Anatomy of the Thorax: Osteology and Muscles of the Thoracic Wall
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
spinous process of T1
In the normal standing position, the cranial scapular angle is next to what thoracic anatomy?
bodies of T4-5
In the normal standing position, the caudal scapular angle is next to what thoracic anatomy?
ventral end of first rib
In the normal standing position, the shoulder joint is next to what thoracic anatomy?
below ventral end of 5th intercostal space
In the normal standing position, the olecranon is next to what thoracic anatomy?
1.) form and protect the thoracic cavity
2.) serve as muscular attachments
Two functions of bones of the thorax
1.) thoracic vertebrae
2.) ribs
3.) sternum
Three types of bones of the thorax
central axis of the body that is made up of vertebrae containing the spinal cord
Vertebral column
50
Approximately how many vertebrae are present in the dog spine?
C7, T13, L7, S3, C20-23
Vertebral formula in the dog
1.) vertebral body
2.) vertebral arch
3.) vertebral foramen
4.) processes
Typical vertebrae consists of four structures:
main portion of the vertebra; thick bulky part of the vertebra
Vertebral body
ribs
costal fovea/demifacet
The vertebral body will articulate with the _______. What is this structure on the body called?
the dorsal part of the vertebra that arises from the body
Vertebral arch
1.) lamina
2.) pedicles
The vertebral arch consists of two structures:
left and right; form the roof (dorsal wall) of the vertebral column
lamina of vertebral arch
left and right; form the base (wall) of the vertebral foramen
pedicles of vertebral arch
surgery to remove the lamina of the vertebral arch; helps to decompress the spinal cord by enlarging the vertebral canal/foramen
Laminaectomy
hole in a single vertebra created by the vertebral body and vertebral arch
Vertebral foramen
canal formed by successive vertebral foramen; houses the spinal cord
Vertebral canal
formed between adjacent vertebrae within the column; space that allows spinal nerves to travel from the spinal cord to the periphery
Intervertebral foramen
processes
The vertebral arch has several bony _____________
1.) transverse
2.) spinous
3.) articular
Three processes of the vertebra:
process jutting out horizontally from the vertebral body
transverse process
process jutting out vertically from the vertebral arch
spinous process
small projections at the junction of the lamina and pedicle that contact adjacent bone
articular process
an intervertebral disc
Adjacent vertebral bodies are connected by...
