Fitness Assessment Exam 1
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
Physical Inactivity Risk
Risk from smoking + Obesity combined
Whats the difference between exercise and physical activity?
Exercise is planned physical activity is not
How much of the population meet both aerobic AND strength guidelines
50% meet one or the other
20% meet both
What does regular physical activity guard against
Non Communicable Diseases (NCD’s)
What do inactive children tend to become?
Inactive adults
Dose-response relationship
Dose = volume of activity
Response = health benefits
Dose response relationship contd.
Some is better than none and more is better than less
Physical Activity (PA) Reccommendations for Adults
Aerobic Exercise: >150 min/week of mod intensity or >75 min/week of vigorous intensity
Strength training > 2 days/week
PA recommendations for children
Aerobic Exercise: >60 min/day of mod to vigorous intensity
> 3 days/week of vigorous intensity
Exercise Intensity
MET = Metabolic Equivalent
1 MET = energy cost at rest
1 MET =
3.5 mL/kg/min
Exercise intensity levels using METS
Light: < 3 METS
Moderate: 3-6 METS
Vigorous: > 6 METS
Examples of Mod intensity exercise
Brisk Walk (3 mph)
Water Aerobics
Slow Bicycling (< 10 mph)
Ballroom Dancing
General Gardening
Examples of Vigorous Intensity
Jogging or Running
Lap Swimming
Bicycling ( >10 mph)
Aerobic Dancing
Backpacking
Why do we need Accreditation
Ensures quality of instruction
Why do we need Certification
Acknowledgment of skill and knowledge
Why do we need Licensure
Credibility of professional
Accreditation
Issued by: independent third pary agency
Awarded to: institutions and academic programs
Certification
Issued by: professional organization
Awarded to: individual
Degree
Issued by: academic institution
Awarded to: an individual
Licensure
Issued by: State government
Awarded to: Individual
Why do we do Preliminary Health Screenings?
Determines client readiness for exercise
Detects presence of or suggestion of disease
Assess likelihood of unexpected cardiovascular event related to exercise
Protect yourself from litigation
ACSM guidelines for medical clearance (KNOW THIS)
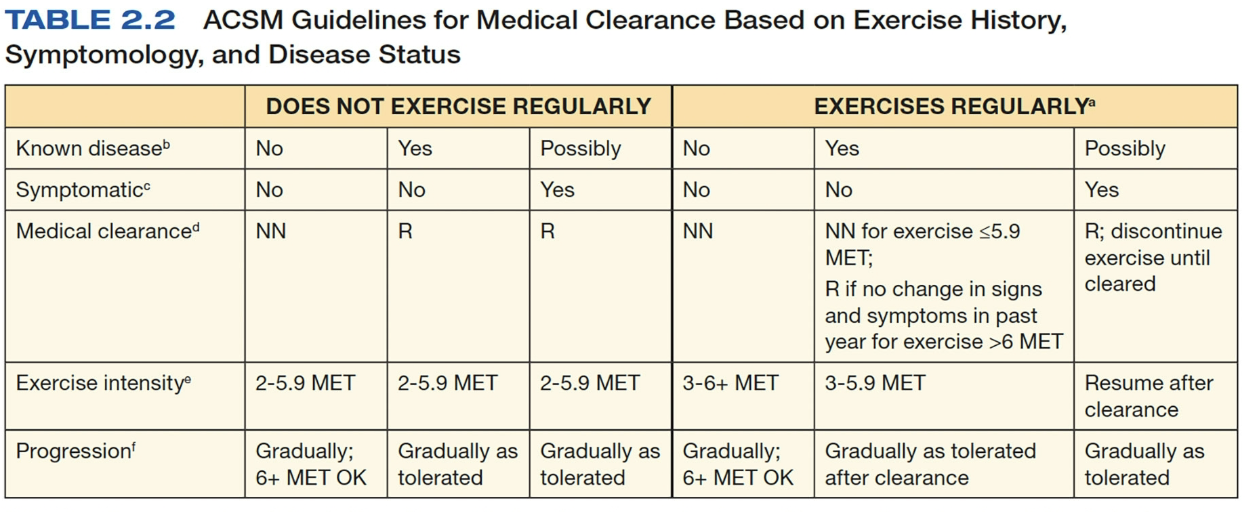
Does the client exercise? If they say “yes” a client must perform
PLANNED physical activity
At least moderate intensity (>3 METs)
At least 30 minutes for at least 3 days/week
Does the client have known diseases
Cardiovascular: Heart Disease, Peripheral Vascular Disease, Cerebrovascular disease
Metabolic: Diabetes Type 1 and 2
Renal: Kidney disease
Signs or symptoms at rest or during exertion of CVD
Discomfort in cheek, jaw, neck, arms, back due to ischemia
Shortness of Breath
Dizziness or Syncope
Orthopnea or Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea
Edema in Ankles
Heart palpitations or Tachycardia
Intermittent claudication
Known heart murmur
Unusual fatigue
Which clients can start at vigorous intensity for exercise?
