General Biology 115 Final Exam
1/315
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
316 Terms
How does long term memory work?
Activated when needed => pulled into short term (working) memory
Long term potentiation
use of information is like a sorting process
T/F: If information is not used, then it is discarded
True
LTP is facillitated by
Chunking
Emeregnce
The whole is greater than the sum of the parts
Emergent Properties
Results from the arrangement and interaction of parts within a system
Reductionism
Reduction of complex systems to simpler components that are more manageable to study
Scientific Method
Make an observation
Do background research
Make a hypothesis
Create an experiment
Evaluate the results of the experiment
If the predictions are wrong, make a new hypothesis and start over from step 3
Revise predictions
Repeat and verify
4 most abundant elements
C, H, O, N
Ionic bonds
Between atoms => the more electronegative elements steals an electron
Van der Waals Interactions
-Develop because electrons are in constant motion
-single interaction is weak but multiple are strong
Hydrogen bonds
-very strong dipole-dipole interaction
-H + F, O, N
Cohesive behavior
-polar molecules side with different charges are attracted to each other
-surface tension is a measure of how hard it is to break the surface of a liquid
Hydrophillic
Ions, salts, polar, "water loving"
Hydrophobic
Lipids, nonpolar, "water hating"
Organic compounds
-carbon based compounds
-carbon bonded to another carbon or hydrogen
Hydrocarbons
-only hydrogen and carbon
-nonpolar, uncharged, hydrophobic
Hydroxyl group
-alcohol
-polar
-form hydrogen bodns with water
-hydrophillic
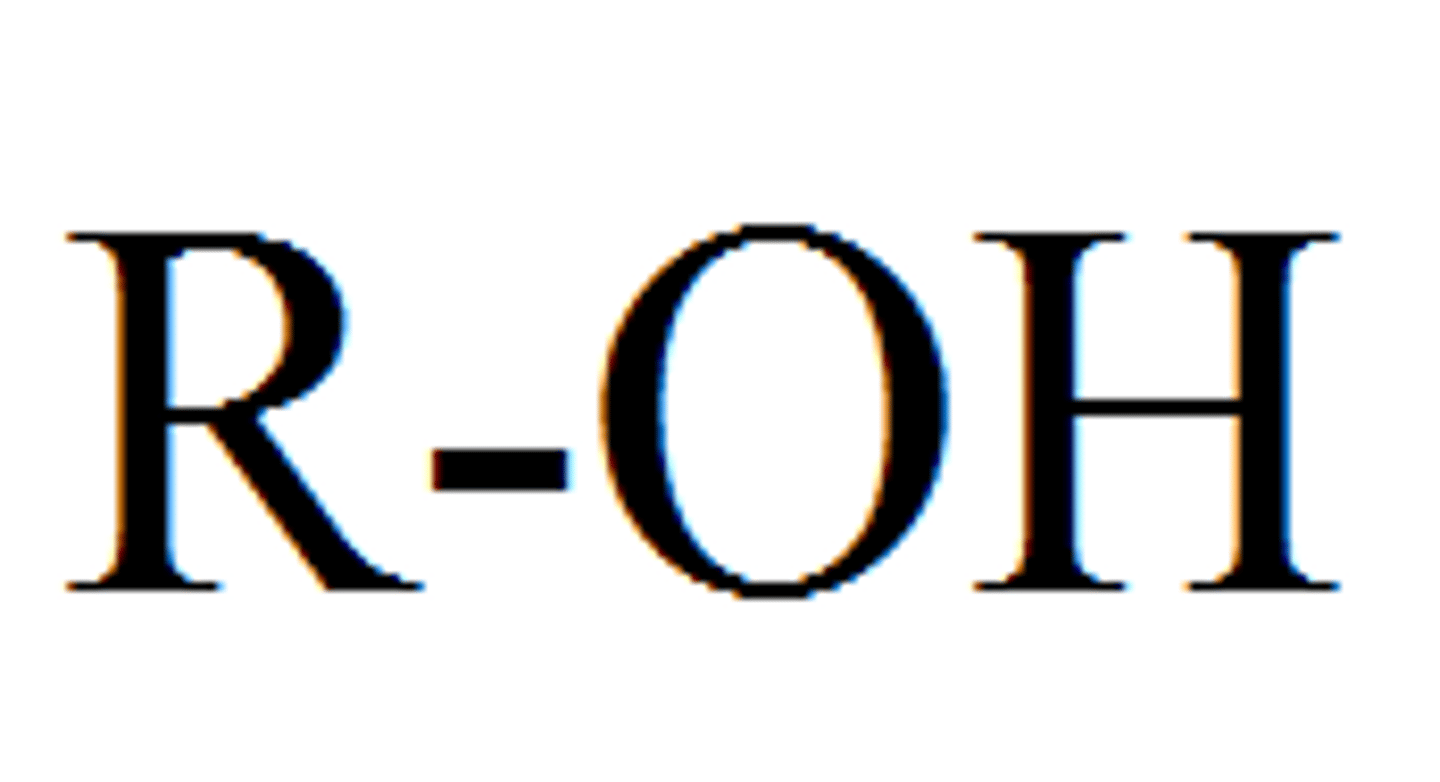
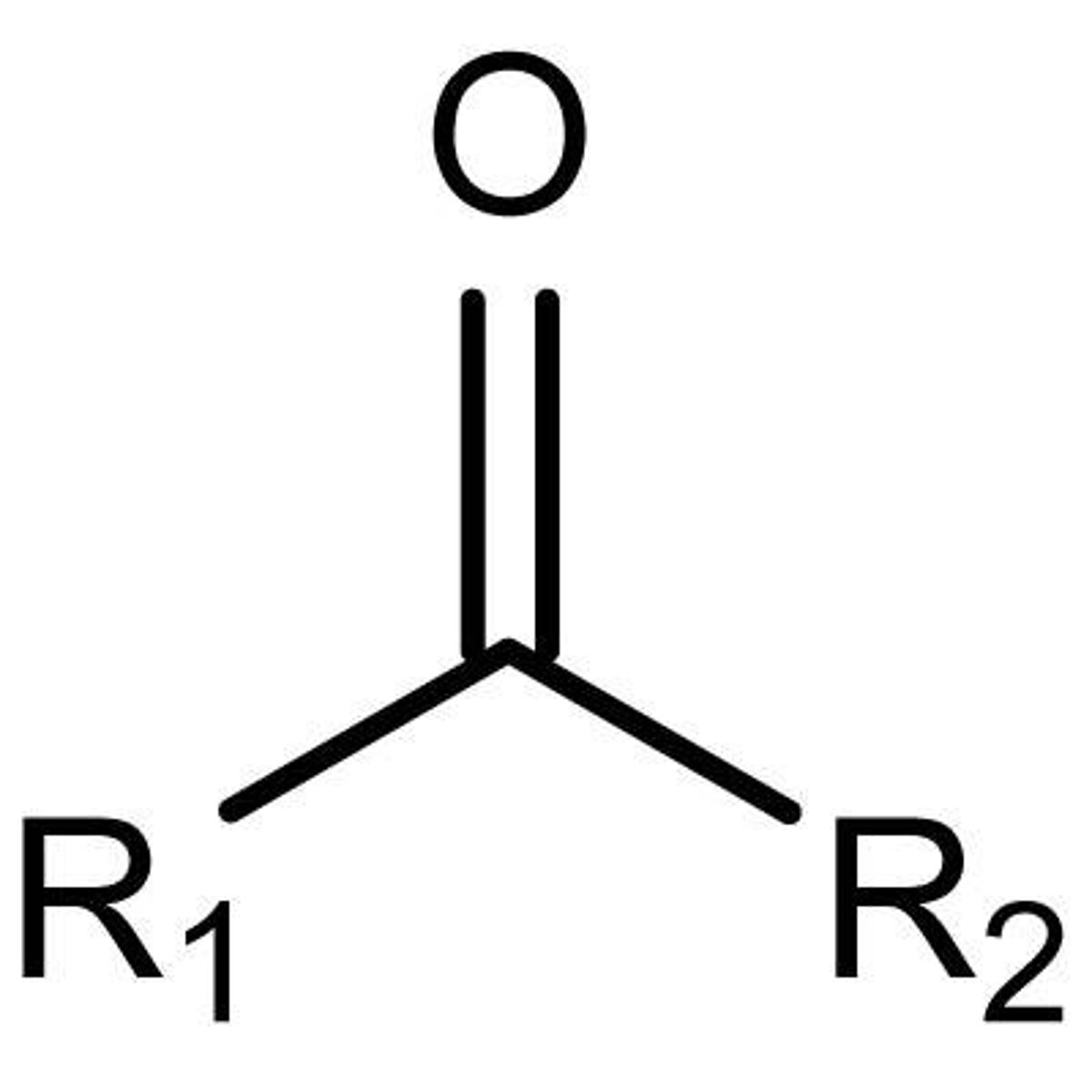
Ketone
-internal carbonyl group
-polar
-hydrophillic
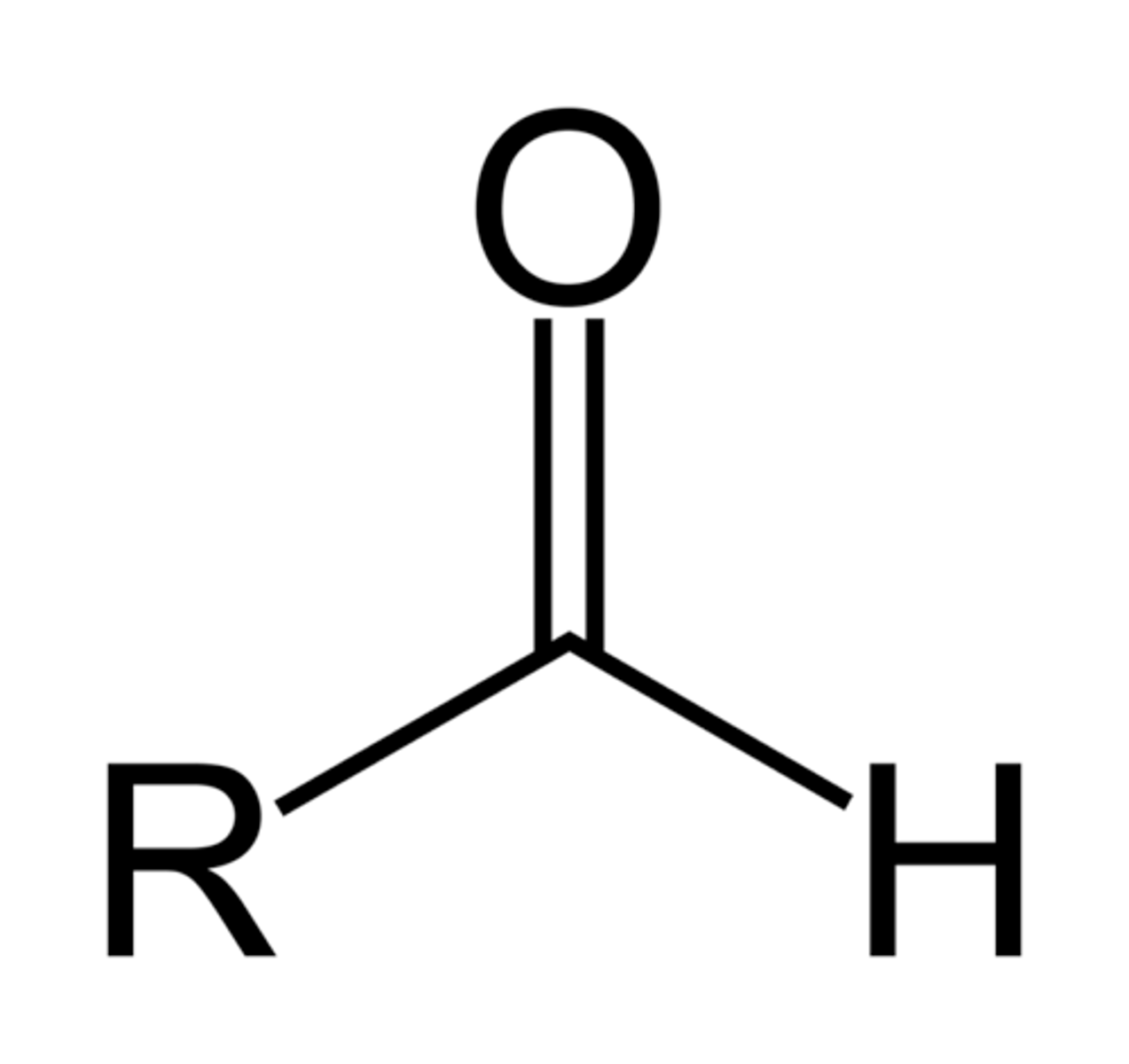
Aldehyde
-terminal carbonyl group
-polar
-hydrophillic
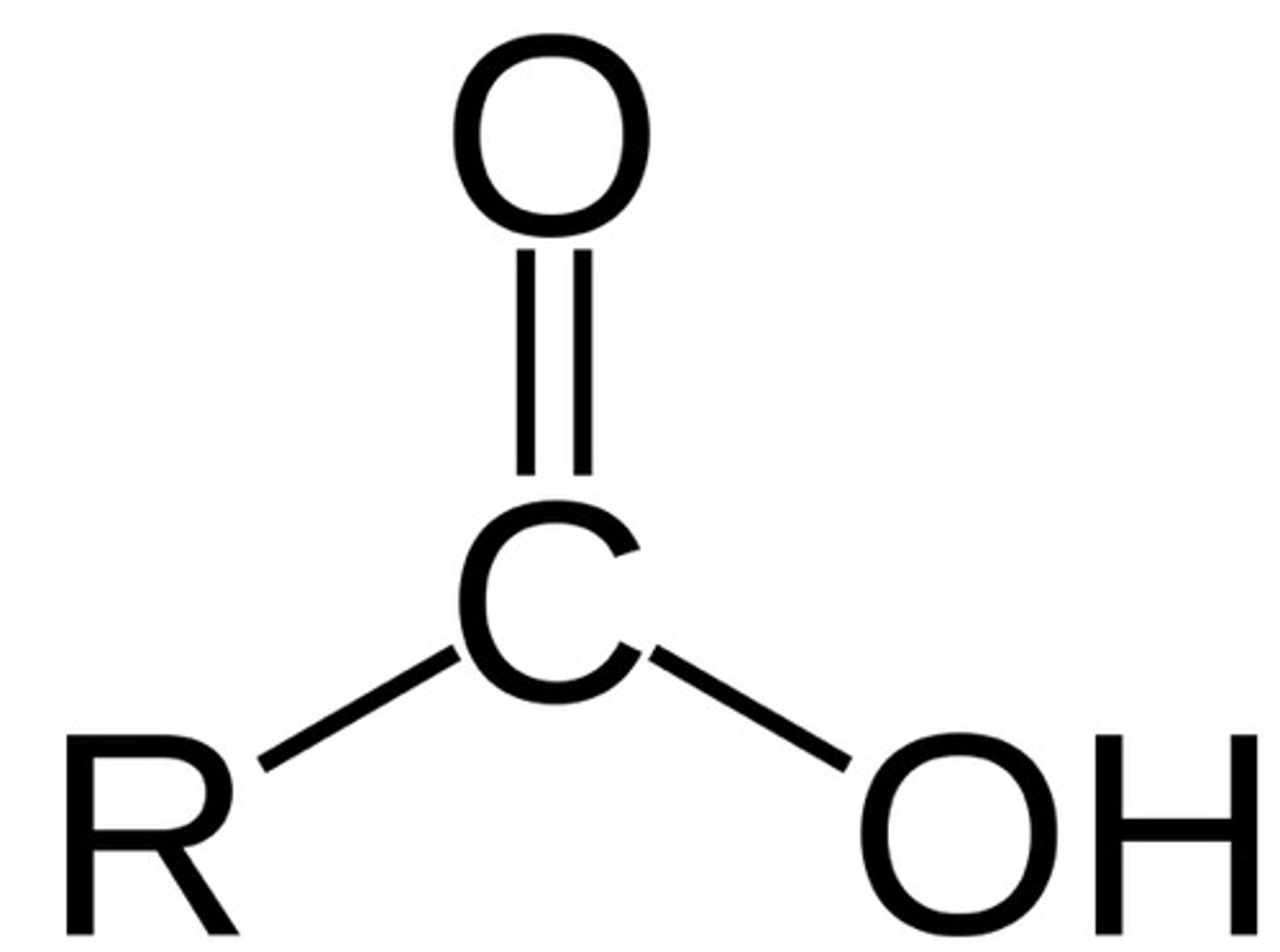
Carboxyl group
-polar
-hydrophillic
-very acidic
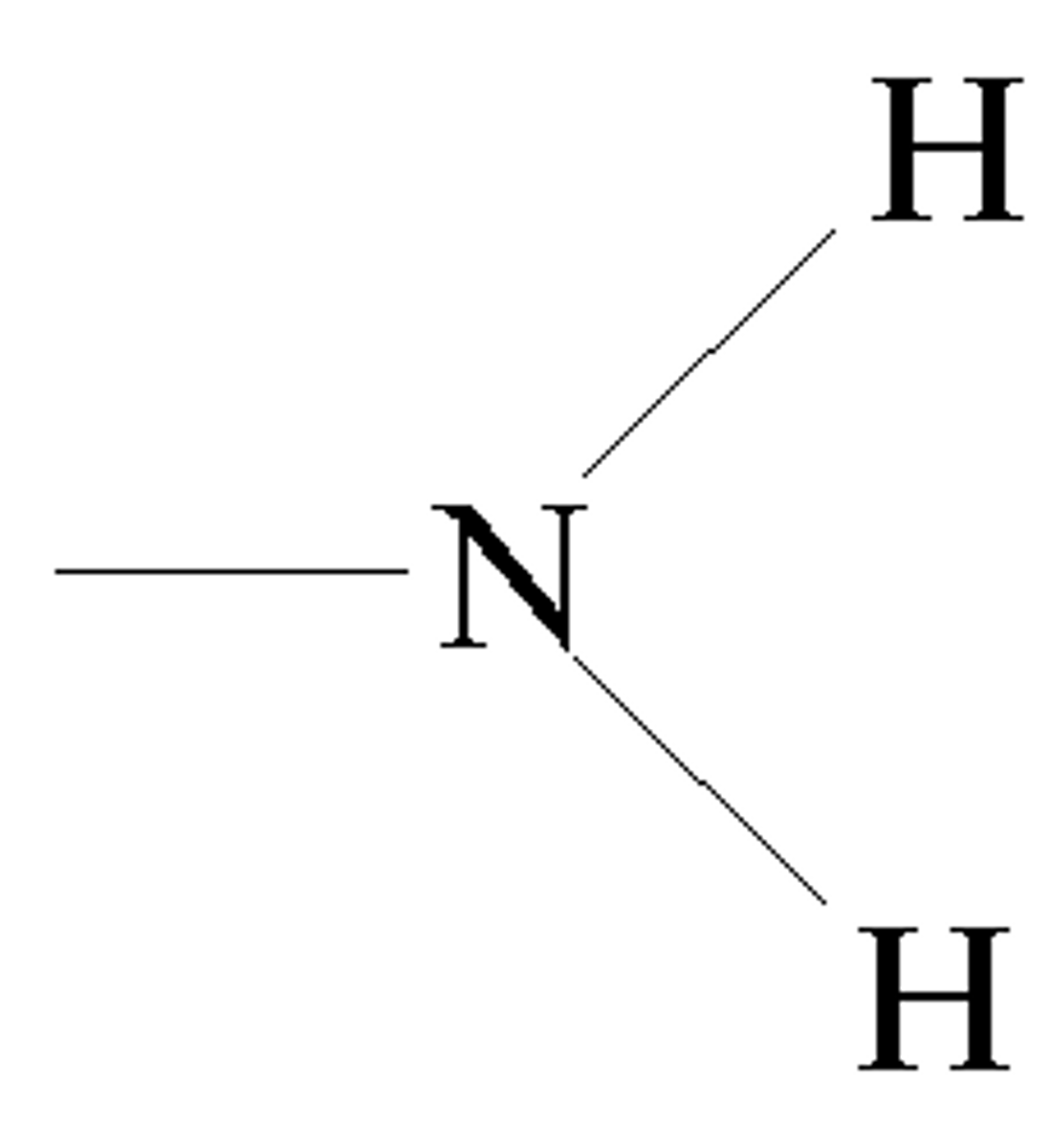
Amino group