fibrocartilaginous structure that is interposed in every intervertebral space, uniting the bodies of adjacent vertebrae
intervertebral disc
1.) anulus fibrosus
2.) nucelus pulposus
Two parts of intervertebral disc:
outer circumferential collagenous fibers of intervertebral disc
anulus fibrosus of intervertebral disc
inner gelatinous core of intervertebral disc
nucelus pulposus of intervertebral disc
rupture of the intervertebral disc; causes the nucelus pulposus to leak out
Herniated disc
C1 and C2
An intervertebral disc is found between every vertebrae except for...
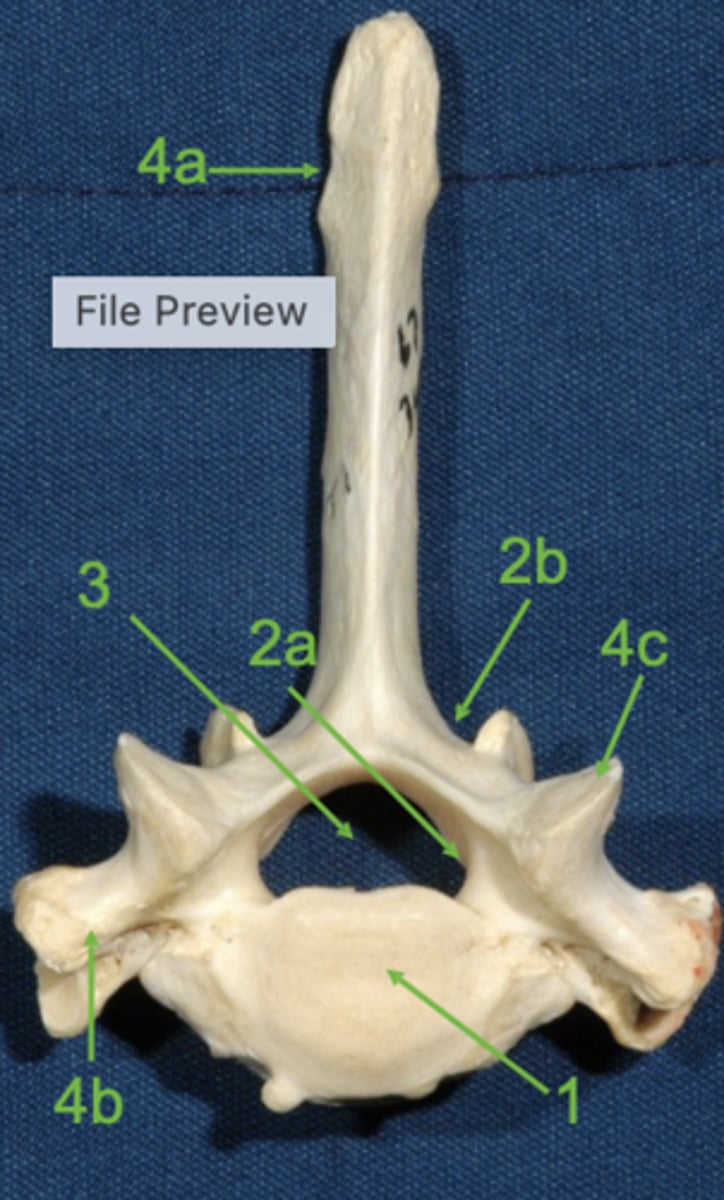
vertebral body
1
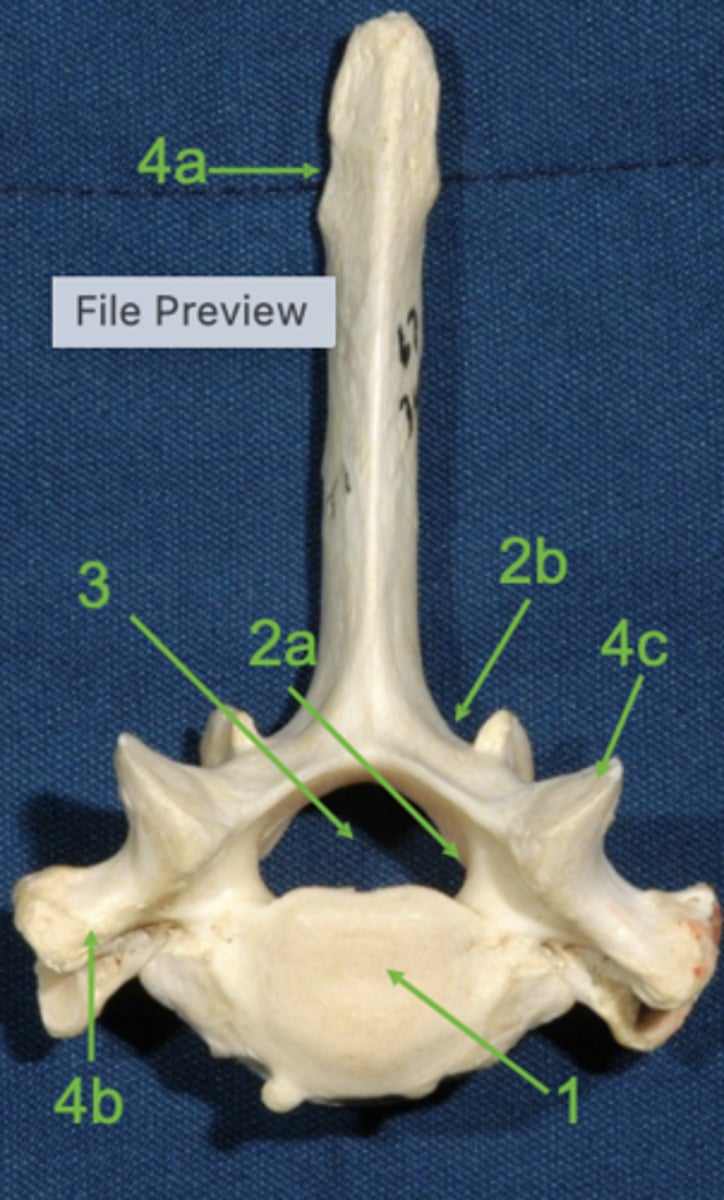
vertebral arch
2
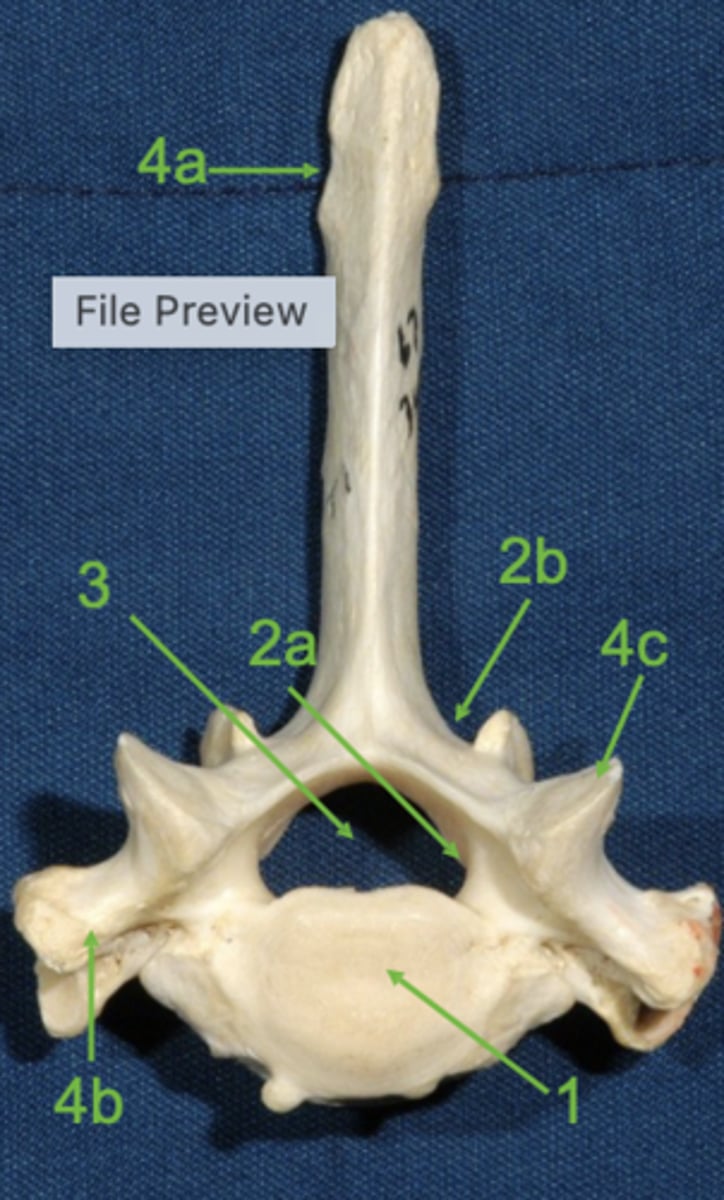
pedicle
2a
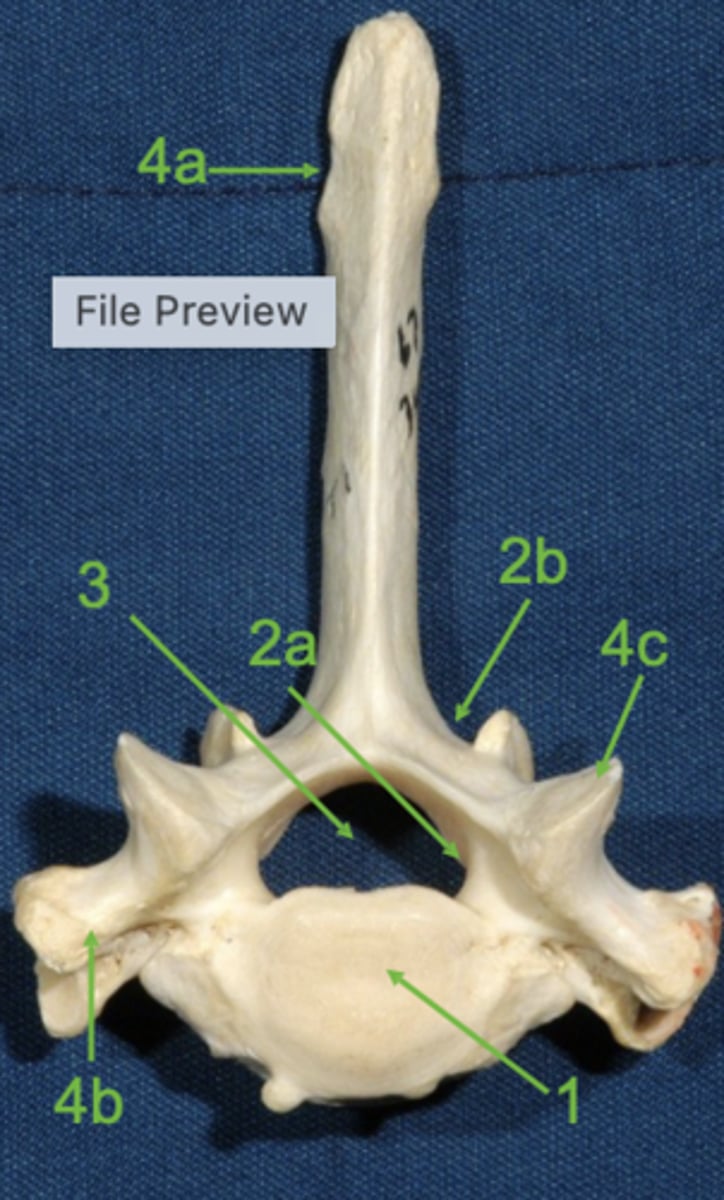
lamina
2b
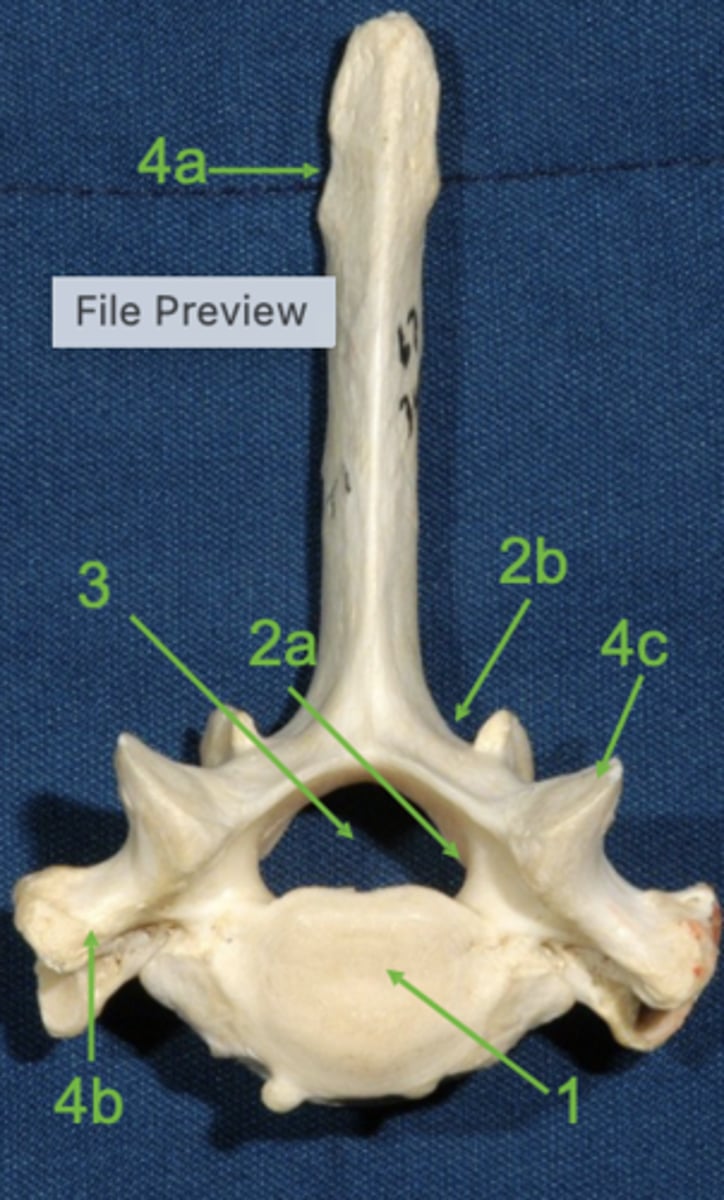
vertebral foramen
3
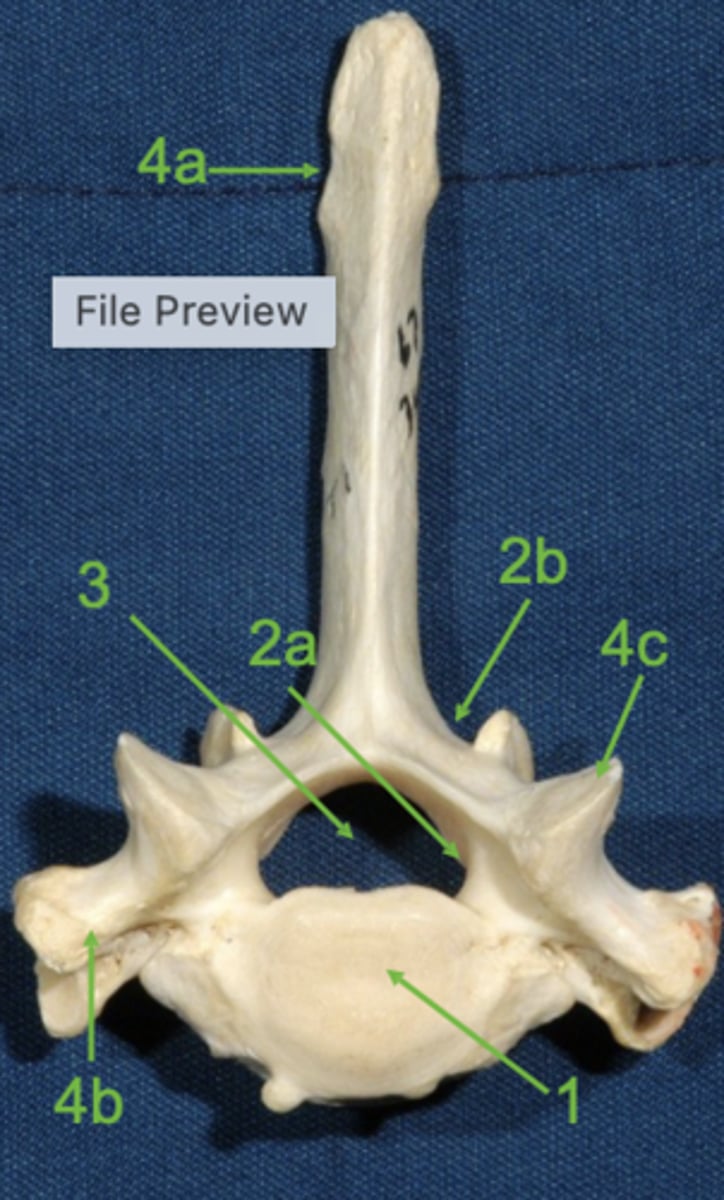
spinous process
4a
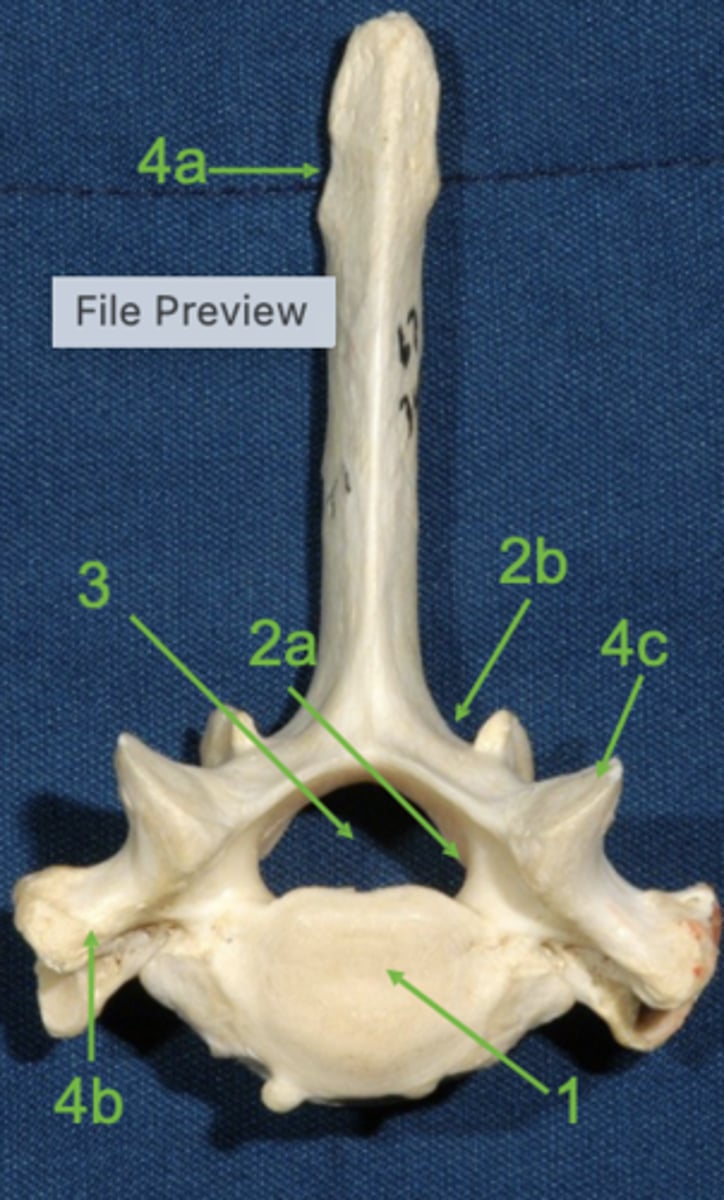
transverse process
4b
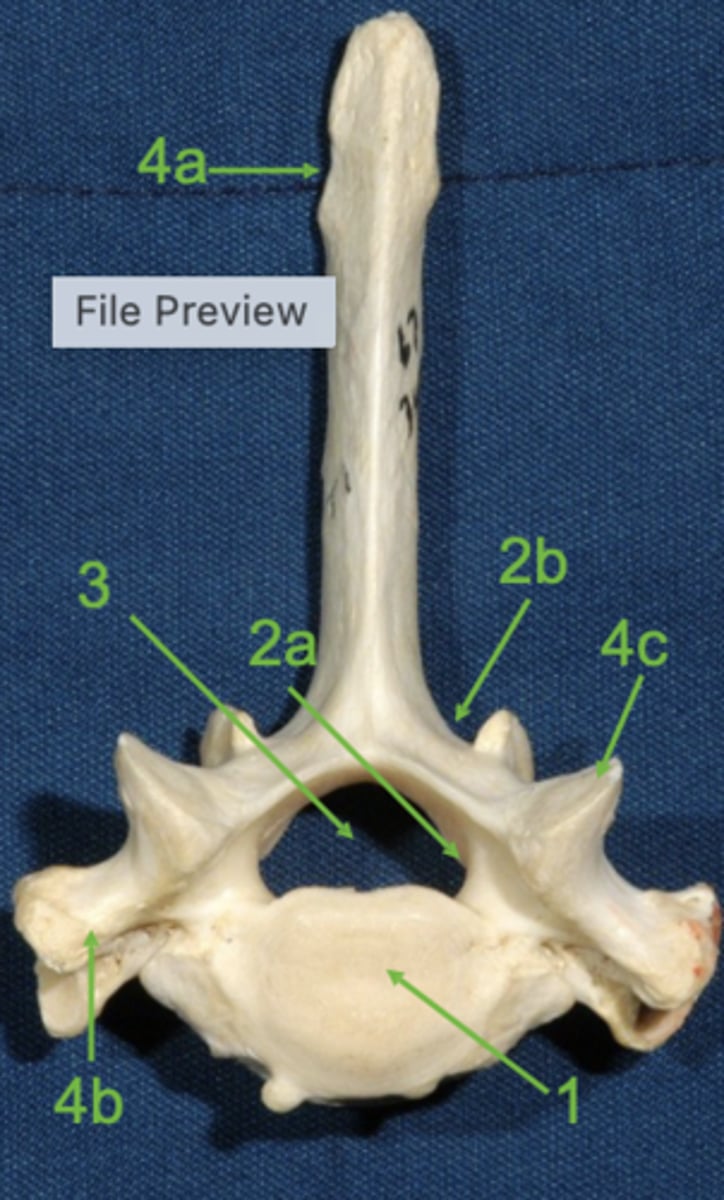
articular process
4c
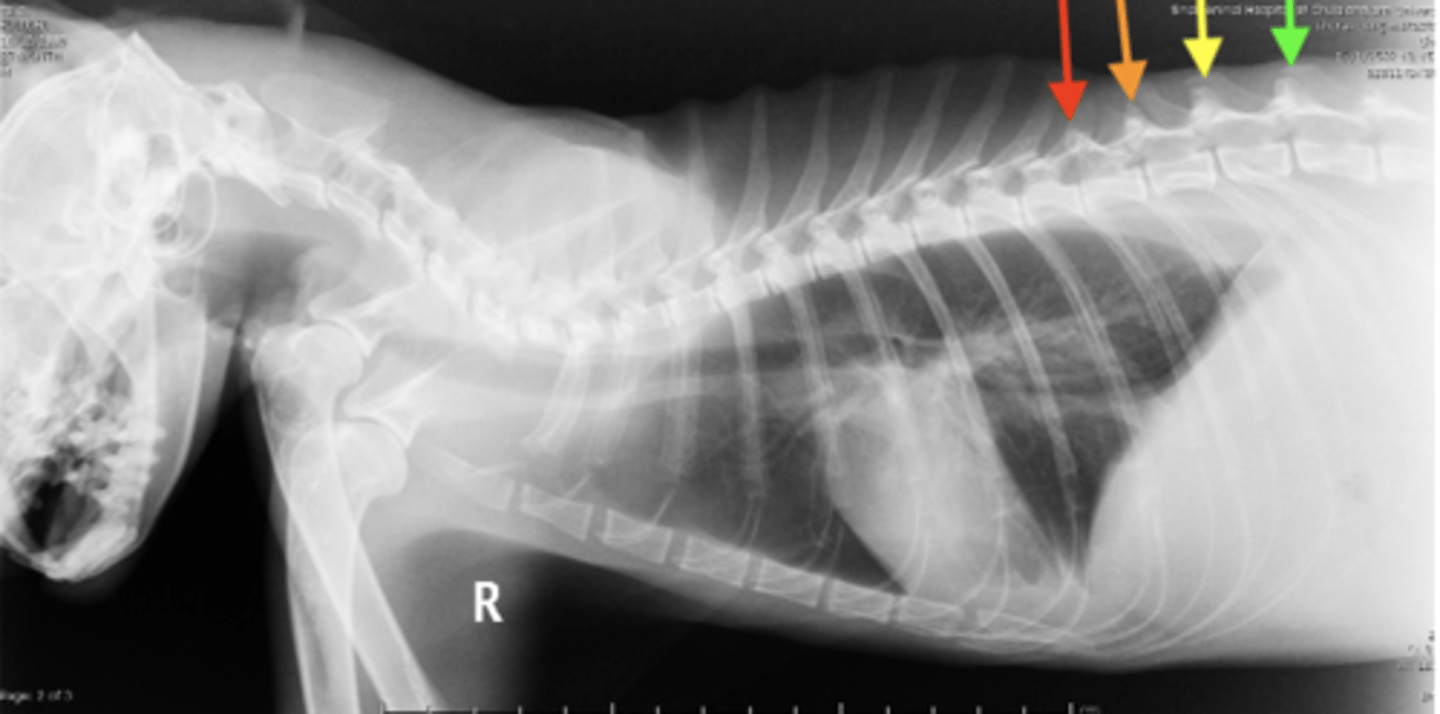
T11 vertebra
Anticlinal vertebra
radiographs; the spinous processes of T1-10 are angled caudally, but after T11, the anticlinal vertebra, the spinous processes are perpendicular to the body
The anticlinal vertebra can be used as a landmark in _________ of the thorax. Why?
