Biology Study Set: Micro Week 2 Terms & Definitions
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
When did Cyanobacteria eveolve?
3 billion years ago
What are the names and shapes of bacteria?
Cocci - sphere shaped
Bacilli - rod shaped
Spirilli - spiral shaped
vibrio - comma shaped
What is the largest bacterial phyla?
B12 preoteobacteria
What bacterial phyla contains gram positive bacteria?
B13 Firmicutes
Where does crystal violet bind to?
Peptidoglycans
Why do we need to stain bacteria?
Staining bacteria adds color to the cells which makes them easier to see using a microscope. The stain is a dye that binds to a cellular structure and provide contrast so that the bacteria appear as colored object against a clear background.
What is the difference between gram negative and gram positive bacteria?
Gram negative bacteria have an inner and outer cell membrane while gram positive bacteria only have one cell membrane and more peptidoglycans on their surface
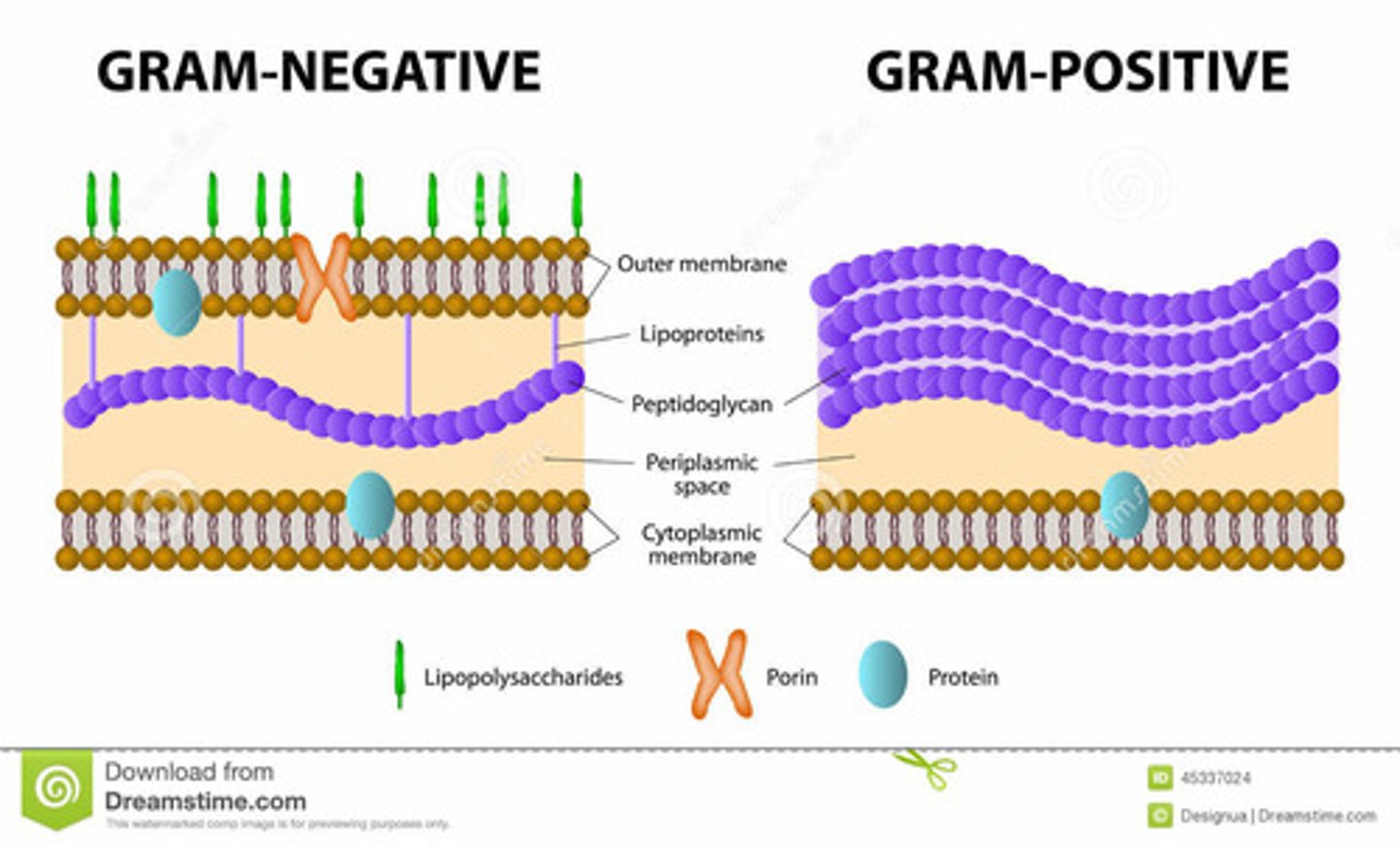
What is the function and purpose of peptidoglycans in bacterial cell walls?
