Earth's Water Resources Flashcards
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards reviewing key vocabulary and concepts from a lecture on Earth's Water Resources.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Freshwater
Less than 2.7% of global water.
Ice caps and glaciers
Where most freshwater is locked in
Water Cycle Reservoirs
The volume of water stored in various parts of the water cycle (oceans, ice caps, groundwater, etc.)
Major Water Reservoirs
Oceans, ice caps & glaciers, groundwater, lakes, soil moisture, atmosphere, streams & rivers, biosphere
Water Cycle
The continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
Hydrologic Cycle
Evaporation, transpiration, sublimation, condensation, precipitation, infiltration.
Major Saltwater Reservoirs
Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, Arctic
Salinity
The saltiness of saltwater, mainly due to sodium and chloride ions.
Seawater Salinity Range
Varies from 33 to 37 parts per thousand.
Ocean Zones
Littoral, Neritic, Oceanic, Benthic
Ocean Temperature Zones
Surface layer (warm, low density), thermocline (rapid temperature decrease), deep zone (uniformly low temperature).
Surface Level
Consists of relatively warm, low density water, extends from the ocean surface to a depth of 100 m. This is the home of most marine plants and animals
Thermocline
Temperature decreases rapidly with depth.
Deep Zone
The temperature low
Thermohaline Circulation
Located in deep zone which is controlled by temperature and salinity. This circulation is propelled by the sinking of cold, salty, and dense water in the Polar Regions and rising of the warm, less salty water of the tropics.
Glacier
Permanent body of ice consisting of recrystallized snow.
Ice Sheet
Mass of glacial land ice extending more than 50,000 km2.
Ice Cap
Miniature ice sheets, covering less than 50,000 km2.
Ice Shelf
Thick slab of ice attached to a coastline, extending over the ocean
Permafrost
Frozen soil, rock, or sediment for more than two consecutive years.
Surface Water Reservoirs
Streams, lakes and wetlands
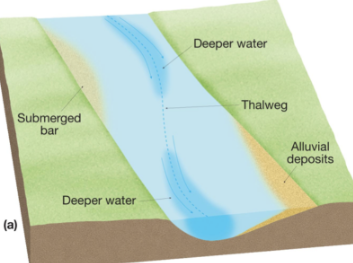
Stream
Moving body of surface water flowing downslope toward sea level.
River
Is larger than a stream.
Stream
is shallower than a river.
Creek
is a small stream of water that is inland. It is more turbulent than a stream
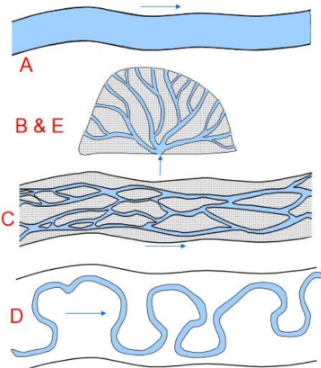
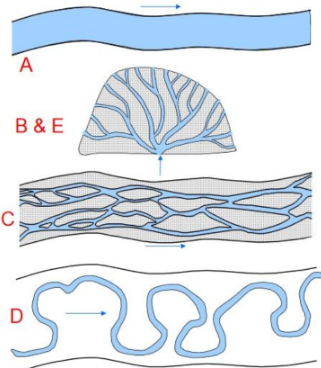
Stream Structures
(A) Straight channel, (B) alluvial fans, (C) braided streams, (D) meandering streams, (E) deltas.
Straight channel
Streams occur toward the heads of rivers and at places they cross high ridges. They are often in canyons, though the “canyon” may not be very deep
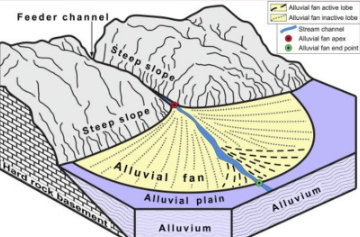
Alluvial fans
occur at places a stream leaves a
relatively steep area and enters a nearly flat one. The form is very similar to “E”, and for the same reason. If a stream never sees such a drastic change in gradient then no fan will be formed.

