mod 9- spinal cord injuries
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
12-18 months
how long after a spinal cord injury for neural axons to regenerate?
heterotrophic ossification
abnormal bone growth in soft tissue, affecting ROM and causing pain and redness
Baclofen
kind of pump that is commonly used for medical treatment of spasticity
autonomic dysreflexia
disconnect between sympathetic and autonomic nervous systems that can cause elevated BP, headaches, stroke, or death
T6
at what level (or above) does a spinal injury have the potential to cause autonomic dysreflexia
time, exercise
what can help improve the symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia over time?
PF, hip extensors, foot
what muscles does a sacral SCI impact?
DF, hamstring, abductors
what muscles does a L5 SCI impact?
quads
what muscles does a L4 SCI impact?
hip flexors, adductors
what muscles does a L3 SCI impact?
L2
injuries at what level can cause paraplegia?
T4
injuries at what level can cause quadriplegia?
hip flexion
what motion is impacted by a L2 injury?
knee extension
what motion is impacted by a L3 injury?
DF
what motion is impacted by a L4 injury?
toe extension
what motion is impacted by a L5 injury?
PF
what motion is impacted by a S1 injury?
elbow flexion
what motion is impacted by a C5 injury?
wrist extension
what motion is impacted by a C6 injury?
elbow extension
what motion is impacted by a C7 injury?
finger flexion
what motion is impacted by a C8 injury?
finger abduction
what motion is impacted by a T1 injury
classification of SCI
what does ASIA score measure?
complete
A on ASIA score
motor loss complete, sensation intact
B on ASIA score
less than half of muscles below the lesion are grade 3 or better
C on ASIA score
more than half of muscles below lesion are grade 3 or better
D on ASIA score
normal
E on ASIA score
central cord syndrome
injury to the central region of the spinal cord, usually by hyperextension of the neck
Brown-Sequard syndrome
damage to one side of the spinal cord, causing motor loss on the affected side and sensory loss on the contralateral side
bullet, knife trauma
most common causes of Brown-Sequard syndrome
motor, sensory
Brown-Sequard syndrome involves (motor/sensory) loss on the side of the injury and (motor/sensory) loss on the contralateral side
anterior cord syndrome
injury that causes full motor loss and partial sensory loss but does NOT impact proprioception. Blood supply may be disrupted and prognosis is poor
proprioception
what sense is not affected in anterior cord syndrome?
posterior cord syndrome
injury that causes loss of vibration and proprioception, but intact motor and pain sensation. Prognosis for ambulation is poor
tumor, disk compression, hyperextension
causes of posterior cord syndrome
L1-2
what level does conus medullaris exit spinal cord
T10
at what level does conus medullaris start to form?
saddle anesthesia, upper and lower motor neuron involvement
symptoms of conus medularis injury
trauma, tumor
causes of conus medularis injury
motor and sensory loss, bowel and bladder may be affected
symptoms of cauda equina injury
good
ambulatory prognosis for cauda equina injury
herniated disc, tumor, lesion
causes of cauda equina injury
spina bifida
open neural tube defect associated with hydrocephalus
motor and sensory loss
neural presentation of spina bifida
hydrocephalus
build-up of fluid inside the head due to myelomeningocele from spina bifida
spina bifida occulta
most mild form of spina bifida
occulta
form of spina bifida where lower back bones fail to form properly. May have a hairy patch, dimple, or birthmark over the area of the defect
meningocele
moderate form of spina bifida
meningocele
form of spina bifida where a fluid-filled sac is visible outside of the back
sac does not contain spinal cord or nerves
key difference between meningocele and myelomeningocele
myelomeningocele
most severe form of spina bifida
myelomeningocele
form of spina bifida where the spinal cord and nerves develop outside of the body in a fluid-filled sac
weakness and loss of sensation below the defect, lack of bowel and bladder
other symptoms of myelomeningocele, besides the sac
lower back
where do 80% of myelomeningoceles occur?
swivel walker
which orthosis uses about 10x as much energy as regular walking to ambulate?
GI function, long bone loading
what can standing help with, in patients with spinal cord injuries?
30-60%
what do we aim for patients to have the speed of, compared to their peers?
sit-stand, independent transfer, independent don/doff, ambulate 75m in 1 minute and 250m without undue stress
functional ambulation goals
5d
what angle of DF is a Scott-Craig usually offset to?
18 mo-4 years
appropriate age range for a swivel walker
40”
up to what height does a swivel walker accommodate?
spina bifida, CP
diagnoses that are most commonly provided with a swivel walker
standing, sitting
movements allowed by ParaPod
swivel walker
what is this?

ParaPod
what is this?

2-6
appropriate age for ParaPod use
spina bifida
common diagnosis for ParaPod use
55 lbs
upper weight limit of Parapod
ParaPod
which of the orthoses covered in this lecture should be physically anchored to something while the patient is standing?
RGO
what is this?

4-12 yrs, or adults for exercise
appropriate age range for RGO
Isocentric
when used in an RGO, this option is very rigid and uses one pivot point
cable-driven
when used in an RGO, this option runs in parallel and is not very efficient
0d
degree of DF set in an RGO
reciprocating gait orthosis
what does RGO stand for?
looped cable
good cabling option for RGO for spina bifida patients if you need room for a meningocele
lean posterior and lateral
how to drive forward RGO
reverse/posterior
good kind of walker to use with an RGO so it doesn’t get in the way
rigidity
requirement for RGO to work properly
inside
in an RGO, do your shoes go inside or outside of the boot?
hip guidance orthosis
what does HGO stand for?
hip guidance orthosis
what kind of an orthosis is the Parawalker?
parawalker
what is this?

very rigid, poor compliance
why are Parawalkers not manufactured in the US anymore?
Walkabout
what is this?

perineal straps, abduction limit makes toileting difficult, slower than RGO
reasons for poor compliant for the Walkabout
lower profile, light, fits in wheelchair
benefits of using a Walkabout
MASP
what kind of joints does a Walkabout use?
C6
at what level of injury can a person still operate a manual wheelchair?
C5
at what level of injury can a person still operate a motor vehicle, with accommodations?
intact neural system
requirement for using FES in combination with an orthosis like an RGO
driven gait orthosis
what does DGO stand for?
powered, not covered by insurance
what makes a DGO unique?
EKSO
FDA-approved powered orthosis capable of 2 mph ambulation and variable terrain. Movements are first controlled by a PT and then adjust to user settings
EKSO
what is this?
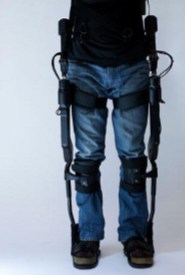
Rex, robotic exoskeleton
what is this?

ReWalk
what is this?

wrist unit
what controls a ReWalk?
motor-assisted HKAFO approved by FDA
what is a ReWalk?