Only clients who currently exercise and have no known disease or symptoms
What is considered vigourous exercise
6+ METS
Who usually starts with light to moderate intensity for exercise?
Someone who doesn’t currently exercise
What is the definition of light or moderate intensity
2-5.9 METs
When do you know if someone needs medical clearance to exercise?
Anyone who has a known disease or any signs or symptoms need medical clearance first!
What are the questionares that must be administered
PAR-Q
Informed Consent
Lifestyle Questionnaire
Medical History
Coronary Disease Risk Factors
Determination of Medical Clearance Requirement
What is on a PAR-Q
Seven yes/no health questions
If answered yes to any of the questions it is followed by a followup question
If a followup question is answered with a yes then professional consultation is needed
What phrase do we always need to state?
You can stop this test at any place at any time for any reason
Are signatures required on an informed consent?
Yes
Informed Consent Describes the following
Procedures
Risks
Benefits
Confidentiality
Voluntary participation (this must always happen)
Lifestyle Evaluation Contains
Clients living habits
Daily behavior patterns
Barriers to physical activity
This helps answer the exercise question for medical clearance
What are the 2 most common barriers to physical activity
Not enough time and Money
Coronary Risk Factors: Modifiable
Cigarette smoking
Hypertension
Diabetes
Dyslipidemia (imbalance in blood lipids can deal with cholestorol)
Obesity
Sedentary lifestyle
Coronary Risk Factors: Unchangeable
Age and Family History
Normal Values for Blood Variables: Tryglycerides
<150 mg*dL-1
Normal Values for Blood Variables: Total Cholesterol
<200 mg*dL-1
Normal Values for Blood Variables: LDL Cholesterol
<100 mg*dL-1
Normal Values for Blood Variables: HDL Cholesterol
>= 40 mg*dL-1
Normal Values for Blood Variables: TC/HDL cholesterol
<3.5
Normal Values for Blood Variables: Blood Glucose
70-110 mg*dL-1
Normal Values for Blood Variables: Hemoglobin
14-18 g*dL -1 (men)
12-16 g*dL-1 (women)
What are some examples of Absolute Contradictions
Acute myocardial infarction (within 2 days) (heart attack)
Ongoing unstable angina (heart doesn’t get enough oxygen)
Uncontrolled cardiac arrhythmias which cause symptoms of hemodynamic compromise (heart cant maintain enough BP or blood flow)
Active endocarditis (infection of inner lining of the heart)
Aortic stenosis (narrowing of the aortic valve)
Decompensated heart failure
Acute pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, deep vein thrombosis
Acute myocarditis: inflammation of the myocardium
Acute pericarditis: inflammation of the pericardium
Acute aortic dissection
Physical disability that precludes safe and adequate testing
If there are any relative contradictions what should you do
Have a doctor check just incase
What are some additional clinical tests
ECG
Echocardiogram
Chest x-ray
Pulmonary function
Comprehensive blood chemistry
How to find max HR
220-age
What are some causes of HR fluctuations
Stressors
Medication
Caffeine
Tome of day
Body position
Meals
Smoking
Drinking
BP medications: Diuretics
Rid the body of excess salts and fluiid
Reduces blood volume
BP medications: Beta Blockers
Reduces HR and cardiac output
Reduces hearts oxygen demand
BP medications: Calcium Channel Blockers
Reduce heart contractility/dilate arteries
Causes relaxation of heart and lower BP
BP medications: Direct Renin Inhibitors
Blocks production of angiotensin ll (raises BP)
Relax blood vessels and reduce BP
BP medications: Potassium Channel Openers
Hyper polarize vascular smooth muscle/endothelial cells
Opening potassium causes relaxation/widening (vasodilation)
BP medications: Sympathetic Nerve Inhibitors
Prevent arteriole constriction
BP medications: Vasodilators
Relax smooth muscle of arterial walls
BP medications: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Disrupt production of angiotension
What is considered Normal BP
Systolic: less than 120
Diastolic: less than 80
What is considered Elevated BP
Systolic: 120-129
Diastolic: less than 80
High BP hypertension (Stage 1)
Systolic: 130-139 or
Diastolic: 80-89
High BP hypertension
Systolic: 140 or higher or
Diastolic: 90 or higher
Hypertensive Crisis (consult Dr. immediately)
Systolic: higher than 140 or higher
Diastolic: higher than 120
What does the Automated (oscillometric) blood pressure technique prevent
White coat effect (persons BP increases in places like a Dr. office)
FMS certification
Squat with bar test
Helps identify problems with mobility, stability, and movement patterns
What is somethin gyou shouldn’t ever do with FMS certifictation
Don’t add “movement” to “dysfunction” you will only make the problem worse
What is the “light system” with FMS certification
Green light: can do all exercises
Yellow light: do both green and yellow exercises; caution w/ red
Red light: don’t do red exercises until higher score is achieved; cautious with yellow exercises
The health fitness performance continuum suggests that
Exercise programs should follow progression
What is the first component for exercise
Improved health
What is something important to think of when setting goals with cllients?
