AP human geographer Semester 2 Vocab, Unit 5-7
1/133
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
17 goals, examples: no poverty, zero hunger, good health and well being, quality education
Just-in-time delivery
Shipment of parts and materials to arrive at a factory moments before they are needed
economies of scale
the property whereby long-run average total cost falls as the quantity of output increases
Export-Processing Zones (EPZs)
Small areas of a country with exceptional investment and trading conditions that are created by its government to stimulate and attract foreign investors and business
Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
specific area within a country in which tax incentives and less stringent environmental regulations are implemented to attract foreign business and investment
primary sector
portion of a country's economy employed in extracting natural resources
secondary sector
portion of a country's economy employed in processing natural resources
tertiary sector
the service sector; consists of providing services to people and businesses
quaternary sector
the knowledge-based sector that includes research and development, business consulting, financial services, education, public administration, and software development
quinary sector
highest levels of decision-making and includes the top officials the top officials in various levels of government and business
Alfred Weber/Least Cost Theory
explains the key decisions made by businesses about where to locate factories; attempts to predict the location of a manufacturing site relative to the location of the resources needed to produce the product and where the final product will be sold (market)
agglomeration
the spatial grouping of businesses in order to share costs, as when several factories share the cost of building an access road to connect with a public highway
outsourcing
contracting work out to non-company employees or other countries
newly industrialized counties (NICs)
country whose national economy has transitioned from being primarily based in agriculture to being primarily based in goods-producing industries, such as manufacturing, construction, and mining
maquiladoras
a type of export processing zone (physical spaces within a country where special regulations benefit foreign-controlled business) located specifically in Mexico
Gross National Income (GNI)
the dollar value of a country's final income in a year, divided by its population; it reflects the average income of a country's citizens
Gender Inequality Index (GII)
a composite index for measurement of gender disparity, which affects a country's development
human development index (HDI)
combines one economic measurement (GNI) with several social measures, such as life expectancy and the average education level
Walt W. Rostow/Stages of Economic Development
postulates that economic growth occurs in five basic stages, of varying length
Immanuel Wallerstein/World Systems Theory (Core-Periphery Model)
a dependency model that postulates that countries do not exist in isolation but are apart of an intertwined world system in which all countries are dependent on each other.
core countries
includes the economically advantaged area of the world and the center of world businesses and finances
semi-periphery countries
includes middle income countries that provide services for core countries
periphery countries
includes the least-developed countries that have a high percentage of jobs in low-skill, labor intensive production
Commodity Dependency
Heavy reliance on export of primary commodities
sustainable development
any economic development that serves the current needs of people without making it harder for people in the future to live well
ecotourism
tourism that attempts to protect local ecosystems and to educate visitors about them
free trade zones (FTZs)
tax-free area where goods can be landed and 'value added', through handling and manufacturing, and re-exported without the intervention of customs
growth poles
the concentration of high-value economic development attracts even more economic development; example - Silicon Valley
European Union (EU)
organization formed to promote development within the member states through economic and political cooperation; essentially eliminated tariffs among member nations and has fostered economic growth.
deindustrialization
process by which companies move industrial jobs to other regions with cheaper labor, leaving the newly deindustralized region to switch to a service economy and to work through a period of high unemployment
indicators of development
sectoral structure of the economy, literacy rates, birth and death rates, access to healthcare, infant mortality rates, gender equality, gross national income, etc.
OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries)
a permanent intergovernmental organization of 13 oil-exporting developing nations that coordinates and unifies the petroleum policies of its Member Countries.
comparative advantage
a situation in which a country, individual, company, or region can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than a competitor
complementarity
the degree to which one place can supply something that another place demands
microlending
The practice of loaning small amounts of money to help people in less developed countries start small businesses.
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
an international organization that acts as a lender of last resort, providing loans to troubled nations.
tariffs
A tax on imported goods
World Trade Organization (WTO)
a permanent global institution to promote international trade and to settle international trade disputes
free trade
international trade left to its natural course without tariffs, quotas, or other restrictions.
