learning and memory
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what is learning?
the response of the brain to environmental events and involves adaptive changes in synaptic connectivity which will then alter behaviour; strengthening and weaking synaptic connections in the brain provides a means by which learning occurs and memories can be formed
describe Hebb’s (1949) hypothesis for how the brain can process and store info
cells that fire together, wire together

describe how associations are formed
initially an individual input might not be sufficient to stimulate the hippocampal neuron (the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is not great enough to fire an action potential)
if this association is made repeatedly, the synapses of cell A and cell B onto the hippocampal neuron will be strengthened so that the individual inputs are strong enough to fire the hippocampal neuron
what is long term potentiation (LTP)?
the mechanism underlying synaptic strengthening
properties of long term potentiation
temporal - summation of inputs reaches a stimulus threshold that leads to the induction of LTP
input specific - LTP at one synapse is not propagated to adjacent synapses
associative - simultaneous stimulation of a strong and weak pathway will induce LTP at both pathways
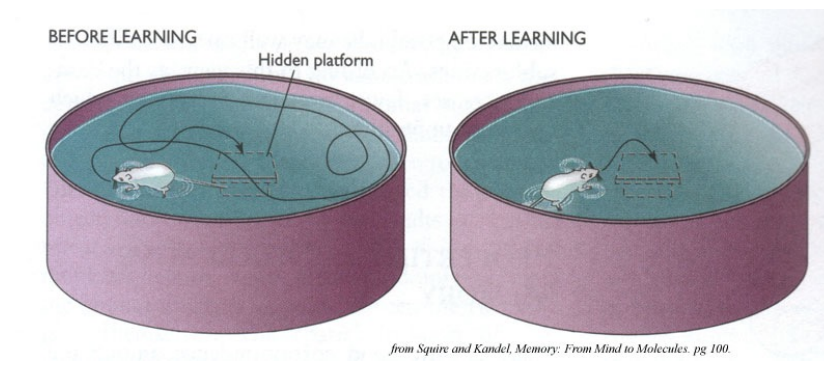
describe the Morris Water Maze test
test of spatial learning
hidden platform in a pool of water
place a rat in the apparatus and it uses cues from the environment to figure out how to escape the water via the platform
trials are repeated and the rat learns to immediately swim to the platform
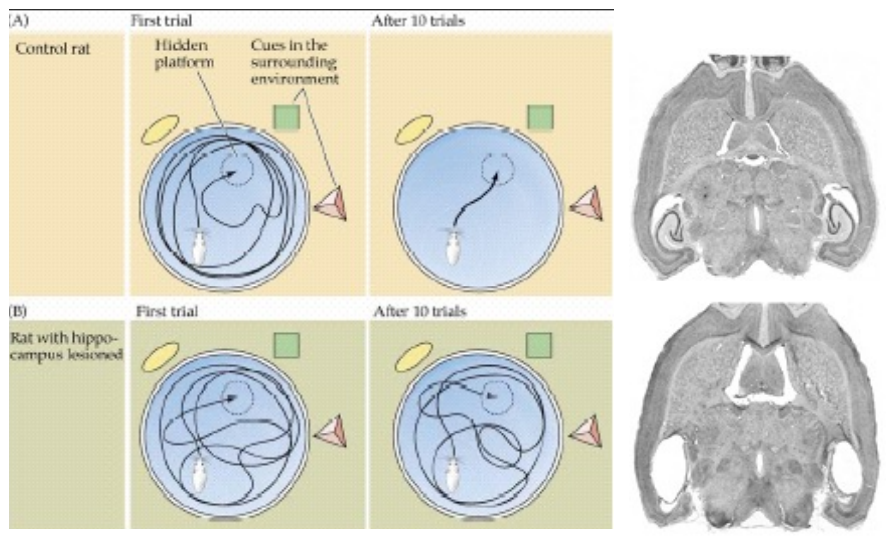
lesion studies with the Morris Water Maze
rats with hippocampal lesions do not improve after multiple trials (doesn’t learn)
glutamate at its receptors in normal neuronal transmission
glutamate is released from a presynaptic terminal and lands on different types of glutamate receptor (AMPA AND NMDA) in the postsynaptic terminal
the AMPA receptor will then open channel and there will be a flux of sodium into the post-synaptic neuron
when binding to the NMDA receptor, there is a magnesium ion inside the channel that blocks any movement of ions through the channel
EPSP only comes through the AMPA receptors
glutamate at its receptors when the postsynaptic membrane is in an excited state
the membrane is going to be depolarised
the magnesium is going to be ejected out of the NMDA receptor
now able to activate both the AMPA and NMDA receptors
influx of sodium and calcium into the postsynaptic neuron, getting a much bigger EPSP
what is happening at the synapse with an inactive cell?