-proton acceptor => basic
-hydrophillic
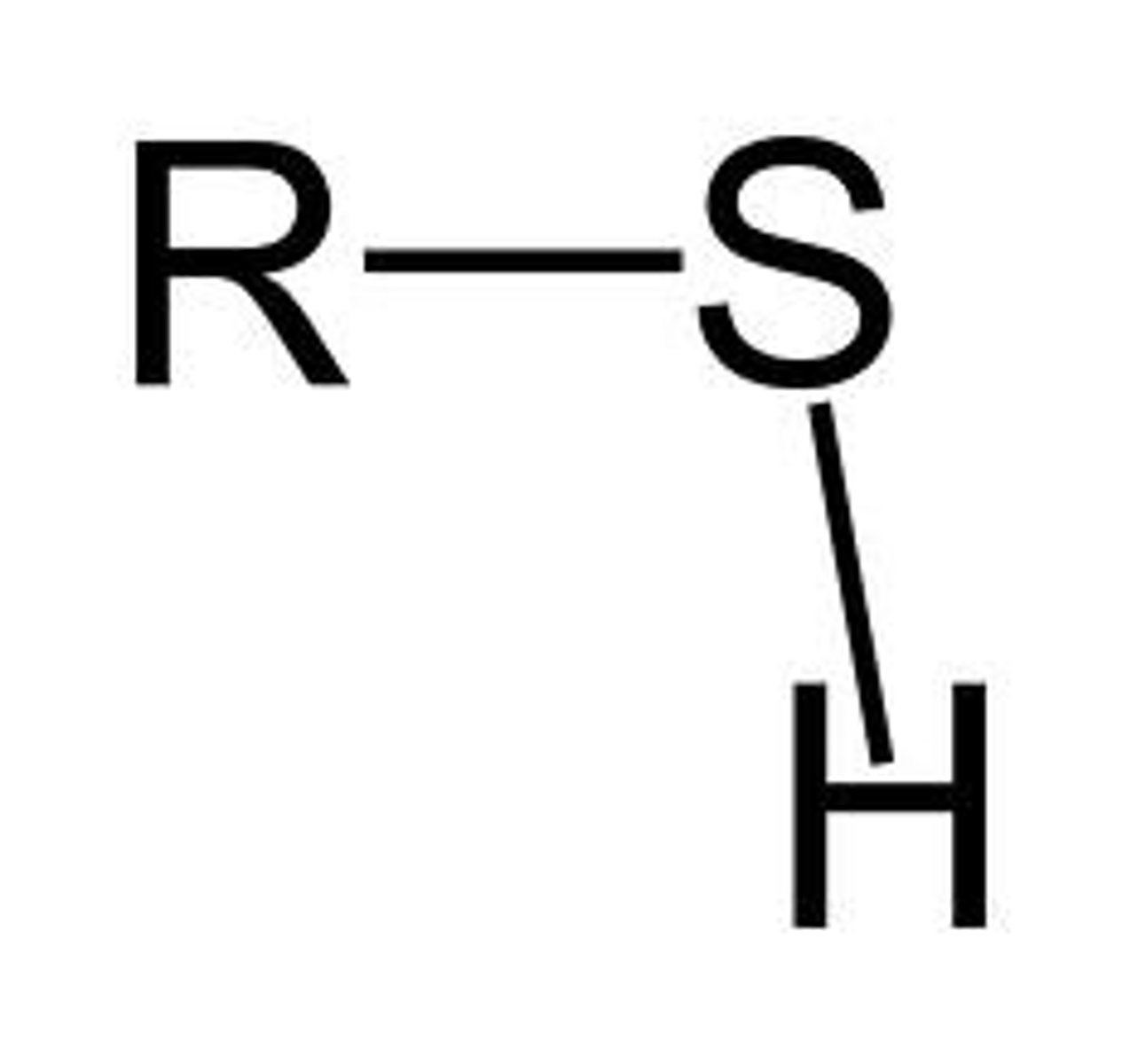
Sulfhydryl group
-structure of some proteins
-less polar than a hydroxyl group
Phosphate group
-contributes a negative charge
-acidic
-hydrophillic
-phospholipids & nucleic acids
Methyl group
-nonpolar hydrocarbon
-hydrophobic
-control of gene expression
-shape and function of sex hormones
Macromolecules
-large complex molecules that are formed by thousands of atoms
-carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Enzymes
speed up chemical reactions
Hydrolysis
-"to break with water"
-using water to break polymers
-regulated by hydrolyses
Dehyration synthesis
-synthesizes monomers together
-removes water
regulated by dehydrogenase
Carbohydrates
-fuel & building material
-hydrophillic
-polysaccharides attached to proteins = glycoproteins or lipids
-cell identification (ex: blood types)
Lipids
-not true polymers
-hydrophobic
-dissolve in nonpolar solvents => nonpolar
-3 important families: fats, phospholipids, steroids
Fats