Dependency Theory
a model of economic and social development that explains global inequality in terms of the historical exploitation of poor nations by rich ones
Microloans
Small-business loans often used to buy equipment or operate a business
Gross National Product (GNP)
The total value of all goods and services produced by a country's economy in a given year.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total output of all economic activity in the nation, including goods and services.
Break-of-bulk point
A location along a transport route where goods must be transferred from one carrier to another. In a port, the cargoes of oceangoing ships are unloaded and put on trains and trucks.
Ecumene
The proportion of the earth inhabited by humans.
Suburbs
residential areas surrounding a city
Settlement
A permanent collection of buildings and inhabitants.
Urbanization
Movement of people from rural areas to cities
Suburbanization
The process of population movement from within towns and cities to the rural-urban fringe.
zoning ordinances
A law that limits the permitted uses of land and maximum density of development in a community.
Site
The physical character of a place
Situation
the location of a place relative to other places
City-state
a city that with its surrounding territory forms an independent state.
Urban hearth
An area like Mesopotamia, China, India, or the Nile Valley where large cities first existed.
Urban area
A central city and its surrounding built-up suburbs
Metropolitan statistical area (MSA)
Contains a core area containing a large population nucleus, together with adjacent communities that have a high degree of economic and social integration with that core.
Time-space compression
the rapid innovation of communication and transportation technologies associated with globalization that transforms the way people think about space and time
Central business district (CBD)
The area of a city where retail and office activities are clustered.
Counter-urbanization (deurbanization)
the net loss of population from cities to smaller towns and rural areas.
Megacities
cities with more than 10 million people
Megalopolis
a very large, heavily populated city or urban complex.
Conurbation
an extended urban area, typically consisting of several towns merging with the suburbs of one or more cities.
World city (global city)
Centers of economic, culture, and political activity that are strongly interconnected and together control the global systems of finance and commerce.
Urban hierarchy
A ranking of settlements according to their size and economic functions.
Gravity model
A mathematical formula that describes the level of interaction between two places, based on the size of their populations and their distance from each other.
Central place theory (Christaller)
explains the spatial organization of settlements and hinterlands, their relative location, and size.
Higher-order services
a good or service usually expensive, that people only buy occasionally, these are usually located in larger towns and cities with a large market area accessible to a large number of people
Lower-order services
provided by small centers, a good or service, usually inexpensive items that people buy often a regular, often daily basis
Primate city
The largest settlement in a country, if it has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement.
Residential zones
the areas of a city devoted to where people live rather than to commercial or industrial functions
Concentric zone model (Burgess)
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings.
Sector model (Hoyt)
A model that shows cities develop in a series of sectors radiating out from a CBD
Multi-nuclei model (Harris and Ullman)
a model of urban land use developed by C.D. Harris and E.L. Ullman based on separated & specialized multiple nuclei
Peripheral model
A model of North American urban areas consisting of an inner city surrounded by large suburban residential and business areas tied together by a beltway or ring road.
Zoning ordinances
A law that limits the permitted uses of land and maximum density of development in a community.
boomburbs
rapidly growing city that remains essentially suburban in character even as it reaches populations more typical of a large city
disamenity zone
The very poorest parts of cities that in extreme cases are not connected to regular city services and are controlled by gangs and drug lords.
Squatter Settlement
An area within a city in a less developed country in which people illegally establish residences on land they do not own or rent and erect homemade structures.
Greenbelts
A ring of land maintained as parks, agriculture, or other types of open space to limit the sprawl of an urban area.
Smart Growth Policies
Legislation and regulations to limit suburban sprawl and preserve farmland.
Rank-Size Rule
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the nth largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest settlement.