yellow arrow
Where on this radiograph is the anticlinal vertebra?
bones in the chest that protect the heart and lungs
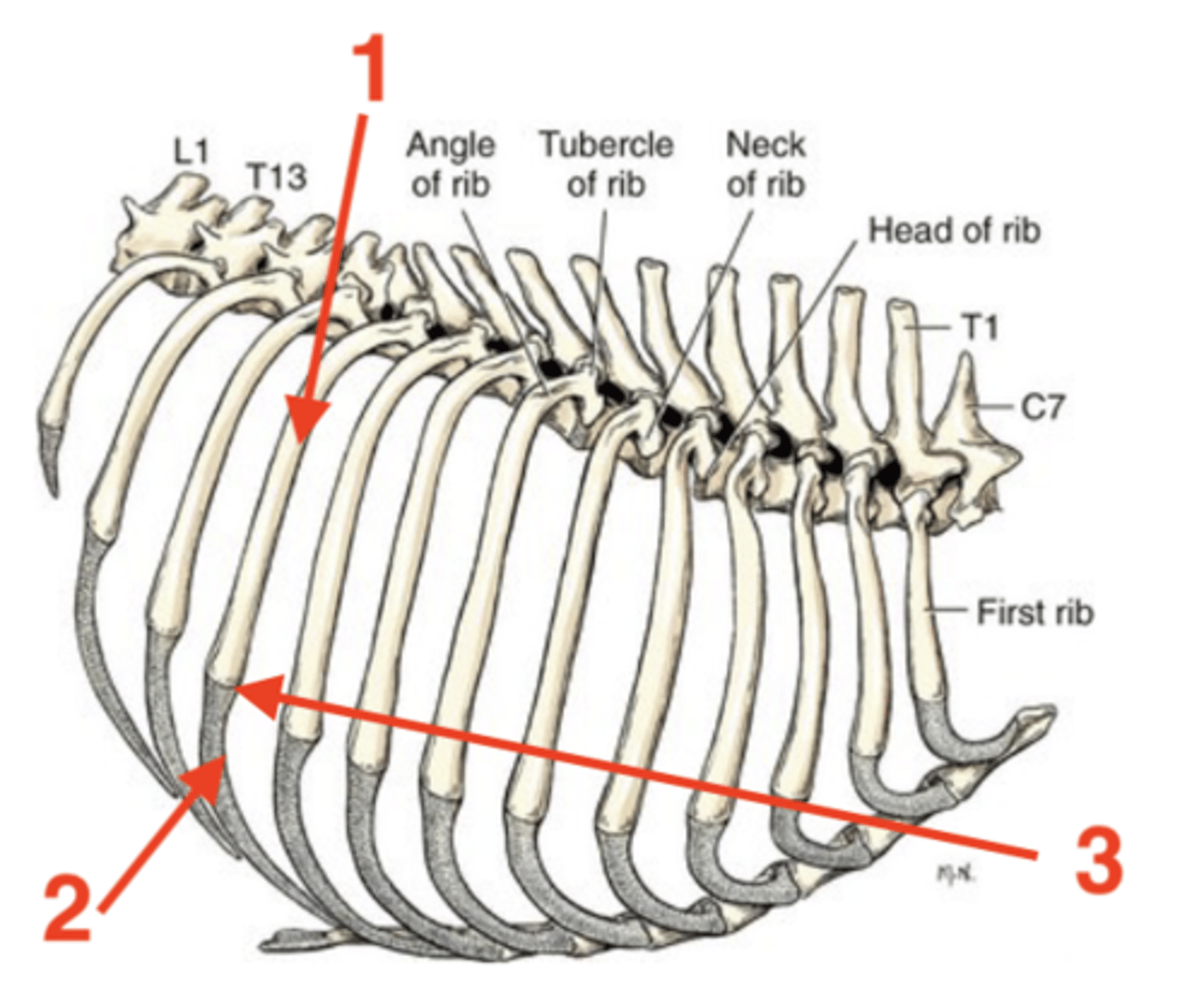
Ribs
13 pairs (26 total)
How many ribs are there in the dog?
1.) sternal ribs
2.) asternal ribs
Two types of ribs:
ribs that are directly attached to the sternebrae (ribs 1-9)
sternal ribs
ribs that are not directly attached to the sternebrae (ribs 10-13)
asternal ribs
the costal arch
Ribs 10-12 attach to the sternum via...
floating; it does not have a cartilaginous attachment to the sternum
Rib 13 is considered to be __________. Why?
