Economic development DAII
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is economic development
Quality of life, education, health, material living standards, reduction in poverty, employment/ higher incomes
Does growth = economic development
If GDP per capita increases
What are the characteristics of developing countries
Low standards of living
Low productivity - working in low pay, insignificant jobs
Low savings - lack of/ lack of trustworthy financial institutions also lack of money to save
High population growth - children needed to work farms ect
Primary sector dominance (Agriculture)
Incomplete markets
Higher unemployment
Low economic power international wise
Define living standards
Usually measured by income or real gdp per capita
Indicates how well of individuals are considering their access to goods and services and the quality of these
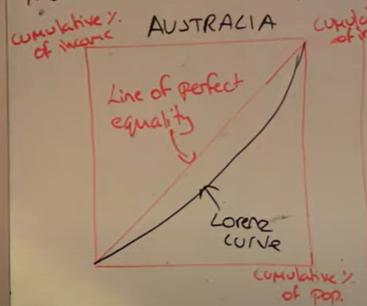
Draw Lorenz curve
What does it show
Income inequality in an economy
What are the aspects of the HDI
Longevity - life expectancy at birth
Knowledge - School enrolment, adult literacy
Standard of living - access to goods and services (GDP per capita)
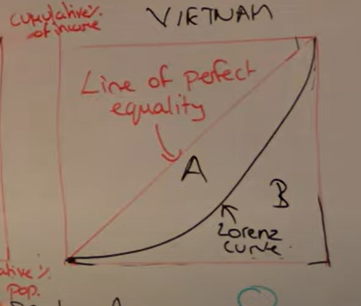
How to work out Gini coefficient
What does coefficient show from 0-1
A divided by B
0 is perfect equality
1 is perfect inequality
What is FDI
When a firm with it’s major headquarters in a country opens a new part of the business/ branch in another country
Benefits of FDI
Injection into circular flow - increased employment
positive BoP effects
Improved productivity domestically
Infrastructure development
Technological transfer
More tax collected
Fills savings gap
Technological transfer
Tax revenue collection increases
Negative effects of FDI
Environment costs
Tax revenue could be lower than expected
Employment may be insignificant if they bring own workers
MNCs may invest in labour saving technology
MNCs could exploit resources and then leave once depleted