-highly concentrated energy
-consists of one glycerol (3 carbon alcohol with 3 -OH) & 1-3 fatty acids
Fatty Acids
-carboxyl group with a long, unbraided hydrocarbon tail
-added to glycerol during dehydration synthesis
-form a covalent bond => ester linkage
-triglyceride = main storage of fat
Phospholipids
-glycerol & 2 fatty acids (hydrophobic)
-phosphate group (hydrophillic
-polar
-acidic
Steroids
-3 rings with 6 carbons & 1 ring with 5 carbons
-differ in side chains or functional groups attached
Proteins
-made of amino acids
-monomers are bound together with peptide bonds through dehydration synthesis => becomes polypeptide
-primary structure => secondary structure => tertiary structure => quatinary structure
Primary structure of proteins
sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain
Secondary structure of proteins
-hydrogen bonds
-R groups do NOT participate
-alpha helix = coil
-beta pleated sheet
Tertiary structure of proteins
-interrelationships of R groups fold into particular 3D shapes
-can have all types of bonds (hydrogen, ionic, covalent, disulfide)
Quatinary structure of proteins
-two or more polypeptide chains
-no more folding
Denaturation
-a loss of a protein's native structure
-biologically inactive
-pH, salt concentration & temperature are all factors that can cause denaturation
-low temperature slows down an enzymatic reaction
-even a short exposure to a high temperature can denature a protein
Nucleic acids
-monomers are nucleotides
-transmit hereditary information & determine protein production
4 factors of abiotic synthesis
1) little / no free oxygen
2) source of energy
3) presence of chemical building blocks
4) time
Miller & Urey experiment
-simulated early conditions of early Earth
-formed amino acids & other organic molecules
Iron-Sulfur World Hypothesis
-life formed at the cracks of the ocean floor => hydrothermal vents
-hot water, carbon monoxide, and mineral such as iron & nickel sulfide released
Steps of abiogenesis
1) abiotic synthesis of monomers
2) synthesis of macromolecules