1.) body
2.) costal cartilage
3.) intercostal space
4.) costochondral junction
Four parts of a rib:
dorsal bony part
body of rib
ventral cartilaginous part
costal cartilage of rib
space in between each of the ribs
intercostal space of ribs
junction between the body and costal cartilage of rib
costochondral junction
body of rib
1
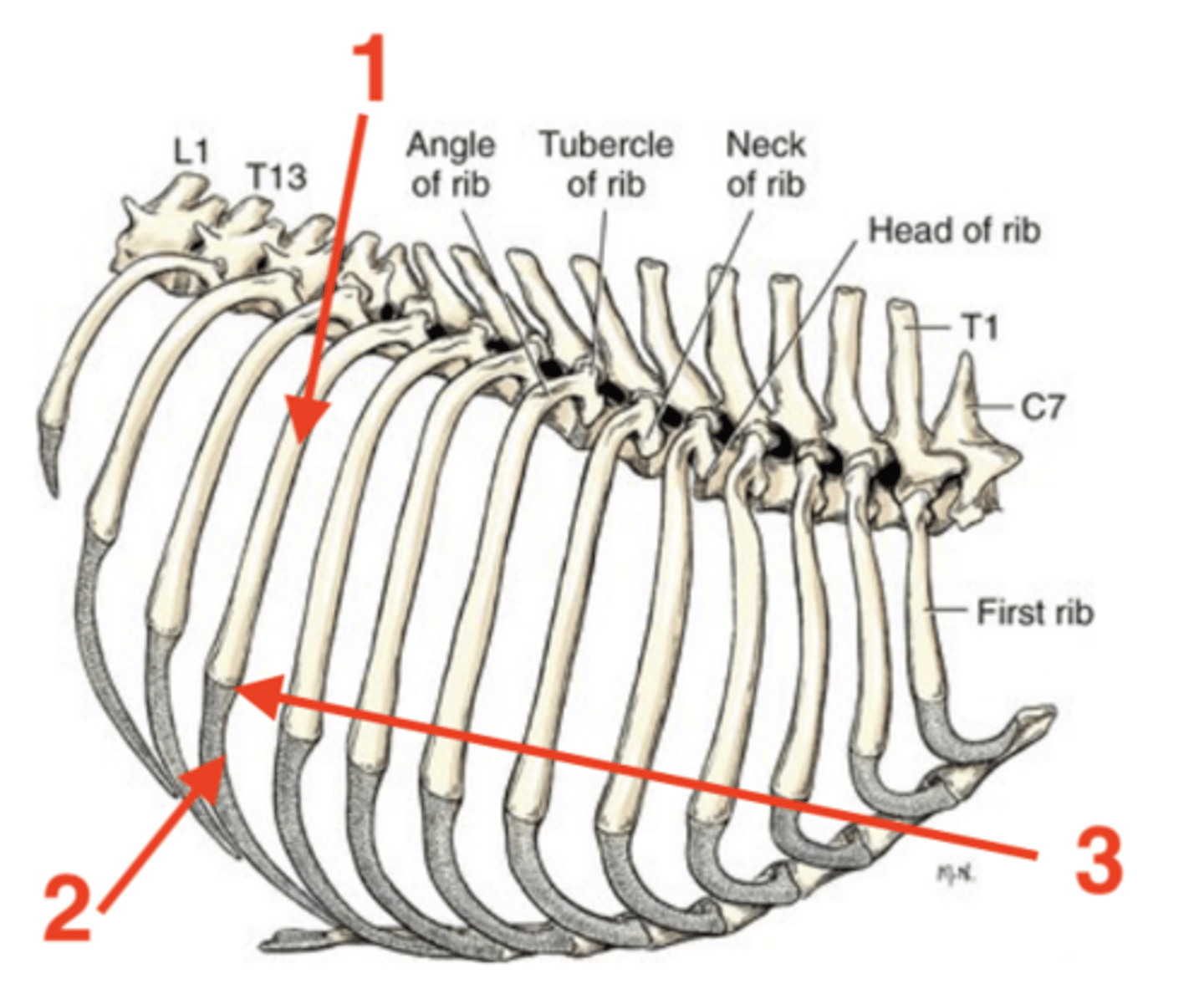
costal cartilage of rib
2
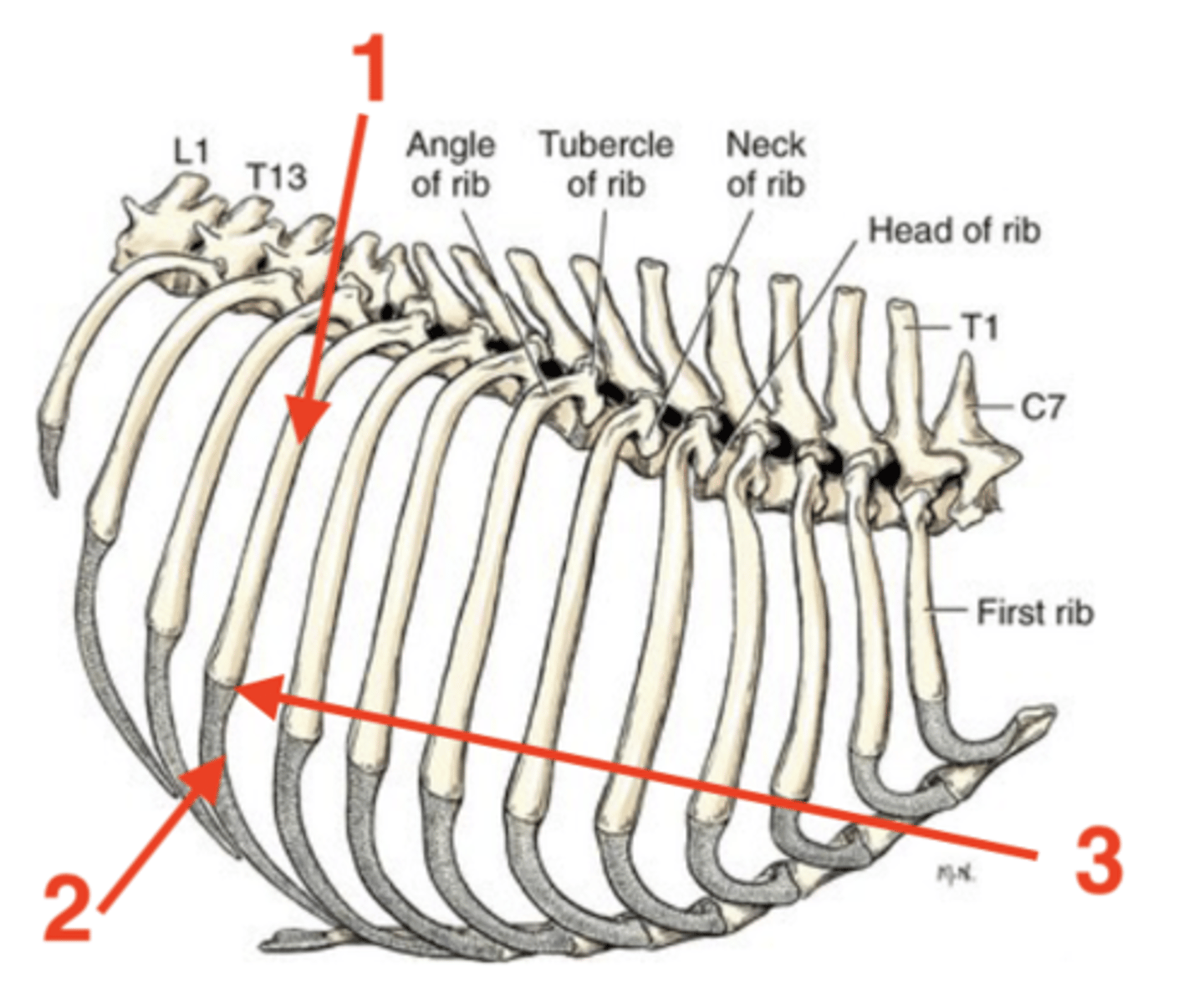
costochondral junction
3
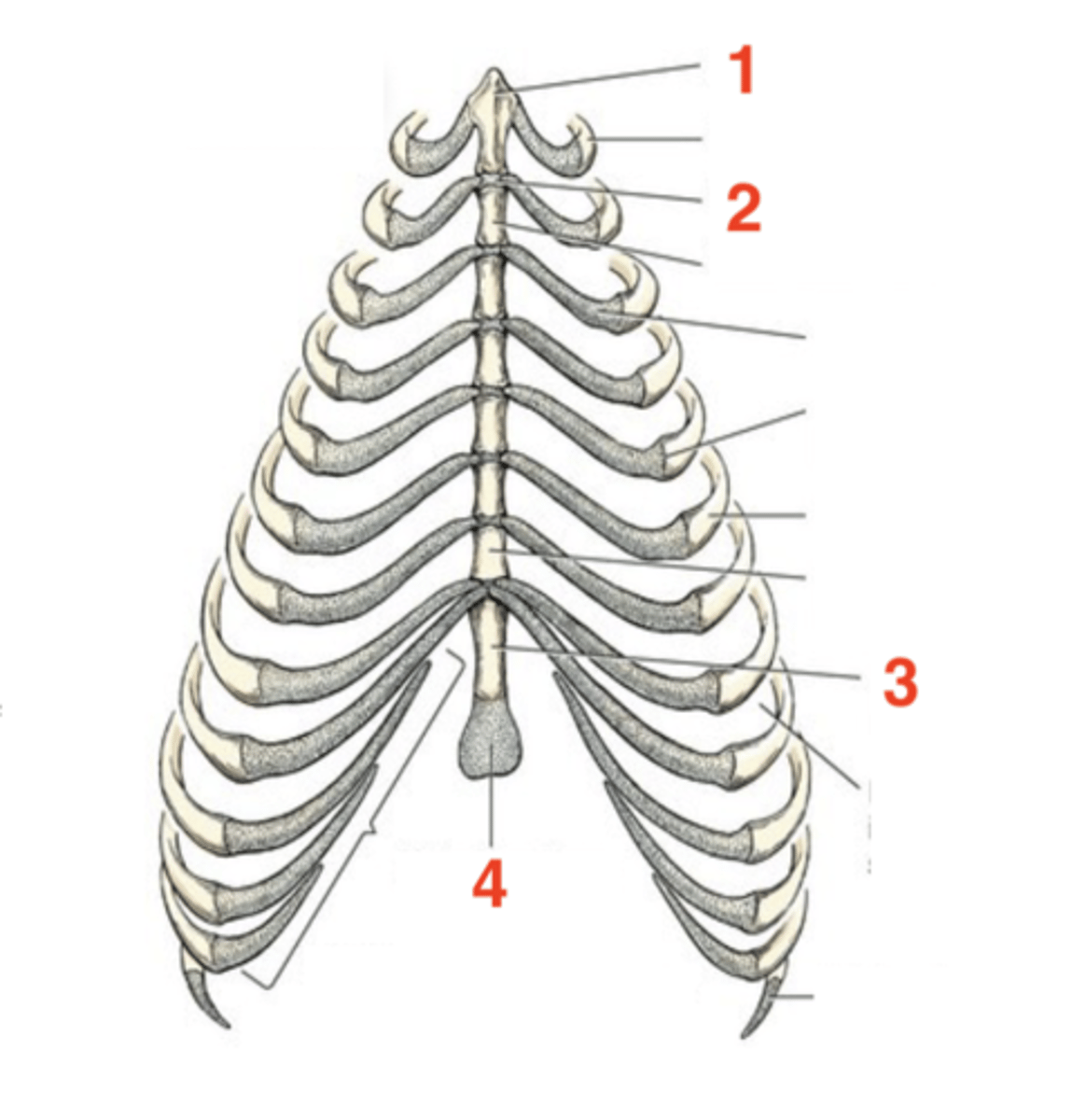
Sternum
located on the ventral floor of the abdomen
8
How many sternebrae are there?