- Provide shape
- withstand turgor pressure
What is a peptidoglycan made out of?
- Protein
- Polysaccharide
- Chains of alternating polysaccharide (NAG and NAM) crosslinked with peptides (DAP)
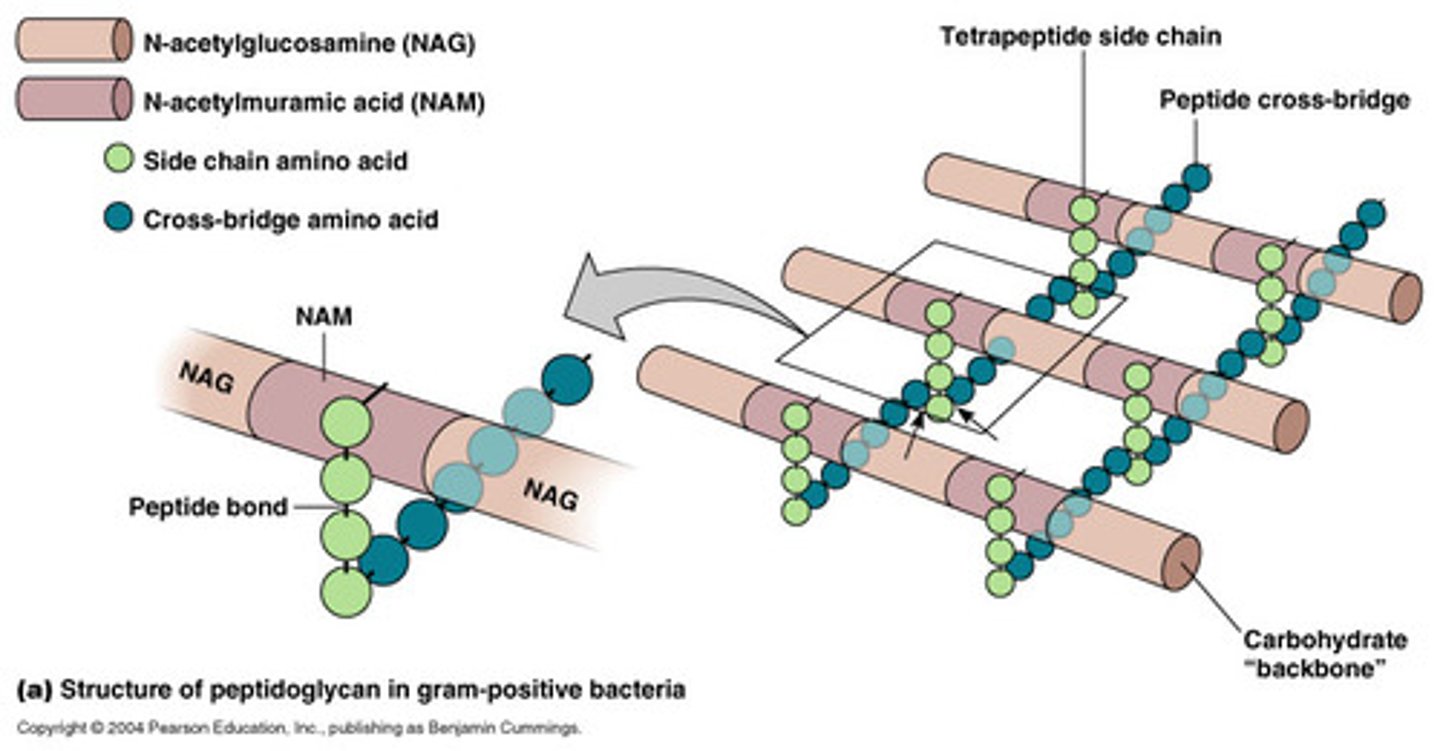
What connects peptidoglycan polysaccharides in gram positive bacteria?
