Chem test
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
what is the difference between nuclear and chemical reactions?
nuclear reactions involve transformation of nuclei and emission of radioactivity
Gamma radiation is the only type of radiation that what?
consists of high energy radiation instead of particles
an alpha particle will collide with the nucleus to produce nuclear bombardment reaction only when what happens?
the positively charged alpha particle is moving fast enough
Radioisotopes cannot yet be used for what?
producing inexpensive, safe fuel
What does e=mc2 mean?
a small mass can be converted into a large amount of energy
a commonly used isotope for dating bio remains is what?
Carbon-14
what is nuclear bombardment?
use of a stream of high speed alpha particles to change and atom’s nucleus
what does radioactive mean?
an atom with unstable nucleus that emits alpha, beta or gamma particles
what is a chain reaction
series of fission reactions producing other fission reactions
what is fission?
the breaking apart of a larger nucleus to form a larger nucleus
what is a Radioisotope
form of an element that can change spontaneously into another element
what is fusion
joining of smaller nuclei to form a larger nucleus
what is a dosimeter
uses exposure of film to indicate radiation received
what is strong nuclear force?
holds neutrons and protons together
what is plasma?
state of matter in which nuclei exist separately from electrons
in E=Mc2 which two items are interchangable?
energy and mass
what is a nuclide?
a particular isotope
Nucleon
nuclear subatomic particles (protons, n, etc.)
Binding Energy
Strong Nuclear force, E used to hold nucleons together
Mass Defect
mass “lost” being converted to energy
nuclear decay most harmful to humans
gamma
What is Beta Decay
Releases Beta particles, is neutron heavy
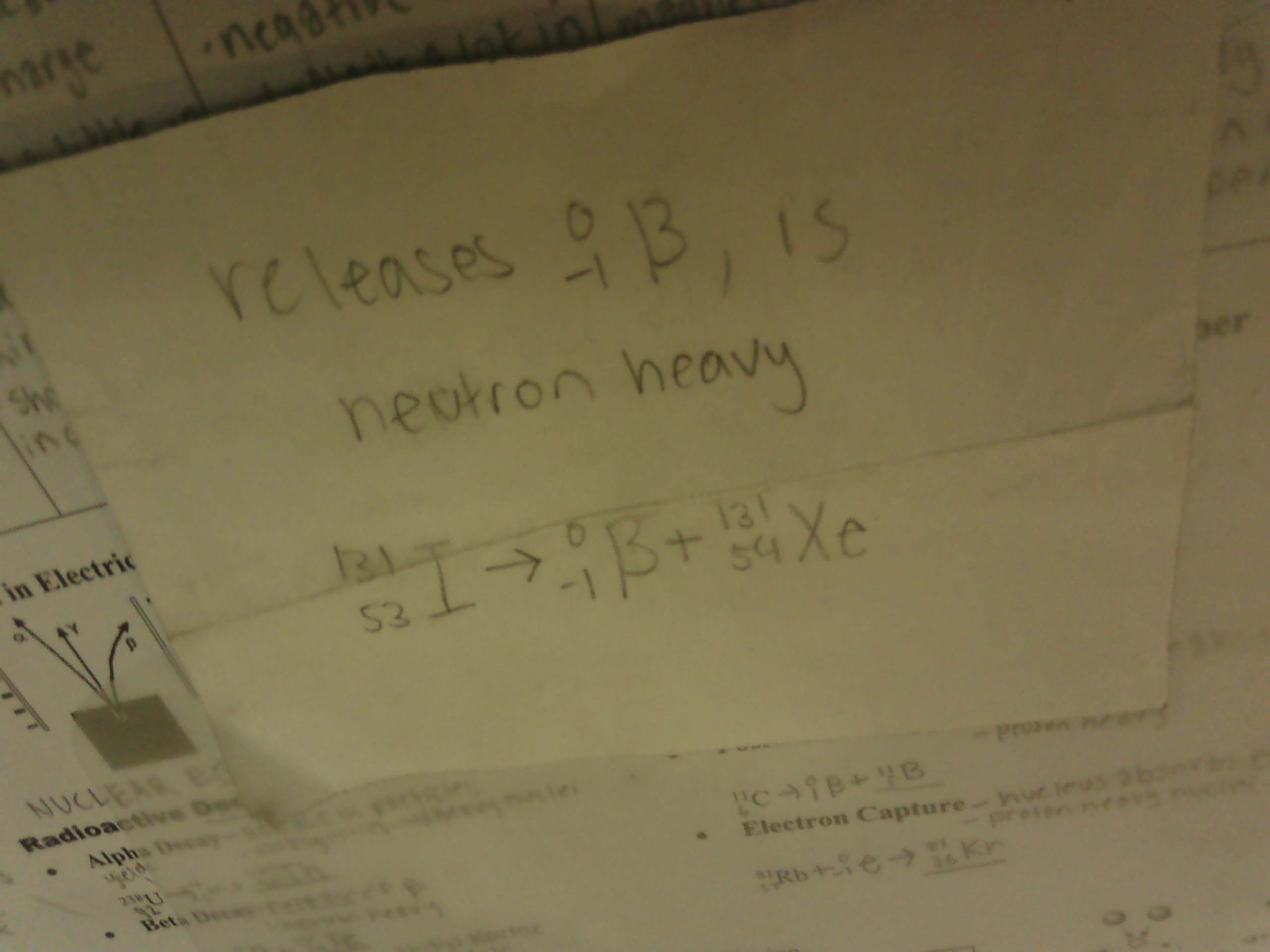
What is positron emission?