3) formation of protocells
4) self-replicating DNA
Synthesis of macromolecules
-formation of polymers from monomers
-monomers polymerize on hot sand or on rock
-negative ions bind monomers
Formation of protocells
-in water, lipids and other organic molecules spontaneously form vesicles
-organic polymers exhibit attributes of living cells (osmosis, homeostasis, division)
-no mechanism of heredity
Self-replicating DNA
-RNA first nucleic acid in protocells
-RNA is capable of replicating itself & catalyzing protein synthesis: ribozymes
-DNA evolved later (double-stranded, more stable)
Order of geologic time
Eons => Eras => Periods => Epochs
Stromatolites
ancient bacterial mats on sedimentary layers
Order that life was formed in
Prokaryotes => Photosynthetic Autotrophs => Aerobes
Endosymbiotic theory
-mitochondria and plastids were initially small prokaryotes
-now are organelles of eukaryotic cells
Cambrian explosion
-535~525 million years ago
-fossils appear to resemble modern animals
-rapid evolution => new animal body plans
Cell theory states that
-all organisms are made up of cells
-all cells have 4 common features and a common evolutionary ancestor
Light microscope
-can see things the size of about 2um
-stains or dyes increase contrast
-you can see nucleus but not smaller organelles
Scanning electron microscope
electrons bounce off the outside of the object
Transmission electron microscope
-electrons go all the way through the object
Why aren't electron microscopes used all the time?
-cells must be killed (sliced / covered in gold)
-may alter their structure
-expensive
-tedious preparation
Features of all cells
-plasma membrane: phospholipids
-cytosol: semifluid substance
-chromosomes: carry genes and make DNA
-ribosomes: make proteins & RNA
Prokaryotic cells
-NO nucleus (there is a nucleoid form => DNA in an unbound region)
-NO organelles but have flagella, plasma membrane, fimbriae & cell wall
Eukaryotic cells
-DNA in nucleus
-membrane bound organelles
-10x the size of prokaryotic cells
Why are cells so small?