Metacity
A city with a population over 20 million
Edge City
cities that are located on the outskirts of larger cities and serve many of the same functions of urban areas, but in a sprawling, decentralized suburban environment
Informal Economy Zone
Economic activity that thrives with curbside, car-side, and stall based businesses that often hire people temporarily and do not follow all regulations; part of the economy that is not taxed
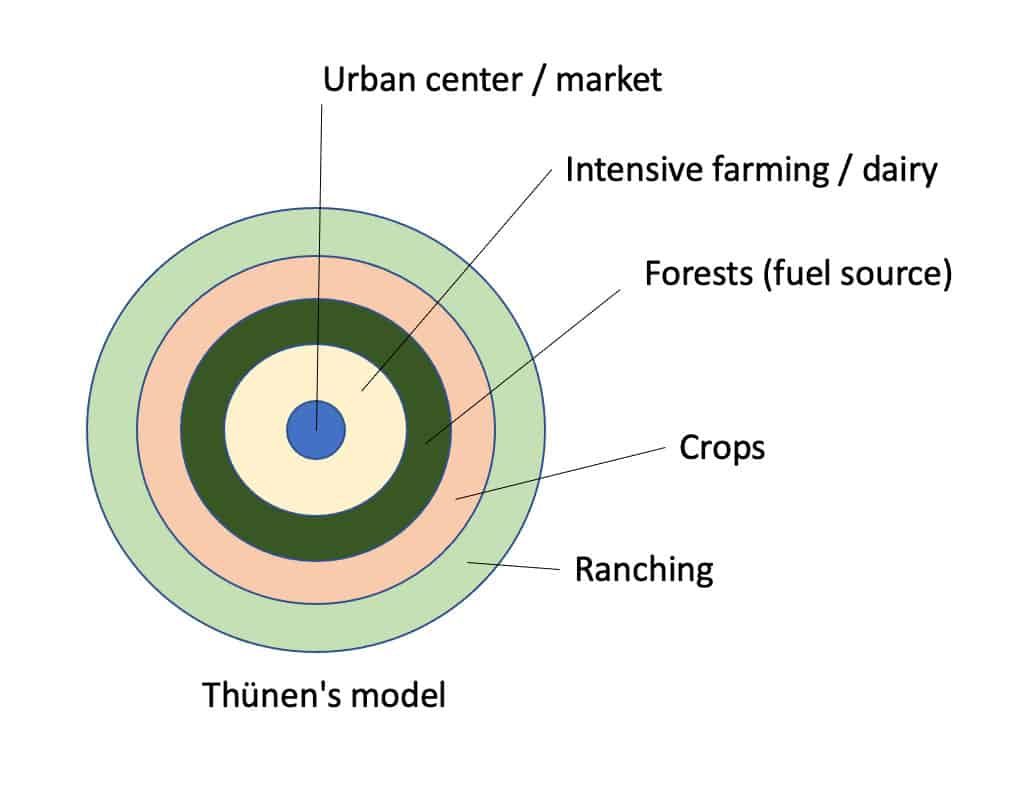
Von Thunen Model
A model that explains the location of agricultural activities in a commercial, profit-making economy.
Mediterranean climate
Weather pattern characterized by mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers
tropical climate
hot humid climate that produces certain plants, such as cassava, banana, sugar cane, sweet potato, papaya, rice, maize
subsistence agriculture
The production of food primarily for consumption by the farmer's family.
commercial agriculture
Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm.
intensive agriculture
expenditure of much labor and capital on a piece of land to increase its productivity. high input / small area
extensive agriculture
An agricultural system characterized by low inputs of labor and capital per unit land area. Low input / big area
pastoral nomadism
A form of subsistence agriculture based on herding domesticated animals.
shifting cultivation
A form of subsistence agriculture in which people shift activity from one field to another; each field is used for crops for relatively few years and left fallow for a relatively long period.
plantation (agriculture)
Production system based on a large estate owned by an individual, family, or corporation and organized to produce a cash crop.
mixed crop and livestock farming
Commercial farming characterized by integration of crops and livestock.
market gardening
The small scale production of fruits, vegetables, and flowers as cash crops sold directly to local consumers.
Livestock ranching
An extensive commercial agricultural activity that involves the raising of livestock over vast geographic spaces.
Mediterranean agriculture
specialized farming that occurs only in areas where the dry-summer Mediterranean climate prevails
transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.
clustered settlements
A rural settlement in which the houses and farm buildings of each family are situated close to each other and fields surround the settlement.