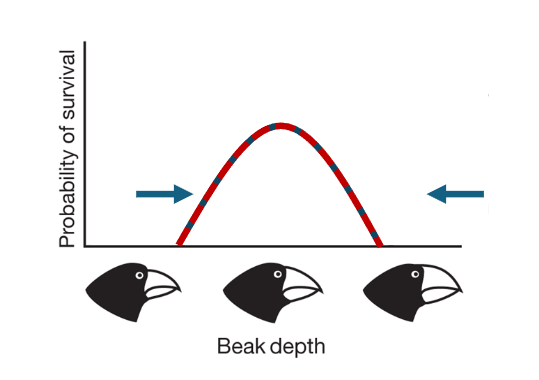
What is stabilizing selection?
when the middle phenotype is favoured, and the extreme ones are unfit, so the avarage stays relatilvely unchanged.
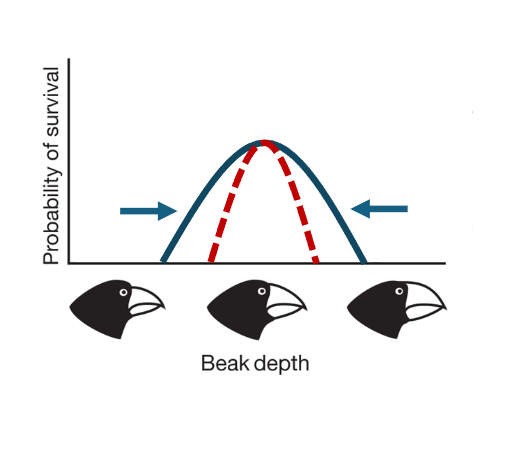
What is disruptive selection?
When the intermediate phenotype is associated with lower fitness so it is no longer present
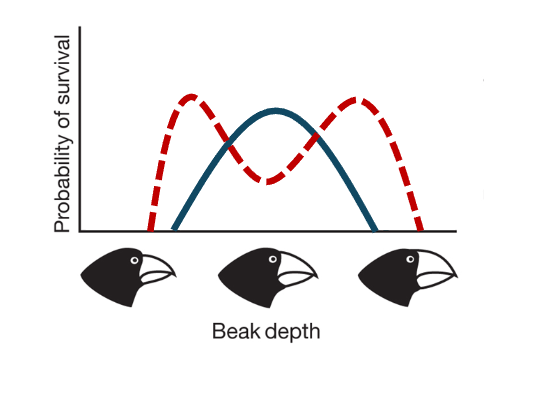
What determines the “fittest” organisms?
Reproductive success alone- lizards who drop dead immediately after having their last kid would be considered equally fit as a lizard who has the same number of kids and lives to 100 after.
What are traits that increase reproduction?
adaptations
What is genetic drift?
changes in allele frequencies that happen by random chance and cause allele frequencies to “drift” up and down over time
Does change in allele frequencies always involve chance?
Yes, always in some amount
What is the founder effect?
When a small subsection of a population moves away and forms a new ppopulation
the smaller the founding population is, the less genetic variation we should expect to see
initial frequency of traits in the population are due to random chance unless there were specific traits that allowed the population to move
smaller founding populations are even more susceptible to further genetic drift
What are genetic bottlenecks?
events such as fire, floods, etc. that have an equal chance of wiping out any member of the population
the traits that do not influence survival of these events are subject to genetic drift
can be dramatic if the remaining population is especially small
How does genetic drift happen?
chance events that are constantly part of reproduction and survival - may have negligible effects in large populations and/ or those under strong selection
dramatic events (founder events, bottleneck events) that may isolate small populations based on chance
What effect does genetic drift have on genetic variation?
Decreases it- can result in alleles disappearing from a population
What is fixation?
when the frequency of a trait becomes 1- only trait present in the population
this trait will not evolve unless mutations appear- main ingredient for evolution is variation
How is genetic drift affected by population size?
occurs regardless of population size
has a greater affect on smaller populations
How does natural selection affect genetic drift?
traits under natural selection will be less affected by genetic drift (because the influence of natural selection is so strong)
traits under weak/ no selection are more prone to being affected by genetic drift
What effect can genetic drift have on deleterious alleles?
It can lead to an increased frequency
How do mutations arise?
errors in DNA replication or exposure to mutagens
What are the 2 main types of mutations?
genetic mutations: change same numbers of nucleotides
chromosomal mutations: change the number or structure of chromosomes
What is the difference between mutation and mutant?
Mutation: something that occurs- the process of changing a gene
mutant: the non- wild type form of a gene
How do mutations affect fitness?
can be beneficial, deleterious or neutral
most mutations are “silent” (neutral)
when they do affect fitness they can be goog or bad, usually minimal although occasionally single mutations can have a large impact
Are mutations random with regards to fitness?
yes- mutations dont just happen because they are needed, they are totally random
What is the source of genotypic/ phenotypic variation?
mutations
What is gene flow?
the movement of genes from one population to another
How does gene flow affect populations?
makes them more genetically similar to each other
How does gene flow affect fitness?
Can increase or decrease, depending if the traits it brings in are well adapted or poorly adapted
What is a model?
A simplified representation of something
What is the general premise of an evolutionary model?
Can’t be a static image/ process, so instead has to translate how allelic and genotypic frequencies change over time into genoptypic frequencies
What 5 assumptions does HWE make?
1) infinite population size (so no population error)
2) no mutations
3) no migration
4) no natural selection
5) totally random mating
What is the purpose of HWE?
To figure out what genotypic frequencies would be given a known allele frequency is evolution was NOT occuring at that locus
if the observed allele frequencies differ from those expected under HWE, we know evolution is occuring
What are observational studies?
Studies that focus on constructing a baseline and require collecting data about a system without doing any intentional manipulations
What are experimental studies?
help gain a better understanding of cause and effect by experimentally manipulating one variable at a time
What do mathematical models do?
Capture essential aspects of a process using an equation or a set of equations
What do computer simulations do?
ramp up complexity compared to mathematical models
What is a population?
A group of individuals from the same geographic area that regularly mate together
What is required for a population to become a seperate species?
genetic isolation
genetic divergence
What is speciation?
The process of genetic isolation and genetic divergence that is responsible for the creation of a new species, results from a lack of gene flow
What is allopatric speciation?
Genetic divergence resulting from geographical barriers
What is sympatric speciation?
Speciation that occurs in the same place, separation is reproductive
Once gene flow is cut off, what causes genetic divergence to happen?
Genetic drift, mutation and natural selection
is there still gene flow between populations undergoing speciation?
Yes, a very small amount because this is not a perfect process
What is a species?
An independent evolutionary unit in nature
What defines a species according to the biological species concept?
Groups of actually/ potentially interbreeding individuals who are reproductively isolated from other such groups
What is xenoparity?
When a mother gives birth to a haploid offspring of another species that has none of her genetic material
What can behaviours depend on?
multiple genes
epigenetics
learning
other environmental effects
Can behaviours be affected by natural selection
Yes
What are altruistic acts?
Acts costly (in a fitness sense) to the actor and beneficial to the recipient
Does natural selection favor altruism?
No, does not favor traits that contribute to survival and reproduction of others, natural selection is inherently selfish
What is inclusive fitness?
When a gene promotes its evolutionary success by promoting the fitness of others who possess that gene
What is kin selection?
Individuals taking care of non- offspring relatives
What is reciprocal altruism?
“ill scratch your back if you scratch mine”
vampire bate feeding each other
requires individuals to keep track of who owes who
What do polyploidy events lead to?
Rapid speciation/ divergence