Units of the Body in Speech and Hearing Science: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Cell
smallest unit of living matter
Tissue
groups of cells with common function
Histology
a branch of anatomy dealing with the microscopic structure of tissue
Organ
two or more tissues with common function (e.g., heart, lung)
System
two or more organs combine in such a manner as to exhibit functional unity.
Connective Tissue
a type of tissue that supports, binds together, and protects tissues and organs of the body.
Muscle Tissue
a type of tissue that is responsible for the movement of the body and its parts.
Nerve Tissue
a type of tissue that transmits impulses throughout the body.
Epithelial Tissue
a type of tissue that covers the body surfaces and lines cavities and organs.
Soft Connective Tissue
includes loose and dense connective tissues, important for structural support.
Loose Connective Tissue
areolar (more delicate fibrous tissue found just beneath skin) and adipose (fat tissue).
Dense Connective Tissue
resisting stretch longitudinally (e.g., tendons, aponeuroses, ligaments).
Irregular Dense Connective Tissue
resisting stretch in all directions (e.g., dermis, periosteum, fascia).
Lymphatic Tissue
includes tonsils and adenoids.
Cartilage
developmentally, most of skeleton are cartilaginous in fetus; types include hyaline, fibrous, and elastic.
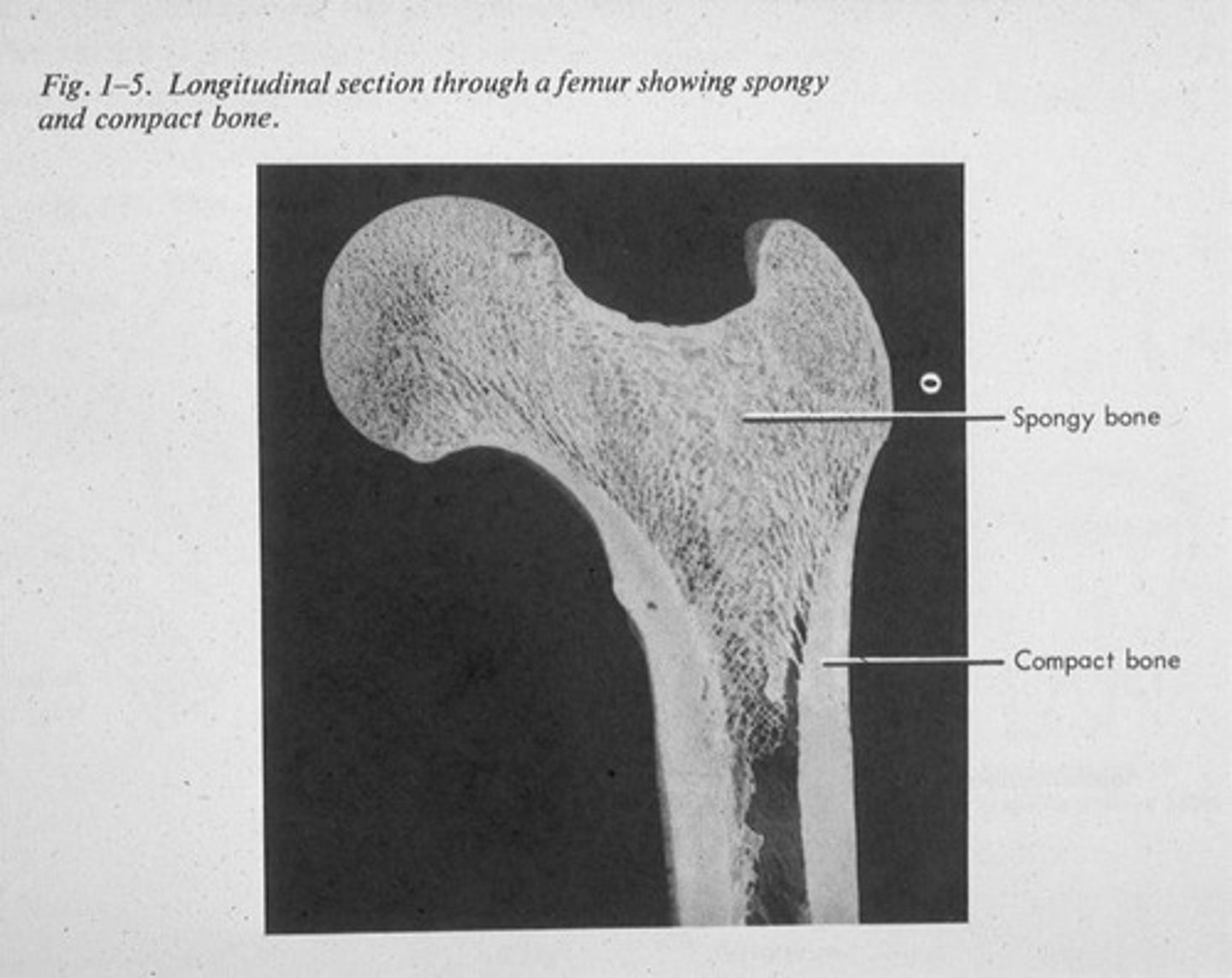
Bone (osseous tissue)
includes dense/compact part (outer part of bone) and spongy/cancellous part (interior part of bone).