Braided streams
Have multiple channels that repeatedly branch and join along the length (“anastomose”) creating many longitudinal bars between the channels. These are usually found close to high mountains and so some streams do not have any braided parts.


Meandering streams
Wander in big loops across a wide flat
floodplain bounded by valley walls.
These are characteristic of lowlands
and so if mountains are too close to
the sea this state may never develop


Deltas
occur where streams enter a standing body of water -- the ocean, usually. If the ocean processes move the sediment as fast as it arrives then no delta will form.

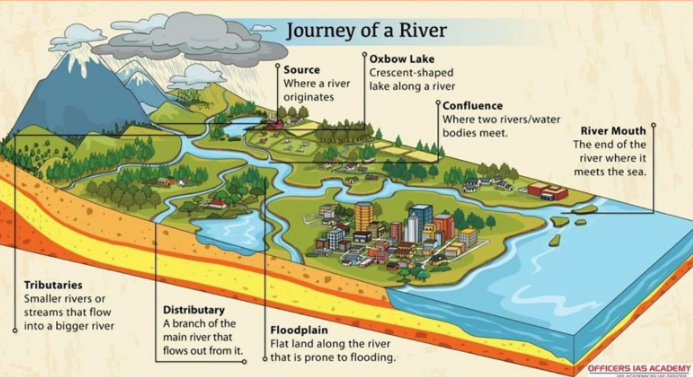
River Components
Source, tributaries, confluence, distributary, floodplain, oxbow lake, river mouth.
Watershed/Drainage Basin
it is a land area in which the water flow into a particular stream.

Lakes
Surface is exposed to the atmosphere and is essentially flat. Water in them came from streams, overland flow and groundwater.

Ponds
Small and shallow lakes.
Dams
Barriers constructed along streams to contain the flow of water.

Wetlands
are land areas where water covers the surface for significant periods. They are biologically diverse environments filled with species that rely on both the land and water for survival.


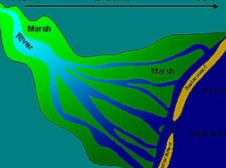
Marsh
Shallow wetlands around lakes, streams, and oceans where grasses and reeds are the dominant vegetation


Swamp
Wetland with lush trees and vegetation, often found beside slow-moving rivers. Mangrove forests are unique example of the ecosystem that tolerates salty conditions.

Estuary
Partly enclosed coastal body of water where freshwater meets saltwater from the sea. It is home to many organisms that can tolerate the sharp changes in salinity due to constant change in salt content.

Groundwater
Freshwater found in rock and soil layers beneath the surface; largest reservoir of liquid freshwater.
Aquifers
Water-bearing rock layers that hold groundwater in tiny cracks, cavities, and
pores
Aquifer Types
Unconfined aquifer, Confined aquifer and Artesian well
Unconfined Aquifer
Aquifer in which groundwater is free to rise to its natural level
Confined Aquifer
Water is trapped and held down by pressure between impermeable rocks
Artesian Well
Well that doesn’t require a pump to bring water to the surface due to pressure in the aquifer.
China, India, South Africa and Middle East
These countries will face water shortage in the next 20 years
Desalination
Removal of salt from seawater to produce freshwater
The Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004 (R.A. No. 9275)
Protect the country’s water bodies from pollution from land-based sources
Evaporation
Part of the hydrologic cycle where liquid water turns into vapor.
Transpiration
Part of the hydrologic cycle where water is carried through plants from roots to small pores on leaves, where it changes to vapor and is released to the atmosphere.
Sublimation
Part of the hydrologic cycle where a solid turns directly into a gas.
Condensation
Part of the hydrologic cycle where water vapor turns into liquid water.
Precipitation
Part of the hydrologic cycle where water falls from clouds as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Infiltration
Part of the hydrologic cycle where water seeps from the surface into the ground.
Source
The origin point of a river.
Tributaries
Smaller streams or rivers that flow into a larger river.
Confluence
The point where two rivers or streams meet.
Distributary
A branch of a river that flows away from the main channel, typically on a delta.
Floodplain
A flat area of land alongside a river that is subject to flooding.
Oxbow Lake
A crescent-shaped lake along a river
River Mouth
The point where a river flows into a lake, sea, or ocean.