glutamate release onto inactive cell (membrane at resting potential)
AMPA receptor activated to create EPSP
NMDA receptor blocked by Mg2+ ion
depolarisation from AMPA activation not sufficient to expel Mg2+
what is happening at the synapse with an active cell?
glutamate release onto an active cell (membrane depolarised)
AMPA receptor activated
Mg2+ block on NMDA receptor is relieved
Na+ through AMPA and NMDA channels
Ca2+ through NMDA channel
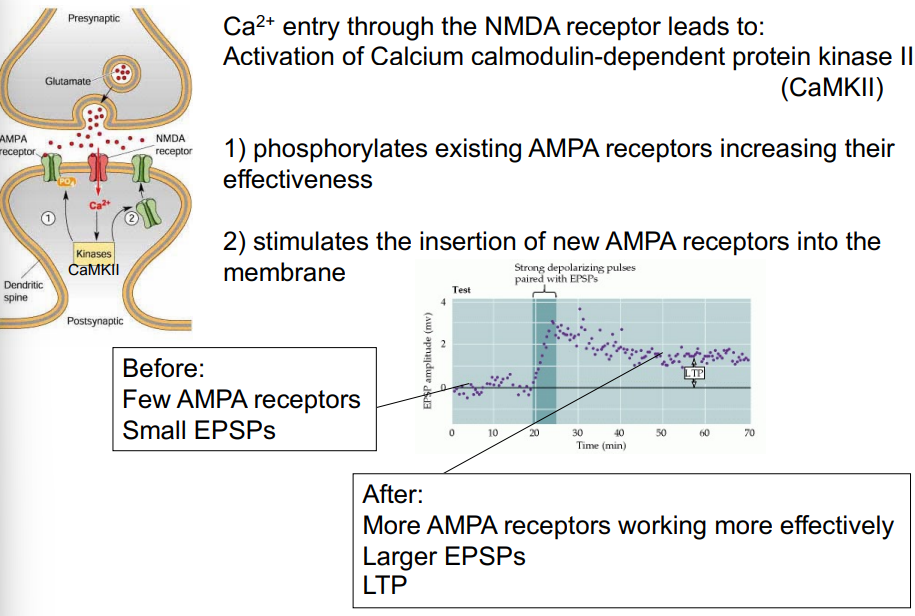
describe activation of calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII)
Ca2+ entry through the NMDA receptor leads to activation of CaMKII
CaMKII has autocatalytic activity - becomes phosphorylated
when phosphorylated it is continuously active and no longer requires Ca2+
maintains phosphorylation, insertion of AMPA receptors etc. after the depolarising stimulus has receded
what is CaMKII?
a molecular switch which maintains increased excitability of neuron for minutes to hours
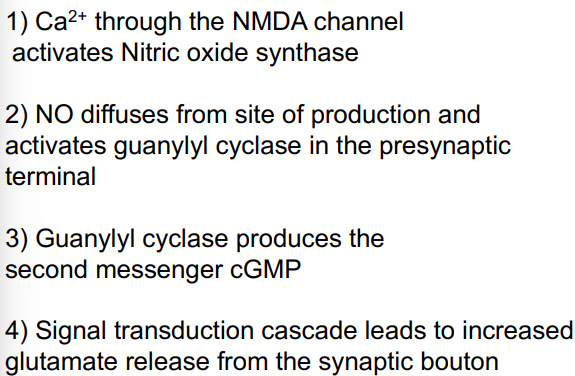
describe presynaptic events in LTP
postsynaptic neurons can feedback to presynaptic neurons by retrograde neurotransmitter - Nitric Oxide (NO)
describe the involvement of protein synthesis on late phase LTP
required of long-lasting LTP
protein synthesis inhibitors prevent the consolidation of long-term memories and LTP
protein synthesis inhibitor injected post-acquisition inhibits recall - necessary for consolidation

describe early phase LTP
lasts a minute to an hour
explained by the actions of Ca2+ through the NMDA receptor and subsequent enhancement of AMPA receptor efficiency presynaptic events etc.
describe late phase LTP
lasts for hours, days or months
requires new protein synthesis and can involve morphological changes and the establishment of new synapses
what is long term depression (LTD)?
acts as an opposite to LTP
weakens synapses instead of strengthening them
NMDA dependent process
AMPA receptors are dephosphorylated and removed from the membrane
low level rises in Ca2+ activate phosphatase rather than kinase

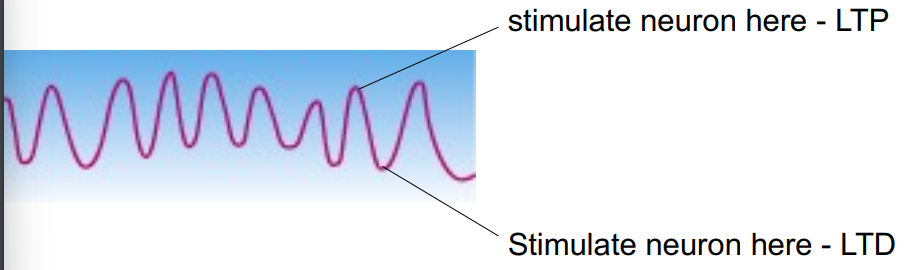
what are theta rhythms?