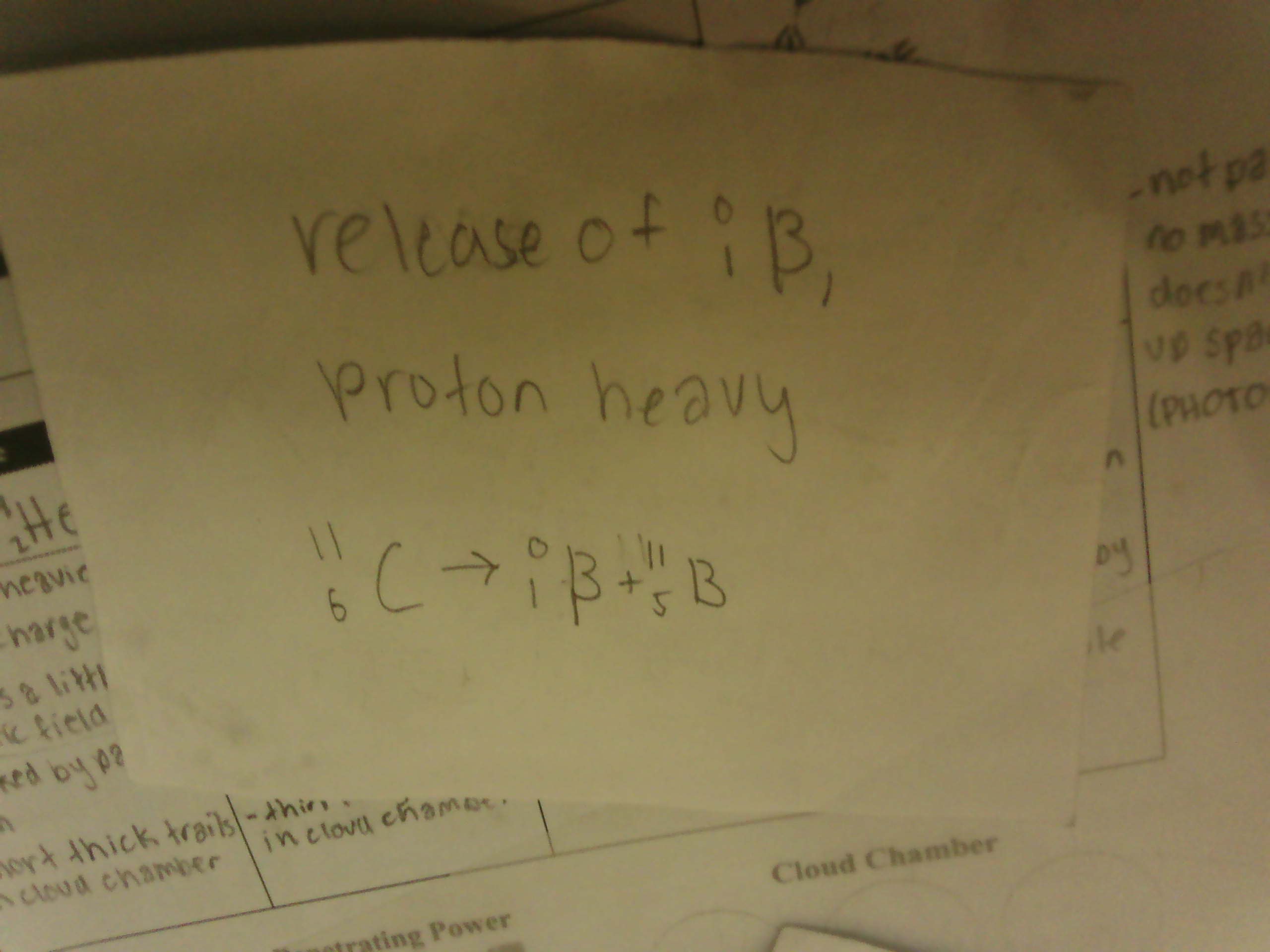
Isotopic notation for Proton
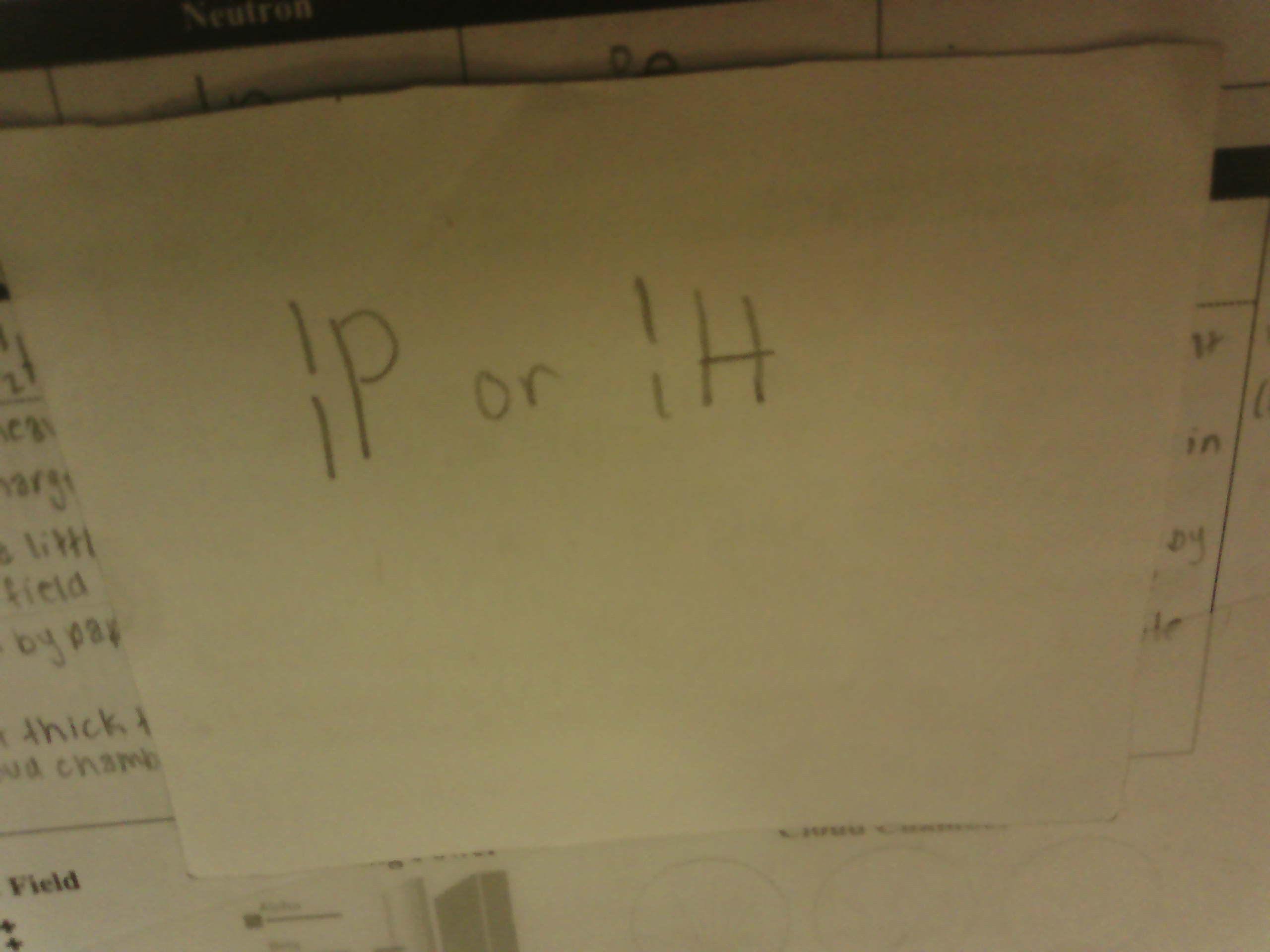
Half Life Equation
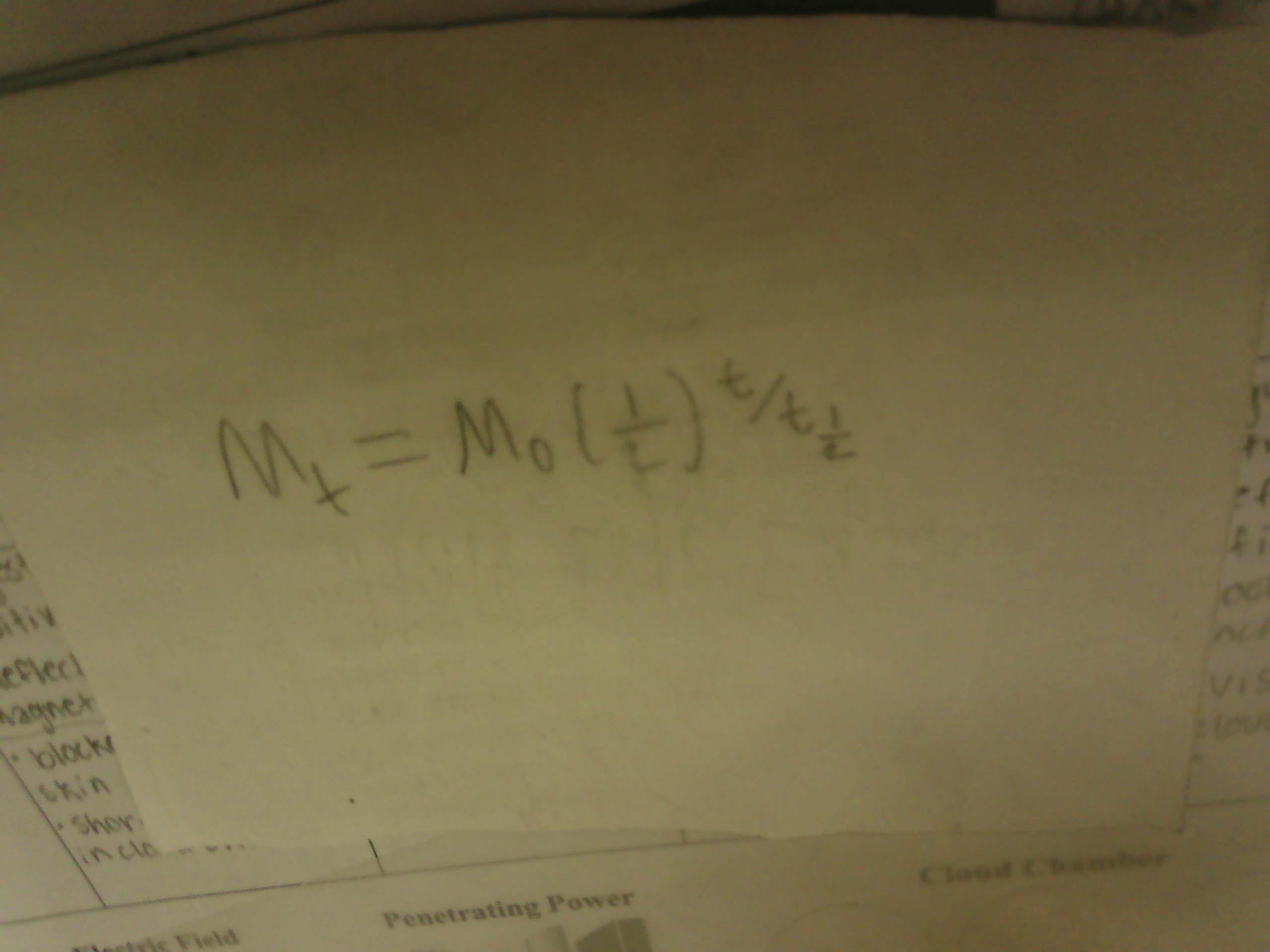
Mass at time
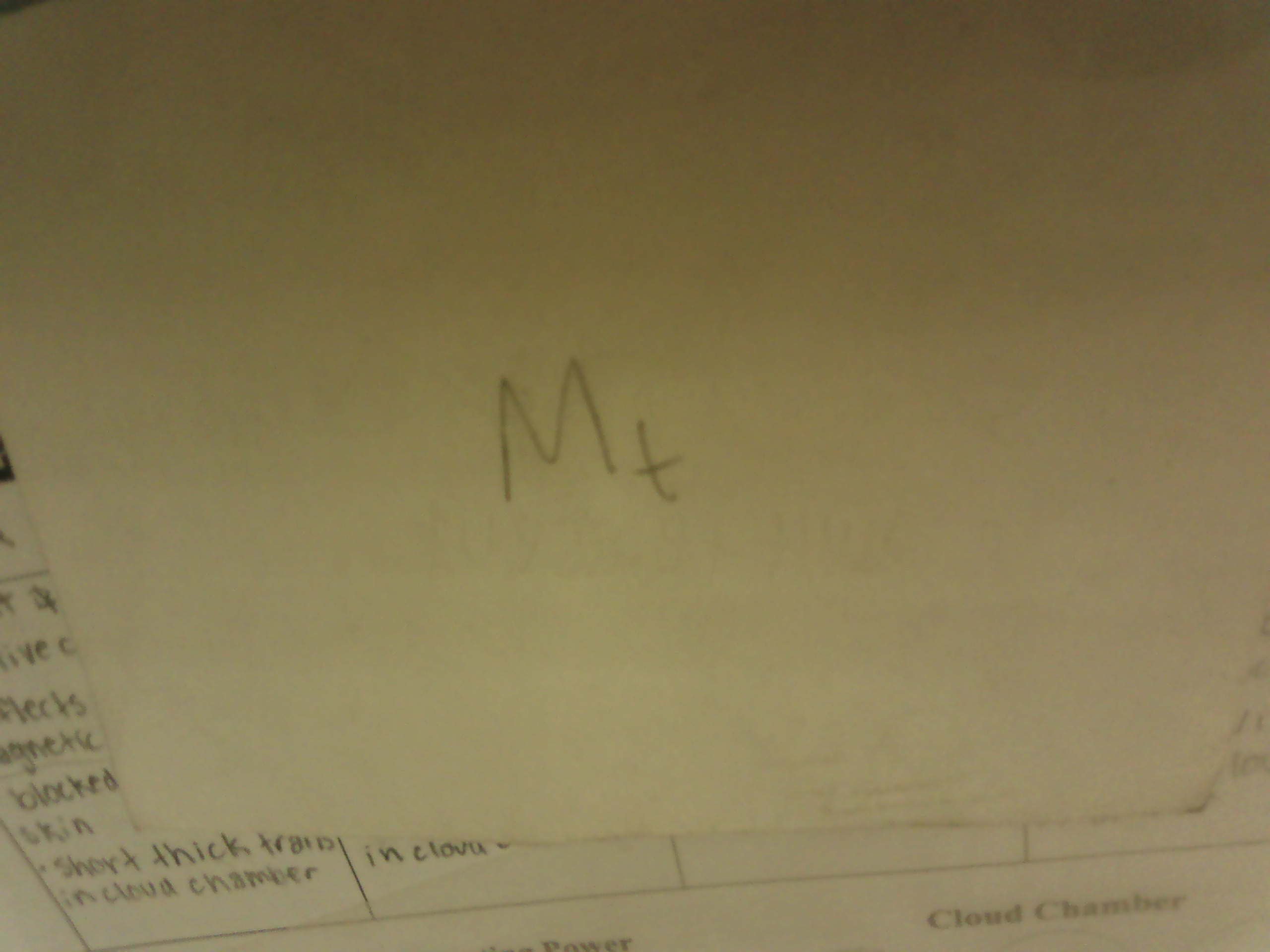
Electron Capture

Initial Mass

isotopic notation for Alpha Particles
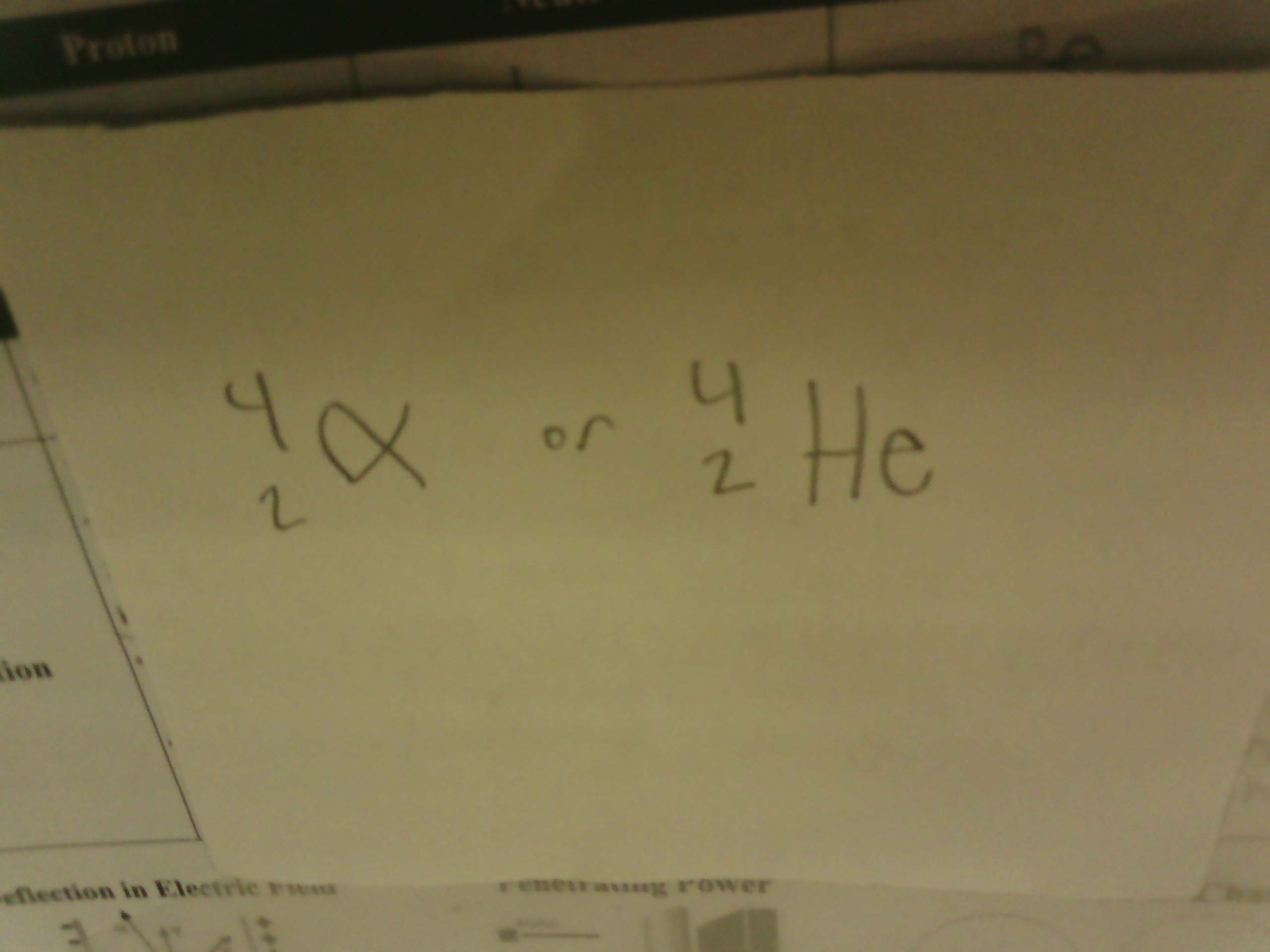
Isotopic Notation for Beta Particle

Isotopic notation for positron
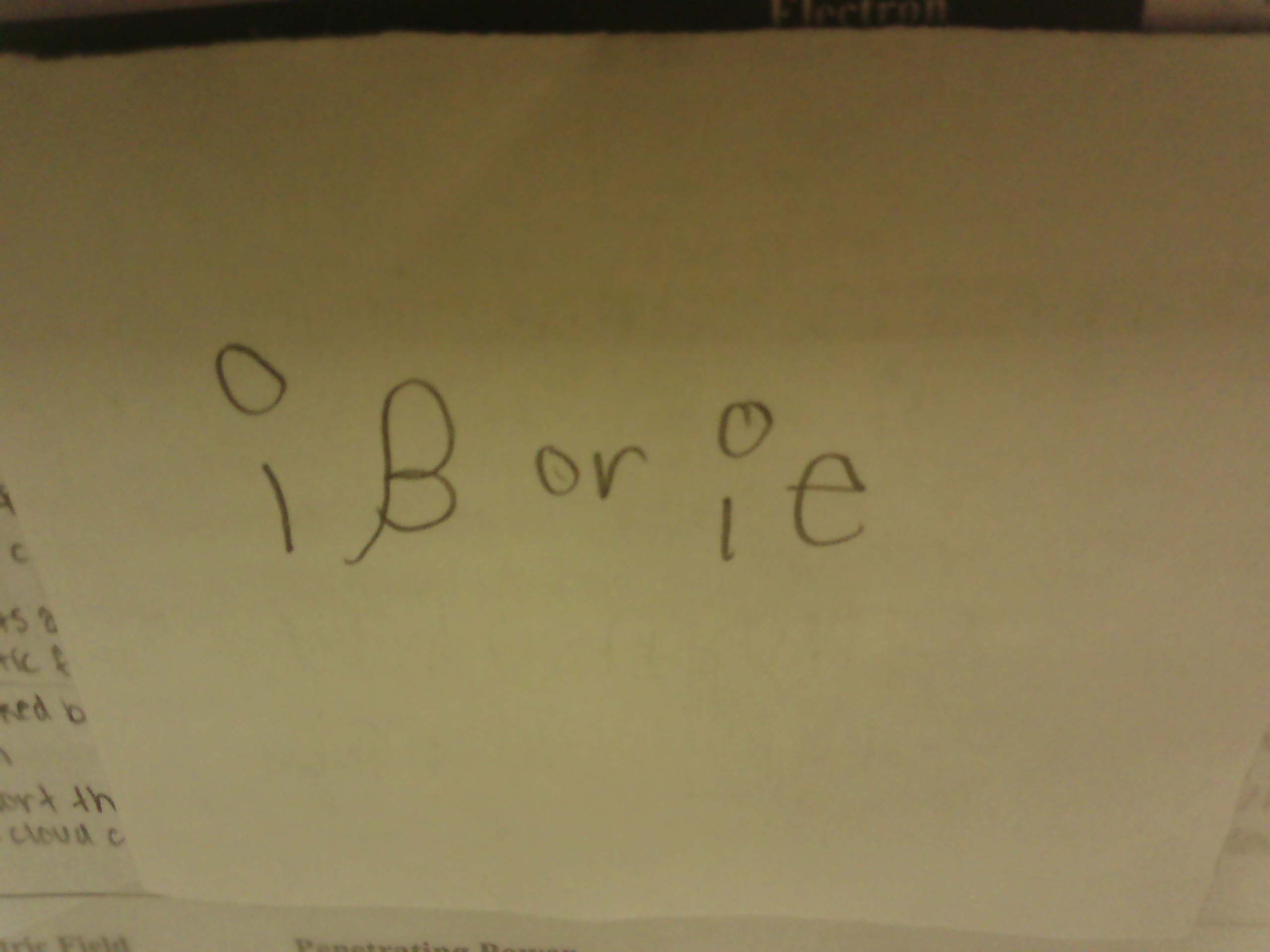
Isotopic Notation for Gamma ray
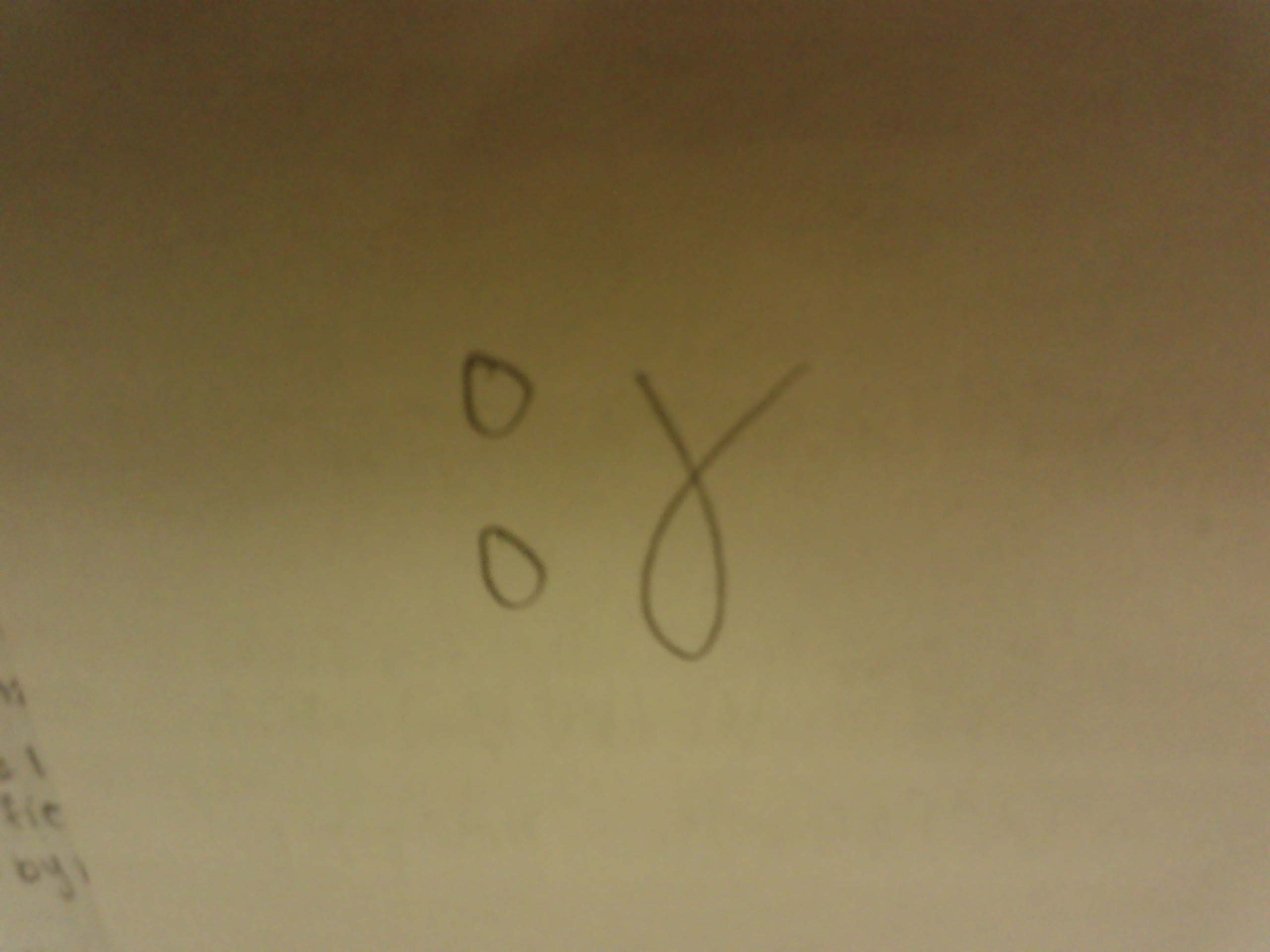
Isotopic notation for Neutron
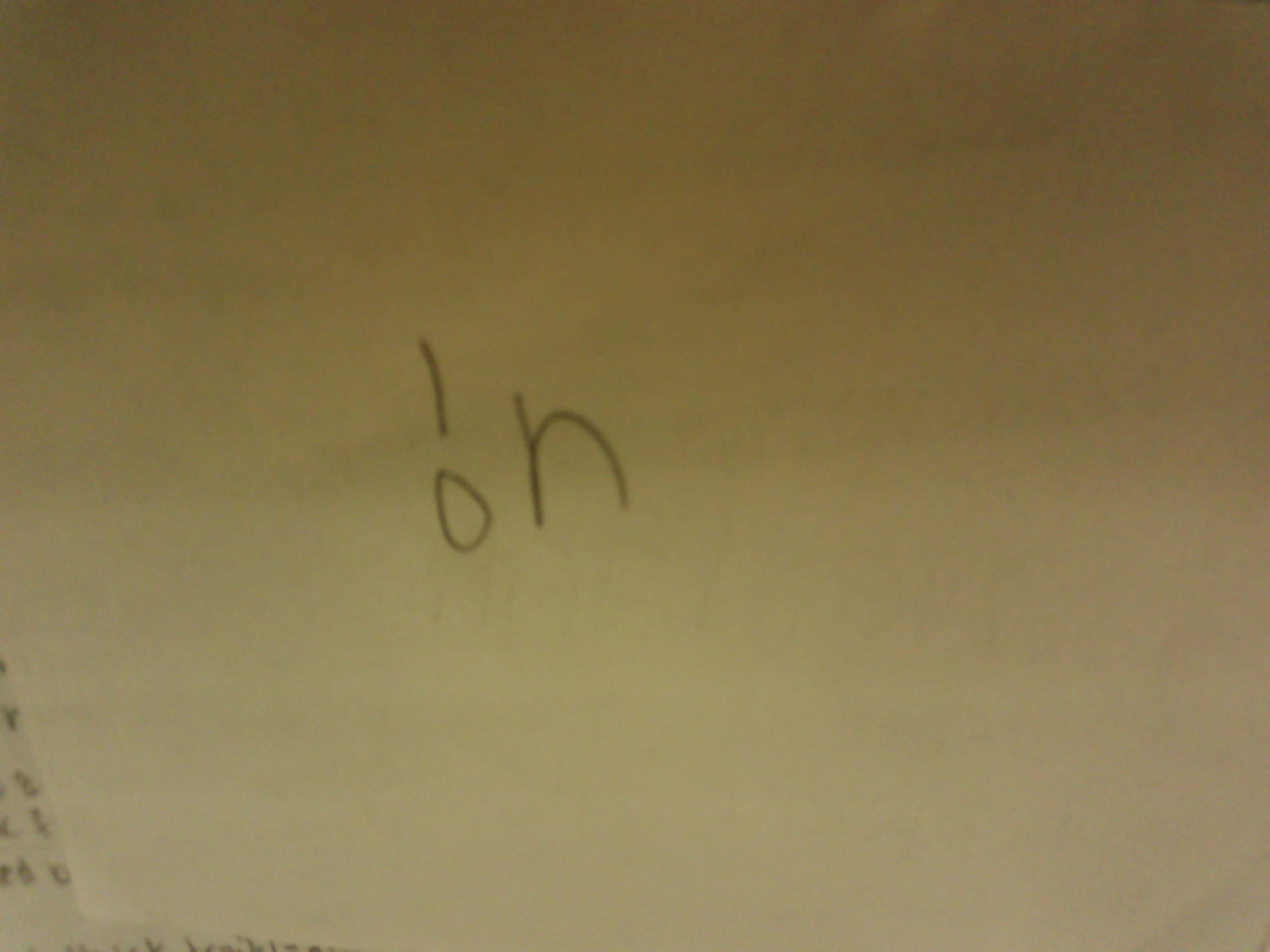
half life
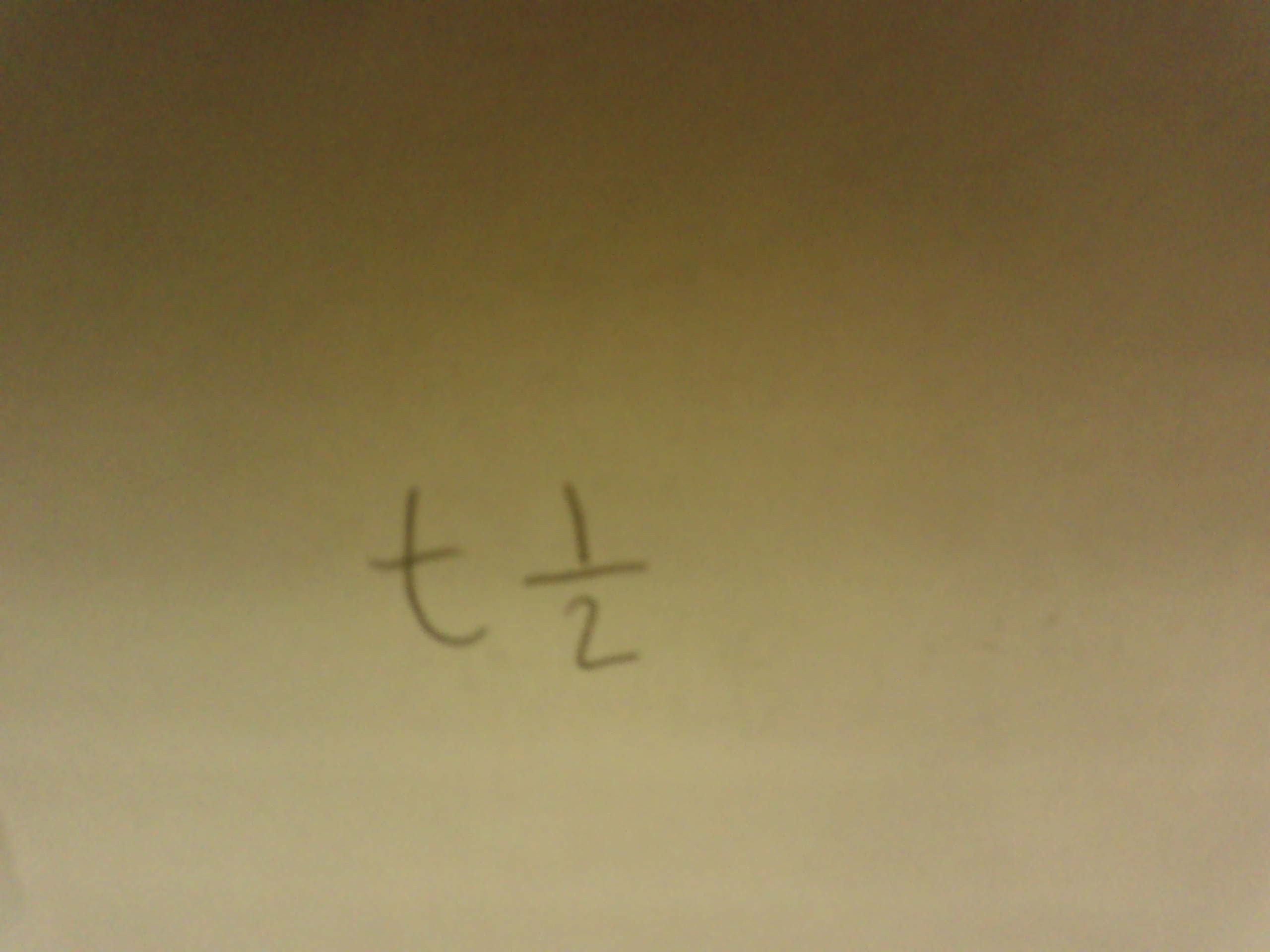
What is Alpha Decay
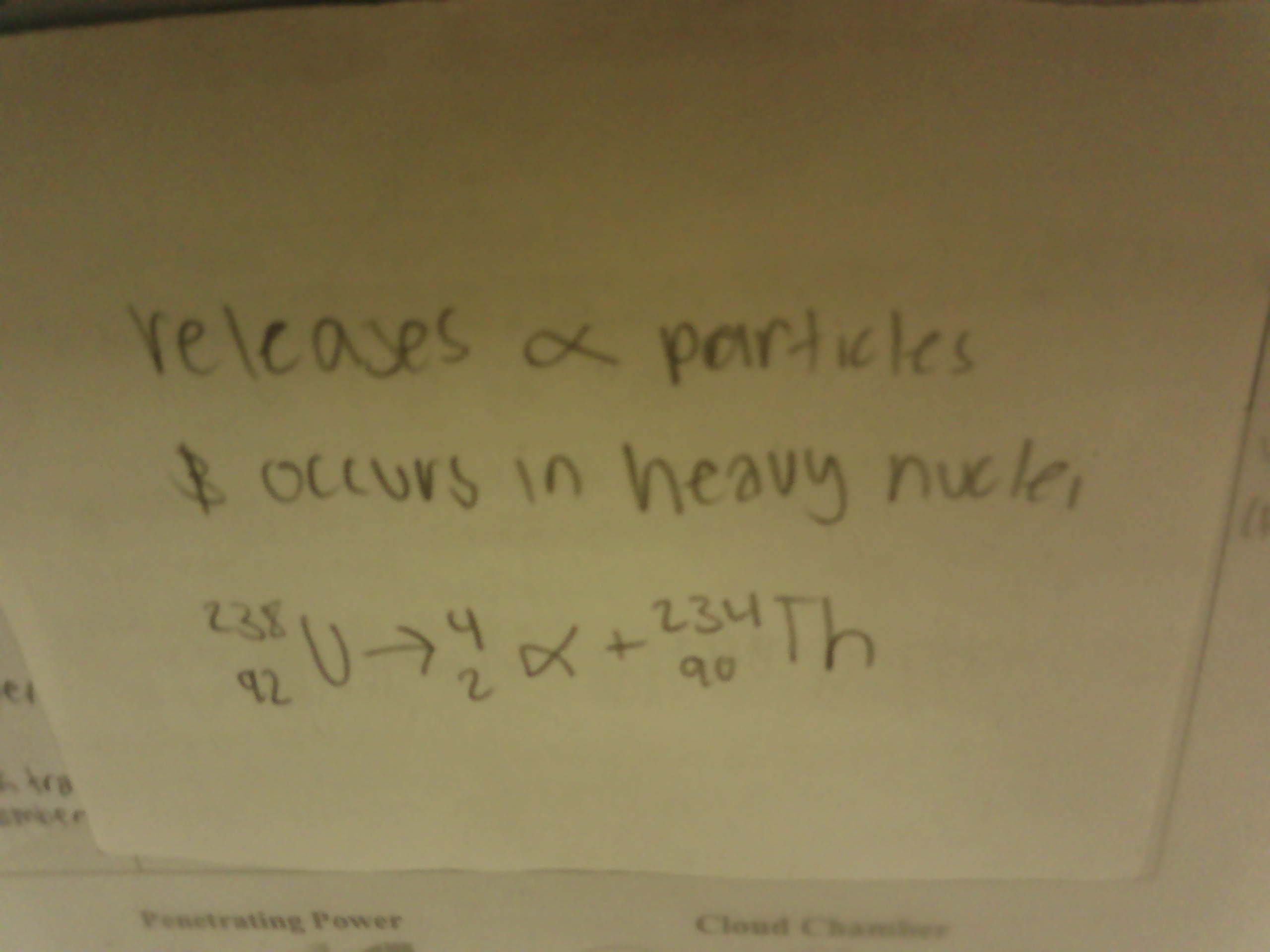
time elasped