-plasma membrane acts as a selective barrier
-surface area to volume ratio (the bigger it is, the more places there are for things to enter / leave the cell)
Endosymbiosis
-both mitochondria and chloroplasts once were prokaryotes
-both mitochondria and chloroplasts have inner membranes, enzymes, their own DNA, their own ribosomes, undergo binary fission and are small
Nucleus
-DNA is organized in chromosomes
-DNA & proteins = chromatin
-RNA is the only thing that leaves the nucleus
Nucleolus
-RNA & proteins
-No membrane
Nuclear envelope
-made of 2 membranes => both are bilipid bilayers
-nuclear pores regulare entry & exit of the molecules
-is lined by nuclear lamina, which is composed of proteins & maintains the shape of the nucleus
Ribosomes
-site of protein synthesis
-not membrane bound => ribosomes are not considered organelles
-free ribosomes => float around in the cytoplasm (both prokaryotes and eukaryotes)
-bound ribosomes are bound on the endoplasmic regulation (only eukaryotes)
Endomembrane system
-made of a lipid bilayer
-separates internal contents from external environment & separates cell into many compartments
-function is to regulate protein traffic & performs metabolic functions in cell
-consists of: nuclear envelope, plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes & vacuoles
Plasma Membrane
-encloses cell contents
-controls material that goes in & comes out of cell
-selectively permeable
-no cell wall
-phospholipid bilayer
Endoplasmic reticulum
-continuous with nuclear envelope
-smooth ER has no ribosomes & rough ER has ribosomes
-lumen = internal space
Functions of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
-has bound ribosomes => makes proteins
-proteins are folded and modified
-secrete glycoproteins (proteins that are covalently bonded to carbohydrates)
-distributes transport vesicles
-is a membrane factory for the cell
Functions of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
-synthesize lipids
-metabolizes carbohydrates to break down glycogen and regulate blood glucose
-detoxifies drugs and poisons
-stores calcium ions
Golgi Apparatus
-cis face is the receiving side of the endoplasmic reticulum
-trans face is the shipping side
-modifies products of the endoplasmic reticulum
-manufactures certain macromolecules
-sorta & packages materials into transport vesicles
-shipping product out of Golgi apparatus using vesicles
Lysosomes
-digestive components
-sacs of hydrolytic or digestive enzymes
-primary lysosomes: buds off Golgi
-secondary lysosomes: primary lysosome fused with another structure
-breaks down complex molecules
Vacuoles
-diverse maintenance compartments
-food vacuoles are formed by phagocytosis
-contractile vacuole: plant cells, organic compounds & water
Membrane Proteins
-tend to be amphipathic
-integral or peripheral
-can move but can't be flipped
-hydrophobic => fold inside the protein
-hydrophilic => fold outside the protein
Functions of Membrane Proteins
-transport
-enzymatic activity
-signal transduction
-cell cell recognition
-intercellular joining
-attachment to the cytoskeleton & extracellular matrix
Fluid Mosaic Model
-membrane components can move laterally within one layer of the membrane
-fluidity depends on temperature, chain length / bends in tail, saturation, and amount of cholesterol
Passive Transport
-doesn't use ATP
-moves with the gradient
-spontaneous
-results in dynamic equilibrium
-cells prefer passive transport
Diffusion
-tendency for molecules of a substance to fill available space
-small gases like oxygen gas, carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas can pass through
-small nonpolar molecules like hydrocarbons can pass through
-small polar uncharged molecules like water can pass through
Osmosis
-diffusion of water across selectively permeable membrane
-water diffuses form a lower to a higher concentration
Solvent
a substance capable of dissolving other substances
Solute
a dissolved substance
Osmosis Tonicity
ability go a solution to cause a cell to gain to lose water
Isotonic solution
-concentration outside = concentration inside
-no net water movement
Hypertonic solution
concentration outside cell is greater than the concentration inside the cell
Hypotonic solution
concentration outside cell is less that the concentration inside the cell
Facilitated diffusion
-facilitated = to make easier
-larger molecules can be transported
-transport using transport proteins
-channel proteins
-some carrier proteins
Active Transport
-uses ATP
-moves against the gradient
-low concentration => high concentration
-not spontaneous
-not carrier mediated
-formation of vessicles
-exocytosis = "out"
-endocytosis = "in"
-phagocytosis = "eat"
-pinocytosis = "drink"
Exocytosis
-waste, proteins, & secretory products
-vesicle fuses with plasma membrane
-releases contents from cell
-vesicle fuses with plasma membrane (PM) => primary mechanism for growing plasma membrane
Endocytosis
-material taken into the cell by forming vesicles derived from the plasma membrane
-3 types: phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor mediated endocytosis
Phagocytosis
-"cell eating"
-cell engulfed large particle
-non-specific
Pinocytosis
-"cell drinking"
-ingestion of fluid & dissolved material
-non-specific
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
-receptor proteins in plasma membrane bind specific macromolecules outside the cell
-form coated pits
-fold inward to form vesicles
-fold inward to form vesicles
-main mechanism for uptake of macromolecules
Metabolism
-sum of all chemical reactions of an organism -> maintains homeostasis
-an emergent property of life
Catabolic Pathway
-breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones
-releases energy => exergonic
-ex: cellular respiration, hydrolysis
Anabolic Pathway
-build complex molecules from simpler ones
-uses energy => endergonic
-ex: synthesis of proteins from amino acids, dehydration synthesis
Energy
capacity to cause change
Potential Energy
stored energy that hasn't been used yet