Pentaglycine bridge
What connects peptidoglycan polysaccharides in gram negative bacteria?
m-DAP
What is the enzyme that cross links peptidoglycan chains?
Transpeptidases
Where do peptides bind on the peptidoglycans?
NAM
What is implied by transpeptidases being penicillin-binding proteins?
Penicillin is able to bind to these proteins and disrupt the structure of these bacteria
What are teichoic and lipoteichoic acids responsible for?
Attachment to mucosal surfaces
What can teichoic and lipteichoic acids do?
Induce septic shock by inducing IL-1 and TNF-a production in macrophages
What type of bacteria have teichoic and lipteichoic acid?
Gram positive
What is murein?
Peptidoglycan
What is in the periplasmic space of a bacteria?
-Proteases
-Phosphatases
-lipases
-nucleases
All enzymes relating to metabolism
Besides digestive enyzmes, what else does the periplasmic space of a bacteria contain?
Virulence factors such as collegenases and hyaluronidases which aid in infection of the host
What is the outer leaflet is composed primarily of?
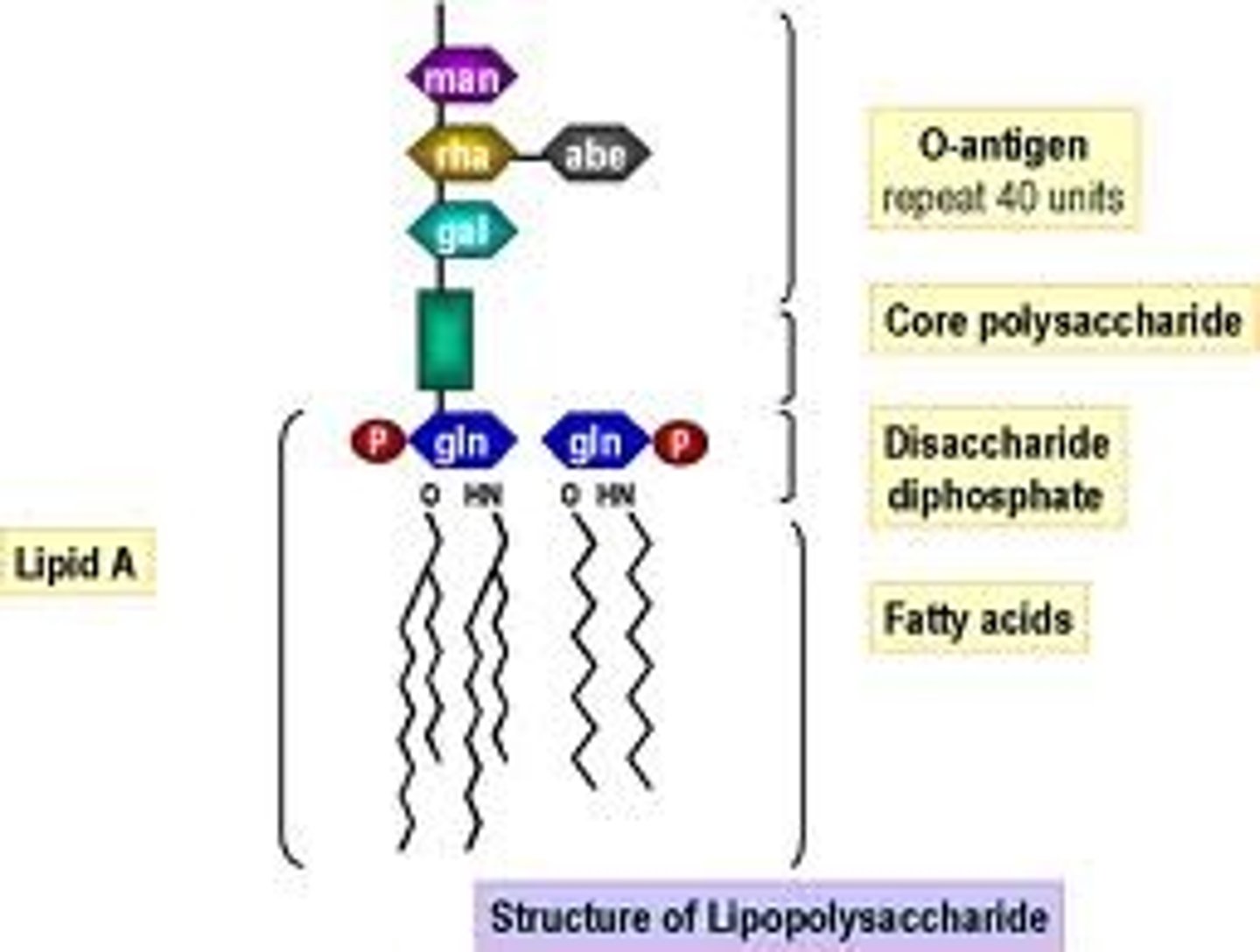
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
What are the segments of a lipopolysaccharide?