What do Gamma rays look like in cloud chamber
Barely visible trails
What particle has the same notation as and electron?
beta particles
What do Beta and Positron look like in a cloud chamber
thin long trails
Isotopic notation for electron

What do Alphas look like in a cloud chamber
short thick trails
What can Gamma rays be blocked by
lead or concrete
What can Beta and Positron particles be blocked by?
Aluminum sheets
What can Alpha Particles be blocked by
Paper and Skin
What doesn’t deflect in a magnetic field
Gamma Rays
Which particles reflect a lot in a magnetic field
Beta and Positrons
Which particle deflects a little in a magnetic field?
alpha particle
Only particle with negative charge
Beta particle
What is a High energy light instead of a particle?
Gamma ray
Which particle is a positive electron
positron
Which Particle is a high energy electron
Beta Particle
What is the largest heaviest particle
Alpha particles
on a figure what is an a move?
← 2 and 2 down
on a figure what is a B move?
1 →
Wavelength
Length of 1 cycle
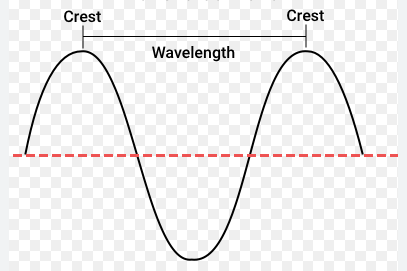
what is a cycle
one complete wave from peak to peak
what is the symbol for wavelength?
Lambda λ
Frecuency
# of cycles per second
symbol for frequency?
Nu (v)
Speed
Velocity, distance a cycle travels in a wave per unit time
units for wavelength
meters (m) or nanometers (nm)
units for frequency
1/s, s-1, Hz (hertz)
Speed units
m/s
all light waves travel at the _______ speed