1.) manubrium
2.) intersternebral cartilage
3.) xiphoid process
4.) xiphoid cartilage
Four structures of the sternum:
first sternebra
manubrium
cartilage that connects individual sternebra to each other
intersternebral cartilage
last sternebra
xiphoid process
cartilage process at the end of the xiphoid process
xiphoid cartilage
manubrium
1
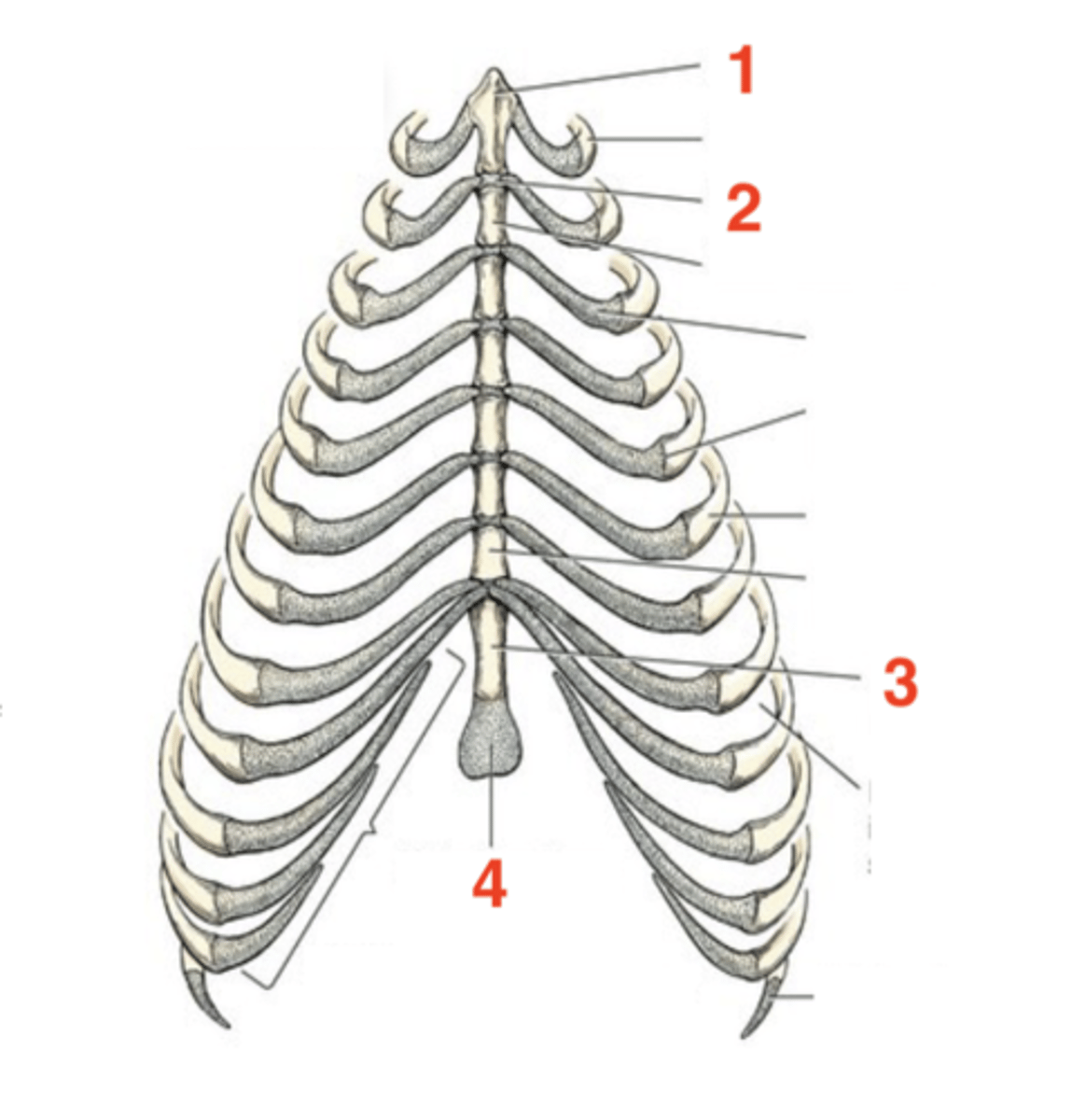
intersternebral cartilage
2
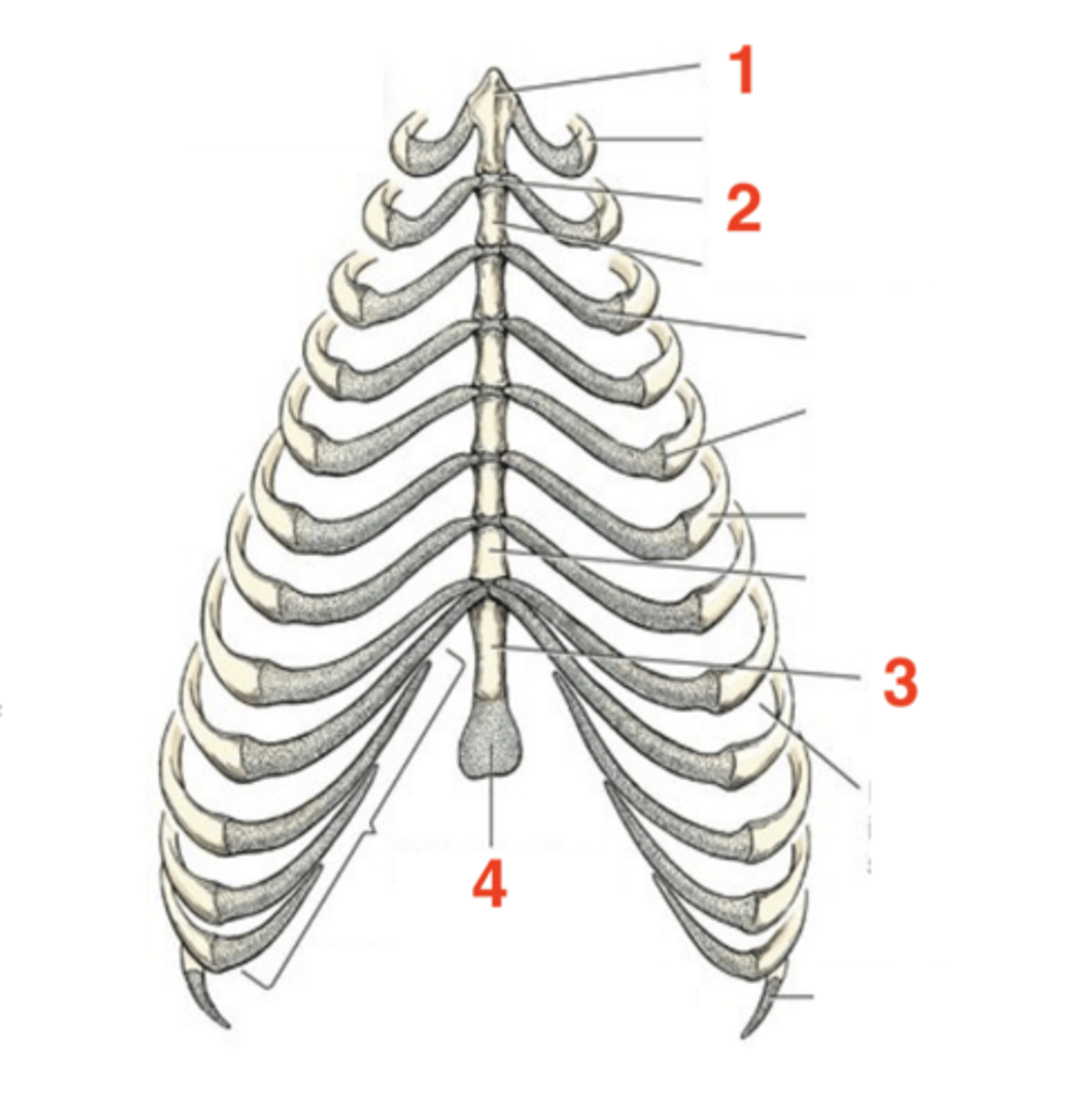
xiphoid process
3
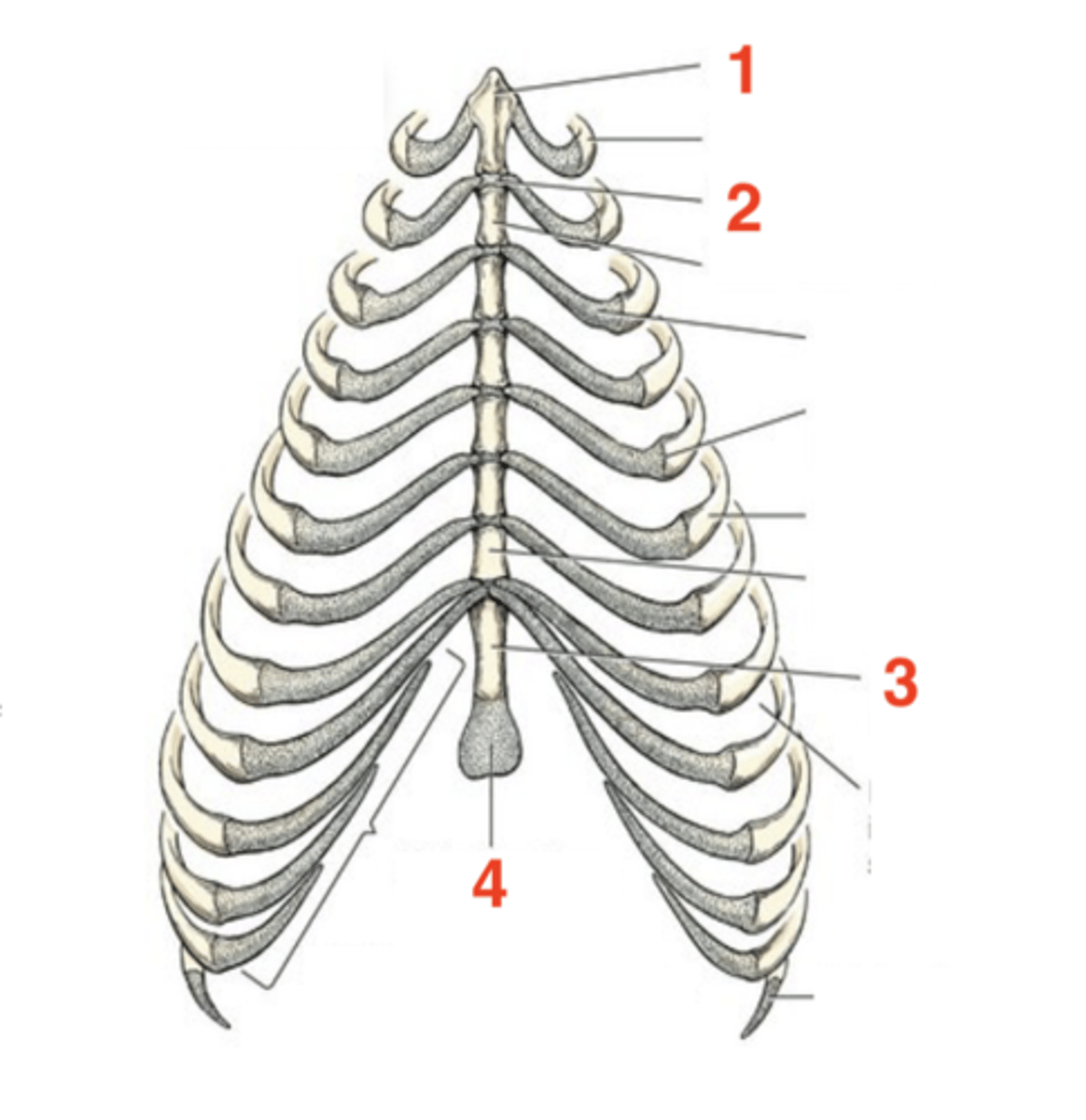
xiphoid cartilage
4
enshroud the thoracic cage and aid in respiration
Function of the thoracic wall muscles
1.) scalenus
2.) serratus ventralis
3.) serratus dorsalis cranialis
4.) serratus dorsalis caudalis
5.) external intercostal
6.) internal intercostal
7.) rectus thoracis
8.) transversus thoraci
Eight muscles of the thoracic wall
intercostal
All of the thoracic wall muscles are innervated by the _________ nerve
intercostal
All of the thoracic wall are supplied blood by the _________ artery
caudomedial
The intercostal nerve and arteries are located ____________ to each rib
caudal ventral
Muscles that aid in inspiration have fibers going in what direction?