- Lipid A
- Core polysaccharide (sugars)
- O antigen (sugars)
What is the function of Lipid A in a lipopolysaccharide?
Responsible for endotoxin activity due to the 2 phosphate grounds on either side
Proteins known as ______ mediate the diffusion of hydrophilic molecules less than 700 Da in size through the external membrane of a gram negative bacteria.
Porins
What are the two types of secretion systems that gram negative bacteria have?
Sec-dependent
Sec-independent
What are examples of Sec-dependent systems?
Type II and Type V
What are example of Sec-independent systems?
Type I, III, and IV
What secretion systems microinject exotoxins into host cells?
Sec-independent Type III and IV
What is the bacterial capsule?
Gelatinous layer composed of polysachharides that mediates attachment
T or F
The capsule can be considered a virulence factor of bacteria.
True; the capsule can help bacteria escape phagocytosis
What structure plays an important role in the pathogenesis of UTIs by E. coli?
Flagella
How are salmonella species indentified?
By their flagella
Describe a flagella
Helical-shaped filament attached to a hook and an anchor that propels the flagella around to move the cell via locomotion
T or F
Bacteria may organize their cytoplasm into membraneless organelles.
True
What are pili?
Little hair like projections that mediate attachment
Do bacteria have a cytoskeleton?
Yes
When are endospores formed?
when essential nutrients are depleted
What is catabolism?
breaking down molecules
What are metabolites converted into in bacteria?
Pyruvic acid
How do molecules enter bacteria cells?
Through porins on the outer membrane then through diffusion or transporter proteins through the inner membrane
What are the three metabolic pathways bacteria use for metabolizing glucose?
- Glycolytic
- Tricarboxylic acid cycle
- Pentose Phosphate pathway
T or F
In glycolysis, every reaction is facilitated by an enzyme
True
What molecules are needed to start the glycolysis pathway?
Glucose and ATP
What is the product of glycolysis?
Pyruvate
Where does pyruvate go after it leaves glycolysis?
Krebs cycle
What is pyruvate converted to in the kreb's cycle?
CO2, NADH, FADH2, and ATP
What is made in the pentose phosphate pathway?
Necessary precursors of RNA (ribose-5-phosphate) and NADH
What is the last step of metabolism in bacteria?
Electron transport chain which generates ATP through the ATPase and an ion gradient
What is the electron acceptor in the ETC?
Oxygen
Describe obligate anaerobes
Organisms that cannot grow in the presence of O2
Describe obligate aerobes
Organisms that cannot grow without O2 (need oxygen)
Describe facultative anaerobes
Grow in the presence or absence of oxygen
What was the basis of the "Transforming principle" that was established from the Fredrick Griffin mouse experiment?
When dead bad bacteria and alive good bacteria were mixed, the good bacteria were able to become bad. There was a transformation of the good bacteria into bad bacteria
What enzyme binds nucleotides together?
DNA polymerase III
Who discovered semi-conservative DNA replication?
Meselson and Stahl
What is the leading strand?
The strand where replication moves towards the replication fork (follows helicase) 5'-3'w
What is the lagging strand?
The strand where DNA replication moves away from the replication fork; short fragments are synthesized called okazaki fragments
What enzyme makes primer for the DNA during replication?