same
Light is made of
photons
Equation for speed using frequency and Wavelength
Speed = Frequency x Wavelength
Equation for Frequency using speed and wavelength
Frequency = Speed/Wavelength
Equation for wavelength using speed and frequency
Wavelength = Speed/Frequency
symbol for Planck’s constant
h
When wavelength is longer what is frequency
lower
the higher the frequency the ________ the wavelength
shorter
what is the wavelength of visible light
400-750
what is visible light
rainbow
rank the parts of the electromagnetic system from lowest to highest energy
Radio, microwave, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, gamma ray
rank the parts of the electromagnetic system from lowest to highest frequency
(F)Radio, microwave, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, gamma ray
rank the parts of the electromagnetic system from lowest to highest Wavelength
gamma, X-ray, ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwave, radio
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
Inverse
What is the relationship between frequency and Energy?
Direct
Bohr Model
proposed that elections orbit the nucleus at specific energy levels, When e- is excited it jumps and absorbs energy when it returns to ground state it releases the energy as light
Electron Shells
primary E level occupied by e-, each shell can only have a certain amount of e-, the farther the e- is from the nucleus, the higher the energy
Quantum Mech. model
current model, views electrons within an atom as waves, not as particles as previously believed
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
The exact position and speed of an electron cannot be simultaneously determined
Atomic Orbitals
region of space where e-s of a certain E are found
what shape are s-subshell
spherical (1 per level)
what shape are p-subshells
dumbell (3 per level)
what shape are d-subshell
dif. shapes (5 per level)
what shape are f-subshells
flower (7 per level)
Aufbau principle
e-s occupy the available orbitals from lowest to highest
Pauli’s exclusion principle
a max of 2 e-s can occupy any orbital before it’s full and they must have opposite spins
Hund’s rule
ride the bus rule
e- configuration
the full written thing
orbital notation
the arrows one
Noble gas configuration
the short one
What are Valence electrons?
e-s in outer most principle quantum number, usually s & p orbitals and basically everything after the noble gas
why are Valence electrons important
because they are held most loosely to the nucleus and are more easily shared or lost in bonding
The octet rule
atoms react to form compounds in such a way as to but 8 e- (an octet) in the valence shell (not including H and He)
Lewis e- dot notation
mark s and p orbitals using dots
which color has the longest wave length?
red
which color has the lowest energy?
red
which color has the shortest wave length?
violet