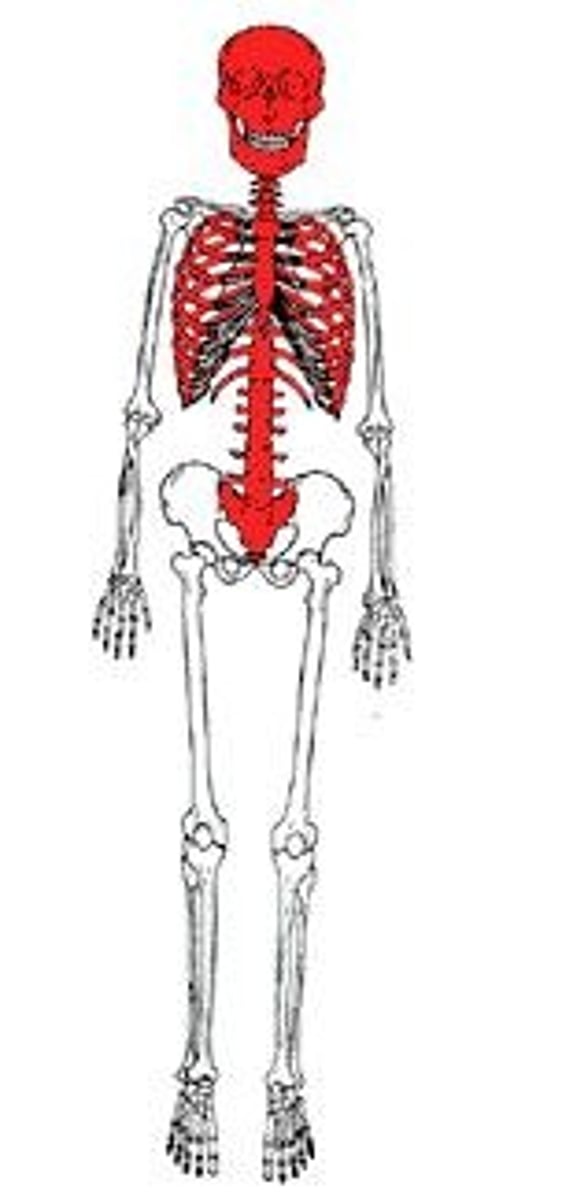
Axial Skeleton
includes trunk and head.
Appendicular Skeleton
includes limbs and immediately attached structures.
Fibrous Joint
immovable joints (e.g., joints in the skull).
Cartilaginous Joint
slightly movable joints (e.g., intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis).
Synovial Joint
freely moving joints, most common type in the body.
Ball and Socket Joint
great motion in all directions, many axes of movement (e.g., hip joint).
Hinge Joint
motion in only one plane (e.g., elbow, knee).
Pivot Joint
rotation along axis (e.g., atlas and axis).
Saddle Joint
all motion except rotation (e.g., thumb).
Condyloid Joint
two types of motion at right angle, no neck rotation or twisting (e.g., wrist).
Gliding Joint
sliding movement, least movement (e.g., vertebral articular processes).