a type of brain waves in the hippocampus where cells in a brain area are activating in a pattern in that brain area over time
hippocampal theta activities accompanies behaviours such as running, swimming, head movements and spatially orientated responses in the rat (seems to play a role in synchronising activity in different brain regions
is LTP physiological?
waves of neuronal activity (hippocampal theta rhythms) involved in arousal, alertness, fire during explosion etc.
depolarising stimulation coincident with peak of wave generates LTP
depolarising stimulation coincident with trough generates LTD
disruption in theta waves causes deficits in learning tasks that are similar to those cause by hippocampal lesions
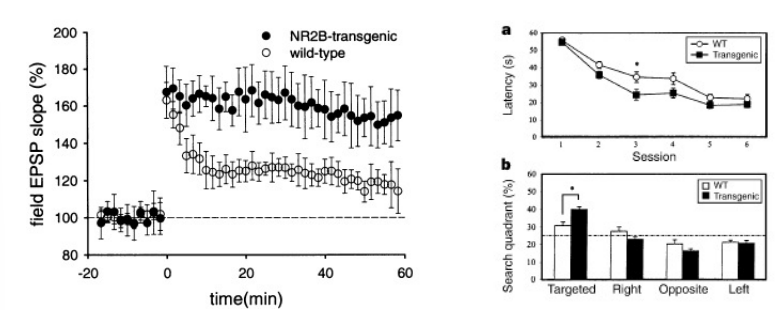
enhancing LTP
genetically - increased amounts of a particular type of the NMDA receptor (NR2B receptor) leads to enhanced LTP
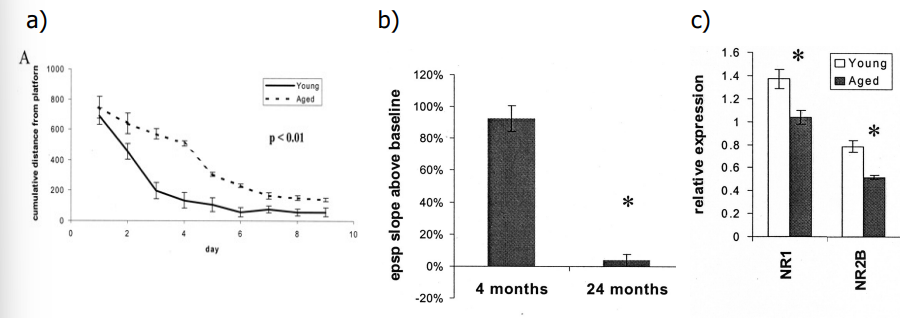
diminished memory and LTP
age - decreased acquisition in the Morris Water Maze; decreased LTP; decreased expression of the NMDA receptors
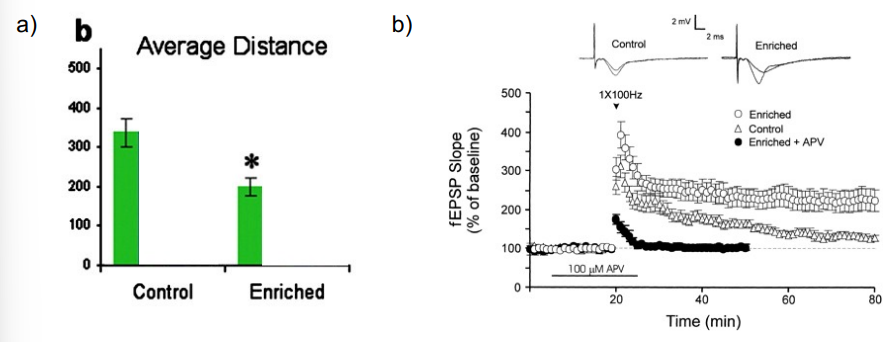
enhanced memory and LTP
enrichment - enhanced acquisition in the Morris Water Maze; potentiated LTP
reversal of aging effects by enrichment - spatial maze task (aged mice in impoverished environment (IE) show greater deficits than those in normal (SE) or enriched environment (EE))
what are the neuronal mechanisms underlying conditioned fear?
synaptic connections in the amygdala
strong input from the unconditioned stimulus leads to depolarisation of the postsynaptic cell
weak input from the conditioned stimulus is ‘strengthened’ by the postsynaptic depolarisation leading to activation of NMDA receptors leading to long-term potentiation of this synapse