That they make realistic goals
What are some areas to set goals in?
Speed
Agility
Power
Vertical Jump
Lactate threshold
Sport specific
What percentage of improvements should occur in untrained clients over 3 months
5-10%
*What are the Basic Principles of Program Design
SPIIDOR pneumonic
Specificity
Progression
Initial values
Interindividual variability
Diminishing returns
Overload
Reversibility
Specificity of training
Def: Training targets specific muscles, movements, and energy systems
Ex: If patient has L Leg injury focus on lower body exercises not upper
Progression
Def: To continue improving, the intensity, duration, or frequency of exercise must gradually increase
Ex: progress a client who starts walking 10 mins to 20-30 mins as their endurance improves
Initial Values
Def: Starting fitness level
Ex: A more sedentary person who starts training might improve their VO2 max quickly while a trained athlete will improve slower
Interindividual Variability
Def: Due to genetic differences, age, sex, health status everyone will respond differently to the same training program
Ex;: two patients do identical strength programs one might double strength fast than the other
Diminishing returns
Def: as fitness increases the rate of improvement slows down
Ex: beginners might quickly gain muscle in first few weeks but after months of training, improvements occur more gradually
Overload
Def: to make physical improvements you must challenge body beyond normal level of activity
Ex: increasing resistance in weight training increases workload
Reversibility
Def: when training stops or load decreases, fitness levels decline
Ex: patient stops pt for a few weeks muscle strength, and ROM will decrease and it sets them back
What are the variables of exercise prescription?
FITTVP
Frequency of exercise
Intensity of exercise
Time of exercise session
Type of exercise session/program
Volume of work done day by day, week by week
Progression: through an exercise program
Physical Fitness Component: Cardio respiritory endurance
Aerobic exercise
Physical Fitness Component: Muscular Strength/Endurance
Resistance training
Physical Fitness Component: Bone strength
Weight bearing/high impact
Physical Fitness Component: Body composition
Aerobic exercise and resistance training
Physical Fitness Component: Flexibility
Stretching exercise
Physical Fitness Component: Balance
Balance training
Stages Of Program Progression
Initial Conditioning, Improvement, and Maintance
Initial conditioning
Lasts 1-6 weeks
Develops basic techniques, habit of exercising
Improvement
Aggressive Pregression toward goal
Lasts 4-8 months
Maintenance
Build on a fitness base
Desn’t mean stop improve rather keep up exercise habits
Add variety and activities of interest to the client
Program Design Concepts
Stabilization (phase 1): stabalizition endurance
Strength (phase 2): Strength endurance
Strength (phase 3): Hypertrophy
Strength (plase 4): Maximal strength
Power (phase 5): power
What does the ACE integrated fitness training model do?
Provides professionals with a systematic and comprehansive approach to exercise programming
What does the Ace IFT model training components and phases help with
Help you be able to know where to start
What are the 4 ACE training phases
Functional movement and resistance training
Stability and Mobility 2. Movement 3. Load 4. Performance
What are the 4 ACE training phases for cardiorespiratory training phases
Aerobic-base 2. Aerobic efficiency 3. anaerobic-endurance 4. Anaerobic power
What is a result for having weak core muscles
Increase injury for risk
What stage do most clients not progress to
Stage 4