Primase
What enzyme join okazaki fragments?
DNA ligase
What enzyme replaces RNA primer with DNA?
DNA polymerase I
Describe inducible vs repressible genes.
Inducible genes mean that the presence of something causes their expression. Repressible genes means that the presence of something causes them to cease being expressed
What is one easy example of a repressible gene?
Lac operon; in the presence of lactose the lac operon is expressed however when there is no lactose present the operon is repressed and transcription stops
What are the 3 types of bacteria gene exchange?
- Transformation
- Transduction
- Conjugation
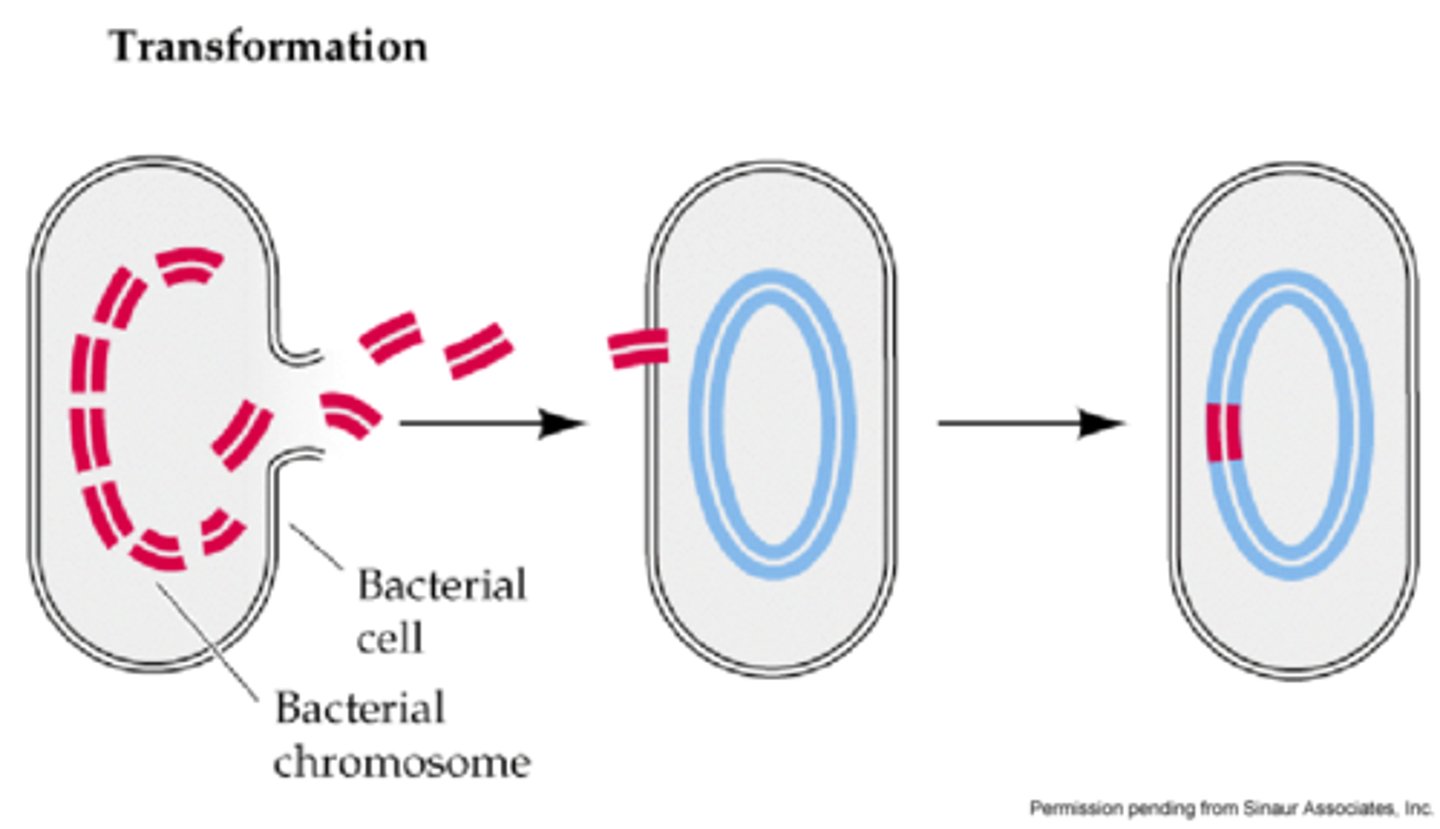
What is transformation (bacteria)?
genes transferred from one bacterium to another as "naked" DNA
What is transduction (bacteria)?