1.) scalenus
2.) external intercostal muscle
3.) rectus thoracis
4.) serratus dorsalis cranialis
Four thoracic wall muscles involved in inspiration
cranial ventral
Muscles that aid in expiration have fibers going in what direction?
1.) internal intercostal
2.) transversus thoracis
3.) serratus dorsalis caudalis
Three thoracic wall muscles involved in expiration
supports the trunk
Serrtaus ventralis function
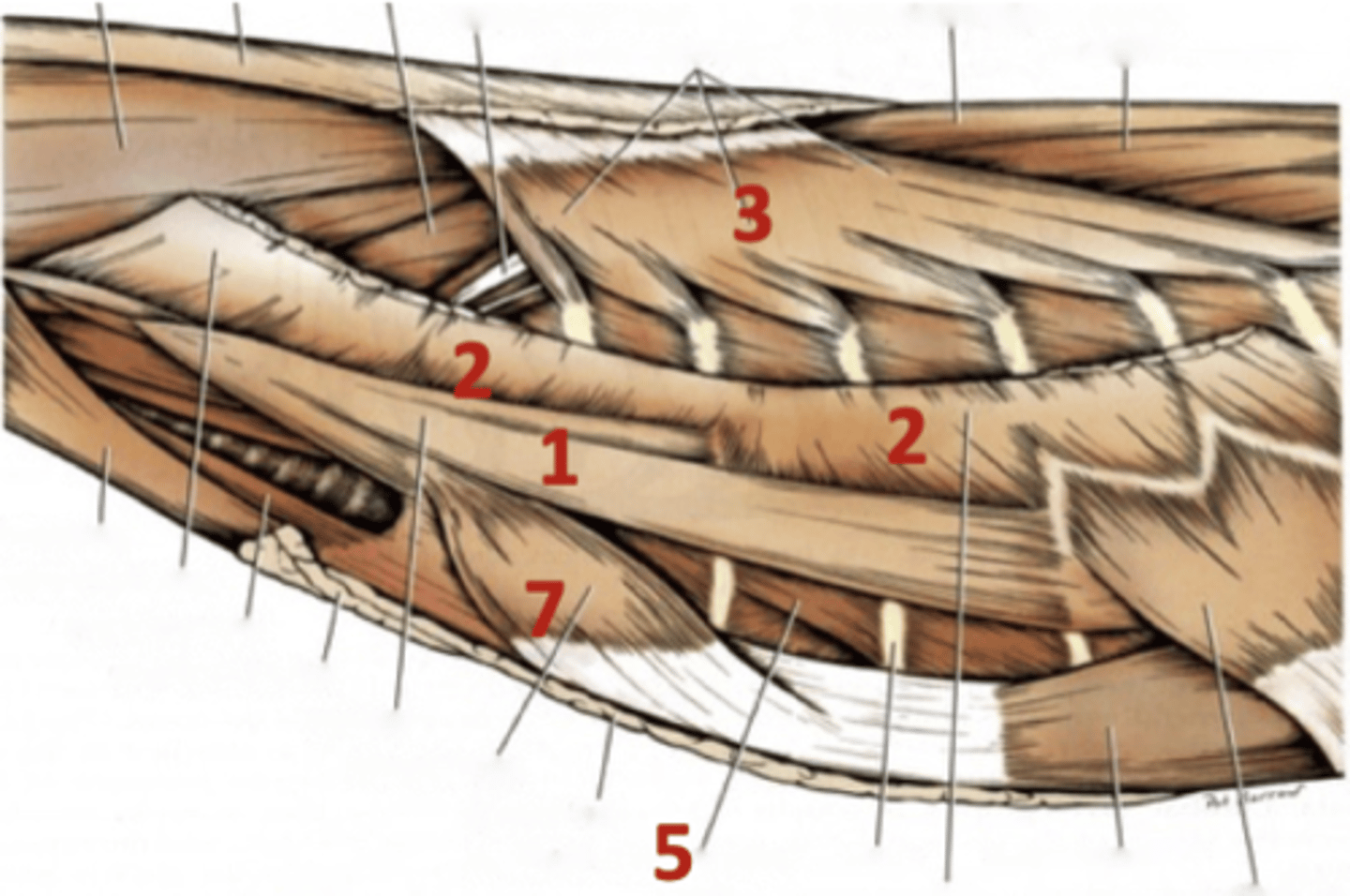
scalenus
1
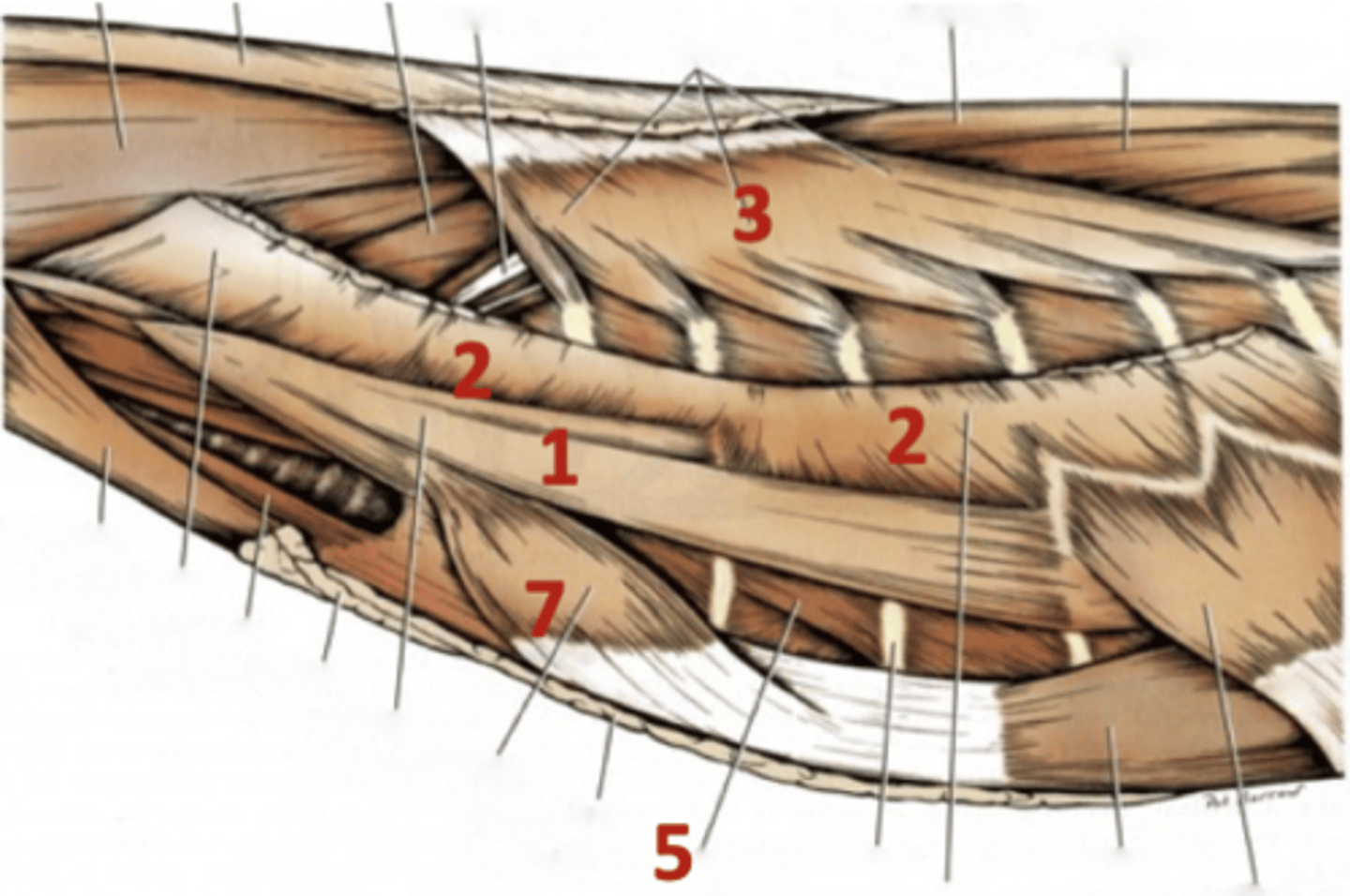
serratus ventralis
2
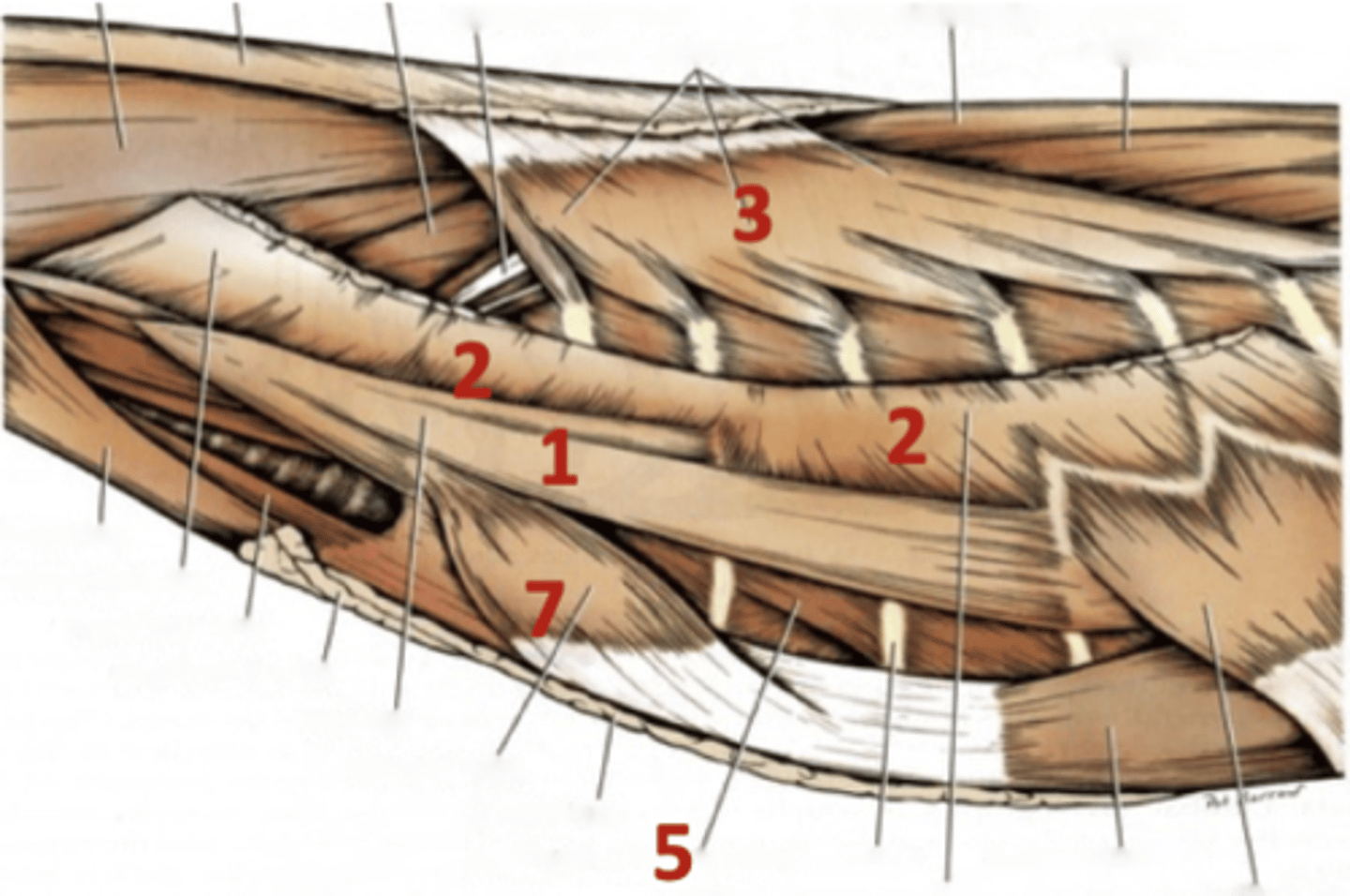
serratus dorsalis cranialis/caudalis
3

external intercostal
5
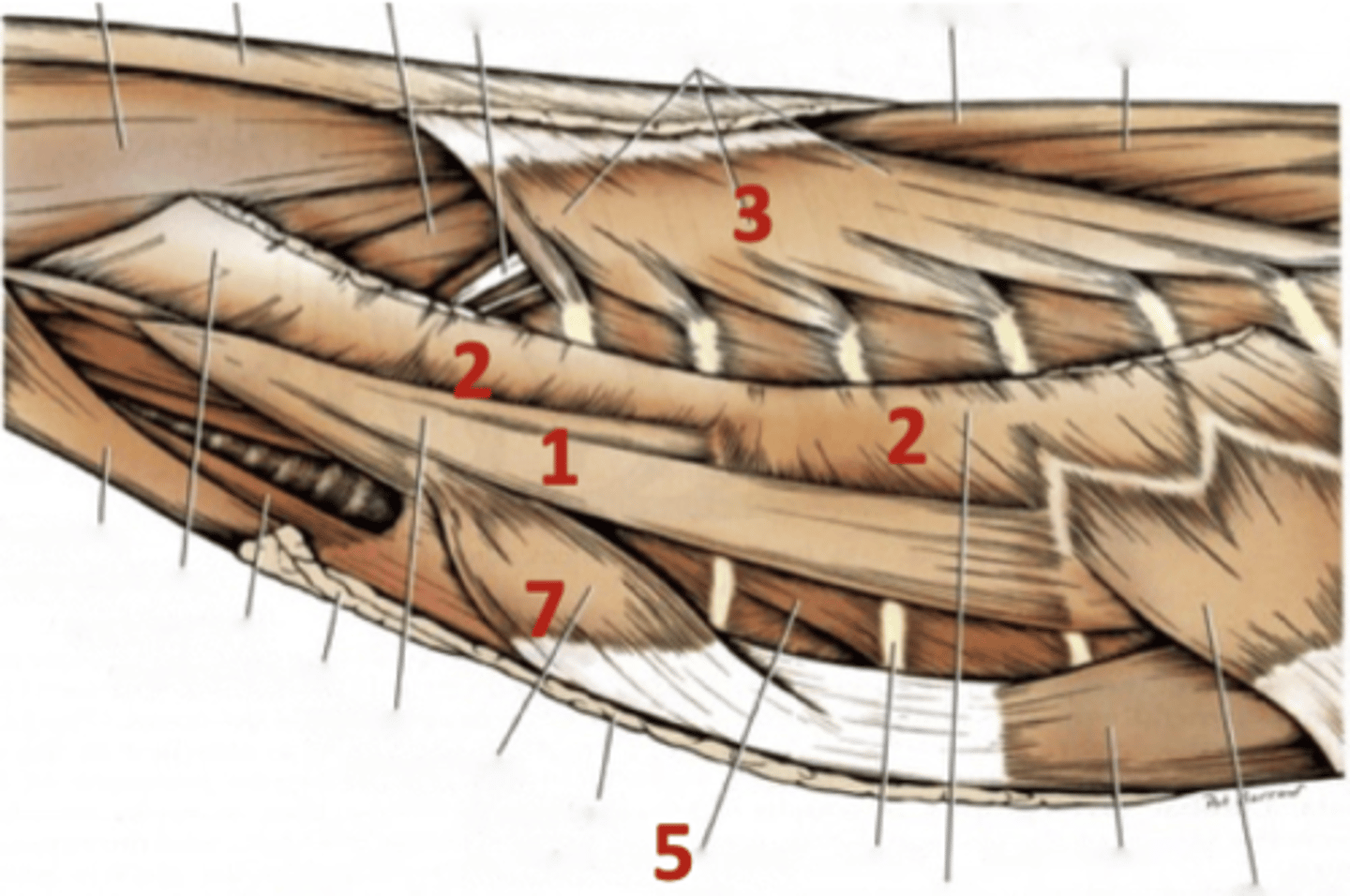
rectus thoracis
7