DNA is transferred from a donor cell to a recipient via a bacteriophage
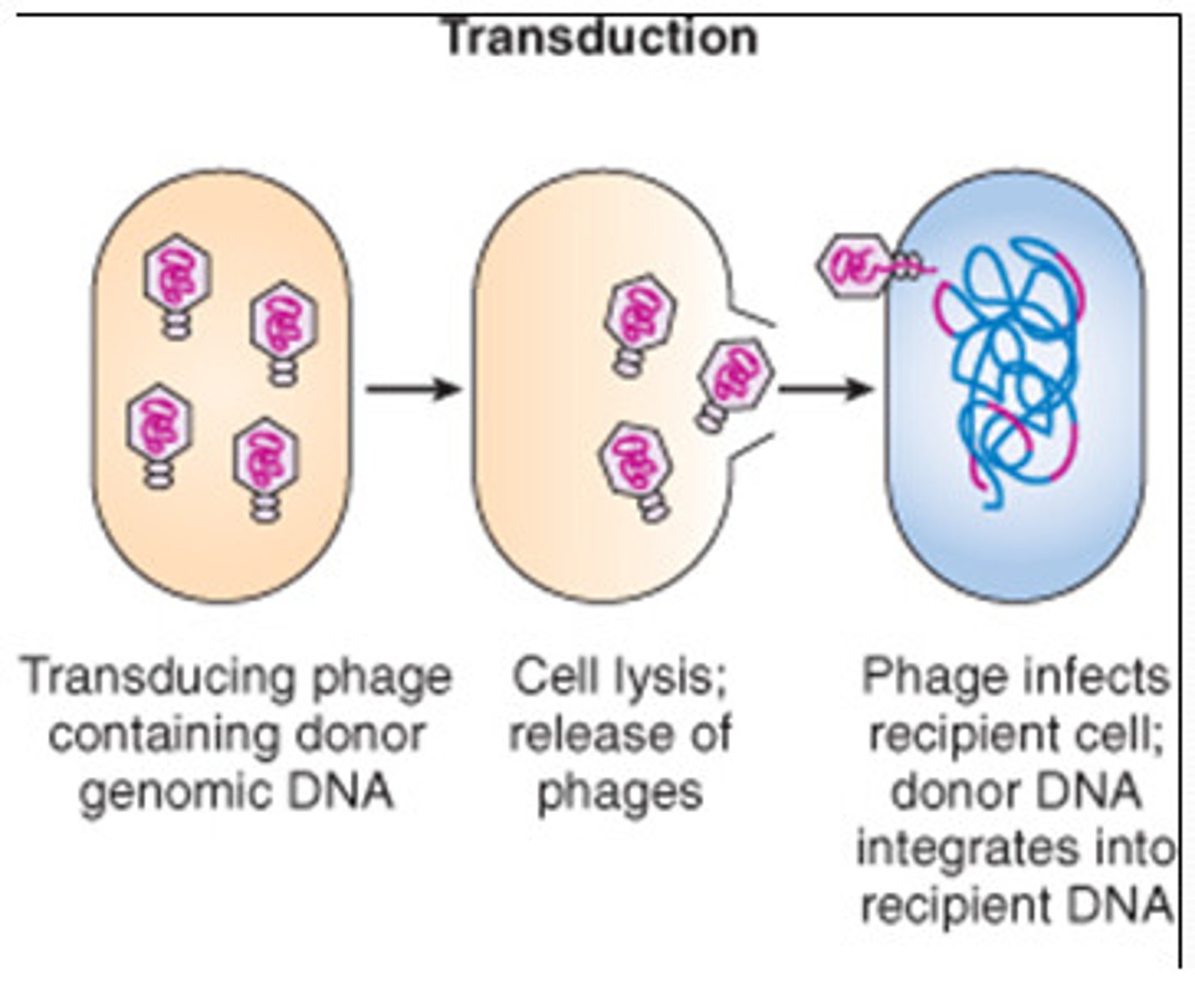
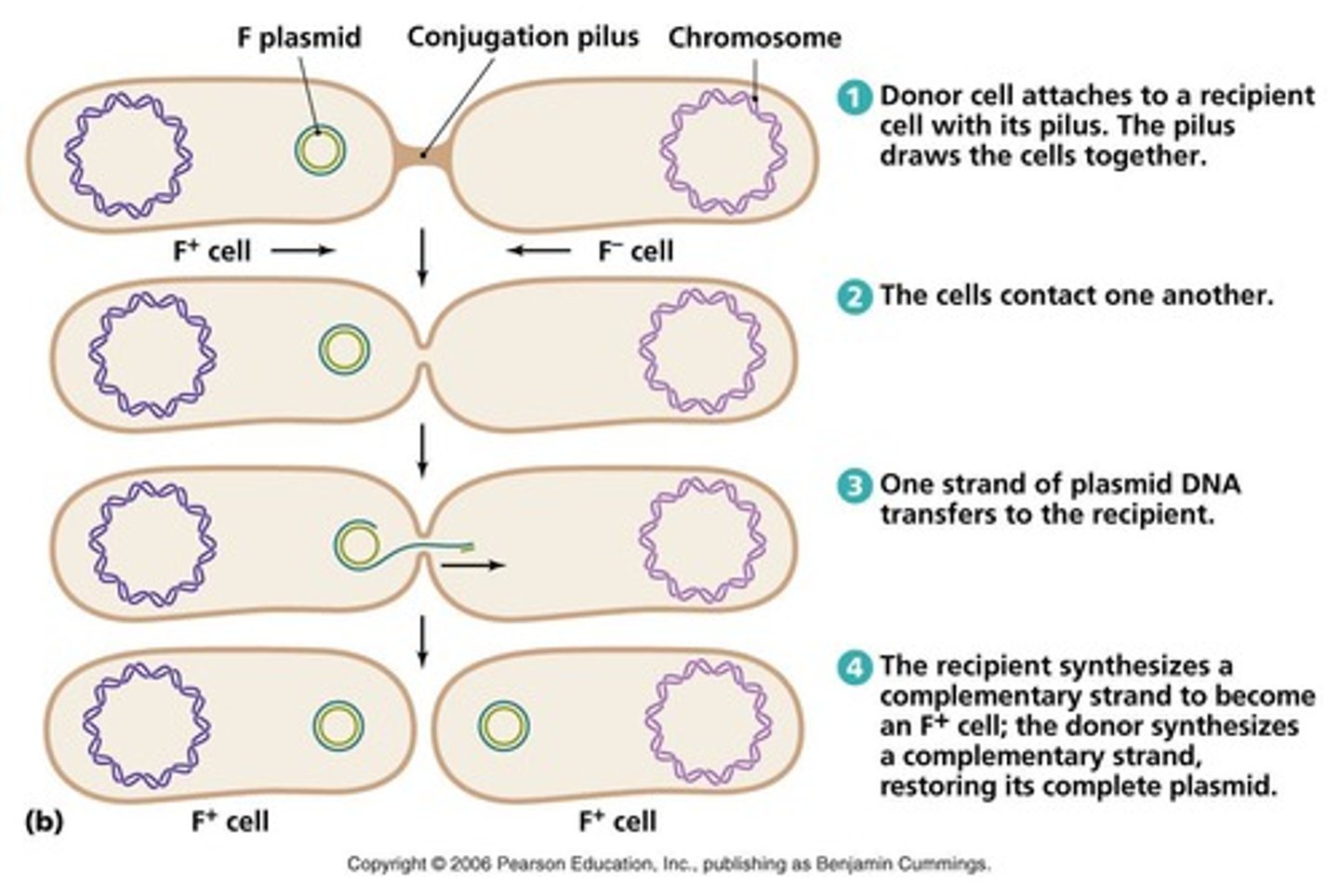
What is conjugation?
A process in which 2 organisms exchange genetic material through a sex pilus
During cell division, what proteins help control the septum formation?
FTsZ and MreB
Which bacteria form spores?
Gram positive
T or F
Bacteria only have a single loop of DNA
True